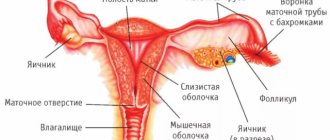
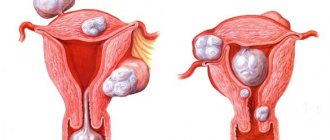
Childbirth occurs in three periods: contractions, birth of the fetus and birth of the placenta. The placenta is the placenta and membranes that contain the fetus. After the birth of the placenta, there should be no remains of it in the uterus, as well as blood clots attached to its walls or blocking the outflow of secretions; cleansing should be complete. All these tissues will rot in the uterine cavity after childbirth, creating a breeding ground for numerous opportunistic and pathogenic microflora living on the surface of the body.
Blood clots remaining in the cavity can interfere with its cleansing after childbirth - the removal of lochia - postpartum discharge - from its cavity. A blood clot can also block a vessel in the wall and then break off after a while, causing severe bleeding. Such bleeding can begin suddenly even a month after birth.
In order to prevent such consequences, they perform cleaning (curettage, curettage) of the uterus after childbirth. If parts of the placenta and fetal membranes remain in its cavity, curettage is carried out immediately after childbirth or within 24 hours after it. If there are blood clots in the uterus that interfere with the cleansing of its cavity, curettage is performed according to indications, depending on the woman’s condition, but no later than the first week of labor. The presence of indications for curettage in modern clinics is confirmed by ultrasound examinations (ultrasound).
The operation is simple, but painful, so it is performed under anesthesia. The doctor uses a medical instrument (curette) to scrape the uterine mucosa, removing its upper functional layer along with the remains of birth tissue. Sometimes vacuum cleaning is carried out followed by ultrasound control.
Important! If the doctor considers cleaning necessary, the woman should not refuse it!
The main criteria for the success of uterine cleansing
The success of the curettage operation after childbirth is indicated (this is worth remembering!):
- absence of a significant increase in the body temperature of the postpartum woman (the norm is up to 37.5˚);
- no bleeding, moderate bleeding for several days (sometimes up to a week) is considered normal; it gradually turns brown and then becomes lighter; the discharge does not have an unpleasant odor;
- pain in the lower abdomen - it gradually decreases, but persists until the uterus contracts completely;
- the woman’s general condition is satisfactory, but slight dizziness may bother her; All these symptoms indicate that the cleansing is going well.
Read also:
Is vacuum cleaning after childbirth dangerous and should you refuse it?
It is important to pay attention to the following symptoms and report them to your doctor:
- increased bleeding;
- complete absence of discharge in the first days after cleansing with a simultaneous increase in pain; this indicates a violation of purification;
- the discharge acquires an unpleasant putrid odor - a sign of infection;
- The temperature rises to 38˚ and above.
Technique
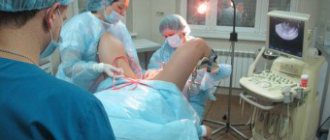
The procedure is performed using general anesthesia. The operation lasts 20 - 40 minutes. Before curettage begins, the genitals are treated with a 5% iodine solution, the cervix with 50% ethyl alcohol. Sterility is very important during cleaning. The inner surface of the uterus is a continuous wound through which infection can easily penetrate.
How to do uterine curettage after childbirth:
- the patient is located in the operating room;
- if necessary, anesthesia is given;
- The cervix is fixed with special forceps;
- expanders are inserted if closure occurs;
- The sharp end of the curette is used for scraping.
When the need for cleaning is detected after an ultrasound examination, special instruments are used during surgery. The procedure is painless. Painful sensations appear at the initial stage during the insertion of dilators of different diameters into the uterine cavity. After a sufficient degree of dilation, the doctor begins the procedure itself. A pointed curette is used for this.
It is very important to clean all mucous membranes. Otherwise, uncleaned areas will provoke an inflammatory reaction. The essence of RDV comes down to performing a study with an accurate diagnosis; during curettage, the formation that arose in the first six months after birth is removed, and the pathology does not develop further.
In order for the surgical intervention to be carried out efficiently, hysteroscopy is also used. The uterine cavity is examined with special video cameras placed inside. They are the surgeon's eyes.
If cleaning is performed immediately after labor, dilators do not need to be inserted. The uterus is dilated enough to allow manual curettage. Blood clots and excess tissue are removed manually. No preliminary anesthesia is required.
Diagnostic curettage of the uterus is carried out 6 months after birth, if during the examination reasons for this are found. For example, there was a hormonal imbalance. Insufficient blood supply and microcirculation of the layer also lead to cleaning at this time.
How is rehabilitation and recovery going?
For some time (4-6 days) after cleaning, the postpartum woman remains in the hospital under the supervision of a doctor. He conducts a daily examination to identify possible complications in a timely manner. Drug treatment is prescribed:
- medications to contract the uterus - this prevents recurrent bleeding;
- antibiotics - to prevent the development of infections.
If the rehabilitation period goes well, the woman is discharged 5-6 days after the cleansing, and further monitoring of her condition is carried out by a doctor at the antenatal clinic. Discharge after curettage (the same as after childbirth) continues for about 6 weeks, gradually becoming lighter and decreasing in volume. Two months after birth, complete cleansing and restoration occurs.
Indications
Curettage of the uterine cavity is the removal of mucous from the inner wall. Among medical personnel, the procedure is called curettage. Previously, to carry it out, they used a special device, a curette, resembling a spoon.
Why is it done:
- solving gynecological problems that require additional examination;
- elimination of diseases associated with women's health through surgery.
This leads to 2 directions:
- diagnostic;
- therapeutic.
