Lumps and formations in the mammary glands are a potential risk for developing cancer. For mastopathy, surgery may be prescribed in several cases, including when there is a risk of it degenerating into cancer. What are the features of this procedure and is it possible to do without surgical intervention?
Indications for surgery and the urgency of its implementation are determined by the attending physician.
The essence of the operation
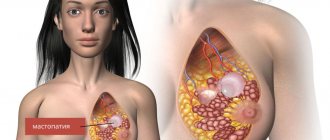
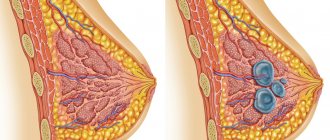
With mastopathy, the glandular tissue of the breast undergoes changes under the influence of hormonal or other factors. Its structure becomes more dense as a result of the formation of fibrous connective nodes. Fluid-filled cysts may also form in the breasts.
Small benign formations in the absence of infection do not cause much concern. At the same time, extensive compactions and tumors in the borderline stage require radical measures to eliminate them. In this case, an operation is performed in which the pathologically altered breast tissue, milk ducts, and sometimes adjacent tissues are removed.
Modern techniques make it possible to preserve the aesthetic attractiveness of the female breast after operations on it.
After surgical treatment of mastopathy, plastic surgery of one or both mammary glands is possible
Let's delve into the essence of what is happening
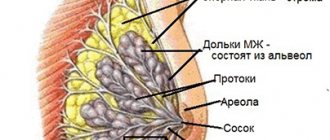
To understand the features of the pathological condition of the breast, let’s first consider a photo of mastopathy of the mammary gland, where you can see how the breast is structured. The structure of the gland is somewhat similar to an orange, since inside there are also small segments (from 15 to 25 pieces), which are located radially relative to the nipple. They are separated from each other by fatty tissue. Due to this, the shape of the breast is formed.
Each such “lobule” contains mammary glands, consisting of branching tubes called milk ducts. At their ends there are small alveoli (vesicles) where special cells (lactocytes) produce milk.
Every month, the female body undergoes cyclic changes under the influence of progesterone and estrogen. Thanks to them, not only the two-phase menstrual cycle is regulated, but also has some effect on the female glands.
Under normal conditions, during the first phase of the cycle (before ovulation), due to estrogen in the glands, cell multiplication begins (proliferative process). When the second phase of the cycle begins (after ovulation, but before menstruation), progesterone is activated, which delays cell reproduction provoked by estrogen. At this moment, the breasts begin to increase in size, although only slightly.
If fertilization of the egg does not occur, the amount of estrogen increases, due to which the female glands undergo reverse changes and the breasts decrease in size. However, during pregnancy there is an increase in the concentration of prolactin in the blood. Subsequently, it begins to affect milk production.
If you pay attention to the reviews about mastopathy of the mammary gland, we can conclude that this problem worries many women of different ages.
Indications for use
Fibrocystic mastopathy is a benign disease, so surgical intervention is not always required. At the initial stages, conservative approaches to treatment are used; in the future, preference is also given to more gentle methods.
You cannot do without surgery in the following cases:
- extensive formation of nodes in the late stage of progress;
- the seal causes serious discomfort to the patient;
- attachment of the inflammatory process;
- suppuration or rupture of the cyst;
The risk of malignancy of nodular mastopathy is a direct indication for surgery
- suspicion of cancer;
- rapid increase in tumors;
- the appearance of new seals in a short period of time;
- lack of therapeutic effect with conservative treatment.
For fibrocystic mastopathy, surgery allows you to get rid of the formation that is bothering the woman, but there is no guarantee that the disease will not return in the future. In addition, the risk of malignancy of breast cells cannot be excluded if all altered tissues are not completely removed.
Signs of nodular mastopathy
- When a node is palpated in the mammary gland, a painful local tumor-like or stringy compaction is detected.
- Sometimes: discharge from the nipple of various types not related to lactation.
- Sometimes: breast deformation.
- Sometimes: enlargement, hardening of the axillary, supra- and subclavian lymph nodes; swelling of the hand.
