The most vulnerable part of the female body to various ailments is the breast. This feature of the organ is due to the fact that this area is quite susceptible to many unfavorable factors.
Statistics from recent years show disappointing results. After calculating data from mammological studies around the world, medical statisticians determined that about 40% of women on Earth suffer from breast diseases.
The most common illnesses are those accompanied by the appearance of fibrous tumors.
Features of the development of the disease
When considering a disease such as stromal fibrosis, you should first consider the structure of the mammary glands. A woman's breasts include fatty and glandular tissues: the first is responsible for the overall shape of the breast, and the second forms the main ducts and gland. But between the described tissues there is also connective tissue, which helps bind them into a single whole.
Also, fibrous tissues form peculiar partitions that connect the skin and the glandular capsule. Connective tissue is not only found in the human chest, so the disease in most cases begins in the liver, prostate and thyroid glands, as well as the lungs.
The uniform distribution of tissue in the mammary gland depends on the woman’s hormonal background, and over time, when the ability to bear a child decreases, the gland tissue begins to be replaced by fatty tissue. If there are problems with the production of hormones in the human body (this is the main regulator of a woman’s breast health), the stroma begins to actively increase in size, which is very dangerous.
It should be noted that fibrosis in its pure form occurs extremely rarely in humans; most often the lesion is one of the manifestations of a concomitant disease - fibrocystic mastopathy. At an early stage of development, stromal fibrosis is not easy to diagnose, and in some cases it is even impossible to diagnose when consulting a doctor. But over time, fibrous tissue spreads, forms nodes and characteristic compactions.
Doctors' answers
Since you did not provide the initial FGDS protocol (before treatment), it is not possible to assess the dynamics of changes. The only thing that can be said is that a negative test for Helicobacter pylori indicates that the eradication therapy was effective and this, of course, is very good. As for the data for gastritis, duodenitis, in order to assess the effectiveness of therapy it is necessary to know the results of the first FGDS (as I already said), as well as the date of the examination and the treatment regimen and duration of therapy that was prescribed. The persistence of inflammation of the gastric mucosa and duodenum may indicate that the inflammation has not been completely stopped and that continued therapy with antisecretory drugs and reparants is required.
Maria
Thanks for the answer. Tell me, I was also excited by words like “stromal edema” and “plethora”. Isn't that bad?
Congestion and swelling of the stroma of the mucous membrane indicate the presence of an inflammatory reaction. This is pathological confirmation of gastritis.
Consultation is available 24 hours a day
We need to know your opinion. Leave a review about our service
The concept of “chronic gastritis” includes a whole group of diseases that are characterized by common pathological development mechanisms and stereotypical changes in the gastric mucosa. However, the causes, symptoms and approaches to treatment of these diseases may differ. So one of the types of chronic gastritis is gastritis of the antrum of the stomach.
Types of fibrosis
The benignity and malignancy of the formation that arises during the development of fragments of stromal fibrosis will directly depend on the structure and location of the nodes. The following types of damage exist:
- Local form. It is characterized by a round or oval formation, which has a smooth surface. It can be easily diagnosed by palpation; the formation is distinguished by its mobility.
- Diffuse fibrosis is a more complex and serious form of stromal fibrosis, otherwise called widespread fibrosis. Connective tissue quickly forms in and near the milk ducts. In this case, the formation does not have clear boundaries, and when palpated, it is not determined in all cases.
- Severe or linear fibrosis appears in a woman when the tissue, spreading along the ducts and moving to the partitions between the lobes of the gland, forms elongated cords.
- Perivascular fibrosis is an endometrial polyp with focal stromal fibrosis. Occurs in the mammary glands with the active growth of connective tissue not only near the septa and ducts, but also blood, lymphatic vessels and capillaries.
Causes of lesions
With severe stromal fibrosis, a woman’s body has serious hormonal problems. In treatment, the main goal is to eliminate the cause of hormonal imbalance. Doctors divide all the causes of problems with a woman’s hormonal levels into external and internal:
- Internal include diseases of internal organs, injury, miscarriage, refusal to breastfeed.
- External causes of the disease include poor ecology in the woman’s place of residence, a poorly designed diet, abuse of bad habits, nervous shock, depression, regular stress, severe physical stress on the body, and fatigue.
When identifying the cause of a problem with the hormonal system, it is very important to eliminate it or try to reduce the strength of its effect on the human body.
For breast fibrosis, treatment always begins with diagnostic measures, testing, improving diet and prescribing a special diet. In this case, the woman must give up bad habits and a stressful lifestyle.
Causes and symptoms of pathology
Stromal fibrosis is a tissue formation in the mammary glands, forming a kind of cavity frame filled with fluid. In itself, it does not pose any danger, but the development of a number of complications and the appearance of unpleasant symptoms for the woman herself cannot be ruled out. That is why it is extremely important not to ignore such phenomena and contact the clinic in a timely manner.
Stromal fibrosis and other fibrous formations in the mammary glands most often appear in the form of fibroadenoma, which is a ball with dense walls filled with fluid (less often just a proliferation of connective tissue).
The formation of compactions of any kind is associated with a disturbance in the secretion of certain hormones (estrogen, progesterone, etc.). The fact is that their ratio is sometimes disrupted, which can provoke the appearance of an unpleasant illness.
In a healthy woman, who is slightly susceptible to adverse factors, the body calmly neutralizes problems with hormones. However, the slightest weakening of protective forces and increased effects of unfavorable factors can activate the development of stromal fibrosis.
Mammologists include the following as the main reasons for the appearance of fibrous tumors in women’s breasts:
- hormonal instability during periods of menstruation, lactation, pregnancy or interruption of fetal development
- constant stress
- frequent overwork
- presence of diseases of the thyroid and pancreas
- adverse effects on the body of toxic compounds or radiation
- the appearance of inflammation of the uterus or ovary
The cause of the disease is a violation of hormone secretion
Recent studies of this disease also do not exclude the risk of its occurrence based on genetic predisposition.
Symptoms of fibrosis
Symptoms of the disease in each case can be different and manifest individually in each woman. The most common and characteristic of this disease include the following manifestations:
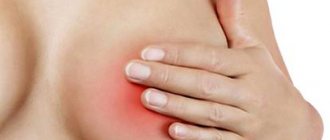
- pain, fatigue, general malaise;
- discharge from the nipples (usually colorless);
- the appearance of characteristic compactions, changes in the shape of the mammary glands;
- change in nipple color and halo.
It is important to remember that all the symptoms described may indicate the presence of other diseases, including breast cancer, so you should not put off visiting a doctor for too long, as this can be very dangerous.
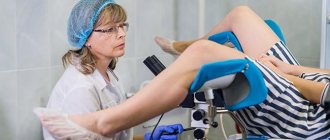
Diagnostic measures
Any lumps in a woman’s mammary gland are an alarming sign, in which it is important to visit a doctor as soon as possible and determine the nature of the disease. It should be remembered: surgery or drug treatment with an inaccurate diagnosis can accelerate the development of cancer.
Diagnostic measures for fibrosis include:
- Examination by a mammologist who will palpate the mammary glands, lymph nodes and determine possible formations.
- Ultrasound and mammography. Also, some women require chromocystography (x-ray of the milk ducts with the introduction of special contrasts).
- Blood test (for hormone levels and general).
- Tissue biopsy, histological examination.
Once the diagnosis has been accurately established, the doctor will prescribe the woman the correct and effective treatment, which will be aimed at eliminating the symptoms of the lesion in a particular case. Depending on the stage of development of the disease and its danger, both treatment with medications only and surgical intervention (up to the removal of a significant part of the breast) may be prescribed.
