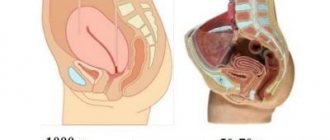
What is uterine prolapse
The uterus is a hollow organ located in the pelvic area. It consists of muscles. In a normal physiological position, it is held by ligaments; each pregnancy and childbirth causes them to stretch and weaken. Women with a history of multiple births are at risk of experiencing the pathology of uterine prolapse. This is a form of pelvic organ prolapse.
The position of the uterus changes under the influence of several reasons. During pregnancy, the organ moves downward. Prolapse of the reproductive organ is a fairly common pathology that affects every 10 women. Old parous women have prerequisites for the development of the disorder. A factor that increases the likelihood of prolapse is the process of natural aging, against which the muscles weaken.
Uterine prolapse is classified by degree:
| Degree | Characteristic |
| I degree | The pharynx moves to the middle of the vagina. |
| II degree | The cervix does not protrude beyond the genital opening. When straining, the cervix protrudes from the genital slit. |
| III degree | The cervix extends beyond the vagina, but the body of the uterus remains outside the vagina. |
| IV degree | The organ prolapses into the perineum. |
The described classification does not take into account the position of the reproductive organ, but depends on the definition of the prolapsed part of the uterus. Foreign gynecologists in their practice use a different classification that takes into account the position of the uterus.
Based on this, it can be stated that:
- uterine prolapse is possible only with stage 1 of the process;
- in the second degree, partial organ prolapse is diagnosed;
- the third stage indicates incomplete loss;
- in the fourth degree, prolapse is diagnosed, which is characterized by complete prolapse of the uterus.
Natural birth and a successful pregnancy are possible only with 1st degree prolapse. If cervical prolapse occurs during pregnancy, pregnancy becomes more difficult, and the pathological process progresses due to the constantly increasing size and weight of the reproductive organ. The woman is indicated for delivery by cesarean section.
How the cervix changes after childbirth
Over the course of nine months, the uterus has stretched and increased in size, so it takes some time for it to return to normal. Immediately after the birth of the child, its weight is about one kilogram, and the upper limit is in the navel area. Under the influence of natural hormones secreted by the mother's body, its contraction occurs, and after 1-1.5 months the uterus becomes the size of a fist, and its weight is no more than 40-50 grams.
After childbirth, the cervix also undergoes changes. In the first hours after the birth process, the diameter of its lumen reaches 10-12 cm, which corresponds to full dilatation. On the second day after birth, the size of the cervix does not exceed 4 cm, but by the tenth day of the postpartum period the muscle ring should close, allowing only the tip of the finger to pass through. After three weeks, the cervix takes on a slit-like shape, which is a diagnostic criterion by which a gynecologist can identify a woman who has given birth.
Due to the fact that in the early recovery period the birth canal is open, there is a risk of penetration of pathogenic microflora, which can cause inflammation not only of the cervix after childbirth, but also of deeper organs.
Is it possible to get pregnant with uterine prolapse?
With 1 degree of prolapse, problems with conception are not traced, provided that there are no other causes of infertility. The initial degree does not complicate the process of fertilization of the egg and does not interfere with the natural attachment of the embryo to the wall of the uterus. The first trimester most often proceeds without complications. Problems appear and progress as the size of the uterus increases.
With degrees 3 and 4 of prolapse, the anatomical structure of the pelvic organs changes significantly. Conception and fertilization are complicated by the following factors:
- impossibility of sexual intercourse with complete loss of the reproductive organ;
- progressive inflammation in the cervical canal and endometrium;
- disruption of the blood supply process;
- changes in hormonal levels, decreased activity of production of female sex hormones by the ovaries;
- inability of the uterus to create the necessary conditions for fetal development.
Attention! A doctor will be able to accurately answer the question of whether pregnancy is possible with genital prolapse after an examination and assessment of the general condition of the pelvic organs. Treatment is based on conservative methods; if it is successful, there are no obstacles to pregnancy and its successful completion.
Complications of pregnancy with uterine prolapse
If conception is successful, a woman should consult a specialist as early as possible so that the necessary conditions can be created for the successful development of the fetus inside the womb. Constant monitoring will reduce the risk of further progression of cervical prolapse and will prevent dangerous complications, which include:
- early termination of pregnancy in the first trimester due to insufficient blood supply to the uterus;
- in women with prolapse of the reproductive organ, ectopic and frozen pregnancies are more often diagnosed;
- premature birth due to early opening of the external and internal os of the uterus against the background of isthmic-cervical insufficiency;
- the risk of premature placental abruption increases.
