Normal discharge after childbirth
Bloody discharge leaving the uterine cavity in the postpartum period is usually called lochia.
Normally, clots that form in the uterus and particles of damaged tissue leave the organ within 6–8 weeks. At the same time, there is a gradual decrease in the volume and nature of such secretions. So, on the first day they resemble menstruation in consistency and color, and by the third day they become serous-sanguineous. By the end of the 3rd week after the birth of the baby, the lochia becomes light and liquid, only occasionally having a pinkish tint. Gradually their volume decreases, and soon the woman notices their complete absence.
How long does discharge last after natural childbirth?
Normally, discharge after natural childbirth stops by the end of the 6th week. During this time, the reproductive organ is completely restored and cleansed. However, some women may notice small amounts of lochia up to eight weeks after giving birth. This is most often recorded in the following cases:
- delivery by caesarean section;
- during multiple pregnancy;
- in case of disruption of the process of normal outflow of secretions (anatomical disorders of the structure of the uterus and genital tract).
How long does the discharge last after a caesarean section?
Thick, bloody discharge after the birth of a baby is recorded by women who gave birth by cesarean section. With this method of delivery, doctors violate the integrity of the reproductive organ and remove the baby, amniotic sac and umbilical cord. After this, the uterus is sutured. As a result of such actions, the uterus loses its contractility due to the presence of sutures on its surface.
All this directly affects the duration of lochia. As observations by experienced gynecologists show, postpartum discharge in such women can be observed for two months from the moment the child is born. If after the specified time the lochia does not stop, you must inform your doctor.
Cleaning
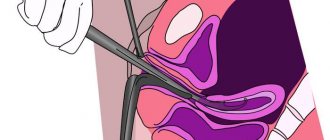
In most cases, the problem is solved surgically: . Many people are afraid of this operation. Women are afraid not so much of pain as of the instruments with which the procedure is performed, because their lack of sterility sometimes causes another infection to get inside.
Don't be afraid of pain. The operation is performed under general anesthesia, so you will not feel anything. After surgery, there is usually no pain either. Here it all depends more on the individual characteristics of the lady. As for the possible entry of harmful bacteria into the genital tract, refusal to undergo surgery poses a much greater health threat.
The most dangerous and... The endometrium can spread to neighboring organs, becoming inflamed there and causing even more serious consequences.
If clots remain in the uterus, only a doctor can determine the cause.
Never ignore the body's alarm bells. Any ailment can serve as a symptom of a dangerous disease. Remember, your baby’s future depends on your attitude towards yourself.
After giving birth, women often leak blood clots from the vagina. With such symptoms, women are sometimes referred for uterine cleaning. Is this procedure really necessary, in what situations can you do without it, and how painful and effective is it?
Blood clots after childbirth are a common occurrence, especially in the first days when the discharge is very intense. The amount of blood loss is comparable to a very heavy menstruation. The uterus is freed from all the “products” of pregnancy, and the endometrium is gradually restored. Problems can arise if debris in the uterus after childbirth is retained as a result of poor uterine contractility or spasm of the cervical canal (cervix). This can happen to a woman of any age.
Typically, postpartum discharge and blood clots are observed for 5-7 days, just before discharge from the hospital. And then they gradually turn into the so-called daub. A bad sign is considered to be heavy discharge that suddenly disappears almost completely. Meanwhile, the woman notes that the uterus remains noticeably enlarged. This may indicate that blood clots remain in the uterus after childbirth and they definitely need to be released. Usually, to make a diagnosis, doctors prescribe an ultrasound examination for a woman. And if a lot of lochia (fluid, blood) is actually found in the uterus, but there is no placental polyp, then drugs that contract the uterus are prescribed, most often oxytocin is administered intramuscularly or by drip.