It should be noted that they try to use surgical intervention as rarely as possible; most often, doctors limit themselves to removing nodes and cysts in the acute course of the disease. Usually doctors prescribe treatment to the patient using traditional and folk methods.
Traditional (otherwise known as drug) treatment includes the complex use of hormonal agents, homeopathic medications and following a special diet. The choice of hormonal drugs is made by the doctor, based on the deficiency or excess of the hormone that provoked the disease. Hormones can be both internal and external - ointments, gels, creams. Homeopathic remedies can be prescribed if a woman has diffuse fibrosis.
In addition to the main methods of treatment, the doctor prescribes a complex of vitamins, iodine products and sedatives. Traditional medicine - herbal decoctions, compresses, lotions - in this case does not bring much effect, but can be used to alleviate some symptoms of the disease. Before using traditional recipes, it is important to consult a doctor.
Stromal fibrosis: features of the disease, causes and reviews
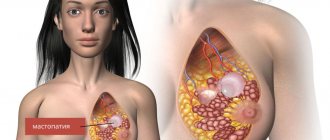
Recently, the number of cases of breast fibrosis in mammology has increased significantly. The disease is a lesion of benign breast tissue – the stroma.
As a result, lumps appear in the mammary gland, which are most often discovered by a woman by chance during an examination by a treating specialist.
And although stromal fibrosis of the mammary gland is not a very dangerous disease, it is important to treat it immediately after its appearance, since any type of neoplasm in the mammary glands can result in a malignant tumor, as well as worsen the appearance of the breasts and affect a woman’s self-esteem.
Description of the lesion
Breast fibrosis spreads to its connective tissues, grows and compacts collagen, elastin, and glycoprotein cells synthesized by fibroblasts, which form the tissues themselves. Such processes provoke the formation of scar neoplasia and problems with the functioning of the mammary gland. The disease can spread to the connective tissues or internal organs of a person.
Features of the development of the disease
When considering a disease such as stromal fibrosis, you should first consider the structure of the mammary glands. A woman's breasts include fatty and glandular tissues: the first is responsible for the overall shape of the breast, and the second forms the main ducts and gland. But between the described tissues there is also connective tissue, which helps bind them into a single whole.
Also, fibrous tissues form peculiar partitions that connect the skin and the glandular capsule. Connective tissue is not only found in the human chest, so the disease in most cases begins in the liver, prostate and thyroid glands, as well as the lungs.
The uniform distribution of tissue in the mammary gland depends on the woman’s hormonal background, and over time, when the ability to bear a child decreases, the gland tissue begins to be replaced by fatty tissue. If there are problems with the production of hormones in the human body (this is the main regulator of a woman’s breast health), the stroma begins to actively increase in size, which is very dangerous.
It should be noted that fibrosis in its pure form occurs extremely rarely in humans; most often the lesion is one of the manifestations of a concomitant disease - fibrocystic mastopathy.
At an early stage of development, stromal fibrosis is not easy to diagnose, and in some cases it is even impossible to diagnose when consulting a doctor.
But over time, fibrous tissue spreads, forms nodes and characteristic compactions.
Types of fibrosis
The benignity and malignancy of the formation that arises during the development of fragments of stromal fibrosis will directly depend on the structure and location of the nodes. The following types of damage exist:
- Local form. It is characterized by a round or oval formation, which has a smooth surface. It can be easily diagnosed by palpation; the formation is distinguished by its mobility.
- Diffuse fibrosis is a more complex and serious form of stromal fibrosis, otherwise called widespread fibrosis. Connective tissue quickly forms in and near the milk ducts. In this case, the formation does not have clear boundaries, and when palpated, it is not determined in all cases.
- Severe or linear fibrosis appears in a woman when the tissue, spreading along the ducts and moving to the partitions between the lobes of the gland, forms elongated cords.
- Perivascular fibrosis is an endometrial polyp with focal stromal fibrosis. Occurs in the mammary glands with the active growth of connective tissue not only near the septa and ducts, but also blood, lymphatic vessels and capillaries.
Causes of lesions
With severe stromal fibrosis, a woman’s body has serious hormonal problems. In treatment, the main goal is to eliminate the cause of hormonal imbalance. Doctors divide all the causes of problems with a woman’s hormonal levels into external and internal:
- Internal include diseases of internal organs, injury, miscarriage, refusal to breastfeed.
- External causes of the disease include poor ecology in the woman’s place of residence, a poorly designed diet, abuse of bad habits, nervous shock, depression, regular stress, severe physical stress on the body, and fatigue.
When identifying the cause of a problem with the hormonal system, it is very important to eliminate it or try to reduce the strength of its effect on the human body.
For breast fibrosis, treatment always begins with diagnostic measures, testing, improving diet and prescribing a special diet. In this case, the woman must give up bad habits and a stressful lifestyle.
Symptoms of fibrosis
Symptoms of the disease in each case can be different and manifest individually in each woman. The most common and characteristic of this disease include the following manifestations:
- pain, fatigue, general malaise;
- discharge from the nipples (usually colorless);
- the appearance of characteristic compactions, changes in the shape of the mammary glands;
- change in nipple color and halo.
It is important to remember that all the symptoms described may indicate the presence of other diseases, including breast cancer, so you should not put off visiting a doctor for too long, as this can be very dangerous.
Diagnostic measures
Any lumps in a woman’s mammary gland are an alarming sign, in which it is important to visit a doctor as soon as possible and determine the nature of the disease. It should be remembered: surgery or drug treatment with an inaccurate diagnosis can accelerate the development of cancer.
Diagnostic measures for fibrosis include:
- Examination by a mammologist who will palpate the mammary glands, lymph nodes and determine possible formations.
- Ultrasound and mammography. Also, some women require chromocystography (x-ray of the milk ducts with the introduction of special contrasts).
- Blood test (for hormone levels and general).
- Tissue biopsy, histological examination.
Once the diagnosis has been accurately established, the doctor will prescribe the woman the correct and effective treatment, which will be aimed at eliminating the symptoms of the lesion in a particular case. Depending on the stage of development of the disease and its danger, both treatment with medications only and surgical intervention (up to the removal of a significant part of the breast) may be prescribed.
It should be noted that they try to use surgical intervention as rarely as possible; most often, doctors limit themselves to removing nodes and cysts in the acute course of the disease. Usually doctors prescribe treatment to the patient using traditional and folk methods.
Traditional (otherwise known as drug) treatment includes the complex use of hormonal agents, homeopathic medications and following a special diet.
The choice of hormonal drugs is made by the doctor, based on the deficiency or excess of the hormone that provoked the disease. Hormones can be both internal and external - ointments, gels, creams.
Homeopathic remedies can be prescribed if a woman has diffuse fibrosis.
In addition to the main methods of treatment, the doctor prescribes a complex of vitamins, iodine products and sedatives. Traditional medicine - herbal decoctions, compresses, lotions - in this case does not bring much effect, but can be used to alleviate some symptoms of the disease. Before using traditional recipes, it is important to consult a doctor.
Preventive actions
Currently, it is impossible to prevent the development of the disease, so it can occur in anyone.
To prevent complications of the disease and begin its timely treatment, it is important to regularly conduct self-examination. The best time for this will be the first few weeks of the menstrual cycle.
It is also important to remember about routine examinations with a doctor (gynecologist and mammologist), ultrasound examinations and relevant tests.
There are factors that can trigger the appearance of breast fibrosis:
- Having a child at a late age. This applies to those women who delay having a child until they are 30 years old or later, the risk of suffering from the disease is much higher.
