What is menopausal syndrome, its symptoms and characteristic signs
There inevitably comes a time in every woman's life when her body begins to age. This period is called menopause. It begins after 45 years and lasts for several years. At this time, certain changes occur, the result of which is the complete extinction of reproductive function. Menopause has 3 stages:
- Premenopause. During this period, the frequency of the menstrual cycle changes, it may become longer (in some cases it becomes more frequent). A woman experiences symptoms such as hot flashes, sleep disturbances, depression and irritability, sudden weight gain with the appearance of a “beer belly.”
- Menopause. The shortest stage, which lasts only 12 months. It begins after the end of the last menstruation. The onset of this stage is indicated by a reduced level of FSH (follicle-stimulating hormone). Only it can be reliable evidence of menopause.
- Postmenopause. After 1 year of absence of menstruation, the final stage of restructuring of the female body begins. Childbearing function completely fades away.
Can there be pain during menopause?
Most women experience the following characteristic symptoms of menopause:
- Tides. This is a sharp, sudden sensation of heat. It lasts from a few seconds to 5-6 minutes. They also end abruptly, the woman feels chills and breaks out in sweat.
- Sleep disorders. Their causes may be hot flashes, depressive states, and other psycho-emotional disorders.
- Dryness of the mucous membranes, their thinning. As a result, intimacy causes discomfort; a woman may feel a burning sensation, pain (and not only during sex).
- Predisposition to fractures, pain in legs, back.
- Increased blood pressure. Occurs due to the accumulation of cholesterol in the body. Plaques complicate the normal flow of blood in the vessels.
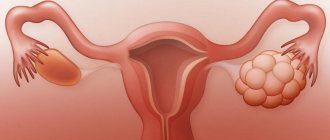
- Gynecological diseases. After 45 years, the risk of developing uterine fibroids, endometriosis, and mastopathy increases.
The listed symptoms can cause such unpleasant consequences as various pains. Any system can suffer, thus signaling possible problems. Therefore, complaints of headaches, muscle or joint pain, and characteristic pain manifestations in the mammary gland can also be considered satellites of menopausal syndrome.
Causes of pain
Menopause is caused by a decrease in the amount of the female sex hormone estrogen. It is produced by the ovaries. This substance takes part in a large number of processes, including: maturation of eggs, ensuring normal pregnancy, absorption of calcium, potassium, magnesium and much more.
A decrease in the concentration of this hormone leads to the following consequences:
- Poor absorption of calcium provokes thinning of bone tissue. As a result, bone fragility increases.
- Estrogen is synthesized in small quantities by fat cells. Therefore, rapid weight gain is possible; a woman notices that her belly is growing.
- The appearance of cholesterol plaques. As a result, blood pressure increases and cardiovascular diseases develop.
- Problems with the pelvic organs. The genital area suffers first. Hormonal imbalance leads to pathological growth of the endometrium, the appearance of malignant and benign neoplasms.
- Changes in the levels of prolactin, estrogen and progesterone lead to chest pain. As a result, fibrous tissue grows, mastopathy and neoplasms develop.
The second common cause is psychological problems. Depressive states and neuroses lead to vascular spasms, causing various dysfunctions of a neurological and physical nature.
Determination of diseases by menstruation
Many women, when premenopause begins and their periods lose their cyclicity, experience uterine bleeding associated with dysfunction of the reproductive system. This condition is characterized by heavy bleeding from the vagina, accompanied by nervous and endocrine disorders.
It is enough to experience a large loss of blood a couple of times for anemia to develop. With uterine bleeding, a woman feels weak and dizzy when her body is in an upright position.
Excessive bleeding may be a sign of:
- estrogen and progesterone deficiency;
- polyposis;
- fibroids.
Prolonged bleeding is not something to joke about. You definitely need to go to the doctor. Typically, patients are immediately prescribed a blood test for iron levels. The mineral stimulates the formation of red blood cells, due to which anemia is quickly eliminated. To normalize your well-being and reduce blood loss, you should take Ibuprofen every 5 to 6 hours.
