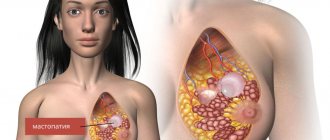
Mastopathy during menopause is a rather serious complication. This disease carries the risk of malignant degeneration of cells, and therefore requires specialized monitoring and mandatory treatment. Let's consider the main signs of pathology, the reasons for its appearance and the features of therapy for menopause.
Mastopathy during menopause
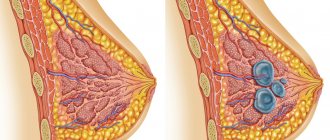
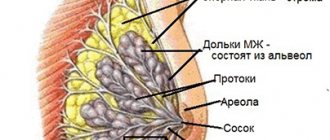
Mastopathy is a fibrocystic formation in the mammary gland. The largest percentage of incidence occurs in menopausal women, however, today this disease is increasingly being diagnosed in young women under 35 years of age.
Mastopathy during menopause occurs so often due to the fact that the female breast is a fragile hormone-dependent organ that responds to age-related changes and the slightest hormonal changes.
Menopause is a serious blow to the body, from which all systems suffer, therefore, special attention should be paid to the susceptible mammary glands.
Types of mastopathy
Mastopathy can be divided into several types.
Fibrocystic – occurs most often. It is an accumulation of mammary gland secretions in a specific location. For example, if there is damage or thickening of tissue (fibrosis) after injury or inflammation, then the secretion will accumulate there, forming a small bubble - a cyst.
The initial stage of fibrocystic mastopathy is called diffuse. Cysts at this stage are very small, it is not always possible to palpate them. This form of the disease is highly treatable and does not require surgery.
However, if the disease is neglected and the symptoms are ignored, the cyst can grow up to 3-4 cm in diameter.
Sometimes such a compaction is noticeable to the naked eye. The woman feels pain in the chest and surrounding areas, and a possible increase in local temperature. This form is called nodular and requires surgical removal.
Breast cell hyperplasia is the proliferation of epithelial cells as a result of taking hormonal drugs or stimulating the activity of the gland with hormones. The cells begin to divide uncontrollably and grow into a benign lump.
Atypical hyperplasia - occurs for the same reasons as hyperplasia, but differs from it in that uncontrolled dividing cells have a disrupted life cycle. They do not change-divide-die, but mutate, divide, accumulate and spread. The accumulation of such cells is called atypical hyperplasia.
At-risk groups.
1. Women who had problems with lactation. For example, if there was none or the period of breastfeeding was very short (it stopped on its own or the woman decided to stop breastfeeding of her own free will).
2. There were cases of mastopathy in the family history. Even if your mother did not have this disease, but your grandmother developed it, then you are still at risk.
3. Diabetics and obese women.
4. There is a history of miscarriages, fetal death or abortions (even “harmless” medical ones). Especially if these incidents happened several times. In all these cases, the body was preparing to bear a fetus, but suffered a severe hormonal imbalance.
5. If your menstruation began early (before 11-12 years), then this indicates improper functioning of the hormonal system.
6. Those who became pregnant after 30 years.
7. There is a history of endocrine disorders. Our entire hormonal system is connected, and if there are problems with the activity of the pituitary gland or ovaries, then the mammary glands may also suffer.
How to recognize the disease in the early stages?
1. You feel sore.
It can be localized in one place of the mammary gland, or it can spread throughout it as a whole. It doesn’t matter whether it is constant or occurs periodically, strong or barely noticeable, sharp or aching, chest pain only when moving or at rest - you should inform your doctor about this as soon as possible.
2. The pain may be localized not in the chest, but in the armpit.
If you feel pain not in the chest, but in the armpit, then do not ignore this symptom - the axillary lymph nodes are connected to the pectoral ones.
3. When palpating the breast, you feel a lump.
It can be one, or maybe several, closely localized or distant from each other. If you can palpate them yourself, then this is very serious - go to the doctor immediately.
4. Change in the shape or symmetry of the nipple.
This also includes the appearance of pigmentation around the areolas. If you notice that one of the nipples (or both) is swollen, retracted, changed shape or became asymmetrical, became painful or too sensitive, or changed the intensity of pigmentation - then this may indicate not only mastopathy, but more serious problems.
5. Nipple discharge.
They may be clear, cloudy, yellowish (signaling inflammation) or bloody. The only exception can be considered pregnancy (but only if the discharge is not yellow or bloody).