- Often: engorgement, swelling, increased pain in the breast 1-2 weeks before menstruation.
How does nodular mastopathy hurt:
- The pain is more severe than with diffuse mastopathy.
- Nature of pain: cyclical/constant.
- Localization of pain: area of nodular compaction.
- The pain can radiate: to the shoulder blade, armpit, behind the sternum, to the shoulder.
Preparation
Before undergoing such a serious procedure as surgery, patients must undergo a thorough examination and undergo a series of tests. During this period, a decision is made whether surgical intervention is really necessary and whether there are any circumstances that are contraindications to such treatment.
A blood test determines the level of gonadotropic (ovarian) hormones and pituitary hormones, fluctuations of which can provoke the development of mastopathy
For mastopathy, an examination by a gynecologist is necessary, as well as blood donation to determine the level of hormones that may affect the development of the disease. In addition, the doctor questions the patient about existing symptoms, characteristics of menstruation, and palpates the mammary glands. Mammographic images and ultrasound diagnostics are used to indicate the operating area. It is important to determine the exact boundaries of the fibroepithelial formation or cyst.
To determine the nature of the tumor, an aspiration biopsy is prescribed, followed by histological and cytological studies. If there are difficulties in visualizing the compaction using standard methods or if cancer with metastases is suspected, computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging is prescribed.
CT or MRI are the most highly accurate research methods
Immediately before the operation, blood tests are taken to determine ESR (an indicator of the presence or absence of an inflammatory process in the body), coagulability and other important indicators. An anesthesiologist talks with the patient to clarify the circumstances regarding the perception of anesthesia and medications.
Diagnostics when identifying nodes
After examination by a doctor with mandatory palpation examination of the breast, the following examinations must be performed:
- take a blood test for a tumor marker (CA-15–3);
- X-ray examination of the mammary glands (mammography);
- ultrasound scanning (women under 35 years old);
- puncture and taking biopsy material from the node.
The possible risk and danger of malignant degeneration when nodular proliferations are detected in the mammary gland are the highest, therefore, in each specific case, the specialist will select the examination and treatment regimen individually.
Execution method
Depending on the extent of the fibrocystic formation, the existing risks and many other circumstances that are revealed during the examination, further treatment can be performed in various ways. Breast surgery has several methods of execution:
- Puncture. Used to remove the contents of a cyst. All liquid is pumped out of the capsule through a puncture.
Depending on the area of the lesion, malignancy and some other factors, surgery can be performed in various ways
- Lumpectomy. The node is peeled off along with a small supply of healthy tissue. Used for small local formations.
- Quadrantectomy or sectoral mastectomy. Resection of the lobe of the mammary gland that has undergone structural changes is performed.
- Mastectomy. Complete removal of the mammary gland and part of the pectoral muscle.
If necessary, lymph nodes are removed, especially if there is a high risk of malignancy of the tumor.
Access to the problem area is through a skin incision under the breast or in the side, armpit or nipple areola. To minimize the consequences in the form of scars, minimally invasive techniques using endoscopic equipment are used.
Thanks to the correct selection of the implant, after surgery it is possible not only to return the previous shape of the gland, but even to improve it
When a significant part of the mammary gland is removed, patients are offered plastic surgery services. By using your own fat tissue or silicone implants, it is possible to restore the correct shape of the breast and the symmetry of both glands, tightening and enlarging them.
During surgery, both general anesthesia and local anesthesia are used. The second method is safer for the body, but it is only suitable for minor interventions. If deep access and related manipulations are required (breast correction, removal of lymph nodes), as well as at the patient’s personal request, general anesthesia is used.
Causes of pathology
Tumor diseases of the mammary glands are usually genetically determined. Proliferating nodular mastopathy often becomes a family disease when close relatives develop the same type of pathology. Hereditary predisposition determines a high risk of the disease in women who have the following predisposing factors:
- age (women over 40 years old);
- general dishormonal disorders (metabolic syndrome, obesity, diabetes, thyroid disease);
- menstrual dysfunction caused by hormonal problems;
- gynecological pathology (leiomyoma, endometriosis);
- characteristics of reproductive function (infertility, frequent abortions, first pregnancy after 35 years);
- unmotivated and complete refusal to breastfeed the baby;
- inadequate lactation (less than six months);
- long-term psycho-emotional stress.