Bleeding caused by hormonal imbalance can be eliminated using comprehensive measures. A woman should be examined not only by a gynecologist, but also by an endocrinologist and a neurologist. The main methods of treating uterine bleeding are curettage and normalization of the nervous system. In addition to iron supplements, hormonal medications and vitamin complexes are prescribed.
If, despite treatment, bleeding does not go away, then the woman is sent for a full medical examination. Perhaps the cause of the pathological condition is hidden diseases of the internal organs.
Pain in muscles and joints during menopause
Lack of calcium leads to wear and tear of bone tissue. This causes joint pain. The legs and back are the first to suffer.
Female hormones are involved in the process of calcium absorption. It is quite logical that a decrease in estrogen causes a deficiency of this mineral in the body. Calcium takes part in the formation of bones and muscle tissue. With age, chronic deficiency leads to the fact that these systems are not able to withstand the loads to which a woman is exposed (frequent swelling in the joints is observed).
Additional sources of the problem are inactivity and eating fatty foods. Muscle atrophy occurs, they no longer support the bone skeleton, increasing the load on it. In this case, the most vulnerable areas suffer: knees, arms, lower back, back.
Under the influence of hormonal abnormalities, two related diseases develop:
- Osteoporosis. This is brittle bones that is common to most women who go through menopause. A slight blow can be enough to cause serious injury.
- Osteoarthritis. The disease affects the joints; they lack minerals for normal functioning. Chronic inflammatory processes develop. Sometimes this disease, diagnosed in women over 45 years of age, is called menopausal arthritis. With it, the limbs swell, hurt, get tired quickly, convulsions may occur, and weakness can be felt.
Often the back and neck may hurt due to the development of osteochondrosis. It is accompanied by dystrophic changes in the ligaments and structure of the intervertebral discs. The muscles lose their elasticity and do not support the so-called corset well. In particularly advanced cases, an intervertebral hernia develops.
Headaches during menopause in women
To the question whether a headache can occur during menopause, the answer is clear. This is a constant companion of menopausal syndrome. Painful sensations are caused by various reasons, including physical dysfunctions of certain systems and psycho-emotional disorders.
Headaches are an inevitable accompaniment of menopause. There are a number of reasons for their occurrence.
Lower abdominal pain during menopause
Pain in the lower abdomen during menopause is associated in most cases with gynecological problems.
Menopause is a blow to the reproductive system. Lack of estrogen provokes a large number of different abnormalities. The appearance of pain in the lower abdomen is a reason to immediately consult a doctor. It may indicate the development of the following diseases:
- Fibroids (fibroids) of the uterus. This is a benign neoplasm that occurs as a result of an excess of estrogen levels over progesterone (an imbalance). It is often diagnosed in women whose menopause began after 50 years of age (late menopause). In addition to nagging or sharp pain, it may be accompanied by bleeding.
- Endometriosis. Refers to estrogen-dependent diseases, manifested in the form of proliferation of endometrial cells. This process is quite unpredictable; its localization can extend to the vagina, cervix, intestines, and bladder. In addition to pain when the lower abdomen is pulled, a woman sometimes observes the appearance of bloody discharge and discomfort in the back.
- Chronic salpingitis. This is a disease that affects the fallopian tube. Often it begins to develop before the onset of menopause, being asymptomatic. But due to low estrogen levels, inflammatory processes intensify. The localization of the pain is on the side with a downward impact, and the temperature also rises.
- Uterine synechiae. Inhibition of the synthesis of female sex hormones leads to atrophy of the ovaries, uterus, and the appearance of adhesions. The process can occur on its own without obvious symptoms; the appearance of pain indicates a possible accumulation of fluid in the cavity. If you ignore this symptom, severe inflammation develops, accompanied by painful attacks that are difficult to bear.
- Malignant tumors. In the early stages, minor aching sensations may occur. Severe pain appears only in the later stages.
Bloating is a sign of intestinal problems. They appear as a result of decreased metabolism. Food is digested worse; many foods are too “heavy” for the female body during menopause. It hurts in the upper part of the abdominal cavity due to problems with the liver, gall bladder, and pancreas.