- The risk group includes women who frequently have abortions and use large amounts of hormonal drugs.
- A woman's refusal to breastfeed also has a negative effect on the body and leads to the appearance of various diseases.
Also, the prevention of this and other diseases will be by maintaining a healthy lifestyle: getting rid of bad habits, playing sports, eating right.
Hormonal levels affect many systems in the human body. It helps maintain sleep and the condition of a woman’s breasts, which react sharply to any disturbances in it.
Breast fibrosis is a common manifestation of disorders in the hormonal system.
Uterine fibrosis
Fibrosis of the uterine stroma can be of several types - diffuse and focal. Changes in connective tissue and the formation of a characteristic compaction, as a rule, lead to the appearance of corresponding symptoms.
It is impossible to independently identify the disease, especially when it is at the initial stage of its development. Symptoms will directly depend on the location of the growth, as well as its extent.
The main symptoms of cervical stroma fibrosis:
- Painful sensations during sexual intercourse.
- Enlargement of the lower abdomen.
- Feeling of strong pressure on the lower abdomen, its distension.
- Problems with urination.
- Pain syndrome in the pelvic area and lumbar spine.
- Long menstruation.
Endometrial stroma with focal fibrosis leads to prolonged and severe bleeding during menstruation, as well as bleeding outside the menstrual cycle. Benign nodes can lead to constipation if they put pressure on the rectum.
As a result of deteriorating immunity, focal stromal fibrosis is formed in the uterine cervical canal, which often leads to infertility or an inflammatory process in the uterus. If timely treatment is not provided, the disease provokes problems with the menstrual cycle.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=XvLvr1N-2NA
You can avoid this condition if you regularly go for examinations to a gynecologist. It is important to remember that with fibrosis of the uterus, blood discharge comes out of the woman’s genital tract between menstruation.
Ovarian fibrosis
Ovarian stromal fibrosis is a benign tumor, most often unilateral, nonfunctioning and characterized by mild symptoms.
Such a lesion cannot be classified as widespread, and it is detected, as a rule, after a significant increase in size.
The tumor is distinguished by its round shape, nodular or smooth surface, and location on a stalk, which gives it mobility. Can be soft or hard.
The stroma with severe ovarian fibrosis is removed through surgery together with the diseased appendage. At a serious stage of development of the disease, the formation can reach up to 12 centimeters in cross section. Small tumors most often do not cause unpleasant symptoms to a woman and do not lead to pain or problems with the functioning of the ovary.
Glandular polyp of the endometrium
The endometrium is the mucous layer of the uterus that lines its cavity. It includes the covering epithelium and the basal layer (base and stroma) with glands embedded inside.
The endometrium can change greatly throughout the menstrual cycle. Under the influence of hormones produced, it can become thicker, thereby preparing for the transfer of a fertilized egg.
During menstruation, the glands branch and secrete a certain amount of secretion with an alkaline reaction.
If the egg does not reach the uterine cavity and is not implanted in it, then the endometrium becomes thinner over time and is rejected, leading to menstruation. In this case, only the covering epithelium is rejected. The basal layer remains in place and helps restore the condition of the endometrium. The process begins again with the onset of a new menstrual cycle.
An endometrial polyp is a benign neoplasm that is formed from its cells. An endometrial glandular polyp is formed from endometrial gland cells in the basal layer. It looks like a node and is located on the bottom or in opposite corners of the uterus.
The glandular polyp is small in size and consists of a separate body and a stalk in which blood vessels are located. If the polyp stalk is not completely removed, in most cases the disease recurs. Sometimes the glands next to the polyp begin to change their shape and overall structure. This condition is called adenomatosis, a disease that can become malignant.
Preventive actions
Currently, it is impossible to prevent the development of the disease, so it can occur in anyone. To prevent complications of the disease and begin its timely treatment, it is important to regularly conduct self-examination. The best time for this will be the first few weeks of the menstrual cycle. It is also important to remember about routine examinations with a doctor (gynecologist and mammologist), ultrasound examinations and relevant tests.
There are factors that can trigger the appearance of breast fibrosis:
- Having a child at a late age. This applies to those women who delay having a child until they are 30 years old or later, the risk of suffering from the disease is much higher.
- The risk group includes women who frequently have abortions and use large amounts of hormonal drugs.
- A woman's refusal to breastfeed also has a negative effect on the body and leads to the appearance of various diseases.
Also, the prevention of this and other diseases will be by maintaining a healthy lifestyle: getting rid of bad habits, playing sports, eating right. Hormonal levels affect many systems in the human body. It helps maintain sleep and the condition of a woman’s breasts, which react sharply to any disturbances in it. Breast fibrosis is a common manifestation of disorders in the hormonal system.
Possible complications and prevention of pathology
Traditional recipes are used in complex therapy of the disease.
As noted earlier, stromal fibrosis in itself is not dangerous, but it is worth understanding that it can mask or be a harbinger of more serious breast diseases in women.
The most harmless complications of the appearance of fibrous formations in the mammary glands are their growth or the onset of inflammatory processes.
In addition, the lack of treatment for stromal fibrosis can provoke:
- suppurative and infectious processes
- breast deformation
- oncological diseases, including breast cancer
- tumor development
Based on this, it is worth stating that it is better not to start the pathology or even to prevent its development. The latter, by the way, is possible if you follow the usual measures to prevent breast fibrosis.
These include:
- wearing corrective bras
- partial cessation of consumption of caffeinated drinks, tea and dark chocolate (it is enough not to abuse them)
- reducing salt in the diet
- organization of healthy eating and exercise
- carrying out preventive breast massages
- isolation from frequent depression
- monitoring the state of hormonal levels and its normalization
- regular examinations with a mammologist and gynecologist
Despite the absence of danger from stromal fibrosis, we note that there are risks of complications that are quite serious. Therefore, we can say with confidence that women should definitely not ignore the appearance of fibrous formations in the breasts. By contacting the clinic in a timely manner and starting treatment, every patient is fully capable of ridding herself of a number of potential problems. Good health to you!
The video shows a specialist talking about the disease:
See also:
- Breast pain before menstruation
- Symptoms of fibrocystic mastopathy
- Goiter 2nd degree and its causes
- Why does an intramural myomatous node appear?
- Women are familiar with chest and abdominal pain
- Leaf-shaped fibroadenoma of the mammary gland: causes, symptoms and treatment methods
- Liver fibrosis 2 degrees: features of treatment of pathology
- Symptoms of mitral valve prolapse
- Homeopathy for mastopathy
(No Ratings Yet)
About the author: Sofia Tutovsky
« Previous entry
Uterine fibrosis
Fibrosis of the uterine stroma can be of several types - diffuse and focal. Changes in connective tissue and the formation of a characteristic compaction, as a rule, lead to the appearance of corresponding symptoms. It is impossible to independently identify the disease, especially when it is at the initial stage of its development. Symptoms will directly depend on the location of the growth, as well as its extent. The main symptoms of cervical stroma fibrosis:
- Painful sensations during sexual intercourse.
- Enlargement of the lower abdomen.
- Feeling of strong pressure on the lower abdomen, its distension.
- Problems with urination.
- Pain syndrome in the pelvic area and lumbar spine.
- Long menstruation.
Endometrial stroma with focal fibrosis leads to prolonged and severe bleeding during menstruation, as well as bleeding outside the menstrual cycle. Benign nodes can lead to constipation if they put pressure on the rectum.
As a result of deteriorating immunity, focal stromal fibrosis is formed in the uterine cervical canal, which often leads to infertility or an inflammatory process in the uterus. If timely treatment is not provided, the disease provokes problems with the menstrual cycle.
