Every woman experiences menstrual bleeding. They first appear at the age of 10-15 years, and end with menopause, which occurs at 45-55 years. Blood clots during menstruation, nagging pain in the lower abdomen and malaise are normal in most cases. However, sometimes the condition takes on a pathological connotation. You can find out what menstruation looks like with pieces of endometrium by looking at the photo:
Every woman needs to understand when bleeding with pieces of the intrauterine layer indicates pathology. The sooner the disorder is detected, the easier the treatment will be. Changes in the menstrual cycle are an important signal that should force a girl to seek advice from an experienced doctor.
Causes of endometritis
The main cause of the inflammatory process is the entry of pathogenic viruses and bacteria into the uterine cavity, which, against the background of decreased immunity or disruption of the integrity of the endometrium, affect the mucous membrane of the uterine cavity.
Pathogenic microorganisms, infections and viruses can enter the uterus both ascending (through the cervical canal of the cervix) and descending (from the fallopian tubes, inflamed appendix, etc.).
The most common cause of inflammation in the endometrium is mechanical damage to the inner lining of the uterus, caused naturally or by surgical intervention. These include:
- abortions, including spontaneous ones;
- C-section;
- various gynecological manipulations in the uterine cavity;
- childbirth.
In all of these cases, the endometrium lining the uterine cavity peels off from it in large pieces, exposing large areas of unprotected walls of the organ. Bacteria and infections that fall on them, introduced through surgical instruments or naturally, find themselves in a favorable environment for their reproduction.
The acute form of endometritis, which in addition to the classic picture of symptoms is accompanied by purulent vaginal discharge, is caused by sexually transmitted diseases, for example, gonorrhea or chlamydia.
Inflammation can also be caused by:
- tuberculosis microbacteria;
- coli;
- protozoal infection;
- diphtheria bacillus;
- mycoplasma;
- group B streptococci, etc.
There are also risks of endometritis during normal menstruation. Blood, which, together with endometrial cells, is removed from the uterine cavity, has a specific effect on the cervical canal. It temporarily changes the acidic environment of the uterine mucosa to an alkaline one, and after this its protective functions are significantly reduced. With improper hygiene, sexual intercourse and frequent use of tampons, the risk of bacteria entering the uterine cavity increases significantly.
For example, a tampon left in the vagina for more than 6 hours or overnight is a potential source of many bacteria, which multiply at high speed in a warm and humid environment.
Intrauterine devices can also be a source of infection; they are installed incorrectly or remain in the uterus for longer than necessary; they cause damage to the endometrium and can provoke an inflammatory process.
Symptoms of endometritis
During endometritis, a woman may feel:
- nagging pain in the lower abdomen, radiating to the anus;
- general weakness;
- headache;
- depressed emotional state or sudden mood swings.
Objective signs of endometritis
Signs of acute endometritis include:
- increased body temperature, accompanied by chills and subsequent fever;
- nausea and vomiting;
- unusual vaginal discharge (with an unpleasant odor, mixed with pus, blood);
- soreness of the uterus on palpation, and its increased size.
With a chronic inflammatory process in the endometrium, the signs are less pronounced. The temperature may appear only occasionally for several days, but it is low and can be easily confused with other ailments. Only a gynecologist can detect the disease through a survey, examination, laboratory and instrumental studies. Also, with endometritis, menstrual irregularities are often observed - the discharge changes in character, it can become scanty or, on the contrary, abundant. The period of bloody discharge after the end of menstruation itself increases significantly. Throughout the entire cycle, mild nagging pain in the lower abdomen is observed.
With long-term chronic endometritis, secondary infertility may occur.
In the acute form, from the moment of infection of the endometrium by pathogenic bacteria and viruses to the clinical manifestations of the disease, it takes from 1.5 to 4 days. Endometritis caused by surgical interventions manifests itself most quickly. With chronic endometritis, the process can last for several months.
