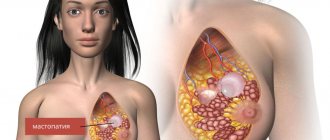
Menopause after hysterectomy
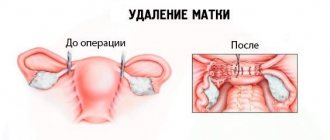
Hysterectomy is the removal of the uterus and is the most common operation performed for certain reasons. According to statistics, approximately a third of women over 45 years of age have had this operation. Therefore, you should not be afraid of it, and in the future you can experience many benefits.
Does menopause occur after hysterectomy?
Pathologies of the female reproductive system can occur at any age. Women over 40 years of age are at increased risk. A number of diseases can only be solved by surgical intervention in the reproductive system.
Indications for operations:
- large fibroids;
- cancerous growths in the cervix;
- infections and inflammatory processes;
- prolapse of the vaginal walls and uterine prolapse;
- chronic uterine bleeding;
- after childbirth with heavy bleeding due to placental abruption;
- with placenta accreta.
Depending on the doctor’s prescription, amputation of reproductive organs in various areas is performed:
- Extirpation of the uterus without appendages. The uterus and cervix are surgically removed.
- Panhysterectomy is an operation to remove the uterus, cervix and appendages.
- Amputation of the uterus without appendages. During the operation, only the uterus is removed.
- Amputation of the uterus and appendages. Surgical removal of the uterus and appendages.
Removal of the uterus without appendages is the most gentle operation that preserves the natural hormonal background of a woman. Due to the fact that the ovaries and cervix remain unharmed, the intervention rarely leads to surgical menopause.
The occurrence of menopause after removal of the uterus and appendages is called artificial menopause. In medical practice, this technique is used to prevent the occurrence of cancer. Despite the fact that all types of oncology are predominantly localized in the uterus, the presence of ovaries increases the chance of recurrent tumors, the likelihood of which increases in proportion to the patient’s age.
Most doctors make it a priority to preserve the appendages, since it is in the ovaries that the hormonal background necessary for the normal functioning of the female body is formed.
Conclusion
A hysterectomy may not affect a woman's life expectancy, but it can improve her quality of life. After getting rid of problems associated with diseases of the uterus and appendages, forgetting about contraceptive methods, most women literally blossom. Almost 65% of patients report increased libido and self-confidence.
After removal of the uterus, disability is not granted because the operation does not reduce the woman's ability to work. A disability group can be assigned only when severe uterine pathology is detected and surgery has led to radiation or chemotherapy. After all, all this significantly affected not only the ability to work, but also the woman’s health.
Sources:
https://ilive.com.ua/health/simptomy-klimaksa-posle-udaleniya-matki_123888i88395.html https://vashamatka.ru/funktsii/klimaks/klimaks-posle-udaleniya-matki.html https://mamazdorova. ru/klimaks-posle-udaleniya-matki/
Postoperative period
Menopause after removal of the uterus and ovaries is an inevitable consequence of the operation, of which the patient is informed before surgery.
The main cause of posthysterectomy syndrome: insufficient blood supply to the ovaries, after exclusion of the uterine arteries and their branches from the system. Due to insufficient blood supply, the ovaries may decrease in size and cease to perform their hormonal function correctly.
Whether there will be menopause after removal of the uterus and the risk of its occurrence depend on:
- volume of operations performed;
- individual structure of the reproductive system before surgery;
- patient's age;
- general health.
The size of the surgical intervention has the greatest impact on the course of the postoperative period. If one additional ovary or cervix was removed, the risk of menopause after surgery increases significantly.
Menopause in women after removal of the uterus is more often observed in adulthood. Each woman’s body contains a constant individual number of eggs, one of which is released with each menstruation. Thus, with age, the female reproductive system may already be quite depleted, and surgical intervention and circulatory disorders in it only accelerate the process of menopause. Whether menopause occurs after removal of the uterus directly depends on the individual structure of the blood vessels of the reproductive system. It is worth considering that the blood supply to the ovaries from the uterine arteries in the female body occurs according to individual volumes, and the higher the blood flow to the ovaries from the uterine arteries before the operation, the higher the risk of PGS occurring after their removal.
