The hormone progesterone is extremely necessary for the female body during pregnancy. Its deficiency can cause miscarriage or abnormal fetal development. This is why doctors prescribe appropriate medications to increase progesterone levels, for example Utrozhestan. But often women are frightened by the discharge from Utrozhestan during pregnancy, which becomes more abundant or slightly changes its color. Here it is important to know what normal leucorrhoea looks like, and what vaginal secretion is considered pathological and is not associated with taking a hormonal drug.
Utrozhestan is also used to normalize menstruation. Find out more about this in the article at the link.
Pregnancy and Utrozhestan
Utrozhestan is quite often prescribed during pregnancy. Its active substances help prevent premature birth and spontaneous abortion. It is also recommended for women who have been unable to conceive a child for a long time due to hormonal imbalance and inadequate ovarian function.
Among all drugs, Utrozhestan is considered the safest. It rarely provokes adverse reactions and does not have a negative effect on the development of the fetus.
Analogs
Analogues of the drug are:
- Ingesta,
- Luteina,
- Krinon,
- Progesterone,
- Progynorm,
- Prozhetin,
- Endometrin,
- Prolutex.
All of the listed drugs have the same active ingredient, and can be prescribed instead of Utrozhestan, as a substitute.
General information about the drug
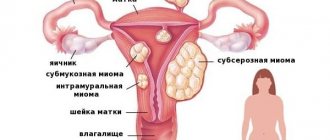
Urozhestan belongs to the group of natural gestagens, the action of which is aimed at restoring hormonal levels. The active component of the drug is micronized progesterone. This hormone is responsible for pregnancy and embryo development.
The main actions of progesterone:
- changes the structure of the endometrium of the uterus, which facilitates the process of implantation of a fertilized egg into it;
- suppresses uterine contractility, thereby reducing the risks of increased uterine tone and spontaneous abortion;
- prepares the mammary glands for lactation.
The capsules are coated with a shell consisting of gelatin, glycerin and sunflower oil. They are pale yellow in color and have no odor. The form depends on the dosage of the active substance. Capsules of 100 mg are round, capsules of 200 mg are oval.
There are several ways to take the medication - vaginally and orally. It has been proven that when used intravaginally, the drug is most effective. Even with the introduction of an average dosage (100 mg per day), rapid penetration of progesterone into the blood is observed, which allows maintaining its optimal level in the body (9.7 ng/ml), necessary during the luteal phase.
Oral administration of Utrozhestan during gestation is undesirable, since the medicine can negatively affect the functioning of the liver and gastrointestinal tract.
Thus, it turns out that taking the medicine ensures successful maturation of the uterine endometrium from the proliferation phase to the secretory phase and has a beneficial effect on the process of implantation of the fertilized egg. And increasing its dosage to 200 mg per day helps to fully compensate the body’s need for progesterone in the first trimester of pregnancy.
Composition of the drug and its release form
The main active ingredient of the product is progesterone. It comes in micro-dosed form. In addition, the capsules contain peanut oil, soy lecithin, glycerol, gelatin and titanium dioxide.
Consumers are presented with two forms of release of this medicine: “Utrozhestan 200” and “Utrozhestan 100”. They differ from each other only in dosage. This is provided for ease of use of the medicine.
Indications for use
Utrozhestan is prescribed to women for hormonal imbalance, which is accompanied by low levels of progesterone in the body. Taking tablets orally is indicated in the following cases:
- luteal insufficiency;
- prevention of habitual spontaneous miscarriage that occurs against the background of a progesterone deficiency state;
- premenstrual syndrome, accompanied by severe symptoms;
- menstrual irregularities (to induce menstruation, instead of injections);
- postmenopause (in this case, Utrozhestan is taken simultaneously with estrogen-containing drugs).
Vaginal administration is indicated in the following cases:
- threat of premature birth;
- prevention of spontaneous abortion;
- premature menopause;
- progesterone deficiency arising from ovarian dysfunction or absence;
- support of the luteal phase in preparation for in vitro fertilization;
- replacement therapy during the postmenopausal period (in this case, capsules are also used together with estrogen-containing drugs);
- infertility that occurs against the background of luteal insufficiency.