Treatment of mastopathy without the use of drugs
If a young woman of childbearing age has a problem with the mammary glands, many experts recommend starting with normalizing sex life, having a child, and long-term breastfeeding. When mastopathy occurs during menopause, many of these methods are impossible due to physiology, but a stable sex life during this period remains an important factor. In addition to stabilizing the hormonal component, psychological stability is also very important during this difficult period for any woman.
An important aid for the treatment of mastopathy during menopause is the correct diet. The diet should be aimed at restoring the functioning of the liver and gastrointestinal tract, improving metabolism and hormonal function of the female body. Recommended:
- A large amount of fish and seafood as a source of iodine preparations, which help normalize the functioning of the pituitary gland without the use of specific medications;
- Products containing large amounts of plant fiber. These are mainly fresh herbs and wholemeal bread;
- Eating a large amount of vegetables and fruits containing increased amounts of potassium and beta-carotene. The main suppliers of these beneficial substances are dried apricots, raisins, rose hips and Brussels sprouts.
Gentle physical labor, walks in the fresh air, and accessible water treatments should help a woman with mastopathy in her treatment.
There are also several prohibitions for patients with mastopathy of the mammary glands during menopause. It is necessary to exclude from your habits any procedures that lead to physical impact on the problematic mammary gland. This may include visiting a sauna and solarium, prolonged exposure to the open sun, problematic tight underwear, which leads to disruption of the trophism of the patient’s breast tissue.
Mastopathy, which manifests itself during menopausal changes in the female body, usually differs from the usual benign dysplasia of a young woman in the severity of its course and possible oncological consequences. There is only one recommendation: if changes are detected in the mammary gland, especially during menopause, you should immediately seek advice from a specialist. By doing this you will avoid many troubles and possibly save your life.
Welcome to the information site about women's breast health! All about anatomy and mammary gland enlargement. The most common breast diseases, as well as their prevention and treatment. How to properly feed your baby and care for your breasts during this period.
The information on the site is provided for informational purposes only. Do not self-medicate. At the first sign of disease, consult a doctor.
Reasons for the development of mastopathy after 50 years
During menopause, the female body is subject to fluctuating hormone levels. This promotes the proliferation of breast connective tissue. Certain factors can cause such a violation:
- early puberty associated with high levels of hormones in the body;
- venereal diseases, especially their chronic forms;
- inflammatory processes in the genital organs;
- disorders during lactation; the risk group often includes women who have not given birth or breastfed;
- abortions that provoke significant hormonal disorders;
- nervous disorders and pathologies, diseases of the central nervous system.
Risk factors may include menstrual and metabolic disorders that have occurred throughout life. Mastopathy is also caused by incorrectly selected oral contraceptives, diabetes mellitus and low iodine content in the body.
Causes
The most important reason for the appearance of mastopathy during menopause is an imbalance of the hormonal system.
It is because of this that irreversible processes occur in women aged 45-50 years , which negatively affect all reproductive organs, including the mammary glands.
In addition, the causes of mastopathy during menopause may be factors such as:
- early puberty in a woman, as a result of which the amount of hormones produced during this period significantly outpaced the development of the mammary glands. Such an imbalance can contribute to the development of mastopathy already in adulthood.
- if a woman has ever suffered from sexually transmitted diseases.
- Abortions are a great shock to the body, since during this period all reproductive organs are rebuilt in preparation for bearing a child. Termination of pregnancy leads to a serious imbalance in the body, which affects the health of the mammary glands in the future.
- if a woman has never become pregnant or refused lactation, this also negatively affected her health. The mammary glands, ready to feed the baby with milk during childbirth, were unable to fulfill their function, which provoked an unnatural balance of hormones.
- During menopause, metabolic disorders occur, which leads to obesity, dysfunction of the mammary gland, and diabetes. And this, in turn, negatively affects the production of hormones such as estrogens, gestagens, prolactin, and androgens.
- uncontrolled use of hormonal contraceptives.
Symptoms of the disorder
Age factors have different effects on a woman’s mammary glands. Under the influence of hormones and age-related changes, the following signs and symptoms of mastopathy of the mammary gland during menopause in women are detected:
- aching chest pain that constantly gets worse, may be absent for a long time, appear and disappear suddenly;
- small nodules gradually form in the tissue, which cause pain upon palpation;
- compactions gradually form and can quickly increase in size, reaching the shape of a walnut.
