Is breast discharge dangerous?
The appearance of any discharge from the nipples should alert a woman, since in many cases it is associated with the development of more serious diseases in the body. Particular attention should be paid to the secretion of an unusual color (green, yellow, bloody) with an unpleasant odor.
If the disease is not diagnosed in time and treatment is not started, there is a risk of serious complications and pathologies, such as:
- development of malignant tumors;
- progression of the disease, which is subsequently difficult to treat;
- detrimental effect on lactation;
- the appearance of cracks in the nipple, which become a favorable environment for the development of infection and the penetration of pathogenic bacteria. They are the ones who provoke inflammation of the nipple, which is called telitis;
- the appearance of inflammatory processes in the gland;
- The discharge may change consistency and color over time, indicating the emergence of new diseases.
The severity of the consequences depends on the cause that caused the appearance of the secretion.
Treatment of breast diseases
Pathological exudate from the breast requires treatment. It depends on the cause that caused the symptom.
Treatment methods include:
- Hormonal therapy.
- Anti-inflammatory and antibacterial treatment.
- Aspiration of large cysts.
- Phytotherapy.
- Surgical removal of benign and cancerous tumors.
- Special treatment methods for oncology (chemotherapy, radiation).
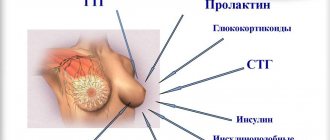
Hormonal therapy is required for mastopathy, hyperprolactinemia and thyroid deficiency. The presence of multiple cysts is a reason to prescribe drugs such as Mastodinon and Progestogel. Medicines must be taken over a long period.
Photos of drugs can be seen on the pharmacy website. In cases of severe mastopathy that is not amenable to herbal medicine, antiestrogenic drugs are prescribed. They influence the pathogenesis of the disease and eliminate the cause of the pathology.
Antibiotics and anti-inflammatory drugs are necessary for mastitis. To get rid of thick yellow droplets, local and systemic therapy is required. Anti-inflammatory drugs help eliminate swelling and get rid of the accumulation of pus in the thoracic ducts. To prevent the disease from progressing, strong antibacterial drugs are prescribed.
The accumulation of brown and green fluid leads to stagnation and the development of the inflammatory process. To prevent this from happening, large cysts are aspirated with an ordinary syringe.
After this, medications are prescribed to treat mastopathy. If intraductal papilloma is detected, surgery is required. The benign formation is excised, after which the bleeding stops.
Possible causes of discharge
The root causes of discharge can be both natural and pathological. In most cases, the color of the discharge indicates the main reason for its appearance.
Green discharge
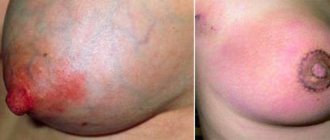
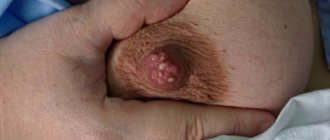
If, when pressed, a secretion of a greenish tint appears from the mammary glands, then in most cases this indicates the presence of mastopathy - tissue proliferation. The discharged substance has a thick consistency with mucus impurities. In addition to discharge, symptoms such as breast hardening and pain appear.
Discharge from the mammary glands when pressed may be a sign of one of the forms of mastopathy
You can get rid of this disease in a short time with a timely visit to a specialist who will identify the form of mastopathy and the stage of its development. Otherwise, when the disease is advanced, the effectiveness of therapy is significantly reduced.
Norm and pathology of discharge from the mammary glands
During menstruation, during pregnancy or after abortion, discharge from the nipples may appear, as some types of discharge are characteristic of these periods. It is important to determine the type of discharge in order to exclude possible pathological conditions.
During menstruation
The appearance of discharge during menstruation is due to the work of special hormones that are responsible for lactation. They are the ones who stimulate the production of secretions. The discharge is usually yellow or white in color and can be either with or without an odor. Discharges during this period occur in small quantities, and their occurrence most often occurs at the very beginning of the cycle.
If fluid with other characteristics is released, and the process itself is accompanied by pain and swelling of the glands, then you should be examined for the presence of pathological processes.
During pregnancy
During pregnancy, a woman's body undergoes a complete hormonal change, causing prolactin levels to increase. This hormone is responsible for milk production. When it predominates, the mammary glands begin to swell due to the expansion of the milk ducts.
Discharge from the nipples during such a period may appear even with minor exposure to them. At different stages of pregnancy, the secretion has a different consistency: at first liquid is released, and over time the secretion becomes thicker, it acquires a specific yellowish tint and a sweet smell.