The listed complications are classified as quite dangerous, but the risk of their occurrence can be minimized through drug support for the expectant mother. If the prolapse progresses, the woman is indicated for hospitalization and constant monitoring.
The list of less dangerous complications, the likelihood of which increases with genital prolapse, includes:
- periodic nagging pain in the lower abdomen, present throughout the entire period of pregnancy;
- exacerbation of infectious processes localized in the female genital organs, the condition is accompanied by active discharge of leucorrhoea, itching and burning;
- disruption of the defecation process, fecal retention, constant constipation (can only be eliminated with the help of laxatives);
- enuresis, or the inability to hold urine due to the constant pressure of the growing uterus on the bladder;
- painful sensations in the pelvic bones that appear due to the incorrect position of the main reproductive organ.
A woman should understand that during pregnancy the baby in the womb is constantly growing, so the listed symptoms will intensify. The uterus, under pressure, will descend and put more pressure on the bladder and rectum. In the last weeks of pregnancy, it is better to be under the constant supervision of a gynecologist. By following the recommendations of the gynecologist, a woman will be able to carry the fetus to term for the entire term and give birth to a healthy baby.
Postpartum complications
A convenient method of delivery for genital prolapse is determined on an individual basis. At the initial stage, when the risk of eversion and massive bleeding is minimal, natural childbirth is possible, but any gynecologist will do his best to dissuade the pregnant woman from giving birth on her own.
Attention! Uterine prolapse of the 1st degree, in the presence of concomitant factors complicating the process of natural delivery (narrow pelvis, multiple pregnancy, large fetus, risk of bleeding), is an indication for a cesarean operation.
During natural childbirth, the following complications are possible:
- rapid progress of genital prolapse during the transition of the disease from the first stage to 2-3;
- lack of labor, leading to the death of the child during childbirth;
- massive uterine bleeding due to the inability of the reproductive organ to contract;
- iron deficiency anemia after childbirth.
The most convenient and safe method of delivery should be selected by the doctor, and the woman should agree with him. If the gynecologist recommends a cesarean section, then this method is optimal. Most often, the technique is chosen to reduce the risk of postpartum progression of prolapse in a woman.
Principles of treatment
What treatment for prolapse after childbirth will depend on the following factors:
- degree of omission;
- the presence of other gynecological ailments;
- need for childbearing function in the future;
- patient's age;
- how much the neighboring organs are lowered;
- what is the degree of surgical risk?
Skein prolapse after childbirth can be treated with the following methods:
- therapeutic exercises;
- traditional methods of treatment;
- gynecological massage;
- hormone therapy;
- surgery;
- wearing a pessary or bandage.
Surgical intervention
If grade 3 or 4 prolapse is diagnosed, and if conservative methods do not produce a positive effect, surgical treatment is prescribed.
There are the following methods for this:
- vaginoplasty . This is a corrective intervention that strengthens the muscles of the genital opening;
- suturing ligaments . It is used to strengthen the strength of the ligamentous apparatus of the uterus, however, in this case there is a risk of subsequent infertility;
- use of alloplastics . These materials fix the position of the uterus and strengthen the ligamentous apparatus;
- hysterectomy . Uterus removal. It is indicated when it is not possible to tighten the stretched muscles, and the woman is no longer planning a pregnancy.
Conservative methods
This treatment is based on the woman performing certain sets of exercises - according to Kegel, according to Yunusov, according to Atarbekov, according to Bubnovsky, and so on. These exercises are aimed at restoring muscle tone, which allows the uterus to return to its anatomically correct place.
NOTE!
It is necessary to understand that such exercises are not effective in all cases. They are prescribed in all stages of prolapse to prevent the progression of the disease, but it is possible to return the uterus to its natural position with the help of exercises only in the 1st and uncomplicated 2nd degree of pathology.
Gynecological massage is performed in the gynecologist's office. It is also aimed at restoring the tone of the uterine muscles and is also more effective in the initial stages of the disease.
In some cases, a woman may be prescribed hormone therapy. It is relevant if prolapse occurs as a result of a decrease in estrogen concentration.
As for traditional methods of treatment, they are auxiliary in nature and must be combined with the main treatment.
Pessary
A pessary is a special device that is inserted into the vagina, with its help the reproductive organ is kept from falling out.
This product is made from biological and hypoallergenic materials, therefore it is completely harmless to the woman’s body.
Initially, the pessary is inserted into the vagina by a gynecologist, but subsequently the woman must learn to insert and remove it independently.
In some cases, wearing a pessary is indicated temporarily. It is used for preventive purposes while the woman receives the necessary treatment.