The main danger of mastopathy is its development into malignant tumors. Also, the symptoms of the disease greatly depend on the form of the disorder.
Classification
There are several forms of mastopathy after 50 years:
- diffuse – the initial stage, in which dense nodules and cords appear in the chest;
- nodular - the nodes become large, reach the size of a walnut, and the lymph nodes in the armpits also enlarge;
- fibrocystic - accompanied by the appearance of neoplasms, fluid-filled cysts, and severe pain.
With form 3 of the disease, bloody and watery discharge from the nipples often begins.
Signs of the disease during menopause
During menopause, women undergo hormonal changes in their bodies, which can negatively affect the condition of the mammary glands.
The appearance of mastopathy during menopause is associated with the action of sex hormones, which cause disruption of the menstrual cycle.
There is a lack of hormones, and in connection with this, serious changes occur in the endocrine system. As a result, during menopause the amount of estrogen sharply increases and an acute deficiency of progesterone appears.
It is in connection with this situation that the risk of mastopathy increases.
who have the following symptoms are at risk
- Genetic predisposition, i.e. if women in the family had problems with the mammary glands.
- If the menstrual cycle began before 12 years of age.
- For diseases of the endocrine system.
- If there were regular failures in the cycle.
- If the first birth was after 30 years.
- Frequent miscarriages and abortions can also contribute to the development of mastopathy.
- If the woman has never been pregnant or given birth.
- If you refuse to breastfeed.
- For metabolic disorders.
Methods for detecting mastopathy
For diagnosis, mammologists use a standard set of procedures and tests:
- blood donation for hormonal factors;
- blood test for the presence of cancer markers;
- Ultrasound allows you to determine the type of mastopathy and see the shape and boundaries of the tumor;
- mammography is necessary to determine early forms of mastopathy;
- A biopsy is performed when diagnosing tumors and cysts of any form.
After the biopsy, the result is sent for histological examination. This method is recognized as one of the most reliable and accurate. The accuracy of the results reaches 90-95%.
When to do an ultrasound of the mammary glands with a long cycle
In women with a long menstrual cycle of 32-36 days, hormonal changes occur more slowly, and ovulation of the egg occurs later - on days 18-21 of the cycle. It is quite clear that the period for optimal examination of the mammary glands will lengthen.
Important: there are many women with irregular cycles and varying duration of menstruation. In such cases, it is difficult to accurately predict the days of ovulation and choose the optimal period for an ultrasound; it can be done on any day.
However, such women should be referred to a gynecologist for examination. An irregular cycle is a sign of hormonal disorders and gynecological diseases.
Treatment methods after menopause
Treatment of mastopathy during menopause should be comprehensive, consisting of different techniques. The main thing in such therapy is constant control of lifestyle. It is necessary to eat right, eliminate bad habits, avoid stress and negative environmental influences. If a woman works in a hazardous industry, she needs to change her field of activity.
You cannot start treatment on your own. Only after receiving a diagnosis confirmed by diagnostic procedures and consulting a doctor can you begin therapy with recommended drugs and natural remedies.
Hormonal drugs
Products based on estrogen and progesterone are widely used in the treatment of mastopathy during menopause. Oral contraceptives are most often prescribed. But only if the cause of the disease is hormonal fluctuations. The most common drugs include: Silest, Diane-35, Ovidon. Other drugs are also used for treatment: Femoston, Janine, Klimonorm, Regulon, Mercilon, Novinet, Triquilar.
Special hormonal therapy with progesterone-based drugs is also used. This may be a product of the same name or Utrozhestan. External agents are also used, including Progestogel. It contains a special form of progesterone, which quickly relieves the symptoms of mastopathy. If a high level of prolactin is diagnosed in a woman’s body, Bromocriptine, Abergin, Parlodel are additionally prescribed.
Treatment
The earlier the disease is diagnosed, the faster it can be treated. Classical methods of therapy involve the use of hormonal-based drugs, non-hormonal therapy and surgery.
Hormones
Normalization of hormonal levels during menopause is carried out after receiving the results of a blood test. If the background is elevated, histogenic agents are prescribed. They help reduce prolactin levels. The hormone estrogen is also suppressed.
Doctors often resort to using contraceptives. This treatment should only be carried out by a qualified doctor.