It often happens that clots after childbirth suddenly appear after 1-3 “clean” days. This may just indicate their retention in the uterus. It is important that there are no symptoms of the inflammatory process - pain, unpleasant odor from the vagina, elevated temperature when measured, for example, in the elbow, that is, not in the area of the mammary glands. After all, the inflammatory process, that is, endometritis, can have a negative impact on a woman’s reproductive abilities. And often in this case, when postpartum bleeding with blood clots is still observed, antibacterial therapy is prescribed. There is no other way to overcome a bacterial infection in the uterus. Antibiotics are usually prescribed those that are allowed during lactation. However, in any case, it is advisable to try to feed the child before taking the drug and give the baby bifidumbacteria to support the intestines and try to avoid side effects of the medications taken by the mother.
The reasons why blood clots appear 2 weeks or a month after childbirth are often due to the formation of a placental polyp in the uterus as a result of the fact that not all of the placenta has left it. In this case, it will not be possible to get by with drugs that contract the uterus and antibiotics. Cleaning the uterus after childbirth or vacuum aspiration is necessary. Moreover, doctors often recommend performing it immediately under optical control in order to accurately remove the polyp and not have to repeat this procedure. By the way, it is performed under general anesthesia and is therefore absolutely painless.
If the remains of the placenta after childbirth were discovered almost immediately, even in the maternity hospital, revision of the uterus is an even simpler procedure, since in the first days after the birth of the child, the woman’s cervix remains slightly open, which means there is no need for its instrumental dilatation, which threatens her with injuries.
If large blood clots come out after childbirth, obstetricians-gynecologists know what to do. While a woman is in the maternity hospital, a blood test is taken for hemoglobin in order to detect excessive blood loss in time. In addition, in most maternity hospitals, for the purpose of prevention, all women are given intramuscular oxytocin for three days. Be sure to undergo daily examinations by a doctor, he pays attention to the soreness and size of the uterus.
Usually, the uterus contracts poorly in women with fibroids, after a multiple pregnancy, if the child weighed more than 4 kilograms.
| 04/13/2019 11:55:00 Losing weight quickly: the best tips and methods Of course, healthy weight loss requires patience and discipline, and crash diets do not bring long-term results. But sometimes there is no time for a long program. To lose weight as quickly as possible, but without hunger, you need to follow the tips and methods in our article! |
| 04/13/2019 11:43:00 TOP 10 products against cellulite The complete absence of cellulite remains a pipe dream for many women. But this does not mean that we should give up. The following 10 foods tighten and strengthen connective tissue—eat them as often as possible! |
| 04/11/2019 20:55:00 These 7 foods are making us fat The food we eat greatly affects our weight. Sports and physical activity are also important, but secondary. Therefore, you need to be careful when choosing products. Which ones make us fat? Find out in our article! |
Childbirth
– this is a complex physiological process that is associated with a large physical and psychological load on a woman’s body and a certain degree of risk to her health.
Full recovery of the body occurs no earlier than 6-8 weeks after the birth of the baby.
One of the natural manifestations of cleansing the body is blood discharge from the uterus, which begins immediately after childbirth. Very often, the discharge is similar to heavy menstruation and comes out along with clots. Many women, not knowing the causes of clots after childbirth, experience fear, viewing them solely as a pathology. However, in most cases this is not the case. Let's consider what volume of discharge and clots is normal and what to do in case of blood clots after childbirth, when they threaten the health of the young mother.
Causes of blood clots after childbirth in the uterus
During childbirth, the uterus undergoes much greater stress and changes than all other organs.
After the birth of the fetus, the placenta is released - the membranes, placenta and umbilical cord. Remnants of the placenta, mucus and blood clots continue to come out throughout the postpartum period. Blood clots are also called lochia. Normally, by the end of the first month after birth, they become scanty and transparent.
The cause of blood clots, especially when they become very intense, is breastfeeding the baby. During the process, the uterus contracts intensely. This promotes its rapid cleansing and restoration. During feeding, many women, especially multiparous women, feel moderate pulling pain in the abdominal area, which is evidence of uterine contractions. In such cases, blood clots that are released from the uterus are considered as a natural physiological process of the uterus returning to its prenatal state.
After 2-3 days, women are usually prescribed an ultrasound examination of the uterus. It is necessary to ensure that the process of cleansing the reproductive organ is carried out in accordance with the norm. It is not uncommon for a doctor to discover remnants of membranes and large blood clots. In this case, clots are an alarming sign, since favorable conditions are created for the penetration and proliferation of pathogenic bacteria. In severe cases, this can lead to endometritis (inflammation of the inner layer of the uterus).