You can avoid this condition if you regularly go for examinations to a gynecologist. It is important to remember that with fibrosis of the uterus, blood discharge comes out of the woman’s genital tract between menstruation.
Focal fibrosis of the endometrial stroma
Tumors in the internal organs of a benign nature form unnoticed by patients and often remain asymptomatic for a long time.
The first signs appear when the changed tissue grows, the growth is compressed, and it degenerates into cancer. Endometrial polyps, including glandular fibrous ones, are often found in women.
The disease requires adequate treatment, otherwise the risk of complications will increase.
General characteristics of the pathology
A glandular-fibrous endometrial polyp is a tumor-like formation that forms on the uterine mucosa and consists of glandular cells and connective tissue. The disease is not dangerous, but if there is no treatment and the symptoms are ignored, it leads to consequences. It can occur at any age, but more often women during menopause encounter pathologies.
The growths are small in size (but can grow greatly). It is a smooth pink substance. Has stroma and body. Situated on a thin stem or on a wide base. The second type is more prone to malignancy. The stalk has many blood vessels that supply it for growth. Polyps with a glandular-fibrous structure can be single or multiple.
Causes
The reason for the formation of formations in the organs of the female reproductive system is an imbalance of hormones. The likelihood of polyps, including those with a mixed fibrous and glandular structure, increases with excessive estrogen concentration and progesterone deficiency. Because of this, focal changes occur in the mucosa.
The disease may be caused by:
- Chronic infections and inflammation of the appendages and uterus. They are accompanied by impaired blood circulation in the endometrium, which creates a favorable environment for tumor growth.
- Genetic predisposition. A woman whose relatives (grandmother, mother) suffered from pathology are at risk.
- Having excess weight, obesity.
- Long-term use of hormones, use of an intrauterine device.
- Artificial termination of pregnancy.
- Injury to mucous membranes.
- Diseases of the thyroid gland.
Polyposis can also be provoked by hypertension, diabetes, decreased immunity, frequent stress, and metabolic disorders.
Classification
The uterine cavity is lined with two types of tissues, which, according to histology, correspond to the types of polyps: functional and basal. The first is considered hormone-dependent, cyclically replaced. The second does not depend on hormones. This is the basis during menstruation. Based on this, glandular fibrous polyps are basal and functional.
Functional type
The appearance of a growth is provoked by the action of hormones. Due to the lack of progesterone and excess estrogen, fertile soil is created for the formation of a polyp. The tumor grows directly from the endometrium.
When fertilization does not occur during active ovulation, the cells of the functional layer of the endometrium are released along with menstrual blood. If there is insufficient exfoliation, the remnants of the endometrium form the basis for a future tumor. In this way, a polyp is gradually formed. With each cycle, the growth changes along with the functional layer.
Glandular fibrous formations of this type do not reach large sizes, but they quickly spread and are often localized in groups. The pathology is very rarely accompanied by any manifestations. Fibrous tumors of the functional type are often detected during ultrasound.
Basal type
The growths from the cells of the basal layer are located on a thin stalk. A characteristic feature of a polyp is the presence of blood vessels. Consists of glandular tissue and muscle fibers. Fibrous tumors of this type are distinguished by a mature structure and a variety of morphological variants. Localized unevenly, chaotically.
Pathology often occurs against the background of stable mucosa in healthy women. Often diagnosed during menopause.
It is distinguished by the non-functionality of epithelial cells and the absence of hormonal dependence on menstruation. There are polyps:
- Indifferent. Characterized by an increase in the number of neutral cells.
- Proliferative. Accompanied by endometrial hyperplasia. They often become inflamed.
- Hyperplastic. They are characterized by the proliferation of internal cells and the formation of a “substratum” of the basal stroma.
Symptoms
Manifestations of fibroglandular endometrial polyp do not always occur. Often the course of the disease is hidden. Only when the growth increases in size, is squeezed or is injured, signs may appear. The intensity of symptoms depends on the diameter and location of the tumor. The pathology is accompanied by:
- menstrual disorder;
- heavy bleeding during menstruation;
- pain during intimacy;
- discomfort in the lower abdomen;
- early termination of pregnancy;
- mucous secretions.
The occurrence of severe pain that radiates to the legs and back may indicate the transformation of the polyp into cancer. Malignancy of cells along with ingrowth into the mucous membranes signals that the formation is metastasizing.
Possible complications
If alarming signs of the disease appear, you must go to the hospital, undergo examination and therapy. Even the slightest delay in treatment (especially with a severe clinical course), refusal to undergo surgery or take medications is fraught with:
- Degeneration of a benign fibrous growth into cancer. With endometrial atypia, a threat to the patient’s health arises.
- Deterioration in the quality of intimate life. With an enlarged formation, a woman experiences pain during and after sexual intercourse. There is a loss of interest in sex (the girl is trying to avoid discomfort).
- Inability to conceive a baby. Due to the strong enlargement, glandular fibrous polyps cover the cervix. Against the background of changes in the endometrium, the egg will not be able to attach to the mucosa.
- Miscarriage. The tissue deformed by the fibrous tumor is not able to support the growing baby. The pathology is accompanied by bleeding, which leads to detachment of the child's place.
- Menstrual cycle disorders. Due to hormonal imbalance, menstruation fails. They become irregular and are accompanied by severe pain. Bleeding with fibrous growth is profuse.
- Anemia. Due to blood loss, a woman experiences malaise and a decrease in the body’s protective properties.
Glandular fibrous formations that follow a functional type can grow. Multiple growths are more difficult to treat.
Diagnostics
When symptoms of a fibrous polyp appear, you need to consult a doctor. Pathology, if you delay its treatment, leads to unpleasant complications. To prescribe the correct therapy, it is necessary to differentiate polyposis from other diseases. During diagnosis, the doctor, in addition to collecting complaints and anamnesis, and also examining in a chair, prescribes:
- Ultrasound. A safe method that allows timely detection of any changes in the membrane (thickening, expansion). Additionally, you can study the condition of the fallopian tubes and ovaries.
- Hysterosonography. A more accurate ultrasound examination technique involves injecting a saline solution into the uterus.
- Colposcopy. Thanks to imaging, any abnormalities in the endometrium are detected.
- Metrography. The growth can be seen under the influence of x-rays.
- Hysteroscopy. The most informative method. The procedure is often carried out in combination with curettage. To study the polyp, a biopsy is performed.
- Laboratory tests - smear for flora, bacteriological culture from the cervical canal, tests for sexually transmitted infections.
- Blood test to determine hormone concentrations.
Similar article – How to remove a callus on the foot
Treatment methods
Treatment of pathology can be conservative or radical. Often, a glandular fibrous polyp is treated in a comprehensive manner, first the growth is removed, and then medications are prescribed to restore the body and heal tissue, and also prevent relapse.
Medication
If the polyp is small and does not cause pain or other symptoms, surgery is not required. If there is a hormonal imbalance, steroids are prescribed.
There are cases when excision of a polyp is contraindicated. One of these is childhood. Pathology can occur even in a 10-year-old girl, for whom surgery is undesirable.
For women under 35, the use of oral contraceptives is indicated. The scheme and duration of the course is determined by the doctor.
Table - Drug therapy for fibrous polyps
Drugs
Effect/properties
When no positive dynamics are visible after drug therapy, surgery is prescribed.