Self-medication with products containing hormones is strictly prohibited.
Phytohormones
They are complex plant-based compounds. They are similar in structure to sex hormones. Soy and sprouted wheat seeds contain large amounts of phytoestrogens.
Phytoestrogens are capable of:
- displace estradiol from the receptor connection;
- act as inhibitors of enzymes that control growth;
- have an antioxidant effect;
- remove steroids from the gastrointestinal tract.
Vitamins
Vitamins for mastopathy during menopause are used as a therapeutic and prophylactic agent.
Prevention of neoplasms and mastopathy
To prevent diseases, a woman should regularly see a mammologist so that she can detect the onset of mastopathy in time. You should also evaluate your health status and visit a doctor when necessary. To prevent illness it is also important:
- visit a gynecologist 1-2 times a year;
- eat well;
- if diseases of the genitourinary and nervous system are detected, treatment must be started;
- playing sports helps prevent any disease;
- Once a month you need to monitor the condition of your breasts;
- you should give up bad habits.
If a woman follows the doctor’s recommendations, it is quite possible to prevent a relapse.
Prevention of fibroadenomatosis during menopause
Prevention of breast diseases during menopause should begin during childbearing age. The main thing is to eliminate as much as possible from your life all provoking factors that could provoke the development of the disease in the future. First of all, it is necessary to give birth to children in a timely manner. Pregnancy before 18 and after 40 years is undesirable, because in both of these cases the mammary glands are not ready for breastfeeding, and the body tolerates hormonal surges extremely negatively.
You should also breastfeed your baby responsibly. Breastfeeding for less than 6 months poses a particular danger to the female body. Forced cessation of lactation provokes serious hormonal imbalances, which become the impetus for the development of the disease.
In addition, it is necessary to promptly treat all infections of the genitourinary system, preventing them from becoming chronic. This is especially true for sexually transmitted diseases, which include not only the well-known gonorrhea and syphilis, but also chlamydia, genital herpes, trichomoniasis, ureaplasmosis, etc. The danger of many of these diseases lies in their asymptomatic course and infection can only be determined during laboratory blood test.
And most importantly, no matter how trivial it may sound, the key to health during menopause lies in a healthy lifestyle. Sports and proper nutrition help the body receive all the substances necessary for proper functioning, stimulate the secretion glands to synthesize hormones, ensure prolongation of youth and good health.
And, probably, the main principle of prevention is regular visits to the gynecologist. With the onset of the first manifestations of menostasis, you should visit a doctor at least once every 6 months. This will allow you to timely identify possible deviations and take measures to quickly eliminate them.
Complications and consequences of mastopathy
If the pathology is not treated, over time it can lead to malignancy, and this is a direct path to breast cancer. The risks are especially high for mastopathy complicated by infections and nodular forms. Symptoms such as intoxication of the body and high temperature are dangerous for mastopathy.
During menopause, a woman faces another significant hormonal change. They can affect the health of the mammary glands and cause mastopathy. Therapy is carried out conservatively, but if the tumors grow rapidly, the doctor prescribes surgery.
Ultrasound examination of the breast
Ultrasound (sonography) of the mammary glands and its lymph nodes is scanning of breast tissue with ultrasound at a frequency of up to 19 MHz (megahertz). During the examination, the sensor is applied to the skin. The echo signal passes through the liquid unhindered and is reflected from the ribs and hard tumors. Ultrasound waves are absorbed differently by healthy and altered glandular tissue.
The echogenicity of the structures appears on the sonographer’s monitor in the form of a black and white picture. The denser the fabric, the lighter the area. The accumulation of liquid is colored black. Inhomogeneous (heterogeneous) lesions contain two colors, shades of gray.
Types of ultrasound for examining the mammary glands:
There are portable models of sonographs: a doctor can be called to your home. This medical service is inexpensive and is useful for examining the mammary glands of people with disabilities.
Ultrasound diagnostics (ultrasound) of the breast is done in the late follicular phase of the ovary, and in emergency cases - on any day of the menstrual cycle. Sonography of the mammary glands is performed for the purpose of preventive research, determining the type of pathology, and monitoring the effectiveness of treatment.
Ultrasound is prescribed before medical or plastic surgery. In the first case, the severity and localization of changes are clarified; in the second, they are used more often for the selection of female breast implants. It is mandatory to evaluate the mammary glands using an ultrasound at the stage of preparation for IVF.