Concerns also arise in those cases when, a few days after childbirth, lochia decreases significantly, or even stops altogether. The cause of this phenomenon may be a large blood clot, which prevents the free passage of secretions from the uterus. It also happens that clots do not appear immediately, but after several “clean” days.
If such phenomena are accompanied by pain, an unpleasant odor from the vagina and an increase in body temperature, this may indicate the onset of an inflammatory process. In such cases, it is necessary to immediately contact your doctor, who will know exactly what to do with blood clots in the body of the uterus that are “in no hurry” to come out.
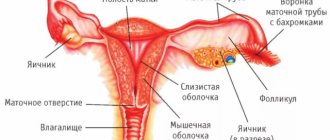
Regeneration and involution of the uterus
The uterus, in which the baby grew, increased more than 500 times during pregnancy, the ligaments stretched and became thinner. As soon as the baby is born, the gradual reverse development (involution) of the reproductive organ begins. During the first day, the uterus does not leave the abdominal cavity; it is still large enough to fit in the pelvis.
Only after one and a half to two months the uterus will reach almost the same size as it was before pregnancy - the uterus will weigh about 60-70 grams, and its volume will be no more than 5 ml.
After childbirth, the myometrium gets rid of excess muscle fibers. And this happens in a very interesting way - the fibers, which have now become unnecessary, are simply blocked from accessing the blood supply - the vessels close, and as a result, the excess fiber, having fulfilled its natural purpose, dies and is brought out in the form of the most common blood clots. The placental wound (the place where the placenta was attached) also bleeds, and already on the second day after birth, natural coagulation processes will lead to the formation of a certain amount of blood clots , which will also come out through the genital tract.
Sometimes, under the influence of a variety of situations, the clots do not come out or do not come out completely, and then those remaining inside the reproductive organ cause severe processes in the woman’s body.
Clots can be suspected based on characteristic symptoms, and the assumption can be confirmed or refuted based on ultrasound results.
In what cases is it necessary to clean the uterus after childbirth?
The most important organ responsible for the successful course of pregnancy and the birth of a child is the uterus. It is she who bears the heaviest load during these processes.
After childbirth, the uterus begins to clear itself of the membranes that have surrounded the fetus throughout pregnancy. This is called the birth of the placenta. The afterbirth, which includes the umbilical cord and membrane of the fetus, must come out completely. If this does not happen, immediately after the birth process, the obstetrician-gynecologist can perform manual cleaning of the uterus to remove the remaining remains. Complete cleansing of the uterus occurs in 7–8 weeks and is a process similar to menstruation.
Timely monitoring of postpartum cleansing of the uterus is important and can prevent the development of complications:
- all residues in the uterus can begin to decompose, creating favorable conditions for the development of bacteria;
- the clot can adhere to the uterus, causing the development of endometriosis.
Cleansing the uterus prescribed to a new mother will most likely delay discharge from the hospital by several days. Carrying out the procedure in the next three days after birth makes it less painful, because the cervix has not yet had time to fully contract and will not have to dilate.
If in the maternity hospital the new mother was not checked for the presence of clots in the uterus, then it is worth contacting the clinic at the place of residence or a paid clinic
If the maternity hospital did not check you with an ultrasound machine for the presence of clots, go to your local clinic or a paid clinic to have your uterus checked.
What are clots in the uterus: physiology
During the period of involution, the uterus pushes out in the form of clots fragments of placental tissue, blood from vessels damaged during childbirth, and mucus from the cervix. This takes up to 8 weeks. That is, postpartum clots are a physiological phenomenon, indicating that a woman’s body is being cleansed and, therefore, functioning correctly. Typically, the volume of discharge - lochia - increases after the young mother begins to move. This is due to the fact that the production of oxytocin, a hormone that stimulates the muscles of the reproductive organ and increases the frequency of its contractions, is intensified. In turn, oxytocin is produced in greater quantities during breastfeeding. And gradually the uterus returns to its prenatal state, is renewed, the wound surface heals, the discharge becomes lighter and by the end of the second month has a mucous consistency. To assess the condition of the uterus and monitor the process of clot release, women must undergo an ultrasound during the adaptation period, 3–4 days after birth. Normally, by the third day, the clots move to the internal os of the cervix for subsequent excretion with lochia. If there are deviations, clots - large and not very large - remain in the area of the body and fundus of the uterus.