Application and action
Utrozhestan is a hormonal drug based on progesterone. This is the hormone that is directly related to the ability of women to become pregnant and successfully bear a fetus. The drug is prescribed when there is a deficiency of this hormone in the body. It acts cumulatively and increases progesterone levels.
If there is a lack of progesterone in the body, then the following may also occur:
- endometrial hyperplasia,
- cyst,
- hyperandrogenism (accompanied by severe hair growth on the body, loss of hair on the head, seborrhea and the appearance of acne).
Used in the presence of the above pathologies, if the test result showed a reduced level of progesterone.
Contraindications for use
Utrozhestan has the following contraindications for oral and vaginal use:
- deep vein thrombosis;
- vaginal bleeding of unknown origin;
- incomplete abortion;
- porphyria;
- oncological diseases affecting the mammary glands or genital organs;
- severe liver pathologies;
- breast-feeding;
- increased sensitivity to progesterone.
Utrozhestan is used with caution for cardiac and vascular pathologies, renal failure, diabetes mellitus, bronchial asthma, photosensitivity, and depression.
Preparatory period for pregnancy
During the period of preparation for pregnancy, the medicine is prescribed in the following cases:
- luteal insufficiency;
- spontaneous miscarriages in the past.
The drug eliminates hormonal imbalance in the body and helps improve the process of transporting a fertilized egg into the uterine cavity. This reduces uterine tone and reduces the risk of spasms. Thus, the likelihood of conceiving a child increases several times.
Taking the medicine can cause a delay in menstruation, and when it occurs, many women note that after Utrozhestan the blood has become thin. The reason for this is altered hormonal levels.
Treatment for uterine bleeding utrozhestan
Utrozhestan for endometriosis suppresses the production of estrogen, as a result of which it ensures the reverse development of lesions. This correction method differs from others in that it allows you to simultaneously plan a pregnancy. Treatment with progesterone-based drugs has a mild effect on the body without causing serious hormonal disorders.
Providing for use
Utrozhestan is a hormonal drug. The drug is used in gynecology for the treatment and prevention of diseases accompanied by a decrease in progesterone levels. The manufacturer recommends using the medication to compensate for the deficiency of the hormone.
This happens in the following situations:
- threat of miscarriage;
- risk of premature birth;
- insufficiency of the second phase of the cycle;
- pronounced PMS;
- mastopathy.
It is also prescribed as an adjuvant for hormone replacement therapy in women after ovarian surgery and at the beginning of menopause.
For patients with endometriosis, the drug is prescribed according to the following indications:
- infertility;
- unstable menstrual cycle, accompanied by prolonged bleeding;
- short second phase of the cycle;
- increased levels of androgens and estrogens;
- pain in the pelvis.
With the remainder of the medicinal product
The active component of Utrozhestan is progesterone, which in its molecular structure is similar to the substance produced by the corpus luteum. The medicine is available in capsules in dosages of 200 and 100 mg, which ensures ease of use. The required amount of hormone for the treatment of endometriosis is determined individually for each woman.
Additional ingredients: sunflower oil, glycerin, soy lecithin, thiatan dioxide.
All components are contained in a gelatin capsule, which dissolves under the influence of high temperatures or liquid substances.
Positive aspects of therapy
The advantages of Utrozhestan therapy are that ovulation is not disrupted in most women. Women's bodies may respond differently to hormone therapy, but when using this drug, a woman is much more likely to become pregnant during treatment than when using oral contraceptives and gonadotropin-releasing hormones.
- has a beneficial effect on the functional layer of the uterus, transferring it from proliferation (active cell division) to the secretory phase (preparing the epithelium to accept the fertilized egg);
- suppresses the contractile activity of the muscular layer of the reproductive organ and fallopian tubes, which prevents the early onset of menstruation and embryo rejection;
- increases the activity of the corpus luteum (temporary endocrine gland that produces progesterone);
- stops the growth of the endometrium, including in pathological areas with focal inclusions;
- has a positive effect on the mammary glands, providing preparation for pregnancy and breastfeeding.
Women who have taken Utrozhestan respond positively to the drug.
Practice shows that in 8 out of 10 patients the menstrual cycle normalizes and pelvic pain disappears. About 50% of women have stopped the growth of endometriosis foci. There are also cases when pregnancy occurred during the therapeutic course.