The normal course of the postoperative syndrome is also negatively affected by chronic diseases and deviations from the norm. In particular, diabetes mellitus, obesity, venous dilatation of the pelvic veins, impaired lymph outflow, hypertension.
General recommendations
The onset of menopause in women is accompanied by severe symptoms if the lifestyle does not correspond to a healthy one. Treatment of menopause with removed ovaries and uterine tissues is ineffective if the patient does not adhere to the following recommendations:
- Creating a comfortable environment .
For a woman to feel normal, it is important to eliminate irritating factors at work and at home. - Proper nutrition
. When surgical menopause begins, fatty and heavily seasoned foods need to be removed from the diet. The menu must include fish, vegetable dishes, fruits, and grains. - Losing excess weight
. Obesity not only puts emotional pressure on a woman, but also causes pathologies of the heart, bone tissue, and vascular system. - Rejection of bad habits
. There should be no cigarettes or alcohol in the life of a woman of any age. In fertile girls, bad habits provoke disruptions in the cyclicity of menstruation, diseases of the reproductive system, and in older women - menopausal problems. In addition, alcoholic drinks and coffee cannot be combined with hormonal medications. - Active lifestyle .
It is recommended to take walks, do gymnastics and walking. - Complete rest
. It is necessary to normalize sleep and wakefulness.
Menopausal symptoms and problems with the appendages after removal of the uterus manifest themselves differently in each woman, but you need to be prepared for this unpleasant condition. By taking prescribed medications and following medical recommendations, a woman can minimize the symptoms of menopause.
If the article was useful, please like, comment and subscribe to the channel.
Our website "StopClimax.Ru" . There you can find all the information about menopause.
Early symptoms of menopause
The natural decline of the reproductive system occurs smoothly. The female body manages to adapt to changes in hormonal levels, so the symptoms of menopause appear less pronounced and are harmoniously tolerated. At the same time, artificial and postoperative menopause after removal of the uterus occurs abruptly, and its symptoms are pronounced and have an increased negative impact on the normal functioning of the female body.
Three weeks after the operation, menopause appears after removal of the uterus. Symptoms are conditionally divided into four categories, based on the localization of the impact.
Physical state
Disruption of the normal functioning of the ovaries causes high and low tides, which are positioned as early signs of menopause after removal of the uterus. Their symptoms appear:
- in sudden changes in temperature;
- in sudden attacks of chills;
- increased sweating;
- sudden changes in blood pressure.
Hot flashes during menopause after removal of the uterus can occur from 30 to 50 times a day and last more than five years. This physical state of the body causes shock and embarrassment in a woman, and a number of additional psychological problems.
How it manifests itself
In some women, menopause occurs physiologically, without any disturbing symptoms. But still, many women face manifestations of menopausal syndrome. The appearance of all changes is associated with estrogen deficiency; during menopause, all estrogen-dependent organs suffer - the uterus, mammary glands, genitourinary tract, brain, skin, heart and blood vessels, bones. All emerging symptoms can be divided into 3 groups: early, mid-term and late.
Early symptoms
Early signs of menopause appear already in premenopause. They include autonomic and neuropsychiatric manifestations.
The main symptom of autonomic disorders is hot flashes. Hot flashes are felt as a sudden feeling of heat, which is localized mainly in the upper half of the body. The feeling of heat during hot flashes may be accompanied by increased sweating. Other autonomic disorders include:
- blood pressure surges;
- orthostatic hypotension;
- dizziness, sudden weakness;
- increased sweating.