After childbirth, it is normal for clots to pass out
Nature of bleeding
In the first days after childbirth, bleeding from the uterus is strong, profuse and saturated in color. Clots are the norm these days. They are dark in color and have a slimy consistency, similar to pieces of liver.
The discharge is especially intense in the first days after labor. Further, the intensity of the discharge decreases and the lochia become more and more transparent.
Clots in the uterine cavity after childbirth are a problem that almost every woman faces. During pregnancy, a woman's reproductive organs undergo enormous changes; this is necessary for the normal bearing of a child. But what happens after childbirth? The birth of a baby starts a long recovery process, a return to the normal functioning of the entire body, including the reproductive system. The formation of clots is a natural process that accompanies the recovery period.
Treatment
Since detection of clots usually occurs in a timely manner, in most situations complex assistance tactics are used. It includes both direct elimination of formations and parallel prevention of possible complications:
- The standard of care is a manual examination of the uterine cavity, which allows for mechanical removal of clots and tissue debris. In this case, the doctor inserts the fingers of one hand through the cervical canal, and with the help of them detects and removes retained structures.
- In parallel with the manipulations, hemostatic therapy is carried out, aimed at preventing uterine bleeding, as well as re-formation of clots.
- Immediately after completion of the manipulations, uterotonic agents (usually oxytocin) are administered intravenously or intramuscularly. They promote rapid contraction of the uterus, which is also aimed at preventing complications.
- Finally, the woman must be prescribed antibacterial therapy aimed at preventing the development of endometritis. First of all, it allows you to “cover up” possible infection of the uterine cavity during manipulation.
Even if by the time treatment begins there are already signs of inflammation, the first stages of assistance are of a similar nature. The changes concern only antibacterial therapy – it is prescribed for a longer period.
How to avoid clot accumulation
In order to improve the process of cleansing the uterus from clots from the blood and mucous membrane and prevent complications, it is important to follow a number of rules.
Recommended:
- Carry out hygiene measures regularly, change pads often. This will help prevent the development of an infectious-inflammatory reaction in the uterus;
- Lie on your stomach periodically. This measure promotes better clearance of clots;
- Place a cold heating pad on the lower abdomen in the first hours after birth;
- Do not lift heavy objects;
- Go to the toilet regularly, even if there is no urge. When defecating, do not push too hard;
- Feed your baby on demand, not on time;
- Add foods that improve intestinal function to your diet;
- Perform special postpartum exercises.
Breastfeeding a baby leads to increased production of the hormone oxytocin. The latter improves the contractility of the muscle fibers of the uterus. Therefore, breastfeeding also serves to prevent the formation of clots after childbirth.
Hematometra - what to do?
When a woman is diagnosed with a hematometra, treatment must begin immediately. The main goal of therapeutic measures is to create conditions for the normal outflow of postpartum secretions from the uterine cavity. Initially, doctors use medications to increase the activity and contractility of the uterine myometrium so that the organ can cleanse itself. In severe cases, when the hematometra is large or becomes infected, the only treatment option is surgery.
Treatment of hematometra with medications
If a woman is diagnosed with a hematometra after childbirth, treatment begins with the prescription of medications. In this case, drugs are used that can increase the tone of the myometrium and enhance its contractility. Thus, doctors try to create all the conditions so that the hematometra leaves the reproductive organ on its own. The basis of treatment is a medicine based on synthetic oxytocin.
If spastic contractions are observed, antispasmodics are used (to prevent a sharp increase in tone):
- Drotaverine;
- Metamizole;
- Pitophenone.