A little about hyperplasia
Excessive growth of the endometrium of a benign nature is called hyperplasia. Under the influence of hormonal imbalance, its cells begin to rapidly divide. This process also occurs during normal development. But in this case, division occurs rather than regular removal of used tissue. Therefore, the endometrium thickens and remains enlarged at all stages of the cycle. Its growth can take a lot of time, so a common sign is a delay in menstruation with endometrial hyperplasia. The parameters of menstruation also change.
There are four types of hyperplasia:
- Glandular. With it, the corresponding components of the organ grow. The glands not only increase in size, but also become curved;
- Cystic. Thickening occurs due to the formation of cavities with fluid in the glands;
- Atypical. It is distinguished by the appearance of cells in the organ that are unusual for a healthy body;
- Focal or polypous, characterized by abnormal thickening on certain parts of the endometrium.
Diagnosis of endometritis
Diagnostic methods
When a patient contacts her, the gynecologist first examines the history of the disease, finds out the number of pregnancies and births, abortions and spontaneous miscarriages.
A gynecological examination is the next mandatory diagnostic point. During palpation, the doctor determines the size of the uterus, how different they are from the norm, and monitors the pain of the reaction to the manipulations performed. Also during the examination, the doctor assesses the nature of vaginal discharge.
Acute endometritis is characterized by sharply increased size of the uterus and severe pain. In chronic endometritis, the pain is mild, the uterus is slightly enlarged.
Laboratory diagnostics. The patient must undergo a general blood test. Elevated levels of leukocytes in the blood are the main marker of the presence of an inflammatory process in the body. Also, the number of leukocytes is counted in a smear from the mucous membrane of the vagina and cervical canal.
The type of bacteria that caused the inflammatory process can be determined by bacteriological examination of the vaginal microflora.
Chronic endometritis is much more difficult to determine, sometimes requiring repeated sampling of material for bacteriological culture.
Additional diagnostic methods
Ultrasound examination helps to diagnose endometritis and distinguish it from other gynecological diseases. An experienced diagnostician using an ultrasound machine can identify:
- endometrial thickness;
- the presence of adhesions;
- changes in tissue echogenicity;
- remnants of the placenta or fertilized egg;
- the presence of blood clots and pus.
Prevention
In order for your periods to proceed normally and the number of clots to be minimal, you need to pay attention to your usual lifestyle.
- Minimize bad habits (alcohol, nicotine).
- Normalize nutrition. Eat more buckwheat, red meat, veal, fish, eggs, apples, liver (beef, pork). This will help replenish iron in the body, improve blood composition and facilitate menstruation.
- Exercise. Run, swim, do morning exercises, spend time walking.
- Avoid stress, rest more, normalize sleep (at least 8 hours).
Treatment of endometritis
Treatment methods for acute endometritis
Treatment of acute endometritis is always carried out in a hospital, since the patient requires bed rest and constant monitoring by medical personnel.
Without waiting for bacteriological tests, broad-spectrum antibiotics are prescribed. At this stage, it is necessary to eliminate the inflammatory process, preventing the spread of infection into the thickness of the uterine wall and to other organs.
Antibiotics are administered intravenously or intramuscularly for 7-10 days.
Also prescribed for endometritis are:
- painkillers and antipyretics;
- topical antibacterial drugs, for example, vaginal suppositories;
- uterine contractants;
- vitamins.
To prevent bleeding and to reduce severe pain, cold is applied to the lower abdomen.
The task of specialists during the treatment of endometritis is to prevent its transformation into a chronic form and prevent the occurrence of possible complications.
After the acute process has been eliminated, physiotherapeutic procedures are prescribed that improve blood flow in the uterus and prevent the appearance of adhesions.
Treatment of chronic endometritis
Treatment of chronic inflammation of the endometrium is a longer process, but the stages of treatment are similar - antibacterial therapy is required, after which hormonal drugs are prescribed. They are necessary to restore endometrial function and normalize the menstrual cycle.
An important stage in treatment is the elimination of the consequences of a chronic disease - adhesions in the uterine cavity, blockage and deformation of the fallopian tubes, etc.
Physiotherapeutic procedures are mandatory as part of the treatment of chronic inflammation of the endometrium. These include:
- electrophoresis;
- pulsed ultrasonic waves;
- UHF, etc.