Postpartum curettage is carried out to remove the remains of the child's place from the genital organ. These include a child's place, blood clots. Cleaning is carried out immediately or a couple of days after the end of labor. It allows you to avoid the inflammatory process, the walls of the uterus contract freely.
Sometimes they need curettage to perform an abortion. This procedure is necessary for frozen, abnormally developing fetus. When an ultrasound shows a stalled pregnancy, cleansing should be done immediately.
During the manipulation, mechanical removal of the remaining placenta in the uterus after childbirth occurs. The new mucous membrane soon grows from the germinal layers of the endometrium. Before carrying out the procedure, it is necessary to take into account contraindications. The main ones are an active inflammatory process, diseases of the internal organs, 3 – 4 degrees of vaginal cleanliness.
Is it possible to do curettage for nulliparous women? The diagnostic cleaning procedure is not considered dangerous. It does not interfere with the reproductive functions of the female body. Therefore, curettage is done for the nulliparous woman.
Is it possible to give birth after curettage? Yes. A woman can become pregnant during the procedure. However, the body needs to get stronger and recover. Therefore, you should plan to conceive a child no earlier than 3–6 months after cleansing.
Complications and consequences after uterine curettage
As with any other operation, complications are possible. Complications can be early or late. Early complications include:
- bleeding due to damage to a vessel located in the wall of the uterus; in this case, heavy bleeding may be from the genital tract, or may manifest itself in the form of hemometra - accumulation of blood in the uterine cavity due to the closure of the exit from the cavity; To prevent hemorrhage, antispasmodics are prescribed - medications that relieve spasms of smooth muscles;
- perforation (violation of the integrity) of the uterine wall with a sharp instrument - a small puncture can heal on its own, but a large one is sutured; As a rule, there are no unpleasant consequences.
These consequences are eliminated on the operating table or with repeated surgery within the first 24 hours. Modern clinics have every opportunity to cope with such consequences.
Read also:
Where does the mother’s umbilical cord, no longer needed by the child, go after childbirth?
Late complications, which can develop after a few days after surgery and last a long time, include infection and associated consequences. If the cleansing of the uterus is impaired, an infectious-inflammatory process develops - acute endometritis, which occurs with high fever, pain in the lower abdomen, and a change in the nature of lochia (they become foul-smelling, cleansing is disrupted). Timely prescribed antibacterial therapy can quickly stop this process and prevent serious consequences.
Important! It is more difficult to cleanse and treat endometritis in women suffering from some kind of hidden infections - chlamydia, ureaplasmosis, etc. Therefore, obstetrician-gynecologists always insist on a full examination and treatment of infection during pregnancy planning. In such cases, endometritis becomes chronic and is accompanied by the development of adhesions. The inflammatory process moves to the fallopian tubes and pelvic organs, where the consequences of inflammation - adhesions - also gradually develop.
Adhesions in the uterus and fallopian tubes are the main cause of infertility. Adhesions in the fallopian tubes can interfere with conception, and in the uterine cavity - with bearing a child and childbirth. The treatment of such processes is long-term. It begins with identifying and treating the infection, which, as a rule, with long-term inflammation, is mixed, caused by different pathogens.
After eliminating the infection, the adhesions are dissected, which is most often performed by endoscopic (without large incisions, using special endoscopic instruments) methods. And only after this the consequences of the infection are eliminated, and the woman can become pregnant again.
Hormonal disorders and disruption of the menstrual cycle can be a consequence of too deep curettage of the walls, when not only the upper functional (regenerating) layer of the endometrium is removed, but also the lower, basal layer, which cannot be restored. This complication is difficult to treat and most often causes infertility.
Read also:
Can regular pads replace postpartum pads and which ones are better to choose?
Consequences for the mother in labor
The list of complications that occur in a woman in labor due to delayed removal of clots from the cavity includes:
- inflammation of the inner layer lining the uterus;
- slow restoration of the functional abilities of the reproductive organ;
- inflammatory process;
- infectious lesion.
The listed complications are dangerous for women, so the condition after childbirth must be monitored independently. Blood clots can get stuck inside, but they need to be removed, so the abundance and duration of discharge must be controlled.
How to speed up the healing process after cleansing
To do this, you need to follow all the doctor’s recommendations. Adviсe:
- keep your genitals clean; take a warm shower twice a day; You cannot wash in a bath, bathhouse, or sauna;
- douching should not be done, all cleansing procedures must be superficial;
- change pads as they fill, but at least 6-8 times a day; in the first days it is better to use diapers (the same as after childbirth);
- even with small discharge, do not use vaginal tampons - this interferes with cleansing;
- any physical activity and tension should be avoided in the first two weeks after cleansing;
- sexual intercourse is possible only after the complete cessation of lochia.
If cleansing after childbirth is successfully carried out and all necessary requirements are met in the postoperative period, as a rule, there are no negative consequences for women. Much more serious consequences occur if cleaning was not carried out in a timely manner.
When does it become necessary to cleanse after childbirth?
Each woman gives birth twice (in one visit to the maternity hospital): a baby and the placenta (afterbirth), with which he was kept for all 9 months. Many women do not even notice the birth of the placenta, since at this time they are already busy looking at the baby, who has buried his small nose in the mother’s chest. But this does not always happen, unfortunately. Sometimes the placenta is too tightly “fused” with the uterus and is born “partially” or does not come out at all, then manual separation of the placenta should be performed, which is always carried out after a cesarean section.
Before discharge from the maternity hospital (on days 2-3), the woman undergoes a diagnostic ultrasound to assess the condition of the internal cavity of the uterus. If the doctor finds traces of placenta or blood clots in the uterus, then the woman in labor is prescribed a cleaning.