Early signs also include neuropsychiatric syndrome - mood changes and cognitive disorders. Menopausal syndrome is characterized by sudden mood swings, increased irritability and fatigue, and sleep problems. During this period, a woman begins to notice that some little things that were previously perceived completely calmly now bring her to tears or aggression. Cognitive functions are impaired: it becomes more difficult to concentrate and remember new information.
Medium-term symptoms
Medium-term symptoms include urogenital disorders and skin changes. Urogenital disorders are a complex of symptoms from the lower parts of the genitourinary system. Menopausal women may experience the following urogenital symptoms:
- vaginal dryness;
- dyspareunia (pain during sexual intercourse);
- burning and itching in the vagina;
- urinary incontinence;
- frequent urge to urinate.
The skin becomes drier and thinner, its elasticity decreases, and wrinkles appear. Due to metabolic changes, a woman can suddenly gain weight, with fat being deposited mainly in the abdominal area.
Late symptoms
Late symptoms can occur even 5-10 years after menopause. These include changes in the cardiovascular system and bone tissue.
In the first few years after menopause, bone loss occurs, which is associated with a deficiency of estrogen in the body. Bones become more fragile, leading to the development of osteoporosis and frequent fractures in old age.
In the postmenopausal period, the risk of cardiac pathology increases several times. Estrogen deficiency leads to loss of vascular elasticity, which is one of the factors in the development of arterial hypertension. Also, in postmenopause, the risk of developing atherosclerosis increases, which is associated with impaired lipid metabolism.
Hormonal disorders
The sex hormone estrogen is responsible for moisturizing the mucous membranes of the vagina and fallopian tubes. Its insufficient quantity leads to disruptions in the functioning of the mucous membranes, during which they become thinner and dry out. The woman feels uncomfortable and prefers to completely refuse intimacy, since the lack of hydration causes pain. Against this background, conflicts in relationships with a partner and prolonged depression are possible.
Estrogen also has a huge impact on the functioning of the brain, especially disrupting cognitive functions and processes associated with them. Impaired cognitive functions cause:
- memory impairment;
- throughput of perception and assimilation of information;
- problems with remembering new information.
These manifestations can be further aggravated by the woman’s stressful state.
Autonomic disorders
According to statistics, more than 60% of women who experienced menopause after removal of the uterus are familiar with this problem. Lack of proper saturation of the body with sex hormones negatively affects the functionality of the autonomic system and contributes to the appearance of:
- decreased performance;
- increased fatigue;
- general weakness of the body;
- frequent headaches that develop into migraines;
- partial short-term numbness;
- tachycardia;
- dizziness and loss of consciousness;
- neurological diseases.
Psychological disorders
No matter how emotionally prepared a woman was before the operation, after removal of the uterus, menopause and severe stress begin. Patients experience inferiority complexes and prolonged depression. Against this background, there arise:
- excessive impulsiveness;
- increased anxiety;
- severe irritability;
- bright outbursts of unreasonable anger;
- prolonged depression;
- lack of excitement;
- tearfulness;
- annoying fears.
The psychological problems that arise do not allow the body to adapt normally to the new condition and, in combination with other consequences of menopause, can develop into chronic pathologies. These problems should be solved immediately, because only by improving the psychological state can a woman feel healthy and again experience all the joys of her old life. Returning to your previous routine should be done gradually. Excessive fatigue and external pathogens can provoke a recurrence of symptoms.
What are the possible pathologies?
When a woman has undergone therapy for pathology on the ovaries or surgical treatment of intrauterine diseases, then due to a hormonal imbalance, fluid appears in the uterine cavity in postmenopause. This disease is called serozometra. If fluid in a woman’s uterus is detected at the postmenopausal stage, then the main method of treatment is surgery.
When performing an operation, the surgeon must check whether there are any tumors accompanying the serosometer, which should also be removed. After the operation, the patient undergoes anti-inflammatory therapy and rehabilitation.
Hysterectomy of the uterus is performed as an emergency when a woman experiences severe bleeding caused by the formation of synechia in the uterine cavity. Synechia refers to adhesions that formed after traumatic manipulation of the endometrium against the background of an inflammatory process.