Treatment regimen and dosage
The treatment regimen is selected individually for each patient with endometriosis. The dosage of the active substance is determined by the following factors:
- degree of disease;
- the presence or absence of cystic formations on the ovaries;
- location of foci;
- the age of the patient;
- hormonal status;
- indicators of the menstrual cycle (regularity, volume and duration of discharge).
For endometriosis, the drug is prescribed for use from the 16th day of the menstrual cycle for 9-10 days. The standard regimen may vary depending on the timing of ovulation. When planning a pregnancy, it is important that the medication is taken after the egg is released from the ovary.
For widespread endometriosis, it is recommended to take the drug from the 5th day from the start of menstruation. The medicine is prescribed for daily use for up to 3 weeks. After this, a break is taken and the course is repeated.
The doctor decides how to take Utrozhestan. The specialist may prescribe oral capsules or vaginal administration. A combination of these methods is also widely used: in the morning capsules are needed for oral administration, and in the evening for insertion into the vagina. The average dose of the drug for endometriosis is from 200 to 400 mg per day.
If pregnancy occurs during treatment, it is unacceptable to stop taking Utrozhestan on your own. It is necessary to continue using the medicine daily at the same dosage and consult a doctor.
A sharp refusal of a hormonal drug can cause an increase in the contractile activity of the reproductive organ, which will result in rejection of the fertilized egg.
For endometriosis, Utrozhestan or other progesterone-based drugs are taken for a long time, and are gradually withdrawn from the second half of the term.
Sometimes patients complain to the doctor that they took a cycle of Utrozhestan, but nothing happened. The drug does not guarantee pregnancy. The hormonal agent only creates favorable conditions for conception and suppresses the activity of endometriosis foci.
Contraindications and side effects
Contraindications for using the drug for endometriosis are:
- intolerance to the active substance;
- high platelet count;
- intracranial hemorrhages, including in the past;
- vaginal bleeding of unknown origin;
- progressive spontaneous abortion;
- breast or pelvic cancer;
- toxic damage to liver tissue;
- lactation period.
While using Utrozhestan, women experience breakthrough uterine bleeding. Mood changes, libido decreases, sensitivity of the mammary glands increases. If any changes that cause concern occur, you should inform your doctor.
Price of the drug and its analogues
The cost of Utrozhestan is variable and is determined by the region of purchase, dosage, and the number of capsules in the package. The average price of 14 tablets in the maximum dosage is 500 rubles. You can buy 28 capsules containing 100 mg of active ingredient at the same cost.
Analogues of the active component are:
In the treatment of endometriosis, Utrozhestan substitutes are also used, which have a different pharmacological effect: Norkolut, Yarina, Zhanin, Buserelin, Zoladex.
Utrozhestan is considered an affordable treatment for endometriosis. Unlike potent substances, it can be used in young girls, women planning pregnancy, and adult patients during menopause. The effectiveness of therapy should be assessed no earlier than after 3 months of taking the drug.
source
Treatment of dysfunctional uterine bleeding
All iLive content is reviewed by medical experts to ensure it is as accurate and factual as possible.
We have strict sourcing guidelines and only link to reputable sites, academic research institutions and, where possible, proven medical studies. Please note that the numbers in parentheses ([1], [2], etc.) are clickable links to such studies.
If you believe that any of our content is inaccurate, out of date, or otherwise questionable, please select it and press Ctrl + Enter.
Goals of treatment for dysfunctional uterine bleeding
General goals for the treatment of uterine bleeding during puberty:
- stopping bleeding to avoid acute hemorrhagic syndrome;
- stabilization and correction of the menstrual cycle and endometrial condition;
- antianemic therapy;
- correction of the mental state of patients and concomitant diseases.
Indications for hospitalization
Indications for hospitalization are:
- profuse (profuse) uterine bleeding that is not controlled by drug therapy;
- life-threatening decrease in hemoglobin (below 70-80 g/l) and hematocrit (below 20%);
- the need for surgical treatment and blood transfusion.
Drug treatment of dysfunctional uterine bleeding
There is evidence of low effectiveness of etamsylate at recommended doses for stopping profuse uterine bleeding.
Stage I. In patients with uterine bleeding, at the first stage of treatment it is advisable to use inhibitors of the transition of plasminogen to plasmin (tranexamic or aminocaproic acid). The intensity of bleeding is reduced due to a decrease in the fibrinolytic activity of blood plasma.