Such discharge is called colostrum, which is characteristic of the late stage of pregnancy or the postpartum period. They are not a symptom of disease and do not affect lactation in any way.
After termination of pregnancy
In the first few months after an abortion, discharge from the breast may appear, since pregnancy has a strong impact not only on a woman’s hormonal levels, but also on the condition of the mammary glands. The normal secretion during this period is yellow discharge, characteristic of the lactation period.
After undergoing medical or surgical termination of pregnancy, the immune system is weakened, so there is a high risk of inflammation and diseases of the mammary glands, such as mastitis and mastopathy. After an abortion, tumors and accumulations of pathogenic bacteria may appear in the breast.
If the discharge is accompanied by pain, redness and other unpleasant sensations, this may indicate pathological conditions, so any changes should be reported to your doctor. This will avoid serious complications in a weakened body.
What happens to breasts during menopause?
After 45 years, any pain in the body is a signal of a disruption in the body’s functioning. Most often, during menopause, chest pain is a fairly common symptom during menopause. Painful sensations may intensify at the beginning of this period, at the time of perimenopause and perimenopause. Before menopause, 70% of women experience discomfort throughout all menstrual cycles. The remaining part feels pain only during menopause. They can be intense, which significantly complicates life, communication with other people, ability to work, etc.
Pain without localization quickly passes, and discomfort in the nipple area is possible. If there is local pain, you should consult a doctor, as it could be cancer.
Hormonal storms are also accompanied by unpleasant sensations in the chest area. During menopause, most women gain weight because adipose tissue contains a large amount of estrogens.
In science, pain in the mammary gland is called mastalgia or mastodynia. This is a generally accepted term used to indicate discomfort, sensitivity or pain in one or both breasts upon physical contact. In addition to pain in the chest itself, it can occur due to an extra-mammary factor - inflammation of the cartilage in the area of the junction of the rib and chest. In medicine, this disease is called Tietze's disease. The disease can be cured by resting well and taking a course of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.
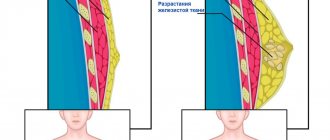
Structure of the mammary gland
Experts recommend that their patients keep a “diary” where all pain, its nature and period are recorded. Each woman experiences menopause differently depending on physiology, genetics and other individual factors.
What should not be done if there is discharge from the mammary glands?
At the first appearance of discharge, you should avoid several actions that negatively affect the condition of the mammary glands:
- take medications without a specialist’s prescription;
- wear tight underwear;
- make warm compresses and other traditional medicine procedures;
- take a hot shower or bath;
- use hormonal medications, including contraceptives, before visiting a doctor;
- squeeze out the liquid yourself.
Any prohibited actions can lead to a worsening of the condition and can also provoke complications.
When should you see a doctor?
There are a number of symptoms, if they occur, you should immediately contact a specialist:
- discharge bothers you for more than two days;
- they contain an admixture of blood;
- the secretion comes out of only one mammary gland;
- the discharge has a thick consistency;
- peeling appears on the skin of the nipple;
- loss of symmetry (increase in size, formation of dense knots);
- the color of the nipple and the area around it changes;
- pain appears in the chest.
The doctor will be able to conduct all the necessary examinations, which include:
- Ultrasound of the mammary glands;
- visual examination of the breast (study of the color of the skin and the shape of the mammary glands);
- palpation;
- biopsy (to examine lumps and tumors to rule out malignancy);
- mammography;
- ductography (to identify pathologies of the milk ducts).
Discharge from the mammary glands when pressed, as well as any changes in this area should not be ignored. Timely visits to the doctor, diagnosis, and therapy will help avoid complications and serious illnesses.
Diagnosis of breast diseases
Based on the causes of the pathology, doctors use a special diagnostic algorithm. After examination and palpation of the breast, an ultrasound examination is required. Ultrasound helps identify the presence of cysts and other formations. In the absence of mastopathy, an in-depth diagnosis is carried out.
This includes:
- Determination of the level of sex hormones: estrogen, progesterone, LH and FSH.
- Examination of the thyroid gland (analysis of TSH, T3 and T4, ultrasound of the organ).
- Determination of prolactin levels in the blood.
- Mammography is an X-ray examination of the breast.
- Ductography is the introduction of a contrast agent into the ducts to identify papilloma.
When exudate is released or aspiration of breast cysts, the resulting fluid is sent for cytological examination. Thanks to this analysis, the cellular composition of the material is revealed.
Also, cytological examination helps to distinguish inflammation from benign formations and cancer.