But sometimes a pessary is prescribed for lifelong wear. As a rule, this appointment is made if the patient is indicated for surgical intervention, but for some reason it is impossible.
With the correct size and correct installation of the uterine ring, the device does not cause any discomfort and is not felt at all.
Wearing a pessary prevents the following consequences of prolapse:
- development of infectious processes;
- displacement of the bladder walls;
- development of cystitis;
- skin diseases in the perineum and genitals;
- necrotic processes in the uterus and vagina due to impaired blood flow.
How to maintain pregnancy during uterine prolapse
At the stage of pregnancy planning when the cervix is prolapsed, a woman should use various techniques to strengthen the pelvic floor muscles. For women who are overweight, gynecologists recommend losing it. Often the cause of excess body weight is endocrine disorders, so when preparing for pregnancy you need to visit a specialized specialist.
After conception, a woman should pay attention to the need to follow these rules to ensure successful pregnancy:
- Correction of the diet based on reducing the consumption of foods containing fats and carbohydrates. This condition is necessary to reduce the intensity of weight gain.
- Refusal of intimacy for the entire period of pregnancy.
- Reducing physical activity, stopping heavy work (a woman should take a vacation at her own expense or provide the employer with a certificate about the need to reduce workload).
- Taking medications to ensure the continuation of pregnancy as prescribed by a doctor in doses regulated by him.
- Constant monitoring of the condition of the cervix using ultrasound.
- Use of a special bandage from the 22nd week of pregnancy.
- If the cervical canal is short and there is a risk of premature birth, the woman is advised to wear an obstetric pessary (a ring placed on the cervix).
Causes of the disease
The following reasons can lead to weakening of the muscular-ligamentous apparatus:
- age;
- problems with tissue innervation;
- hormonal imbalances;
- excessive physical activity;
- lifting weights;
- cystic and myomatous neoplasms;
- injuries that occurred during surgical intervention in the genital organs;
- congenital malformations;
- heredity.
In nulliparous girls, the causes of prolapse can be chronic illnesses, which are accompanied by insufficient blood circulation of the pelvic organs; not the least important factor in the development of pathology is heavy physical labor.
Labor legislation specifies standards for lifting heavy weights for women and girls who work in production.
CAREFULLY! The maximum a girl can understand is 10 kg, but unfortunately, women do not always adhere to this norm, thereby increasing the risk of developing prolapse.
In some cases, the causes of prolapse in girls may be hormonal deficiency, hereditary predisposition, or sudden weight loss.
Constipation increases the likelihood of prolapse - with strong and periodic straining, the pelvic floor muscles weaken, which becomes the cause of pathology.
Prevention of prolapse should begin in childhood. The girl must be warned about the dangers of the concept of weights so that she does not encounter this problem later.
As for postpartum prolapse, it can be associated both with the unskilled actions of the gynecologist, and with the woman’s neglect to prevent the disease during the recovery period.
Unprofessional management of pregnancy, the use of obstetric forceps during childbirth, poor-quality suturing of the perineum for ruptures, multiple births, non-compliance with recommendations and failure to perform special exercises that help restore the elasticity of the vaginal walls during the recovery period - all these are factors that increase the likelihood of postpartum prolapse.
In older women, prolapse is most often associated with a decrease in estrogen in the blood, which is a natural phenomenon during menopause.
Without correction, this phenomenon leads to a weakening of all muscle structures of the body, including the pelvic floor muscles.
What is the danger of uterine prolapse during pregnancy?
The following symptoms indicate cervical prolapse during pregnancy:
- pain in the lower abdomen and lumbar region;
- shooting pain in the pubic area;
- painful intercourse;
- feeling of fullness in the vagina;
- colorless or bloody discharge;
- disturbance of urine outflow;
- involuntary urination;
- difficulty in bowel movement.
If the uterus is below the required position during pregnancy, this condition can lead to dangerous complications. In the early stages, the risk of spontaneous abortion increases 10 times, so the woman is recommended to go to the gynecological department for preservation.
Attention! Against the background of uterine prolapse, there is a risk of premature birth.
In the third trimester of pregnancy, a woman with uterine prolapse is advised to be hospitalized; such a recommendation from gynecologists is associated with the risk of a rapid onset of labor. You need to understand that prolapse in the first trimester is much more dangerous than in the later stages.
The descent of the uterine fundus immediately before childbirth is a natural process that ensures spontaneous delivery. If this process began after 30 weeks of pregnancy, there is nothing to worry about. In case of premature birth, the child and mother will be able to provide the necessary assistance. Premature children do not differ from those born at term, but in the first year of life they lag behind in development.