Tranexamic acid is prescribed orally at a dose of 4-5 g during the first hour of therapy, then 1 g every hour until bleeding stops completely. Intravenous administration of 4-5 g of the drug is possible during the first hour, then drip administration of 1 g per hour for 8 hours.
The total daily dose should not exceed 30 g. With large doses, the risk of developing intravascular coagulation syndrome increases, and with the simultaneous use of estrogens, the likelihood of thromboembolic complications is high.
It is possible to use the drug in a dose of 1 g 4 times a day from the 1st to the 4th day of menstruation, which reduces the amount of blood loss by 50%.
It has been reliably proven that a significant reduction in blood loss in patients with menorrhagia occurs with the use of NSAIDs, monophasic combined oral contraceptives and danazol.
Danazol is used very rarely in girls with uterine bleeding during puberty due to severe adverse reactions (nausea, deepening of the voice, hair loss and increased greasiness, acne and hirsutism).
NSAIDs (mefenamic acid, ibuprofen, nimesulide), by suppressing the activity of cyclooxygenase types 1 and 2, regulate the metabolism of arachidonic acid, reduce the production of prostaglandins and thromboxanes in the endometrium, reducing the amount of blood loss during menstruation by 30-38%.
Ibuprofen is prescribed 400 mg every 4-6 hours (daily dose - 1200-3200 mg) on days of menorrhagia. For mefenamic acid, the starting dose is 500 mg, then 250 mg 4 times a day. Nimesulide is prescribed 50 mg 3 times a day. Increasing the daily dose may cause an undesirable increase in prothrombin time and lithium content in the blood serum.
The effectiveness of NSAIDs is comparable to the effectiveness of aminocaproic acid and combined oral contraceptives.
In order to increase the effectiveness of hemostatic therapy, the combined use of NSAIDs and hormonal therapy is justified and advisable. The exception is patients with hyperprolactinemia, structural abnormalities of the genital organs and pathology of the thyroid gland.
Methylergometrine (methylergobrevin) can be prescribed in combination with ethamsylate, however, if you have or suspect the existence of an endometrial polyp or uterine fibroids, it is better to refrain from prescribing methylergometrine due to the possibility of increased bleeding and pain in the lower abdomen.
Source: https://sfmggu.ru/lechenie-pri-matochnyh-krovotecheniyah-utrozhestan/
Use during pregnancy
Quite often, doctors prescribe Utrozhestan to their patients after pregnancy has occurred. And to understand why this is being done, it is necessary to return to his testimony again. During gestation, the drug is used for:
- the presence of a risk of spontaneous abortion in the early stages of gestation;
- deficiency of progesterone in the blood;
- high probability of premature birth.
If a woman has had repeated spontaneous abortions in the past, suppositories can be prescribed to prevent miscarriage. As a rule, the drug is started at the stage of pregnancy planning and treatment is continued after its onset.
Also, among other indications for using the medicine in women, there are situations when:
- the child was conceived using IVF;
- previous pregnancy ended in premature birth;
- the woman has a shortened cervix;
- Infertility was previously diagnosed as a result of disruption of the second phase of the menstrual cycle.
First trimester
Utrozhestan is prescribed quite often during early pregnancy. It is recommended to insert capsules into the vagina once a day at the same time. This use of the drug allows you to avoid the negative effects of the active components on the liver and gastrointestinal tract.
In the 1st trimester of gestation, the medicine is prescribed for the purpose of:
- relieving increased uterine tone;
- prevention of uterine hypertension;
- normalization of the nervous system;
- prevention of spontaneous abortion;
- replenishment of progesterone deficiency in the body.
The drug does not have a negative effect on the development of the fetus. Only in isolated cases can it cause the development of hypospadias (anomaly of the urethra) in a child.
Second trimester
The second trimester begins at 14 weeks and lasts three months. During this period, taking Utrozhestan is usually not required. It is prescribed only in cases where:
- the child was conceived using IVF;
- a woman experiences shortening of the cervix or cervical insufficiency.
During normal pregnancy, the drug is not prescribed. If its use began in the first trimester, then treatment can be extended indefinitely if the woman has a history of:
- operations on the uterus;
- spontaneous miscarriages;
- premature birth.