Surgical
If fibrous polyps are large, multiple and accompanied by severe symptoms, they are removed. The most harmless and effective methods of excision of growth:
- Hysteroscopy. Low-traumatic method. The operation is performed using light anesthesia on the third day after menstruation. The duration of the intervention is on average 30 minutes. It consists of inserting a hysteroscope through the dilated cervix (to examine the cavity, determine the size and number of formations). Then the tumor is cut off with a surgical loop or forceps and the remains are scraped out.
- Laparoscopy. This method is preferred if there is a high risk of cancer. It involves removing the polyp along with the uterus. The procedure is performed using general anesthesia. During the operation, several incisions are made in the abdomen through which a device with a camera is inserted. After examining the organ, it is excised.
- Laser treatment. Removal of glandular fibrous polyps with a laser beam is a non-traumatic method. After the operation, no scars remain, and reproductive function is still preserved.
For rapid tissue healing and restoration of the body after the intervention, the use of antispasmodics (Papaverine, No-shpa), antibiotics (Ceftriaxone, Sumamed), gestagens (Marvelon, Triquilar), and vitamins is prescribed.
After excision of a polyp, you cannot take a bath, visit a bathhouse, sauna, have sex, or swim in ponds.
Features of pathology during menopause
Changes in hormonal levels during menopause can provoke the appearance of fibrous polyps in the uterus. Small growths are treated with hormones, and in case of severe growth, with surgical methods.
During menopause, it is not easy to identify pathology. One of the manifestations is disruptions in the menstrual cycle, which, in principle, are normal during the onset of menopause.
Glandular fibrous polyp and pregnancy
Growths in the uterus interfere with conception, but even with their presence, fertilization is possible. However, education left unattended by a doctor can lead to the inability to get pregnant in the future. This is one of the reasons why doctors advise removing the tumor as soon as it is discovered. Fibrous growths are dangerous during pregnancy, as they increase the likelihood of miscarriage.
Prevention
After removal, polyps may appear again. Reducing the risk of relapse helps:
- treatment of concomitant diseases;
- regular examinations by a gynecologist;
- leading an active, healthy life;
- rejection of bad habits;
- exclusion of casual sex.
conclusions
Glandular fibrous tumor in the endometrium is an unpleasant disease that every girl can face. With adequate therapy, the prognosis is favorable - women's health is preserved. Ignoring the manifestations of pathology or refusing treatment is fraught with complications, including infertility and cancer.
Questions and answers on: endometrial stromal fibrosis
Hello! I am 31 years old and gave birth to a 13 year old child. I want more children. There was one eco protocol; the histology conclusion was unsuccessful; scraps of cervical epithelium of a typical structure, a small polypoid fragment with endometrial glands of the proliferative type and stromal fibrosis; scraping from the uterine cavity; endometrium with glands of the early and middle stages of the proliferation phase , in the stroma there is diffuse pronounced lymphoplasmacytic infiltration, perivascular and periglanudular fibrosis. Conclusion: chronic endometritis. glandular fibrous polyp of the endometrium. What does this mean? Is it possible to treat such a diagnosis? Do they do eco thanks!
Hello. At 10.5 weeks, an ultrasound scan was taken. First pregnancy, planned, all previous tests are good, 39 years old.
The result of histology is as follows: “During histological examination, the presence of tissues of the decidua and villous chorion with chorionic plate is noted. The decidua is infiltrated with lymphocytes and plasma cells, with foci of edema, fibrinoid necrosis, and necrobiosis.
In the basal part of the decidua there is focal, superficial invasion of interstitial trophoblast, spiral arteries without signs of gestational restructuring. The chorion is represented by mesenchymal type villi, which are covered with trophoblast of varying thickness with proliferation phenomena.
Most villi have an avascular stroma without signs of angiogenesis, often with signs of fibrosis. Single villi contain fetal capillaries, in the lumen of which nuclear erythrocytes of the fetus are visible. Large foci of villi with symptoms of necrobiosis are also found, as well as villi “embedded” in fibrinoid.
Diagnosis: impaired development of pregnancy in early gestation 6-7 weeks; anomaly in the development of the villous chorion: impaired vascularization and maturation; decreased invasion of the interstitial trophoblast into the endometrium with impaired decidualization.”
Analysis of fetal genetics.
Conclusion: 46,XY nuc ish (DXZ1x1,DYZ3x1,D18Z1x2)x/(RB1,D21S341)x2/(D16Z3,D15Z3,BCR)x2
Source: https://lechenie-nog.info/ochagovyj-fibroz-stromy-jendometrija/
Ovarian fibrosis
Ovarian stromal fibrosis is a benign tumor, most often unilateral, nonfunctioning and characterized by mild symptoms. Such a lesion cannot be classified as widespread, and it is detected, as a rule, after a significant increase in size. The tumor is distinguished by its round shape, nodular or smooth surface, and location on a stalk, which gives it mobility. Can be soft or hard.
The stroma with severe ovarian fibrosis is removed through surgery together with the diseased appendage. At a serious stage of development of the disease, the formation can reach up to 12 centimeters in cross section. Small tumors most often do not cause unpleasant symptoms to a woman and do not lead to pain or problems with the functioning of the ovary.
Glandular polyp of the endometrium
The endometrium is the mucous layer of the uterus that lines its cavity. It includes the covering epithelium and the basal layer (base and stroma) with glands embedded inside. The endometrium can change greatly throughout the menstrual cycle. Under the influence of hormones produced, it can become thicker, thereby preparing for the transfer of a fertilized egg. During menstruation, the glands branch and secrete a certain amount of secretion with an alkaline reaction.
If the egg does not reach the uterine cavity and is not implanted in it, then the endometrium becomes thinner over time and is rejected, leading to menstruation. In this case, only the covering epithelium is rejected. The basal layer remains in place and helps restore the condition of the endometrium. The process begins again with the onset of a new menstrual cycle.
An endometrial polyp is a benign neoplasm that is formed from its cells. An endometrial glandular polyp is formed from endometrial gland cells in the basal layer. It looks like a node and is located on the bottom or in opposite corners of the uterus.
The glandular polyp is small in size and consists of a separate body and a stalk in which blood vessels are located. If the polyp stalk is not completely removed, in most cases the disease recurs. Sometimes the glands next to the polyp begin to change their shape and overall structure. This condition is called adenomatosis, a disease that can become malignant.
Reasons for appearance
Glandular polyps of the endometrium with stromal fibrosis can appear as a result of exposure to various factors. Most often, their appearance is associated with glandular hyperplasia of the endometrium (formation in the mucous layer that occurs when the number of glandular cells increases). Such a lesion develops rapidly due to problems with hormones in the body (excessive amounts of estrogen and lack of progesterone). Hyperplasia manifests itself in small areas of the uterine wall in the form of foci, which then change to glandular endometrial polyps.
Glandular polyps with focal stromal fibrosis can appear in a person of any age category. But most often they occur in women who are in a transition period (puberty or menopause). This can be explained by the fact that during this period of time there are problems with hormones in their body, which provoke the appearance of such formations.
- Chest pain
- Heartache
- Lower abdominal pain
- Nipple discharge
- Discomfort during intercourse
- Dyspnea
- Shallow breathing
- Diarrhea
- Loss of appetite
- Weight loss
- Appearance of bruises
- Vomit
- Decreased libido
- Reduced field of view
- Dry cough
- Heaviness in the right hypochondrium
- Enlarged spleen
- Prolongation of menstruation
- Increased breathing
Fibrosis is a disease that is characterized by an accelerated process of collagen production and the proliferation of connective tissue in any organ of the body due to inflammation. The disease leads to tissue compaction and scar formation. When fibrosis of a particular organ develops, its functionality can deteriorate significantly. As a result, this disease leads to the development of all sorts of pathologies.