When a hematometra is formed as a result of trauma to the birth canal or extensive postpartum hemorrhage, hemostatic drugs (Etamzilat) are included in the complex treatment.
After the clots are eliminated and the uterine cavity is cleansed, hormonal drugs may be prescribed to restore the endometrial layer:
- Duphaston;
- Utrozhestan.
Vacuum aspiration hematometers
To prevent possible complications, doctors always examine the uterine cavity after the placenta has passed. In this way, it is possible to reduce the risk of hematometra formation. If there is a large amount of blood left in the uterus after childbirth, vacuum aspiration is performed - a surgical procedure to cleanse the uterine cavity.
Using a special device that operates on the principle of a vacuum cleaner, the remaining pieces of tissue, placenta, and blood clots are removed. A similar cleaning of the uterine cavity is also carried out in case of suppuration. The next pregnancy after hematometra is planned no earlier than six months, after examination and permission from the doctor.
How to treat
If, despite preventive measures, a clot still forms after childbirth, continuing treatment at home is prohibited. Yes, you will have to seek help from a doctor to find the cause of the ailment. If the cause of delayed recovery is inflammation of the appendages, antibiotics, vitamins, and immunomodulators are prescribed.
You can detect inflammation on your own: the discharge becomes more voluminous, and an unpleasant putrid odor appears.
If the tone of the appendages is reduced, hormonal drugs are prescribed: “Oxytocin” or “Pituitrin”, which stimulate contraction and, as a result, the removal of unnecessary tissues from the body.
How the uterus is cleansed after childbirth
The appearance of clots in the uterus after childbirth is a natural phenomenon that is associated with the course of physiological processes, therefore such a disorder does not always have a pathological basis. Clots in the uterus can occur for physiological reasons, which are classified depending on the time factor.
In the third, postpartum period, the uterus rejects the placenta and membranes, they become detached from its walls. The internal surfaces covered with the endometrium begin to bleed. As a result of contraction, pressure is exerted on the vessels to stop the release of blood. Clots form on the inner surface, closing the lumen.
The endometrium is restored gradually - in the process of rejection of maternal tissue along with blood clots, therefore, in the first days after birth, lochia flows abundantly, after a week the amount of discharge decreases.
Attention! All clots should leave the uterus by 8 days after birth. This process is monitored using ultrasound
If the bleeding does not stop, the doctor cleans the cavity.
During the normal course of the regeneration process, after a week the lochia become sparse and there are no clots in them. Starting from the second week, bleeding in abundance becomes similar to normal bleeding, but with a duration of about 40 days. Deviations from the schedule are often associated with the characteristics of the body and injuries received during childbirth.
Causes of bleeding
During labor, a woman's uterus is subjected to severe stress. After the fruit and its shell come out, damage remains on the walls. Over time, the internal tissues heal, and residual tissues and clots are released along with the blood.
This discharge during the postpartum period is called lochia. Normally, lochia can be secreted for 6–8 weeks after birth, gradually becoming less abundant and saturated. By the end of the second month after the birth of the baby, the lochia should stop; if this does not happen, you need to consult a doctor.
In order to exclude the presence of postpartum complications, specialists at the maternity hospital carefully monitor the intensity of discharge. Before the mother and baby are discharged home, the woman should undergo an ultrasound examination. Nowadays, this analysis has become mandatory and in all maternity hospitals in the country, doctors are required to conduct an examination. If you were not given the opportunity to be examined before discharge, be sure to visit the antenatal clinic for an ultrasound scan.
Symptoms of pathology
Since the body of a new mother is unpredictable, during the adaptation period, even if the condition of the uterus is normal after an ultrasound on days 3–4, complications associated with the release of clots may arise. These include:
- cessation of lochia (stopping the rejection of clots may be evidence that the cervical canal is blocked by a large blood clot, or the cervix is narrowed);
- pain in the lower abdomen;
- bright red discharge with clots for several weeks (this usually happens when the remnants of the placenta are caught in the uterine lining and cannot come out on their own);
- weakness, fever and unpleasant-smelling discharge (these signs of the inflammatory process are in most cases observed in combination);
- the appearance of bloody spots after the completion of the physiological period for the release of clots;
Discharge with blood after the physiological period of expulsion of clots has completed should alert the woman
What can a woman do on her own?