Article last updated 12/07/2019
Every woman experiences menstrual bleeding. They first appear at the age of 10-15 years, and end with menopause, which occurs at 45-55 years. Blood clots during menstruation, nagging pain in the lower abdomen and malaise are normal in most cases. However, sometimes the condition takes on a pathological connotation. You can find out what menstruation looks like with pieces of endometrium by looking at the photo:
Every woman needs to understand when bleeding with pieces of the intrauterine layer indicates pathology. The sooner the disorder is detected, the easier the treatment will be. Changes in the menstrual cycle are an important signal that should force a girl to seek advice from an experienced doctor.
Ovarian cysts
The cause of the problem lies in the excess content of vitamin B in the body. Copious discharge occurs with inflammatory diseases of the reproductive organs. A functional ovarian cyst is detected by a simple visual examination: a significant increase in the organ is noticeable. On ultrasound, neoplasms are clearly visible. When they appear, pain and discomfort may occur during sexual intercourse. The disease affects hormonal levels: often periods become irregular and heavy.
Causes of menstruation with clots
To notice the pathology, you need to understand why pieces of the endometrium come out during menstruation. The inner layer of the uterus, the endometrium, is functional. It grows, creating favorable conditions for a fertilized egg. If pregnancy does not occur, menstruation begins. Due to the contraction of the uterus, unnecessary endometrium is rejected along with bloody discharge. Within 3-5 days, the entire exfoliated layer will be completely removed.
Two conditions indicate disturbances in the female body - a complete absence of clots and too large pieces of meat.
In the first case, we can conclude that the endometrium is underdeveloped and there are possible problems with conception. The second is about changes in the functioning of a woman’s reproductive system. Why this happens is difficult to say without a medical examination.
The most common reasons:
- Hormonal imbalance. It is disruptions in the functioning of the endocrine system that most often cause the endometrium to peel off in large pieces. Improper production of hormones can lead to serious complications. Causes imbalance: stress, nervous tension, fatigue. The situation can be corrected by eliminating the irritants; sometimes hormone therapy is required.
- Availability of an IUD. After the installation of an intrauterine device, designed to protect the body from pregnancy, the nature, color and smell of menstruation always changes; during menstruation, clots similar to meat or liver come out. This is due to the fact that the IUD does not always take root; in addition, it causes egg rejection.
- Adhesive processes. They arise due to a violation of the structure of the walls of the uterus. If there are a lot of adhesions, this leads to scanty periods with clots. Often the pathology ends in infertility.
- Endometriosis, endometritis, fibroids, hyperplasia. These pathologies are characterized by changes in the structure of the endometrium. When it comes off and comes out with your period, large pieces form. These pathologies require serious treatment. Their danger lies in the absence of pronounced symptoms for a long time. Menstruation is the only way to suspect irregularities.
Childbirth, termination of pregnancy, abortion can also cause menstruation with clots and pieces of meat.
After an abortion, heavy discharge is normal, but if it lasts longer than 10 days or this symptom is associated with others (fever, pain), you should consult a doctor as an emergency.
Do heavy menstruation occur with inflammation of the endometrium?
This happens in both acute and chronic forms of the disease. Heavy discharge on critical days with endometritis occurs due to a decrease in the restorative capabilities of the basal layer of the uterine mucosa. With the disease, the organ also loses its normal ability to contract smooth muscles. And since the ovaries also suffer, the development of the endometrium occurs more slowly and it is rejected over a longer period of time. Menstruation may not stop for more than a week. The vessels that penetrate the functional layer of the organ also reduce their ability to “seal”, since the ability of platelets to stick together and prevent blood from leaking out is reduced. The combination of all of these features makes menstruation more abundant, sometimes requiring emergency care.
What to do
Discharge during menstruation that looks like pieces of meat is an alarming symptom, so you should immediately go to the doctor. Only a gynecologist can determine the causes of this symptom. To do this, the specialist uses ultrasound data, results of blood tests, and smears. Sometimes diagnostic hysteroscopy is performed, and biological material is taken for histological examination.