Nodular mastopathy and breast cancer are successive links of one pathological chain in women with an unfavorable combination of several factors (genetic predisposition, infertility and lack of lactation, hormonal imbalance and chronic stress).
Rehabilitation
After surgery for mastopathy, the woman remains in the hospital for some time. The first day is spent completely recovering from anesthesia. At this time, doctors are monitoring her condition to prevent complications from developing. If everything is normal, after 1–3 days the patient is discharged from the hospital and sent home. For major surgery, you must stay in the hospital for at least a week.
Several days of complete rest are necessary for successful rehabilitation
During the recovery period, it is important to follow the doctor's recommendations. The key aspects are:
- Regularly change the dressing and clean the wound. This is necessary to speed up healing and prevent infection.
- Taking prescribed medications. The doctor may prescribe hormonal drugs, antibiotics, anti-inflammatory and wound healing agents.
- Maintaining a rest regime. You need to spend at least 3-4 days in bed to regain strength and prevent the stitches from coming apart.
- Complete nutrition. It is extremely important in the postoperative period to continue to adhere to a properly balanced menu.
For mastopathy, foods rich in plant fiber and vitamins are recommended.
You must come to the hospital at the appointed time to have stitches removed if necessary, and also undergo an examination by a doctor. If everything is in order, the patient is prescribed a further course of therapy at home.
Preventive actions
The main goal of preventive measures is to prevent the formation of nodules in the mammary glands. It is optimal to prevent nodular mastopathy than to treat it. This is especially important for women at high risk of cancer. Important preventive measures are:
- refusal of artificial termination of pregnancy;
- use of oral contraceptives;
- timely treatment of hormonal disorders and gynecological diseases;
- performance of childbearing function;
- longest possible lactation.
Nodular mastopathy, the treatment of which is most often surgical, is a disease that requires timely diagnosis and comprehensive therapy under long-term supervision of a mammologist. It is undesirable to treat FCM with nodulation with folk remedies: traditional methods of therapy are the basis for a successful fight against a dangerous pathology.
Forecast and consequences
In most cases, scar healing occurs without complications, and the treatment itself allows you to completely get rid of the problem.
The prognosis is favorable provided that surgical manipulations are performed by a qualified specialist and the necessary treatment is subsequently carried out.
A barely noticeable mark remains at the site of the incision, and aesthetic problems can be completely solved thanks to modern medicine and cosmetology.
Periodic visits to the doctor minimize the risk of disease recurrence
However, you should never rule out the possible risk of breast cells degenerating into cancer. Even after the operation, such a prognosis exists. Therefore, it is necessary to regularly visit the hospital and undergo a preventive examination by a mammologist. Such recommendations apply not only to women who have undergone surgery or simply have problems with the mammary glands, but also to absolutely healthy women, regardless of age.
Unpleasant consequences may be associated with the patient’s health characteristics or violations of the operating technique. The following complications may occur after surgery:
- bleeding;
- formation of a hematoma in the resulting cavity in the chest;
- wound infection and development of inflammation, suppuration;
- asymmetry of the mammary glands;
After surgery, significant asymmetry of the breasts may occur, requiring correction.
- nerve damage (forced measure during mastectomy);
- atrophy of the pectoral muscle;
- vascular damage.
In some cases, some pathologically altered tissue remains due to incorrectly defined tumor boundaries, which can lead to relapse of the disease.
Mammography
With this study, an X-ray of the glands is taken, as a result of which even small compactions that cannot be detected by palpation can be detected. For all women over 40 years of age, this procedure is mandatory to undergo annually.
During mammography, X-rays of the breast are taken in two planes: (direct and lateral), which makes it easy to detect lumps and the extent of their spread, if any.
By combining radiography with ultrasound, pathology can be more likely to be determined. Just remember that this type of research is not carried out for women who are under 30 years old. In addition, the procedure is done no more than once a year.