To watch a video of how ultrasound diagnostics are performed before mammoplasty:
Features of the procedure for children
Children (boys, girls) have the same diseases as adult women, plus the likelihood of birth defects and chromosomal disorders. A child can have a breast ultrasound at any age, including the neonatal period. There are no differences between the preparation and procedure for performing the procedure for children and adults.
Varieties
Mastopathy during menopause can be of several types:
In the diffuse form, small cords and nodules are felt. The pathology is characterized by pain and engorgement of the glands, which is noticeable during menstruation, regardless of whether they have stopped or not.
Nodular mastopathy is a frequent companion to menopause
The nodular form is a single benign tumor in the breast. The knots can be either the size of a pea or the size of a walnut. The number of nodes also varies. The nodes can be easily felt by touching the chest. The pain persists regardless of the day of the cycle.
With a mixed form of mastopathy, a woman experiences both nodes and diffuse changes throughout the mammary gland. In the mixed form, breast mastopathy brings tangible symptoms. It hurts for women to even raise their arm; the discomfort radiates to the shoulder blade and arm. Watery discharge mixed with blood appears from the chest.
Which doctor should I contact?
Already during menopause, a woman must be observed by a gynecologist. Therefore, if this condition is met, the doctor first of all pays attention to the changes that occur not only in the ovaries, but also in the mammary glands.
Often it is a specialist who detects the presence of mastopathy in a woman during menopause.
Only after examination by palpation can the doctor issue a referral for other diagnostic procedures in order to accurately establish the diagnosis, identify benign formations in the breast, or if there is a suspicion of cancerous tumors.
Symptoms of mastopathy during menopause
Symptoms of breast mastopathy during menopause do not differ from signs of pathology in women of childbearing age. To diagnose mastopathy on time, women should know its signs:
- chest pain;
- possible discharge from the nipples;
- uneven surface of the breast, palpable or visual lumpiness;
- asymmetrical position of the breasts;
- cracked nipples;
- the appearance of swelling, puffiness;
- enlarged axillary lymph nodes.
Pain during mastopathy during menopause coincides with the onset of menstruation, even if it does not begin and gradually stops. However, the mammary glands live according to their own “hormonal clock”, so the symptoms of mastopathy in women during menopause are not always clear to them, and they miss the early stage of the development of the pathology, turning to them only with late changes.
Preparing for breast sonography
There is no need to change the diet of children or adults during preparation for an ultrasound examination of the mammary glands. It is enough to follow the recommendations regarding the day of the menstrual cycle. You are allowed to eat and take medications. The need to interrupt the course of hormones and oral contraceptives is agreed with the doctor.
Before the procedure you cannot:
- sunbathe;
- visit the sauna, solarium, baths;
- supercool;
- take a hot bath;
- lactating women should feed the baby and express milk before the procedure;
- It is forbidden to heat the space-occupying lesion (it may cause deterioration).
You can eat any food, drink coffee, sparkling water before the ultrasound. They do not distort the result of breast diagnostics. In preparation for a preventive study, there is no need to submit biomaterial for laboratory tests.
You need to go for the procedure after cleansing the breast skin of medicinal or cosmetic products; do not use soap or gel during the shower. Because of them, the echo signal penetrates the epidermis less well.
During what period and how often is breast ultrasound done?
It is better for women of reproductive age to undergo routine ultrasound diagnostics of the mammary glands annually. Over 40 years of age, ultrasound or digital mammography is recommended once every 6 months. It is advisable to go to a doctor for a medical examination with an ultrasound protocol.
For teenage girls or women of childbearing age, it is recommended that ultrasound be performed between the 4th and 11th day of the cycle. It is advisable to examine the mammary glands in the first days after the end of menstruation. If there are no periods during lactation, sonography is performed at any time.
Regardless of the phase, breast cancer is examined urgently if breast cancer, metastases, or other dangerous diseases or injuries are suspected. An ultrasound can be done any day for children, women during menopause/menopause, girls after menarche (first menstruation) until the cycle stabilizes.
Not the best days for a planned ultrasound:
- during full menstruation or when smearing;
- ovulation + days before/after egg release;
- before the onset of menstruation 0.5–1 week.