Third trimester
Indications for the use of Utrozhestan in the last stages of gestation are:
- prolapse of the uterus and low position of the child;
- premature softening of the birth canal;
- short cervix.
Taking Utrozhestan in the last stage of pregnancy is advisable only if there is a high risk of premature birth.
The need to use Utrozhestan in the 3rd trimester of pregnancy is considered individually.
During this period, the female body is subjected to severe stress and the use of any medications can negatively affect the functioning of the liver.
When is Utrozhestan prescribed vaginally?
The drug Utrozhestan is recognized as an effective means of hormonal therapy, used to replenish progesterone that is missing in a woman’s body, secretory transformations in the endometrium of the uterus, reducing the excitability of the fallopian tubes - creating the most favorable conditions for restoring reproductive function, successful egg transplantation. Capsules with micronized progesterone are a universal remedy: Utrozhestan can be used vaginally and orally.
pharmachologic effect
Utrozhestan is available in capsule form, although sometimes women associate them with tablets (vaginal, oral) or suppositories. The advantage of a hormonal drug is the possibility of topical application of capsules with an effect comparable to systemic therapy.
Utrozhestan is presented in the form of round or oval capsules made from a combination of gelatin, glycerin, soy lecithin, titanium dioxide, which provide a homogeneous structure of the drug.
Progesterone, as the main component of the drug, has identical characteristics with the natural sex hormone produced by the endocrine glands, which explains its widespread use in gynecological practice.
Due to rapid absorption, it is rational to use Utrozhestan vaginally, reducing the number of possible side effects.
The drug begins to act 2 hours after insertion into the vagina and retains a sufficient quantitative composition in the blood plasma throughout the day.
Conducted clinical studies confirm the fact that accumulating in the uterus, the concentration of the sex hormone corresponds to the first 3 months of pregnancy.
6 hours after using the hormonal drug, the amount of the active substance gradually decreases and is removed from the body through the excretory system (mainly by the kidneys).
How to calculate the dose?
The amount of active substance required to provide a therapeutic effect is calculated by the attending physician individually according to the indications. In the instructions, the drug manufacturer indicates doses that correspond to the expected effect.
| Indications | Daily dose (mg) | A course of treatment | Features of application |
| Prevention of the threat of fetal loss and complications of labor | 200 | 22-34 weeks of pregnancy | Once a day (preferably at night) |
| Threat of early miscarriage | 200-400 | 1-16 weeks of pregnancy (according to indications up to 24 weeks) | In the morning and in the evening |
| As part of complex estrogen therapy | 100 |
| 1 time per day2 times per day |
| Progesterone deficiency after oophorectomy or egg donation | |||
| Treatment of infertility caused by corpus luteum dysfunction | 200-300 | 17-26 days MC | Once a day at night |
| Hormone replacement therapy after IVF | 200-600 | 1-24 weeks of pregnancy | 1-3 times a day (in combination with human chorionic gonadotropin) |
Utrozhestan is not a contraceptive to prevent or terminate pregnancy. Uncontrolled use of the drug can disrupt natural hormonal levels and cause side effects.
To achieve a positive treatment result, it is advisable to use Utrozhestan capsules several hours after meals. During treatment, you must follow the recommendations of your doctor and undergo regular examinations. The risk group includes patients with a history of:
- diseases of the endocrine system (diabetes mellitus, thyroid dysfunction);
- liver and kidney diseases (liver dysfunction, renal failure);
- cardiovascular diseases;
- photosensitivity (chloasma);
- eye diseases (retinal damage, partial loss of vision);
- allergy to plant protein (soy, peanuts) and other components of the drug;
- psycho-emotional instability (prolonged depression, post-stress state).
An absolute contraindication to the use of hormonal agents is oncology and uterine bleeding of unknown etiology.
When using a combination of estrogens with progesterone for a long time, it is necessary to take into account the risk of significant side effects, one of which is breast cancer.
Contraindications and side effects
If you take capsules longer than prescribed by your doctor, there may be a risk of side effects such as:
- allergic reaction to the active substance in the form of rashes, anaphylactic shock;
- the appearance of cholestatic jaundice;
- migraines, dizziness;
- phenomena of dyspepsia;
- lack of insulin;
- psycho-emotional instability (euphoria, aggression, apathy);
- menstrual irregularities, including absence of menstruation;
- spotting or breakthrough bleeding;
- itching and hyperemia of the vagina, inner thighs;
- changes in the microbial landscape of the vagina, the appearance of discharge;
- soreness of the mammary glands;
- increased appetite;
- hypertension;
- obesity;
- hyperhidrosis;
- decreased libido.