The most common fibrosis occurs in the breast and liver, lungs and prostate gland. As a result of the replacement of organ cells with connective ones, tissue elasticity decreases. In general, fibrosis is a specific reaction that tries to isolate the inflamed area from healthy tissue.
Classification
Focal sclerosis is divided according to the location of the lesion:
- Sclerosis of the gastric stroma.
- Sclerosis of the endometrial stroma.
- Sclerosis of the parathyroid gland.
- Sclerosis of the myocardial stroma.
Pathology of the stomach and inner layer of the uterus
What is OSS of the stomach? This is a pathology in which the tissues of the stomach change due to their replacement with connective tissue, which performs completely different functions. In this case it is observed:
vomit;
- nausea;
- dysbacteriosis;
- loss of appetite;
- stool disorder.
What is endometrial OSS? This is the result of long-term inflammation of the inner layer of the uterus (endometrium), which is caused by pathogenic bacteria or viruses or gynecological interventions. With this disease, the growth process and endometrial rejection are disrupted, which can lead to disruption of:
- menstrual cycle;
- uterine bleeding;
- infertility;
- disruption of the pregnancy process.
Reasons for appearance
The main causes of fibrotic changes are inflammatory processes and chronic diseases. The disease also occurs after injury, radiation exposure and allergic reactions, infections and due to weakened immunity.
Different organs may have specific causes for the development of the disease. For example, in the liver this disease develops as a result of:
- hereditary diseases;
- immune system disorders;
- inflammation of the biliary tract;
- viral and toxic hepatitis;
- portal hypertension.
Pulmonary fibrosis develops as a result of the following factors:
- pneumonia;
- inhalation of dust microparticles for a long time;
- chemotherapy procedures;
- irradiation of the chest area;
- granulomatous diseases;
- tuberculosis;
- smoking;
- long-term use of antibiotics;
- living in an environmentally polluted area.
Types of disease
The classification of fibrosis varies among specific organs. In the liver, the type of disease depends on the location of the scars in its lobules:
- focal;
- perihepatocellular;
- zonal;
- multibular;
- bridge-like;
- periductular;
- perivenular.
Pulmonary fibrosis can be local and diffuse. Fibrosis of the prostate gland can be focal and with nodose hyperplasia, with cyst transformation and parenchymal atrophy. Sometimes a congenital form occurs.
Local and focal fibrosis is the initial stage of the disease, when isolated areas of tissue are damaged. With a diffuse disease, the damage covers most of the organ. Cystic fibrosis is characterized by damage to the exocrine gland, the ducts become blocked and cysts form. This leads to the development of disorders in the respiratory organs and gastrointestinal tract.
Among the sensory organs, epiretinal fibrosis of the eye occurs, when changes of varying degrees occur in the structures of the vitreous body and retina. Men may develop cavernous fibrosis of the penis. Women in some clinical situations may develop linear breast fibrosis.
Symptoms of the disease
Fibrosis develops slowly and at first the patient does not have any complaints. In rare cases, people experience health problems and consult a doctor. There may be regular fatigue. Then disturbances in the functioning of organs appear, in some cases blood flow worsens.
With liver fibrosis, general malaise is initially observed. After a slight blow, bruises appear on the skin. Liver destruction lasts six to eight years, after which critical symptoms occur. Liver function is significantly impaired as scar tissue cells grow and close together. Further, the spleen increases in size. Other complications include varicose veins of the esophagus and bleeding from them. Then either anemia, thrombocytopenia or leukopenia develops.
At the first stage of development, clinical tests show that fibrotic changes in the liver are insignificant. The disease can be determined by the fact that splenic and portal pressure has increased. Ascites may sometimes appear and disappear. There is also a feeling of heaviness in the right hypochondrium and problems with digestion. Sometimes itching and rashes occur on the skin.
Pulmonary fibrosis can be signaled by shortness of breath, which worsens over time and is accompanied by a dry cough. Then chest pain and rapid shallow breathing occur. Cyanosis is noted on the skin. Frequent bronchitis and heart failure may indicate the progressive development of the disease.
Women may develop focal fibrosis of the mammary gland during hormonal changes. It can be felt by palpation only when the compaction reaches a size of 2–3 millimeters or more. The skin over the affected area will change color. Over time, discomfort in the chest occurs, and then the pain increases. As the disease progresses, there may be a clear or pale discharge from the nipple. There is a feeling of fullness in the chest and heaviness in it. Then the pain intensifies, becomes aching and constant, radiating to the armpit and shoulder.
The danger of uterine fibrosis is that fibroids can be a complication. Pain in the lower abdomen and prolonged menstruation, as well as discomfort during sexual intercourse, may signal the development of the disease.
Symptoms of pancreatic fibrosis are decreased appetite and decreased body weight, diarrhea and vomiting, pain in the hypochondrium on the left side and flatulence.
Cardiac fibrosis is characterized by changes in blood pressure and shortness of breath, as well as disturbances in the rhythm of the heart. Initially, aortic valve fibrosis does not show any symptoms. Over time, pain in the heart and dizziness occur, and then the heartbeat quickens, shortness of breath occurs and the patient may lose consciousness.
In men, pain in the perineum and lower abdomen, discomfort during intimacy and urination may indicate prostate fibrosis. Then erection problems arise and libido decreases. Complications may include pyelonephritis, renal failure and hydronephrosis.
Fibrous changes can occur in different parts of the eye - in the lens, retina or vitreous body. Symptoms are a decrease in the field of vision, a decrease in its acuity and painful sensations.
All about uterine fibrosis: etiology, clinical picture and treatment
Fibrosis is a layer of connective tissue that forms on a woman's reproductive organ. As a result of layering, fibroids begin to form, characterized by a benign course.
The disease affects 10 to 20% of women, most often suffering from this pathology at the age of 30 years. About 25% of patients do not know about the presence of the disease, since uterine fibrosis goes unnoticed for a long time.
Main reasons
Scientists have not yet figured out the exact cause of the disease. They suggest that the female hormone estrogen plays an important role in the development of this disease. That is, the main cause of the disease is hormonal changes. There are several factors that can influence the formation of fibrosis in the uterus:
- genetic predisposition;
- development of inflammatory diseases in the female reproductive organs;
- excess body weight;
- frequent stressful situations at work and at home;
- pregnancy increases the production of estrogen and progesterone, fibroids develop and grow rapidly during this period;
- secondary immunodeficiency states.
Cervical fibrosis is provoked by frequent abortions and cleaning during abortion. Poor nutrition and abuse of bad habits contribute to the development of pathology.
The main predisposing risk factors are wearing an intrauterine device, injury to the organs of the reproductive system, and forced cesarean section.
Knowing all the risk factors and causes of fibrosis, the doctor will be able to reduce the likelihood of the appearance of nodes to a minimum.
Clinical picture
Fibromatosis of the uterine body is of two types: diffuse, focal. Changes in connective tissue and the appearance of compaction most often do not go away without leaving a trace.
It is impossible to independently detect fibrosis, especially when the pathology is at the initial stage of development. Symptoms depend on the location and size of benign tumors, as well as their number.
Fibroids may decrease in size during and after menopause. The main signs of fibrosis:
- pain during intercourse;
- enlargement of the lower abdomen;
- feeling of pressure or fullness in the lower abdomen;
- frequent urination;
- pain in the pelvis and lumbar spine;
- menstruation lasting longer than usual.
Fibrous formation causes increased and prolonged menstruation (menorrhagia), as well as intermenstrual bleeding outside the menstrual cycle (metrorrhagia). Benign nodes provoke constipation (obstipation) if they put pressure on the rectum.