This is due to the fact that in the ovulatory period and in the second half of the cycle the concentration of progesterone is increased. The functions of the reproductive organs, including the breasts, are reconfigured for pregnancy. As menstruation approaches, hormonal levels change again. These fluctuations can distort the validity of the survey. After ovulation, ultrasound is prescribed only if hormone-dependent diseases are suspected.
Ultrasound can be done frequently, even daily, during breast examination/therapy. Ultrasound is safe, helps the doctor to see deviations in a timely manner and adjust the treatment method.
Diagnostics
Only a doctor can diagnose pathology. When palpating the mammary glands, it is too early for women to make a threatening diagnosis - everything can be found out only after consulting a mammologist. Although fibrous mastopathy during menopause manifests itself as a constant set of symptoms, additional examination is required to make a diagnosis.
Mammography will help make the final diagnosis:
Diagnostics includes:
- initial examination of the patient’s mammary glands;
- palpation in a standing and lying position;
- mammography;
- ultrasonography;
- puncture.
Modern methods make it possible to diagnose even small seals. Detection of pathology at an early stage gives encouraging prognoses for treatment. Therefore, when visiting the clinic, women undergo recommended diagnostic procedures. Ultrasound examination will detect connective tissue nodules even 1 mm in size. The study is safe and has a high diagnostic value.
If problem areas are detected, the doctor takes a puncture and sends the biomaterial for histological examination. A number of additional tests are prescribed. Histology will determine the presence of tumor markers, atypical cells and make an accurate diagnosis, determine further tactics for managing the patient.
What is breast ultrasound and what does it show in women?
Ultrasound examination or sonography is based on the ability of tissues, depending on their structure and density, to transmit or reflect high-frequency sound waves - ultrasound.
The denser the fabric structure, the less passable it is for sound waves , the more of them are reflected and enter the device’s sensor and are projected on the screen in the form of light shadows.
Such areas are called echo-positive or hyperechoic (from echo - reflection). Inflammatory lumps, fibroadenomas, and malignant tumors that are easy to detect in the breast have these properties.
Conversely, less dense areas transmit ultrasonic waves more and reflect less, and less of them enter the device’s sensor. On the screen they look like echo-negative or hypoechoic foci and are dark in color. This is what cavity formations look like - abscesses, cysts.
Technology is constantly improving. A simple or 2-dimensional (2D) examination allows you to obtain a black and white image in 2 dimensions - the length and height of the lesion. A more accurate 3D ultrasound reflects the 3-dimensional size of an object - length, height, thickness, and 4D ultrasound - a study in dynamics, the relationship with surrounding tissues. Moreover, modern ultrasound scanners make it possible to obtain color images.
Possible pathology options
A common variant of breast pathology in older women is fibrous mastopathy, in which the risk of complications is minimal. During menopause, the negative impact of hormonal disorders associated with hyperestrogenism decreases, so there are no proliferative processes in cells. Age-related involution leads to the replacement of glandular tissue with fibrous and fatty tissue. Mastopathy during menopause is manifested by the following diseases:
- diffuse pathology with fibrosis of mammary gland tissue;
- fibrocystic variant of the disease;
- nodular form of FCM;
- mammary cancer.
During menopause, you should be very careful about breast health: after 50 years, the risk of cancer increases, so all women should visit a doctor regularly. Preventive medical examinations are especially important in the presence of a family predisposition and proven genetic risk.
Mastopathy during menopause shows clear enough symptoms to force a woman to see a doctor. They are especially noticeable in postmenopause, when the sensations caused by the disease cannot be attributed to PMS. But even in the initial period of menopause, while menstruation is still coming, it is possible to detect changes in the breasts, since sensations may differ from what they had before the disease.
Malaise provokes the appearance of:
- Pain in the mammary glands. Symptoms of mastopathy during menopause from this series have a different character, they can be aching, shooting, pressing, dull. The pain can also be localized in different parts of the chest and radiate to the shoulder. However, for some this sign is absent for the time being;
- Firm areas in the chest. They can be felt as enlarged lobules or represent foreign formations due to tissue proliferation and the formation of nodules;
- Discharge from nipples. The sign does not always appear, but during self-examination you need to pay special attention to this part of the mammary glands.
Symptoms of mastopathy during menopause appear due to hormonal deficiency that occurs during menopause. The functionality of the immune system and the production of useful substances also decrease, and age-related changes throughout the body accelerate. That is why women during menopause are susceptible to many diseases that affect the female organs. The mammary glands are a secondary sexual characteristic because their growth is determined by the level of estrogen in the blood.