Other types of pain during menopause
Chest pain is a common occurrence during menopause. There may be several reasons for this:
- Breast dysfunction. Lack of hormones leads to tissue replacement with fibrous and fatty tissue. Mastopathy, other benign and malignant tumors.
- Problems with intervertebral discs. Their wear and tear causes the space between the vertebrae to expand and hernias to form.
- Cardiovascular diseases. These are frequent companions of menopause.
In some cases, so-called goose bumps appear. This is the result of a lack of hormones and vitamins, low collagen levels.
Why is there pain during menopause?
Most often, women experience pain in the lower part of the body, namely the lower abdomen, lower back, and thighs. Sometimes the pain is so severe that it seems as if the whole body hurts. This condition can be caused by the following disorders:
- Disorders that are associated with intestinal function.
- Problems in the functioning of the reproductive system organs.
- Diseases that are associated with the bladder and other organs of the excretory system.
Pain is an unpleasant and abnormal phenomenon, but in this case it is understandable from the point of view of medical statistics. Every woman who experiences menopause may experience pain in one area or another of the body.
Typically, the most difficult phase of adaptation to the “new woman” lasts about 5-10 years. Menopause begins at about 45 and lasts until age 60. However, all numbers are very individual. Under the influence of life conditions and circumstances, for some women menopause may begin later, and for others earlier.
In order to keep your body in order, you will need to consult a gynecologist, and if menopause occurs with complications, then more specialized specialists.
Attention! Menopause can occur either for completely natural reasons on its own, or it can be caused artificially with the help of certain medications. This is usually done in cases where older women experience bleeding or endometriosis.
How to treat pain during menopause?
The most common problem with the appearance of pain of various types after the age of 40-45 is insufficient levels of hormones. Everyone knows that it is easier to prevent a disease than to treat it. For this reason, doctors prescribe hormone replacement therapy. Drugs in this category help avoid the development of hormonal imbalance.
To prescribe medications and treatment, the doctor will conduct a preliminary comprehensive examination. This includes a personal examination, ultrasound diagnostics, and laboratory blood testing for hormone levels. Additionally, a consultation with specialized specialists, for example, a neurologist, cardiologist, or mammologist, is prescribed. You can make an appointment and get a free consultation on our website. Just follow the link https://45plus.rf/registration/.
Once the diagnosis is made, a decision is made to prescribe other drugs:
- To relieve pain. The choice of remedy depends on the location of the pain and the causes that cause it.
- Prescribing sedatives. They help relieve nervous tension and irritability. Severe conditions may require taking antidepressants.
- Specific medications to treat a specific disease.
It is unacceptable to take any medications or remedies on your own without a prescription from a specialist. This is fraught with serious consequences and the development of complications. This also applies to folk remedies (herbs, tinctures, herbal teas). They have low efficiency and a large number of side effects.
You don't know what to do if you feel pain? This is a good reason to see a doctor immediately!
How to stimulate the ovaries during menopause
The longer a woman’s ovaries maintain their full functioning, the later irreversible age-related changes will begin in the body. How to make the ovaries work more actively?
The foundation of any positive transformation should be a change in lifestyle. This concept includes a whole range of activities.
Proper nutrition
Nutrition is of great importance. Preference should be given to foods of plant origin (vegetables, fruits, berries, herbs, cereals), fermented milk products, dietary meats and fish. It is important to reduce the amount of animal fats consumed and give up fried, smoked, and overly salty foods.
It is equally important to drink enough drinking water. To function properly, the human body requires about 1.5 liters of clean water per day.
In order to support the functioning of not only the reproductive organs, but also the entire body as a whole, during menopause, you can supplement your diet with vitamin and mineral complexes. The modern pharmaceutical market offers a huge selection of drugs of this kind. Their composition is designed taking into account the changes characteristic of menopause. For example, these could be:
Active lifestyle
Equally important is regular physical activity. It helps to avoid the occurrence of congestion in the pelvic organs, thereby preventing the development of pathological processes, helps reduce pain during menstruation, and helps the woman’s reproductive system work in a balanced manner.