Further actions depend on the diagnosis. Initially, doctors prescribe medication. These can be hormonal drugs, enzymes, etc. At the same time, traditional medicine recipes (decoctions, infusions, douchings) are used. If conservative methods are ineffective, the doctor will talk about surgically cleaning the uterus.
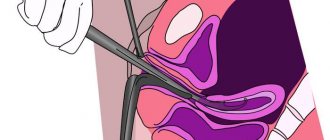
Curettage is considered a simple surgical operation. During the procedure, the doctor will use an instrument to exfoliate damaged areas of the endometrium or remove the entire functional layer.
More gentle methods designed to cope with intrauterine pathologies are:
- laser ablation;
- cryodestruction;
- microcurrent therapy.
After any of the presented procedures, spotting is noted, which disappears within a week. Innovative techniques are safe, painless and have a minimal rehabilitation period. Menstruation after cleansing occurs in 28-35 days. To minimize the risks of complications, after the procedure the doctor prescribes the woman anti-inflammatory and antibacterial agents and a course of vitamins. All this is necessary to prevent infection and speed up recovery.
What happens to menstruation after treatment?
How quickly menstruation recovers and what it looks like after treatment for endometritis largely depends on the method and quality of therapy, the woman’s age and the form of the disease.
After curettage, a bloody smear is noticed for 3-10 days. Heavy discharge requires urgent help, as in this case there is a risk of complications. Their absence will make specialists suspect a narrowing of the cervical canal, which also needs to be treated.
Menstruation with endometritis is far from the only sign of the disease. But the changes happening to them dictate the need for examination. Endometritis, if allowed to develop, can negatively affect not only the well-being, but also the reproductive capabilities of a woman. And in order not to give him a chance, you should beware of casual relationships, choose contraceptives together with a doctor and be regularly examined.
Before using any medications, you should consult a specialist doctor. There are contraindications.
Reviews
To better understand what causes menstruation with pieces of the endometrium, whether this condition is dangerous, and how to cope with it, you should study the reviews of those who have encountered a similar problem and have experience in solving this issue.
Christina, 29 years old
“For several months there have been heavy periods with huge clots, but after delays. Last month a lump the size of a walnut came out. I went to the doctor. I was prescribed an ultrasound, a blood test for hormones, a smear, and then the doctor sent me for a biopsy of endometrial tissue. As a result, a diagnosis of hyperplasia was made. A procedure was prescribed to remove the inner layer of the uterus with nitrogen. Everything went well, I recovered quickly. Now I feel good, but I visit a gynecologist once every three months to monitor the condition of the endometrium.”
Tatyana, 28 years old
“My husband and I tried to conceive a child for a long time, but to no avail. Ultimately, a diagnosis of endometritis was made. I was treated for a long time. Then I had a delay, at first I was happy, but then bleeding began with large clots. When I went to the doctor, I immediately asked if a fertilized egg could come out with menstruation? The gynecologist confirmed my fears. The chunks in the discharge were not random. Cleaned up. After which my husband and I started thinking about IVF.”
Galina Sergeevna
“My daughter was diagnosed with endometrial hyperplasia at the age of 45. Based on the test results, hormone therapy was prescribed. The doctor said that the problem could be solved without surgery, since she sought help in time. She had no signs of illness, the only thing that bothered her was the large pieces during her period. After a course of hormones and vitamins, all the symptoms went away, she feels great, heavy bleeding no longer bothers her.”
Elena Pavlova, published June 20, 2021, 10:00
The uterus is a female organ whose true purpose has been forgotten. Many cruel manipulations lead to injury to the uterus, but perhaps they injure not only the organ? Maybe these scars arise in our female soul? The uterus is scraped to remove polyps, which will grow back if nothing is changed. It even comes down to removing the organ itself if you hesitate and do nothing.
Hyperplasia and cycle length
A common manifestation is a delay in menstruation due to hyperplasia. Normally, the menstrual cycle is controlled by estrogens and progesterone. The first ensures thickening of the endometrium at its beginning, the second helps stop the growth of the organ and loosens it to accept the fertilized egg. When the volume of both substances decreases, menstruation occurs.