If clots are found in the uterus after childbirth, what should you do? By following simple tips, a woman can independently provoke the release of mucus. Ask doctors at your maternity hospital about these methods. Here are some recommendations.
- Put your baby to your breast more often. Stimulation of the nipples and the baby's sucking movements promote the production of natural oxytocin and contractions of the uterus. This is especially noticeable in the first days after childbirth. As soon as the baby begins to suckle, the reproductive muscle
- Lie on your stomach. The abdominal wall and muscles do not immediately return to their original state after the baby is born. Therefore, a bend in the uterus may occur, which is why clots form. To prevent this from happening, lie on your stomach more often.
- Lead an active lifestyle. If you have no contraindications, then you need to move more. Walk, walk, carry your baby in your arms. The higher the physical activity, the faster the uterus will contract.
- Use available tools. After childbirth, if there are no contraindications, tighten your stomach. To do this, you can purchase a special bandage or use a sheet.
- Do Kegel exercises. Rhythmically squeeze and unclench the muscles of the vagina and anus. It may not work out well at first. But such gymnastics not only promotes the release of clots, but also accelerates the recovery process.
- Watch your stool and empty your bladder more often. After childbirth, a woman practically does not feel the urge to urinate. But it is necessary to urinate. Contractions of the bladder and intestines also increase uterine tone.
Preventive measures
To prevent the problem from affecting you, it is important to follow some rules in the first hours and days after childbirth. Not everything on this list depends on the woman herself, but what depends on her must be strictly followed.
- After the birth of the placenta, women apply ice to the abdomen. And although doctors have recently been trying to dispute the benefits of this action, long-term practice is exactly this: ice is needed to stop bleeding in the placental wound. Too much blood loss can lead to a variety of complications.
- Put your baby to your breast more often, especially in the first few days after birth - each attachment stimulates the production of oxytocin.
When mom needs to be wary
A specialist can judge how the uterus is returning to its normal appearance and functions based on the results of an ultrasound. It is carried out 3-4 days after birth, and if everything is fine, the woman is discharged home.
But problems with recovery may arise later, when there is no constant medical supervision. And the woman will have to assess her own condition, the type of discharge. You should consult a doctor when you notice:
- Abrupt cessation of discharge early after childbirth. This may be evidence of blockage of the cervical canal with a large clot, narrowing of this part of the organ, or bending of the uterus. With any of the complications, pain is felt in the very lower abdomen.
- The discharge remains red and contains noticeable tissue particles for several weeks. The remains of the placenta in the uterus after childbirth may not come out on their own, but remain attached to its mucous membrane. This causes prolonged bleeding and profuse discharge.
- Deterioration in general health. As a rule, it occurs against the background of rising temperature. And the discharge smells unpleasant.
- The contents of the uterine cavity continue to be released in a constant large volume for a long time. Normally, by the end of the second week it becomes lighter and decreases quantitatively.
- The discharge acquired, as it should, a light color, but then blood was found in it again.
- Clots that come out at any time after childbirth are large in size.
Symptoms of pathology
If you notice any deviations from the norm, then this is a reason to urgently consult a doctor. These symptoms include:
Stopping discharge. If the clots stop being released, this may be the cause of blockage of the cervical canal or severe narrowing of the cervix of the uterine cavity.
- Severe pain in the lower abdomen.
- The color of the discharge (clumps) is bright red. This may indicate that the remnants of the placenta are attached to the uterine cavity and cannot come out on their own.
- Severe weakness, increased body temperature not associated with a cold, dizziness.
- The discharge has a persistent unpleasant odor. This indicates an inflammatory process in the body.
- Continued discharge of clots after 8 weeks of birth.
- The clots are very large in size.
Treatment
Since detection of clots usually occurs in a timely manner, in most situations complex assistance tactics are used. It includes both direct elimination of formations and parallel prevention of possible complications:
- The standard of care is a manual examination of the uterine cavity, which allows for mechanical removal of clots and tissue debris. In this case, the doctor inserts the fingers of one hand through the cervical canal, and with the help of them detects and removes retained structures.