As a result of a violation of general and local immunity, focal fibrosis of the endometrial stroma forms in the cervical canal. It leads to the fact that a woman cannot bear a child, possibly infertility or inflammation of the uterine appendages. If left untreated for a long time, the disease leads to menstrual irregularities.
You can avoid such complications if you visit a gynecologist in a timely manner. Endometrial fibrosis is characterized by bloody discharge from a woman’s genital tract between menstruation, a discrepancy between the thickness of the mucous membrane of the uterine cavity and the day of the menstrual cycle, most often the endometrium becomes thinner.
Research and diagnostics
Most often, fibrosis is discovered completely by accident, for example, when the patient came for a routine examination, which should be carried out every six months. If a woman seeks help with complaints characterizing fibrosis, the doctor first performs a gynecological palpation examination (through the vagina, rectum and abdominal wall).
- Having discovered a tissue compaction, the gynecologist sends the patient to undergo a pelvic ultrasound. An ultrasound examination allows the doctor to see the internal structures of a woman's reproductive organs. Ultrasound detects nodes. Sometimes a transvaginal ultrasound is required, in which an ultrasound probe is inserted into the vagina and provides clearer images because it is closer to the uterus.
- It is advisable to use magnetic resonance imaging or computed tomography.
- If fibroids are pressing on the ureter, you will need to check the kidneys and urinary tract using ultrasound and x-rays using a contrast agent.
- If necessary, a blood test is taken from the patient (if anemia is suspected), as well as to measure hormone levels.
Existing treatments
The doctor develops a treatment plan depending on the patient’s age, the size of the benign node and general health. Conservative treatment of the disease includes the use of the following drugs:
- nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (Ibuprofen);
- birth control pills (Marvelon, Femoden, Logest, Microgynon);
- hormonal contraceptives (Zhanin, Yarina);
- gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonists (Triptorelin, Goserelin, Buserelin).
If fibromatous nodes are combined with endometrial hyperplasia, the doctor will prescribe gestagens. Be sure to use vitamins B, A, E. Vitamin therapy has an effect similar to gestagens. Their continued use improves menstrual function and reduces the manifestations of the disease.
Attention! Self-administration of drugs is prohibited. You can use medications only after medical consultation. Each drug has contraindications; before use, you should read the instructions.
Large formations must be removed. Surgery occurs with minimal damage to the uterus.
Healing after myomectomy does not last long, but the recovery period depends on the competence and professionalism of the attending physician. Myomectomy can be hysteroscopic or embolization.
The choice of type of surgical intervention depends on the clinic, the size and weight of the benign tumor, as well as the location of the fibroma.
Source: https://ZdorovieLedy.ru/matka/fibroz-matki.html
Diagnosis and treatment
The early stage of damage to any organ occurs without obvious signs and complaints about health. First of all, blood and urine tests are taken for diagnosis, and an ultrasound examination should also be performed. Specialists also perform a biopsy - they take tissue from a specific organ for analysis with a special needle and examine it under a microscope. All other diagnostic techniques depend on the specific organ in which fibrosis is suspected.
If there are complaints about liver function, the patient should be examined by a gastroenterologist. He is obliged to prescribe an ultrasound and fibrotest, fibromax, fibroelastography. To detect pulmonary fibrosis, a chest x-ray should be performed. Magnetic resonance or computed tomography and spirography are also performed. If you have pain in the mammary gland, you need to do a mammogram, ultrasound, cytological and histological examination.
The Metavir scale is often used for diagnostic purposes. It helps determine not only the degree of development of the disease, but also clinical indicators. The scale determines the degrees: F0, F1, F2, F3, F4.
Treatment of fibrosis is prescribed by a specialist who has studied the patient’s medical history and reviewed the results of his examination. The doctor may prescribe one or more types of treatment:
- exclusion of influences. It is necessary to give up bad habits and normalize hormonal levels;
- treatment is conservative. In this case, techniques are used to slow down the development of pathology. Oxygen therapy may be one of these;
- treatment with medications. To treat the disease effectively, the doctor prescribes medications that the patient must take according to the regimen. Over time, the pain decreases and the symptoms of the disease disappear;
- surgical intervention. Surgery is necessary if the situation is critical and excision of the affected tissue is required.
Treatment for fibrosis depends on the organ affected and the type of disease. Inpatient treatment is often required. You need a healthy diet and an optimal amount of physical activity, avoid stress and perform breathing exercises. In addition, you need to take anti-inflammatory and antibacterial drugs. Vitamin therapy and physiotherapeutic procedures are recommended.
In general, the treatment plan looks like this:
- treatment of the underlying disease;
- slowing down the production of scar tissue cells - inhibiting the development of the disease;
- reduction of inflammation;
- destruction of seals and scar tissue;
- prevention.
As soon as characteristic symptoms appear, you need to go to a medical facility for diagnosis and examination of the body’s condition. Qualified specialists will conduct numerous studies, make an accurate diagnosis, determine the causes of the disease and prescribe comprehensive treatment. Fibrosis is a disease that should not be treated with traditional medicine. It is better to trust professionals - people with education and experience. You should absolutely follow all the doctors’ instructions and set yourself up for a successful early cure, and then carry out fibrosis prevention.
Treatment
- It is extremely important to undergo a preventive examination and examination by a specialist who will determine the disturbance in the body’s functioning at the initial stage and prescribe the necessary additional instrumental and laboratory tests for the timely start of therapy.
- Treatment involves eliminating the causes that led to sclerosis of the endometrial stroma (inflammation, STIs), and then is aimed at regenerating the structure and functions of the endometrium (local therapy - sanitation of the vagina and uterus, if necessary - infusion treatment, immunomodulating methods, physiotherapy).
Physiotherapy is carried out at the initial stage, as it is the fastest, easiest and most painless way to get rid of the disease. This includes electrophoresis, ultrasound treatment, procedures using cryogenesis, heating, vacuum-vibration therapy.
- Along with hospital treatment, patients must follow the doctor's recommendations, which will depend on the stage of the disease. Sometimes bed rest and care from a third party will be required.
- After eliminating the source of the disease and symptoms, you need to undergo examinations for six months to consolidate the result and restore the body, weakened by pills and injections.
Antibiotics and antiviral drugs
In case of a bacterial infection, antibacterial treatment (antibiotics) is mandatory . Because different bacteria are vulnerable to different types of drugs, there is no general treatment regimen for all patients who suffer from the disease. The treatment regimen will depend on the causes of endometritis in each particular case.
Reference! If a herpes virus is found in the uterine cavity, then special antiviral treatment and medications that enhance immunity (immunomodulators) are prescribed.
If a smear analysis of the flora shows the presence of bacterial vaginosis or thrush (candidiasis), then appropriate treatment is also prescribed.
Since endometrial stromal sclerosis is based not only on infectious factors , but also on growth disturbances and endometrial rejection, the doctor may recommend taking hormonal medications (usually birth control pills) for 5 months. Taking them will allow you to restore the normal menstrual cycle, and after stopping the use of contraceptive drugs, women often manage to get pregnant due to supercompensation of gormans.
Prevention of complications
Adhesions (synechiae) may form in the uterine cavity. Synechiae are septa made of fibrous tissue, which are one of the main causes of infertility. In order to prevent the formation of synechiae and destroy existing ones, doctors recommend proteolytic therapy (drugs Wobenzym, Longidaza, etc.)
To normalize microcirculation in the uterus and accelerate local metabolism, vitamins and physiotherapeutic techniques (electrophoresis, laser therapy, etc.) are also prescribed.