The disease in question is caused by various reasons. But all of them are associated with an imbalance of sex (and not only) hormones. This explains the absence of menstruation with endometrial hyperplasia. The layer grows, the cells continue to grow, and this can take tens of weeks. The functioning of the ovaries is almost always impaired. There is a deficiency of progesterone, which interferes with the maturation of the egg. Estrogen, on the contrary, is abnormally high.
In most cases, glandular endometrial hyperplasia is diagnosed if there is no menstruation. Estrogen promotes the expansion of the tubular areas. Thickening of the endometrium is also ensured by an increase in the number of stromal cells, that is, those that make up the connective tissue. Progestins are already to blame for this.
In ancient times, the uterus was the main organ for a woman.
The symbol of the uterus was a fruit with a seed, most often a pear or an apple. A seed is a symbol of the birth of a new life. The womb and women's ability to bear children were admired. The womb was considered a sacred place for bearing children, a cradle of emotions and ideas for creativity. With each cycle, the uterus is renewed. The endometrium grows, ages and is rejected. Together with the endometrium, we, our ideas, emotions, feelings, are renewed.
A stable hormonal balance, when the amount of estrogen is equal to the amount of progesterone, makes the uterine lining smooth, the menstrual cycle painless, and nothing interferes with the implantation of the embryo during conception. If the thickness of the uterine lining is more than 15 mm, this makes it difficult for the embryo to attach. And an increased number of estrogen receptors in the muscular layer of the endometrium provokes the appearance of polyps.
The nature of menstruation with hyperplasia
A normal menstrual cycle lasts 21-35 days. This process is controlled by hormones - estrogen and progesterone.
While these substances in the blood are at a high level, the endometrium grows; as soon as the hormone level drops, menstruation occurs. The proliferation of hyperplastic cells causes hormonal imbalance, and menstruation does not come on time, ovarian function is disrupted, progesterone drops, estrogen goes off scale.
Menstruation is the only, and not always obvious, sign of hyperplasia. The more momentum the pathology gains, the clearer the symptoms will become.
With endometrial hyperplasia, menstruation of one of two types is observed. It can be:
- Scanty periods. Such discharge is characteristic of focal hyperplasia, when the inner layer grows unevenly. When menstruation occurs, only part of the endometrium is shed, so the amount of blood is much less. However, in the middle of the cycle, a woman may experience bleeding. They are associated with thinning and fragility of blood vessels.
- Copious bleeding . This option is more common with hyperplasia. Usually, menstruation occurs after a delay. The consistency of the discharge changes, it becomes more liquid, and dark clots appear. Acute menstrual pain may occur.
- Menstruation with pieces of endometrium: photos, reasons for appearance
Women's periods should be even. If any deviations are observed - bleeding or delay, pain, the duration and intensity of discharge changes, this is a reason to seek medical help. Untreated pathology is often the cause of infertility.
Bleeding due to endometrial hyperplasia is common among young women. They can be cyclic or acyclic. In the first case, heavy uterine bleeding coincides with the days of menstruation, but differs in duration, which can exceed 20 days. Acyclic bleeding also lasts for weeks, but occurs between the days of menstruation. Only a doctor can stop uterine bleeding.
What signs indicate a thick endometrium and the development of a polyp?
- irregular menstruation;
- heavy bleeding, when one tampon lasts for 2-3 hours;
- bleeding between cycles;
- painful menstruation;
- pain during sex.
What is the cause of thickening of the endometrium?
- With hormonal imbalance and absence of menstruation, the endometrium is not renewed, which leads to its thickening. Proliferation of the endometrium and an increase in the number of estrogen receptors are observed with the development of endometriosis, which may be accompanied by retrograde menstruation. In this case, endometrial particles with reverse blood flow enter the peritoneal cavity and not the vagina. This leads to the proliferation of endometrial cells in the abdominal cavity.