- In parallel with the manipulations, hemostatic therapy is carried out, aimed at preventing uterine bleeding, as well as re-formation of clots.
- Immediately after completion of the manipulations, uterotonic agents (usually oxytocin) are administered intravenously or intramuscularly. They promote rapid contraction of the uterus, which is also aimed at preventing complications.
- Finally, the woman must be prescribed antibacterial therapy aimed at preventing the development of endometritis. First of all, it allows you to “cover up” possible infection of the uterine cavity during manipulation.
Even if by the time treatment begins there are already signs of inflammation, the first stages of assistance are of a similar nature. The changes concern only antibacterial therapy – it is prescribed for a longer period.
Diagnostic measures
Identification of organic particles that remain in the organs occurs during the assessment of involution (reflex reduction) of the uterus and appendages. After childbirth, the following medical procedures are performed:
- questioning the patient about the intensity, duration, consistency of discharge and other characteristic symptoms;
- palpation of the uterus and examination of the birth canal on a gynecological chair;
- ultrasound examination, including echography;
- laboratory analysis of smears and scrapings.
In the normal course of postpartum recovery, the first diagnostic study is carried out a week after birth, the second - after the lochia has stopped (6-8 weeks). Verification of standards for reducing the weight, volume and thickness of the walls of the uterus, as well as examining cavities for accumulation of blood and other fluid, allows you to confirm normal involution or detect problems in time, avoiding complicated inflammatory processes and deformation of organs.
Deviations from the norm
Assessing the nature and intensity of discharge is an effective method for preventing complications. There are situations when the presence of postpartum clots in the uterus does not fit into the norm and poses a potential danger.
Emergence. Inclusions in the lochia should not appear for the first time a few days after birth. If at first liquid lochia flowed out without lumps, and then, for example, a large clot came out at home a week after giving birth, you should consult a doctor.
Duration. It is imperative to monitor how many days the clots come out after childbirth. At 2-3 weeks there should be no fragments in the discharge. By this time, the lochia becomes more liquid and lighter in color. If after a month you notice discharge with lumps, you should not hesitate to visit a gynecologist.
Dynamics. The situation requires special attention when normally occurring lochia, with or without inclusions, suddenly stops long before the due date, for example, after two weeks. This is the main sign of clots in the uterus, indicating the accumulation of lumps in the cervical canal or above it, which interfere with the free evacuation of contents.
Organoleptics. An unpleasant odor, large fragments, and the addition of pus often indicate a complication of the recovery period. A blood clot the size of an egg or fist is not normal. Typically, lochia contains inclusions with a diameter of no more than 5 kopecks or a teaspoon.
What clots look like after childbirth:
- coagulated blood resembles a jelly-like lump, rich red in color. Sometimes there are black clots that resemble liver. This indicates that the oxidation process has begun;
- the remains of pregnancy products look like a dense piece of red mucus or film, irregular, elongated in shape. Unlike blood, it does not smear when rubbed or pressed.
It is also necessary to pay attention to the accompanying symptoms of clots in the uterus. Accumulated fragments serve as a favorable environment for the proliferation of pathogenic bacteria
Therefore, if blood clots remain in the uterus for a long time after childbirth, then there is a high probability of developing endometritis or metroendometritis. As a result of inflammation, acute pain occurs in the lower abdomen, an odor appears from the vagina, and body temperature rises.
ethnoscience
If a woman is not breastfeeding, she has the opportunity to resort to the use of herbal infusions, but only after prior consultation with a doctor. Herbal infusions can cause allergies in the baby, so if you still choose this treatment for yourself, stop breastfeeding for the duration of therapy.
Here are some recipes for decoctions:
- Nettle decoction. Half a liter of boiling water requires 4 tablespoons of dried herbs. Pour in, leave until completely cool, strain. The decoction is ready for use. Take 100 ml three times a day.
- Shepherd's purse. Pour 4 tablespoons of chopped herbs into 2 cups of boiling water and leave until completely cool. We filter. During the day, you need to drink the entire decoction in several doses.