Use of infusions and decoctions
The safest option for influencing the functioning of the ovaries may be the use of infusions and decoctions of medicinal plants rich in plant estrogens. Phytocompositions based on these plants can perfectly complement the main treatment of menopausal changes in the ovaries :
- sage;
- hog uterus;
- red brush;
- red clover;
- shepherd's purse.
Taking phytohormones
An improved option may be the treatment of ovarian dysfunction with drugs based on plant estrogens. These funds help achieve a milder course of menopausal changes, as well as prevent the development of pathologies, including those of the ovaries. Their choice today is huge, each individual drug has its own characteristics and effect on the female body. Therefore, treatment should be entrusted to an experienced specialist. The most popular and effective means are:
Use of HRT
Another option for stimulating ovarian function is hormone replacement therapy (HRT). Drugs in this category can be produced in the form of gels, ointments (Estrogel, Divigel), tablets (Premarin, Proginova, Synestrol) and skin patches (Extraderm, Dermestril). All of them contain artificial female sex hormones. This treatment can help the ovaries work more actively again. The hormonal levels are normalized in a fairly short time. However, it is HRT that requires a more careful attitude, as it has a number of contraindications and side effects. An experienced specialist should determine whether the ovaries need to be forced to function longer.
The hormonal revolution that occurs during menopause cannot pass without leaving a trace on any organ of the female body. The changes that the ovaries undergo are by far the most significant and large-scale. And trying to minimize the risk of developing the adverse effects of menopause is the main task of a woman, which she must fulfill in order to preserve her health . Timely diagnosis of menopause and associated changes is the key to successfully overcoming this stage of life.
Sources:
https://stopclimax.ru/bolezni/razmer-yaichnikov https://vklimakse.ru/razmery-yaichnikov-pri-menopauze.html https://mesyachnyedni.ru/klimaks/lechenie/pri-klimakse-chto-proisxodit- s-yaichnikami.html
Pain and bloating in the lower abdomen during menopause: causes of symptoms and their treatment in women during menopause
Menopause, or menopause, is the process of natural aging of a woman’s body, during which the gradual decline of sexual functions begins. Usually begins at 49-50 years old.
During this period, ovarian activity ceases, the woman cannot have children, and menstruation disappears. Dramatic changes are difficult for a woman to bear, causing depression and a nervous breakdown.
Among the many manifestations and symptoms of menopause is pain in the lower abdomen. They can appear for various reasons, but do not panic, as this does not always indicate serious illness.
Vitamins for early menopause
Vitamins A, E, C help well as auxiliary methods for reducing the symptoms of menopause.
If a woman cannot take HRT for any reason, the doctor selects homeopathic medicines:
- Klimadinon;
- Remens;
- Sulphiricum acidum;
- Glonoin.
Also, to improve a woman’s well-being, physiotherapeutic methods are possible, for example, plasmapheresis, which can reduce the frequency of hot flashes and their intensity.
Causes of pain in the lower abdomen during menopause
Menopause is a serious challenge for a woman. The body is accustomed to high levels of hormones, which decrease sharply during this period. The uterus and ovaries undergo structural changes: the uterine epithelium changes, the ovaries dry out.
Women experience symptoms such as:
The head, chest, joints, lower back may hurt, and there may also be a feeling of pulling in the lower abdomen. The causes of such pain can be both physiological and psychosomatic.
Also read how to do a menopause test.
Joints
The pain is felt most severely during physical activity. That is, directly when bending the limbs, when working the joints.
Causes
Menopause is characterized by the fact that calcium is actively washed out during this period. In addition, the amount of collagen in the body also decreases. The elasticity of the joints also decreases. All these phenomena together can cause menopausal arthritis, which is a normal and natural physiological phenomenon.
Symptoms
Discomfort may occur periodically or be constant. Moreover, it can appear in a variety of joints, always the same or in different ones alternately. Most often, these symptoms affect the knee joints, as well as the elbows, and to a lesser extent, the wrists.
How to get rid of it?