With age, breasts sag and lose firmness.
- volume decreases;
- subcutaneous tissue loses tone, wrinkles appear;
- breasts sag.
Treatment of mastopathy during menopause is carried out using two methods:
- Surgical intervention.
- Conservative method.
Treatment may involve surgery.
The second is based on following a strict diet. Depending on the patient’s condition and the course of the disease, the diet may exclude, limit, or, conversely, add certain types of food to the diet. Contraindicated products are:
- cocoa;
- coffee drinks;
- soda (especially colored soda).
The surgical method is rarely used, usually after an ineffective conservative technique. In some cases, experts recommend using Klimadinon for mastopathy. The drug has proven itself to be an effective treatment and prevention.
How does mastopathy manifest?
Signs of mastopathy of the mammary gland during menopause manifest themselves in painful sensations of varying degrees in the chest area. This is due to the abnormal growth of benign tissue, which can subsequently turn into cancer. Although the disease is classified as benign, it is the first cause for the development of other oncological problems.
If you notice swelling or feel severe pain, these are alarming symptoms
Mastopathy manifests itself as follows:
- the appearance of tubercles, bumps or spherical seals of various shapes;
- pain in the chest;
- swelling or swelling of the mammary glands.
During menopause, the disease manifests itself more clearly, which makes it possible to exclude pregnancy or menstruation. Any change in the breast area should be diagnosed by a specialist.
Classification
Mastopathy is distinguished depending on the nature of the proliferation of connective tissue:
- Nodular is a form of the disease characterized by easily palpable nodular formations and tuberosity. The pain radiates to the armpits, forearms, shoulders, and under the chest.
- Diffuse - characterized by small nodules without a clear shape. At the same time, the pain is of a pulling nature.
It is easier to suspect a nodular type of change on your own - a cyst or fibroadenoma. Treatment of non-lactation mastopathy in menopause depends on the type of tissue proliferation: the nodular form of the disease often requires surgical intervention.
Hormones
Mastopathy can be treated with initial menopausal syndromes. Treatment may include taking oral contraceptives. A chemical blood test is performed and if a hormone imbalance is detected, the following may be prescribed:
- Regulon;
- Janine;
- Femoston;
- Mercilon;
- Novinet.
With menopause, which is already in full swing, such treatment will be useless and can even be harmful to health. Often, pathologies in the hormonal background that provoke mastopathy occur due to the predominance of estrogen hormones. In this case, there is a need to neutralize their effect on the increase in mammary gland tissue with the help of substances with gestagens:
- Duphaston;
- Utrozhestan;
- Progesterone.
Suppression of estrogen formation is also possible with the use of drugs containing testosterone:
- Norgestel;
- Danazol;
- Linestrinol.
Postmenopause allows the use of the drug Livial, which has an effect on the size of sex hormones and androgens. In addition to its therapeutic effect for mastopathy, it also relieves menopause syndrome. To determine the exact dosage and not harm your body, you should definitely consult a doctor.
Vitamins
If there is mastopathy during menopause, therapy is certainly expanded by taking vitamins. The most significant medications for the well-being of the mammary glands are the following:
- Retinol;
- Tocopherol;
- Ascorbic acid;
- Pyridoxine;
- Folic acid.
They normalize metabolism, activate hormonal balance, have antioxidant and antitumor properties, and improve the functioning of the nervous system.
Reviews
Irina Kravchenko, 50 years old: “After a course of drug therapy, mastopathy resumed. The attending physician claims that a small lump on ultrasound will soon be recognized as normal, as it is diagnosed in almost all women during menopause. Girls, the pathology should be treated in any case! Mastopathy is fraught with serious health complications, including the development of cancer.”
Svetlana Kogan, 36 years old: “When treating mastopathy, my doctor used an integrated approach. Therapy involved the use of vitamins, diet correction, and the use of medications and special supplements. Only in this case can you expect a positive result. I do not recommend resorting to self-medication! All drugs must be approved by a mammologist.”
Yulia Sotnikova, 39 years old: “Untimely treatment of mastopathy provoked the development of fibrocystic form. The doctor offered me surgery, but first prescribed medication. After the course, the nodes noticeably decreased in size and pain disappeared. I hope the second course will help cope with the disease. I strongly recommend sticking to the therapy prescribed by your doctor! The disease can be cured."