- Blood red geranium. It's better to cook in the evening. Two teaspoons of geranium are poured into 400 milliliters of cold water and left to infuse overnight. In the morning everything is filtered and drunk throughout the day.
Herbal medicine tones the uterine muscle very effectively.
Signs of dangerous blood clots after childbirth
If blood clots form in the veins immediately after birth, the body may not be able to dissolve them. Sometimes these clots or blood clots can break away from the veins and travel through the bloodstream to the lungs. This medical condition is called pulmonary embolism.
Much less common is the formation of blood clots in the arteries of the heart and brain, which lead to heart attacks and strokes.
Because women have an increased risk of developing blood clots in their veins after having children, they need to know the signs that may indicate life-threatening clots have formed.
Signs and symptoms of dangerous blood clots include:
- pain, redness, swelling, warmth in one leg, which may indicate deep vein thrombosis;
- shortness of breath or other difficulty breathing;
- chest pain;
- dizziness or fainting;
- increased heart rate;
- chills and clammy skin.
Some women have an increased risk of developing blood clots. Risk factors include:
- history of blood clots before birth;
- family history of blood clots or bleeding disorders;
- excess weight;
- age exceeding 35 years;
- prolonged lying or sitting positions during pregnancy;
- birth of twins, triplets;
- the presence of other medical conditions such as autoimmune disorders, cancer, diabetes.
Summarize
If a woman develops clots in the uterus after childbirth, treatment should only be carried out by a gynecologist. Never try to get rid of mucus lumps on your own. If you are breastfeeding, it is strictly forbidden to take any medications without prior medical advice. Speedy recovery to you!
The postpartum period is a kind of transition, during which the primary adaptation of the female body occurs after the resolution of pregnancy. It is characterized by profound changes in the reproductive system, ensuring its return to its original state. But this process does not always proceed smoothly, which is accompanied by insufficiently rapid restoration of organs and tissues.
The most common phenomenon observed is lingering blood clots in the uterus, which in themselves are not pathological structures. Such formations are normally observed during the first days of the postpartum period, indicating the normal healing process of the internal surface of the organ. The situation is different if they are large in size or remain in the uterine cavity for a long time.
In this case, the most common reasons for their persistence are determined, after which standard diagnostic and therapeutic measures are carried out. Currently, in maternity hospitals, such a symptom can be detected in a timely manner, which helps prevent possible complications. Accordingly, thanks to such a serious approach, it is now possible to effectively combat postpartum infectious diseases.
Prevention
The blood in the tract should not stagnate, and at the same time it should not flow continuously, so it is very important for a woman to know what to do so that she gets out and stops in time.
- To prevent the vessels from being destroyed, ice is placed on the mother’s stomach (but only if the placenta is completely removed).
- To stimulate uterine contractions, so that clots in the uterus do not linger for a long time after childbirth, hormonal drugs are taken, in particular.
- A little physical activity will help prevent the formation of large lumps and relieve swelling. You can start with a banal daily warm-up. large formations.
- Do not lift heavy objects under any circumstances. or a tight strip of fabric. This facilitates movement, and also helps the organs take their original place and supports the stomach. If surgery has been performed, the bandage will prevent the seams from coming apart.
- Breastfeed your baby. This stimulates the production of hormones necessary for uterine contractions. In addition, feeding itself provokes compression of the reproductive organs, due to which they are quickly freed from lochia.
- Empty your bladder and bowels often. Avoid constipation. Otherwise, there is internal pressure on the reproductive system and the vessels inside it, which can cause blood stagnation.
If any abnormality is found, contact a qualified service technician. Timely assistance will help avoid many complications.
By examining a woman, the doctor is able to detect the location of the formations. This happens by palpation. If a lump of mucus is found, a massage is performed, the purpose of which is to increase the tone of the appendages. By pressing on the lower abdomen, the doctor pushes the lumps towards the “exit”. This procedure is carried out every 2-3 hours. This is quite painful and unpleasant, but, unfortunately, you cannot do without it.