Like back pain, it is quite difficult to get rid of it. It is recommended to use injectable analgesics and relieve excessive stress on the group of joints most often affected by this symptom.
Nature of symptoms
Such symptoms have a pulling, aching character. Abdominal pain is localized, mainly in its lower part; but often not only the stomach hurts, but also the lower back. This may be caused by changes in bone tissue. Bones become thinner due to increased leaching of calcium, low estrogen levels provoke joint pain, and they lose their elasticity.
In this case, the pain in the lower back becomes painful and nagging, radiating to the leg or shoulder.
Often pain from the lower back spreads to the stomach area. This condition indicates problems in the gastrointestinal tract or kidneys .
If a woman experiences pain during urination and in the pubic area, this indicates inflammation in the bladder .
With polycystic disease, the pain is localized in the lower abdomen and in the side on the side of the tumor.
During menopause metabolism slows down significantly , so many patients gain excess weight. The load on the lower limbs increases. In this case, pain from the abdominal area spreads to the legs, which indicates the beginning of varicose veins.
At the same time as her stomach, a woman may have chest pain. Any touch to the mammary glands brings discomfort. This occurs due to strong hormonal fluctuations.
Urgent medical attention is required when:
- the pain does not stop even after taking analgesics;
- the pain is acute, throbbing in nature;
- against the background of pain, the temperature rises. This may be a sign of incipient inflammation;
- blood pressure increases;
- signs of general deterioration appear: nausea, vomiting, indigestion, weakness;
- there is a serious psycho-emotional disorder.
Whatever the nature of the pain, you cannot drown it out with painkillers. A full examination and consultation with a qualified specialist is necessary.
What consequences can menopause have?
The consequences of menopause can be very diverse, it all depends on the state of the body, the severity of its course and accompanying symptoms. Some consequences are mental in nature, others are physiological. Mental disorders include various kinds of phobias, constant irritability, tearfulness, and depression. Any of these conditions can last for years and require the intervention of a specialist, since this disrupts the usual way of life.
Physiological negative consequences can be provoked by a number of deviations that occur in some body processes during menopause:
- metabolism;
- process of hematopoiesis;
- tissue restoration.
Menopause can cause complications in any part of the body or body system.
Musculoskeletal system and joints
The cessation of hormone production causes changes in processes in bone and cartilage tissue. Typically, estrogens and progestins stimulate the predominance of components that promote bone density over components that destroy it. When menopause begins, everything changes - substances that contribute to the destruction of bones are produced in the same quantities, but the production of the former is significantly reduced. Accordingly, this entails bone fragility.
Osteoporosis is a very common condition during menopause. It not only increases trauma, but is a trigger for degenerative changes in the joints. Diseases such as osteochondrosis, arthrosis or arthritis during menopause begin to progress very quickly. If these ailments were not observed, the likelihood of their development is very high. If no measures were taken for the initial symptoms, very soon the symptoms intensify:
- pain in the joints and muscles appears;
- posture changes, curvature of the spine is observed;
- With increased physical activity, the risk of bone fracture increases.
To increase bone strength, you need to take calcium.
Skin and mucous membranes
Dry skin and fine wrinkles are also a consequence of menopause. The lack of sufficient amounts of sex hormones has a very adverse effect on the condition of the vaginal mucosa. It becomes very vulnerable, the acidity level is disrupted, resulting in access for microorganisms. During menopause, women very often suffer from various infectious diseases or experience discomfort during sexual intercourse.
Heart and blood vessels
What is dangerous about menopause is its negative impact on the functioning of the cardiovascular system. After all, hormones throughout life ensured the normal functioning of the heart muscle, good blood composition, frequency and elasticity of blood vessels. With the onset of menopause, tremendous changes occur, hence the appearance of hot flashes and heart rhythm disturbances, resulting in increased load on the capillaries. The consequences of menopause can be:
- blood pressure surges;
- disturbance of blood supply;
- heart attack or stroke.
The lack of estrogen causes the formation of cholesterol plaques on the walls of blood vessels.