When using Utrozhestan, you need to remember that its simultaneous use with certain medications may interfere with the therapeutic effect. The group of interacting substances includes:
- antibiotics (penicillins, tetracyclines);
- antifungal drugs;
- immunosuppressants;
- antiepileptic drugs;
- anticoagulants;
- sorbents;
- oxytocin;
- barbiturates;
- and other substances.
During treatment with progesterone, the possibility of a shortening of the menstrual cycle or the occurrence of breakthrough bleeding cannot be ruled out.
If you have such symptoms, you should consult your doctor regarding further use of the drug.
Perhaps the doctor will select a medicine with a similar therapeutic effect under a different name, to which the body will not react with hypersensitivity (for example, Progestogel, Duphaston, Iprozhin, Progesterone).
Features of use during pregnancy
Utrozhestan during pregnancy is indicated to prepare the body for the process of fertilization and gestation. The main task of progesterone is to create a favorable environment for egg transplantation into the uterine cavity in the second half of the menstrual cycle by thickening its inner layer and reducing the contractility of the myometrium.
- Utrozhestan suppositories are indicated during pregnancy as a result of in vitro fertilization to ensure its full course.
- Utrozhestan capsules (tablets) are prescribed to pregnant women with endometriosis to prevent the growth of atypical endometrial cells into the deep layers of the uterus, which pose a threat of miscarriage and provoke complications of labor.
- Utrozhestan is recommended for women of late reproductive age (35-45 years) who are planning to conceive a child or have already become pregnant, in order to ensure a comfortable pregnancy and prevent unpleasant symptoms associated with sudden changes in hormonal levels.
- Utrozhestan in the vagina will have to be used by pregnant women with a history of isthmic-cervical insufficiency in order to prevent fetal loss or premature birth due to softening of the cervix and partial opening of its pharynx.
- Completion of treatment with progesterone in high doses should be smooth so as not to provoke breakthrough bleeding. Cancellation is carried out gradually with a step-by-step dose reduction over several weeks. How much and how to take the medicine is decided by the doctor based on the test results.
- Utrozhestan is prescribed with great caution and only according to strict indications in the 2nd and 3rd trimester due to the high risk of developing cholestasis. Regular monitoring of liver and gallbladder function is recommended.
The introduction of additional doses of progesterone into the body of a pregnant woman requires mandatory consultation with the attending physician. Self-correction of the Utrozhestan dosage regimen is unacceptable.
During hormone replacement therapy, it is necessary to take into account the characteristics of the body. If the expected effect is not obtained, this does not always indicate an incorrect choice of treatment tactics.
Genetic factors and inflammatory processes in the reproductive organs in half of the cases cause termination of pregnancy at different stages.
Regular consultations with the attending physician, compliance with his recommendations, a protective regime and the absence of provoking factors increase the chances of a successful treatment outcome.
Source: https://DrLady.ru/apteka/kogda-naznachajut-utrozhestan-vaginalno.html
Instructions for use of the drug
The dosage and duration of taking Utrozhestan is prescribed individually, depending on how the pregnancy progresses. And to get a positive effect from it, the medicine must be used correctly. You need to drink it at the same time of day. For oral administration, the following regimen is used:
- take the drug 2 times a day - morning and evening;
- a single dosage is 100-150 mg.
If there is a threat of premature birth, it is recommended to take the medicine every 7-8 hours. A single dosage can vary from 200 to 400 mg.
When used intravaginally, suppositories must be placed once a day. In this case, the daily dosage is 200 mg. It is better to lie on your side during the procedure. It is not recommended to get up after this. Therefore, tablets should be inserted into the vagina immediately before bedtime.
You cannot have sex during treatment.
If a woman is at risk of spontaneous abortion in the early stages of pregnancy, Utrozhestan is taken 2 times a day with an interval of 12 hours. Single dosage - 200 mg. Duration of treatment is up to 12 weeks.
Interesting topics
- While carrying a child, a woman becomes vulnerable and sensitive. She often experiences mood swings and increased anxiety; this can provoke a slight tone of the uterus during pregnancy. However, it can also be caused by other reasons.