Description
A woman’s breasts have a rather complex structure - under the skin lies a small layer of fat cells that have a protective function. 15-20 lobes extend inward from the nipple, consisting of glandular tissue and separated from each other by connective tissue. Each lobe is divided into small slices.
With various disorders, connective tissue can either grow rapidly or change. In any case, such processes are accompanied by inflammation. The connective tissue stroma is represented by two types:
The latter directly surrounds the ducts and has a fibrous structure, which consists of fibroblasts, macrophages and lymphocytes. Between the ducts, which are fenced by the periglandular stroma, thick septa are distinguished from thick collagen fibers of the interlobular supporting stroma.
When any factor provokes fibrous (connective) tissue to change, either a thickening - a cyst, or a pathological growth of a cavity with various kinds of transudate - can form.
Fibrous tissue may be in the form of capsules, or may not have clear boundaries. Due to these parameters, fibrosis can be of several types:
- Diffuse fibrosis. Extensive growth of connective tissue inside the gland, which does not have clear boundaries. During ultrasound of the breast, these modifications have reduced echographic signs. It should be remembered that the same signs are characteristic of age-related changes. Diffuse fibrosis develops gradually, often without any symptoms. It is usually discovered during diagnostic procedures (ultrasound, mammography) or during preventive examinations.
- Focal fibrosis. It has clear boundaries and is often detected by palpation and at home if it is of sufficient size. The second name is local fibrosis, which is explained by its dense walls. Nodular mastopathy can be represented by one or multiple foci of pathological tissue growth. There may be liquid inside these formations. The disease is typical for women over 40 years of age due to hormonal changes. This is a benign process, but it requires strict control and constant monitoring.
Focal stromal fibrosis can be called the most common type of fibrocystic mastopathy. If it is detected in a timely manner, the prognosis for treatment is very favorable.
By severity
According to the signs of explicitness, stromal fibrosis of the mammary gland can be of the following forms:
Moderate fibrosis is characterized by small areas of altered tissue. The formations are small, often acquiring a granular appearance. All pathological fibrous tissue is localized in one place.
Severe fibrosis is represented by extensive tissue proliferation. In advanced cases, the gland becomes modified and deformed. Surgical treatment is required.
Fibrosis is also distinguished after any impact on the mammary gland:
- post-traumatic: after operations for implantation, operations for diseases, operations for breast plastic surgery and after various injuries
- radiation: after chemotherapy for malignant tumors
By shape and location
They are classified according to the form of formation and location:
- Periductal fibrosis. This type is characterized by the formation of thick collagen strands around the milk ducts. A variation of this fibrosis is a dictal change in the ducts, while other tissues are not affected. The perivascular form of periductal fibrosis is characterized by widespread proliferation of connective tissue around the lymph nodes, blood vessels and ducts of the mammary gland.
- Linear fibrosis is characterized by the appearance of cysts and the formation of dense strands along the ducts. This process is very clearly visible on the monitor of an ultrasound machine and during mammography.
Treatment at home and folk recipes
The basis of treatment for stromal fibrosis is, of course, conservative or surgical therapy. However, to alleviate unpleasant symptoms, it is possible to use some folk remedies prepared at home. Before using this method of therapy, it is advisable to consult with your doctor.
So, the most effective folk recipes for breast fibrosis are:
- St. John's wort tincture. To prepare, brew 30 grams of dry herb in a glass of boiling water for 4-5 hours. After time has passed, strain the product. It is important to use the tincture in the form of a compress, after moistening a piece of gauze and applying it to the epicenter of chest pain.
- A little cream and a decoction of celandine. Another compress, the basis of which is a mixture of melted butter and boiled liquid in equal proportions. This product can simply be rubbed onto an open, sore area of the chest, and then washed off after about 3-5 hours.
- Herb tea. Any similar drink has a calming and relaxing effect on the sore spot.
- Olive oil and garlic. By mixing a glass of olive oil with 10 crushed cloves of garlic, you can prepare an excellent remedy for oral administration. It is important to take the medicine for about 3-4 weeks, a teaspoon once a day.
A compress made from cabbage leaves is considered an effective treatment for the disease, which is quite simple to prepare: you should grease one cabbage leaf with melted butter. The compress is applied to the chest (at night) and secured with a bandage.
Causes
The mammary gland functions thanks to the complex mechanism of the endocrine system. The main hormone-dependent causes of fibrosis of the mammary gland stroma are:
- diseases of the thyroid and other glands of the body (pituitary, pancreas and adrenal glands)
- menstrual dysfunction
- genetic inheritance
- menopause and premenopausal conditions
- metabolic disorders, including diabetes mellitus
- late labor and pregnancy
- endometrial hyperplasia of the uterus and ovaries
- frequent abortions and early miscarriages
Non-hormonal factors that provoke stromal changes include:
- inflammatory processes in the uterus and pelvic organs
- frequent stress and mental fatigue
- hypovitaminosis
- diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, such as constipation, dysfunction of the liver and gallbladder
Other causes may include poor diet, consumption of alcohol, large amounts of coffee, carbonated drinks, and chocolate (these products contain methylxanthine, which promotes fluid stagnation in tissues).
Prevention
Follow the correct diet.
- Do not overuse fried or fatty foods.
- Try to eat only thermally processed foods to reduce the risk of infection from outside.
- Engage in light physical activity to normalize your metabolic processes.
- Sleep enough time so that the body has the opportunity to rest and repair its damaged tissues.
- Give up alcohol and the use of tobacco products, which disrupt the functioning of the entire body as a whole, but it is already affected by the disease and is puzzled by its elimination.
Symptoms
Most often, the symptoms of breast fibrosis remain hidden. The manifestation of unpleasant sensations is observed with extensive and fairly large formations. Women report pain before and during menstruation, as well as when feeling their breasts. Cystic changes of sufficient size are easily palpable. Less commonly, there may be colorless secretion from the nipples.
Heaviness and engorgement of the mammary glands during sexual relations and before the onset of menstruation is an indirect sign, but it should not be ignored. You should consult a doctor even if the skin in a certain area of the mammary gland darkens.
Diagnostics
Regular visits to the doctor will allow you not to miss the disease, and if you have worrying symptoms, you will receive a detailed explanation.
The mammologist will carefully examine the glands and lymph nodes. In addition to palpation and examination of the organ, there are instrumental diagnostic methods that can be used to identify the disease at the earliest stages:
- ultrasonography
- mammography
- chromoductography - x-ray with the introduction of a contrast agent into the ducts
- biopsy followed by histology if a malignancy is suspected
- Doppler sonography allows you to examine the condition of blood vessels with severe tissue proliferation
- computed tomography determines the extent of stromal damage
Laboratory tests are also required: general and biochemical analysis of blood, urine, cytology of mammary gland secretions.
Treatment options
In case of large damage to the gland and a confirmed diagnosis of a malignant process, complete or partial resection is necessary. After this, radiation therapy and a course of rehabilitation measures are prescribed, which include psychological support if desired - surgical restoration of the organ through plastic surgery.
For other forms of fibrosis, conservative treatment of breast fibrosis is indicated, which includes:
- psychological stabilization
- treatment of concomitant pathologies
- giving up bad habits and normalizing proper nutrition
- prescription of vitamin complexes
- regularity of sexual activity
Drug therapy includes anti-inflammatory drugs, sedatives, and diuretics. If you are pregnant, you should not refuse further breastfeeding.
If the cause is a hormonal imbalance, then contraceptives are prescribed for a therapeutic effect. Regular visits to the mammologist will allow you to monitor the process of fibrosis.