Metabolic disease
During menopause, hormonal disruption is almost inevitable, and this is fraught with a sharp increase in body weight. The body begins to accumulate fat, trying to compensate for the lack of estrogen. During this period, the craving for sweets increases greatly, since the body is very hungry for endorphins. Obesity can also lead to heart attack.
Brain
Since many parts of the central nervous system and the cerebral cortex need hormones produced by the genitals, their deficiency leads to disorders. During menopause, the central nervous system and brain experience increased stress due to hot flashes, frequent mood swings, pressure surges and other symptoms. Therefore, during the postmenopausal period, women may begin to develop Alzheimer's disease, senile dementia and other mental disorders. Of course, such consequences are not mandatory, but you need to listen to your body in order to help it in time.
Menopause and its consequences may not be so terrible if you make an effort and help the body fight them.
What to do if your lower abdomen starts to hurt
Treatment of pain syndrome begins with a complete examination of the woman and determination of the root cause.
First of all, it is necessary to exclude oncology, fibroids and other neoplasms in the pelvis. Next, you need to examine the gastrointestinal tract, kidney function, and bladder function. Tests are performed to look for osteoporosis or arthritis, which causes bone pain.
If none of the diseases are detected and the cause of the serious condition is only hormonal fluctuations, the doctor prescribes homogeneous replacement therapy.
If a woman cannot bear the pain, then the doctor may prescribe painkillers as symptomatic treatment.
They help a lot:
Hormonal medications that normalize estrogen levels, eliminate hot flashes, and protect against unwanted pregnancy help reduce the symptoms of menopause.
Among the frequently prescribed:
However, the drugs have a number of side effects:
- swelling;
- thrombosis;
- weight gain;
- the appearance of neoplasms in the mammary glands.
Hormonal drugs should not be taken if you have heart disease, tumors in the ovaries, or stomach ulcers.
There are a number of non-hormonal drugs designed to reduce the negative symptoms of menopause:
To normalize the psycho-emotional state, antidepressants are prescribed. They reduce excitability, normalize sleep, and reduce hot flashes.
Commonly prescribed antidepressants:
Can treatment with folk remedies help? Yes, but they do not have much effect alone; they are used in complex treatment.
Here are some useful recipes:
- yarrow . Can be taken as a decoction or tincture. Helps with hot flashes and excessive sweating.
- decoction of raspberry leaves . Contains phytoestrogens, helps relieve spasms and reduce pain.
- infusion of wormwood . Relieves pain, spasm, normalizes sleep.
Causes of changes occurring in the ovaries
Throughout the life of the female body, the ovaries tend to change slightly in size, which depends on:
- age indicators;
- number of births and abortions;
- day of menstruation;
- use of contraceptives containing hormonal substances;
- taking hormonal medications.
With the onset of puberty, the ovaries begin to become involved in the functioning of the woman’s reproductive system and subsequently, within normal limits, can change in size. During pregnancy, these organs, under the influence of increased blood flow necessary to ensure adequate nutrition of the fetus, increase in size. Moreover, with the increasing period of pregnancy, the ovaries can change their location, since the growing uterine organ with its dimensions displaces all nearby organs and tissues to a certain level. The size of the woman’s gonads increases by a couple of millimeters, and the previously occurring ovulation processes cease during pregnancy. Instead, the ovaries begin to produce progesterones, which play a critical role in normal gestation and an easy delivery process.
With delivery, the size of the ovaries in an involutionary mode begins to decrease, along with the uterus.
The circulatory processes in the placenta stop, the speed of general blood flow decreases, which leads to a gradual return of the ovaries to their original form. This, in turn, leads to the resumption of estrogen production and the subsequent preparation of the female body for the full functioning of the entire reproductive organ system, if the woman does not feed her baby with breast milk. In the event that breastfeeding is still used, the restoration of the reproductive functionality of the reproductive system will occur only after the end of lactation processes in the mammary glands.
As women age, reproductive functionality begins to gradually fade away. This also affects the size of the ovaries, which begin to decrease at a leisurely pace. And by the period of premenopause, both glands become the same in all sizes.