- Another common manifestation of estrogen and progesterone imbalance is polyps. This is the growth of a separate area of the endometrium in the uterus or in the cervix. Polyps often appear with weight gain, when estrogen begins to be more actively produced by fat cells. We get estrogen dominance, and as a result, PCOS. Pelvic infections, pelvic congestion. During pregnancy, the lining of the uterus naturally thickens to support the fetus.
Here is a story from my life.
In 2010, an ultrasound scan diagnosed me with enlarged endometrium in the uterus. Then, with the ultrasound doctor, we regarded this as a possibility of implantation of the fertilized egg, but a week passed, there was no implantation, a second one began and a slight bleeding began, which did not stop, but intensified. The story ended with increased bleeding, a diagnosis of ectopic pregnancy, and hospitalization. Another ultrasound in the hospital helped avoid curettage, which is usually prescribed in this case. For me it was a nightmare, since I was planning a pregnancy and was expecting a happy motherhood. This outcome made me think and start working on myself. I began to learn to understand my body and its desires, because I did not want a repetition of this condition. I wanted to become a mother.
Endometrial structure
The endometrium contributes to the implementation of the menstrual cycle mechanism. Another of its tasks is to provide the most suitable conditions for fixation of a fertilized egg in the uterus, its full development, and obtaining everything necessary from the mother’s body.
The endometrium of the uterus consists of 2 layers:
- basal – layer directly adjacent to the uterine walls;
- functional - the surface layer that is shed during menstruation. The basal layer ensures its complete restoration before the start of the next cycle.
The hormonal background of the female body is responsible for the thickness and structure of the internal mucous layer. It increases monthly - this happens during the 2nd phase of the monthly cycle. The process of its blood supply also increases. This indicates that the organ is ready to receive the fertilized egg. Rejection of the functional layer occurs when a woman does not become pregnant - menstruation begins.
What to do to prevent changes?
To do this, start working on reducing estrogen, which is the cause of the main problems described above. Scraping is a procedure of last resort, since you will remove the inner layer, but the cause will remain.
- I began my healing by strengthening my body’s resistance to stress, since my hormonal imbalance was caused precisely by problems at work. To reduce stress, I used St. John's wort and preparations with it. Increased the amount of magnesium to relieve irritability and anxiety.
- To remove excess estrogen from the body, make sure you have enough vegetables and fruits in your diet. In winter, it is better to have processed fruits and vegetables, stewed or baked. Since raw fruits and vegetables in large quantities in winter can increase the amount of mucus in the intestines and gas formation. During other periods, there may be more raw vegetables and fruits.
- Make sure there is no soy in your diet, as it increases estrogen, with the exception of fermented soy - miso, soy sauce, tempeh.
- Minimize the amount of foods that irritate the intestines - flour, sweets, dairy, coffee, alcohol.
- Make sure you have enough protein in your diet. Chicken, turkey, fish, beans, lentils, buckwheat, quinoa, corn, brown rice.
- Cruciferous vegetables - broccoli, cauliflower - contain indole-3-carbinol, which reduces estrogen dominance. The recommended dosage of this substance should be 100-200 mg per day. In my practice, I use such drugs as “Super Indole” and “Indofort” from Vitamax.
- To replenish iron levels after heavy bleeding, I use the drug “Green Magic”, which contains chlorella with a broken wall for effective absorption of iron.
- I restore progesterone levels to reduce estrogen dominance using a cream based on wild yam.
- Pads and tampons are treated with chemicals containing parabens and phthalates to bleach the cotton, which can be an additional source of xenoestrogens, so I switched to using a menstrual cup, which is convenient and practical. Also, a menstrual cup allows you to assess the amount and color of menstrual fluid.
Cycle recovery
Curettage for hyperplasia is carried out under anesthesia. In order not to further disrupt the functioning of the endocrine system, the procedure is scheduled for the day on which the expected menstruation should occur. The first two weeks after the procedure, the patient may experience scanty, odorless bleeding. This is due to damage to the internal walls and blood vessels. If there is pain in the lower abdomen and the woman has a fever, this indicates inflammation or infection. Seek medical attention immediately.