- Preeclampsia during pregnancy is a rather dangerous pathology, but in order to prevent this problem, you need to know as much as possible about it.
- Stress, trauma, or genital tract infections can cause a woman to go into labor prematurely. Find out their signs and what to do if premature labor has already begun.
- Frozen pregnancy means cessation of development and death of the fetus in the early stages. Even scientists cannot accurately determine all the causes of this pathology, but you still need to know about it and take certain measures to preserve the embryo.
Girls, have you used these candles? Why did your gynecologist prescribe this particular drug to you? Describe its effect in your comments.
Cancellation of Utrozhestan
Considering that Utrozhestan belongs to the group of hormonal drugs, it must be discontinued gradually. If treatment is abruptly interrupted, this may cause vaginal bleeding and spontaneous abortion. The most favorable way to discontinue therapy is to reduce the daily dosage of the drug to 100 mg every week or by 50 mg every 3 days.
If a woman begins to take Utrozhestan during pregnancy, upon completion of treatment she should be constantly monitored by a doctor so that timely measures are taken when bleeding occurs.
How does it work?
The drug belongs to the group of steroid hormones, the active substance of the drug is the sex hormone progesterone. The hormone is synthesized from plant materials. Taking the drug is safe for the woman and the fetus, since its use does not affect the production of hormones in a natural way, but simply increases the level of progesterone in the blood.
The drug can be prescribed during planning and after pregnancy.
Side effects
Side effects during treatment with Utrozhestan are rare. As a rule, they appear due to non-compliance with the rules for taking the drug or due to individual intolerance. Among them are:
- amenorrhea;
- vaginal bleeding;
- drowsiness;
- absent-mindedness;
- headache;
- skin rashes;
- nausea;
- bowel disorders;
- jaundice.
When using the drug intravaginally, local reactions may occur in the form of itching, swelling, and redness. Also, many women undergoing therapy note a change in vaginal discharge. They may acquire a liquid or thick consistency, become abundant or completely absent. Such phenomena indicate hormonal changes and are considered normal.
But, if there are inclusions of blood in the discharge, this is no longer normal. This may indicate an insufficient dosage of the drug or intolerance to it. In the latter case, it is necessary to replace the medicine with another drug. But given the high risks of bleeding when stopping Utrozhestan, switching to another medication should be done carefully.
Can there be discharge while taking Utrozhestan at different times?
During use of the drug, discharge may appear. They usually occur when using vaginal capsules, but ingestion is no exception.
Thus, the mucous membrane signals the presence of a foreign body in it.
Also, do not forget that remnants of the medicine and the shell of the capsule itself may come out.
Discharge also occurs when the level of the hormone progesterone rises.
If the discharge does not have a specific smell or strange color, then everything is fine. More details below.
If the discharge is beige
A beige color without an unpleasant odor is the norm. Increased secretion occurs when using any form of the drug. The main thing is that the color is not bright. Light, calm shades do not relate to pathological phenomena.
When pink discharge
Light pinkish discharge is also allowed. If their color darkens or becomes bright, this is a reason to immediately go to the hospital.
If white discharge
Leucorrhoea should also be perceived as normal. The main thing is that they have a neutral smell and are not cheesy.
How to distinguish normal discharge from pathological ones
A pathological secretion will have an unpleasant aroma, bright or dark color, and a cheesy consistency.
Rush to the doctor immediately if:
- Discharge of a cheesy nature. Such symptoms indicate candidiasis, chlamydia, ureplasmosis, etc.
- Dark or bright yellow. This is a sign of bloody inclusions or inflammation. Perhaps the problems are just beginning and the worst can be prevented right away.
- Scarlet, dark red, brownish. This secretion occurs with low progesterone, perhaps the dose needs to be increased. Also, blood on underwear indicates a possible placental abruption, miscarriage, pregnancy outside the uterus, etc.
- Watery secretion. It may indicate that amniotic fluid is leaking. Often such discharge is not pathological.
- Greenish discharge. Sign of infection. To prevent intrauterine infection of the fetus, treatment should be started immediately.
Whatever discharge you have, you should not leave everything as is. Consult your doctor about this. A specialist will examine the woman. A swab will be taken to be examined in the laboratory. Only after receiving the results can we say anything for sure.