The norm in the premenopausal stage of menopause is the following values of ovarian size:
- In a volume from 1.5 to 4 cm3;
- Length – from 20-25 mm;
- Width – 12-15 mm;
- Thickness: 9-12mm.
The first two to three years of the postmenopausal period may be accompanied by the production of single follicles, despite the fact that there is no menstrual cycle. This explains the slight changes in size indicators in the ovaries.
Treatment of bloating during menopause
During menopause, bloating is a fairly common occurrence. It is triggered by a hormonal surge that disrupts the normal functioning of the digestive and excretory organs. This causes a woman a lot of suffering and inconvenience.
In addition to the fact that the stomach is bloated and painful, unpleasant symptoms appear such as:
Causes of bloating:
- gastrointestinal diseases (pancreatitis, gastritis, cholecystitis);
- eating disorders;
- hormone fluctuations;
- fluid retention;
- chronic diseases (diabetes).
Treatment begins with nutritional adjustments:
- Spicy, salty, fried foods, and sweet carbonated drinks are excluded from the diet. It is worth reducing the consumption of baked goods and sweets;
- It is recommended to choose a diet balanced in proteins, fats and carbohydrates;
- eat lean meat, fish, water-based cereals, and fermented milk products;
- reduce salt intake, as it retains water in the body;
- stick to fractional meals.
If symptoms persist and are very bothersome, your doctor will prescribe medications that reduce gas formation, such as Espumisan.
You can relieve pain with No-shpa, Papaverine.
Probiotics and sorbents help improve digestion and normalize microflora:
The main stages and types of menopause
In medical science, it is customary to distinguish 3 different stages that a woman experiences during menopause. These are premenopause, menopause itself and postmenopause. Each of these periods is characterized by certain characteristics.
- Premenopause . This period is characterized by the fact that the level of sex hormones gradually begins to decrease, menstruation does not stop completely, but there is no longer a regular cycle.
- Menopause . We can talk about the arrival of menopause as such only when there has been no menstrual flow at all for more than one year.
- Postmenopause . At this stage, the woman’s body is completely rebuilt to new operating principles. Postmenopause lasts until the end of a woman's life.
What kind of pain can occur during menopause?
Doctors call the following points the main provocateurs of pain during menopause:
- First of all, this is a hormonal change in the body.
- A disorder of the nervous system, which is provoked by depression, stress, and nervous tension.
- Excessive, inappropriate physical activity.
- Acute lack of calcium in the body, as a result of which joints and bones suffer.
- Diagnosis of menopausal arthritis.
- The development of neuralgia, which can disturb the cervical spine area.
Physiological changes in the ovaries
It is the reproductive system of the female body that undergoes the most serious changes during menopause. To understand the essence of the processes occurring in the ovaries at this time, one should remember what function this organ performs and what its significance is.
What is an ovary
The ovary is an oval gland, which with one edge is attached to the uterus, and the other is directed towards the fallopian tube. A mature ovary consists of a cortex, medulla and the so-called gate. It is in the cortex that the follicles are located, inside which the eggs mature. Every woman's body contains a certain number of follicles. This is a kind of reproductive reserve, the reserves of which are not renewed throughout life.
In each menstrual cycle, one follicle matures, giving a chance for the birth of a new life. The ovary produces vital hormones such as estrogens and androgens. Estrogens are of greatest importance for the full functioning of the female body.
Changes during menopause
During menopause, the structure of the ovaries changes dramatically. These changes are irreversible; their final result is the complete completion of reproductive function. As menopausal changes progress, the place of the follicles is gradually replaced by connective tissue, and the place of the former corpus luteum by hyaline lumps. This dynamic process leads to changes in the size and structure of a given organ. Gradually, the ovaries decrease in size, and tissue atrophy occurs.
Read about at what age women's periods end and how to prolong the youth of the body in the article at the link.
Types of pain during menopause
Menopause is a very difficult period for a woman, accompanied by various negative symptoms, and pain is one of them. Moreover, they can be of very different nature and localization. Doctors distinguish the following types:
- Abdominal pain. The main reason is hormonal changes, and due to a decrease in vaginal discharge and a decrease in the size of the birth canal, pain in the lower abdomen may occur during menopause in women. If the latter is cutting in nature, accompanied by a burning sensation when urinating, the most common cause in this case is an infection that affects the urinary tract.
- Headache. The most common cause of headaches in women during menopause is depression, which develops against the background of hormonal changes in the body, although migraine can also be triggered by overstrain of the muscles of the back, cervical spine, and shoulders. If it is accompanied by a feeling of heaviness in the back of the head and swelling of the face, this may be a consequence of hypertension. It is often provoked by taking a number of medications.
- Pain in the joints, muscles and aches in the lumbar region - this may indicate the course of osteochondrosis and osteoporosis, developing against the background of a lack of estrogen and calcium in the daily diet. In this case, the cartilage and bone tissue becomes fragile, wears out quickly, frequent fractures and intervertebral hernia may occur.
- Pain in the chest area. Most often, this is a sign of the development of coronary disease affecting the heart - it is usually accompanied by shortness of breath and attacks of dizziness, rapid heartbeat. IHD is a consequence of atherosclerosis, therefore, when the walls of blood vessels harden and the diameter of the vessels narrows, the heart receives less nutrition and therefore requires immediate consultation with a doctor.
- During menopause, pain in the mammary glands may occur. The cause may be both hormonal changes and the occurrence of neoplasms. It is recommended not to wait until your breasts begin to hurt during menopause, but to be examined by a doctor every six months, and have a mammogram once a year.
Symptoms preceding pain
In addition to pain, during menopause a woman may be bothered by other negative symptoms that precede them. In this case, doctors talk about the following symptoms that precede pain and are a consequence of hot flashes:
- Excessive sweating, especially at night.
- Increased body temperature.
- Attacks of chills and nausea, frequent shortness of breath.
- Disturbance of sleep and nervous system functioning.
- Decreased sexual desire.
- In addition, in some cases, sudden weight loss occurs.
- The nipples on the breast may change color (lighten or darken).
- The breast changes shape and becomes flabby.
- The number of wrinkles increases.
- Legs swell and varicose veins may worsen.
Reasons for missed periods
Delayed menstruation during premenopause is normal. This means that the body is preparing to enter the menopause stage without failure. Changes in the menstrual cycle and other features of the premenopausal period are individual for each woman. But perimenopause should always end in the same way - the complete cessation of menstruation.
Scanty, spot-like periods during perimenopause are normal and should not be a cause for concern. But you need to go to the doctor when bleeding either becomes abundant and prolonged, or is completely absent at the initial stage of menopause.
Treatment with medications
The use of medications to relieve pain during menopause is a very common practice among women. Not every one of them can fully relax and therefore resorts to the use of “magic” pills.
Among the most common remedies in the case of migraines, Analgin, Citramon, and Ibuprofen are most often used. To relieve pain in the lower abdomen, No-spa, the same Ibuprofen, and Ketanol are used.
To balance hormonal levels, after undergoing appropriate studies, the following may be prescribed:
- Janine is a contraceptive that not only protects against unwanted pregnancy, but also helps relieve pain, fever and excessive sweating.
- Divina also helps relieve attacks of severe pain, as well as all kinds of disorders caused by hormonal changes in the body.
Regarding the use of non-hormonal drugs to relieve pain in the lower abdomen, headaches and negative symptoms of menopause, doctors may prescribe:
- Efevelon helps relieve migraines and normalize the functioning of the central nervous system.
- Catena relieves muscle spasms and attacks of pain in the back and lumbar region.
- Klimaton is a herbal-based drug that perfectly copes with mood swings and migraine attacks, eliminating symptoms such as excessive anxiety and bouts of sweating.
With regular use of these drugs, the negative feeling of discomfort in the lower abdomen and chest is reduced, and migraines go away. For severe attacks of pain in the ovaries and lower abdomen, drugs from the analgesic group are prescribed or recipes from the arsenal of traditional medicine are used.
Why does an unpleasant odor appear during and after menstruation, how to treat it?
Is it possible to have sex immediately after an abortion, or is it better to wait? Find out here.