Synechia often occurs after a frozen pregnancy. When a woman undergoes cleaning, the endometrium can be damaged. If the inflammatory process is not treated in time and it becomes chronic, then the risk of developing synechia is very high. If there is no bleeding, then synechiae is treated with medication.
Late menopause symptoms
Signs of menopause after removal of the uterus may first appear after a long period of time:
- Diseases of the genitourinary system. The condition and structure of the walls of the genitourinary system directly depend on hormonal levels. Some time after surgery, their deficiency can cause thinning of the urethra, pain when urinating, or urinary incontinence.
- A woman's body stops producing collagen and elastin. This causes dry skin, accelerated aging, hair loss, and brittle nails. The consequence of metabolic disorders can also be rapid weight gain.
- Cardiovascular diseases. Estrogen is involved in cardioprotective functions, and its deficiency can cause arterial hypertension, thrombosis, arteriosclerosis, stroke and heart attack.
- Osteoporosis. Hormonal imbalance often causes bone diseases and can reduce bone density and cause fragility and brittleness.
After the operation, you should carefully monitor the condition of your body and often visit a doctor for examination in order to identify diseases at an early stage.
How long does menopause last in women?
The duration of menopause varies greatly depending on individual characteristics. The duration of menopause can be influenced by heredity, number of births, bad habits (especially smoking), concomitant diseases and the general condition of the body. On average, menopause lasts 5–8 years from the moment the production of estrogen by the ovaries begins to decline. The course of menopause can be divided into 3 periods - premenopause, menopause and postmenopause.
Premenopause
The first symptoms of menopause appear during the menopausal transition. At this stage, there is a decrease in the production of sex hormones by the ovaries, but estrogen deficiency is not yet very pronounced. A woman’s body is trying to adapt to changed conditions. The main manifestation of menopause is disruption of the menstrual cycle - its duration changes, periods become irregular. Other symptoms may occur, but in a mild form. Women usually experience premenopausal changes at age 45. The average duration of premenopause is 3–5 years.
Menopause
Menopause begins from the moment of the last independent menstruation and lasts 12 months. The fact of the last menstruation is determined retrospectively after 1 year. In most cases, menopause occurs at age 50. This stage is characterized by the extinction of the hormone-producing function of the ovaries, the level of estrogen in the blood is sharply reduced. Estrogen deficiency causes the development of menopausal syndrome. During the menopausal period, the early symptoms of menopause are pronounced - hot flashes, psycho-emotional disorders, weight gain, skin changes. Climacteric phenomena are more pronounced with the sudden onset of menopause, when the body has not yet had time to adapt to the deficiency of sex hormones.
Postmenopause
1 year after the onset of menopause, a new period begins in a woman’s life - postmenopausal. Postmenopause lasts until about age 75, when estrogen production stops completely. However, the symptoms of menopause disappear earlier. Hot flashes and emotional disturbances bother a postmenopausal woman for another 1–2 years, and then menopause ends. However, postmenopausal women are at greater risk of developing osteoporosis and cardiovascular disease.
Types of surgical menopause
Menopause after removal of the uterus is a complication from surgery. It can occur in various forms, go away on its own or require long-term treatment and medical supervision. In order to understand what actions should be taken, it is necessary to understand the nature of the complication.
Postoperative menopause can be:
- early - manifestations of menopause symptoms occur a short time after the operation;
- late – symptoms begin to appear after several months to a year;
- transient – symptoms appear early and disappear on their own after a few months;
- persistent – symptoms have a persistent nature of manifestation and a tendency to worsen.
You should not make a diagnosis yourself. To identify the symptoms and types of menopause, you should consult a gynecologist. Only an experienced specialist can determine how long menopause lasts after removal of the uterus and what its nature is in each specific case.
Treatment methods
Previously, it was believed that artificial menopause after removal of the uterus and ovaries could not be treated, but modern doctors and pharmacologists have developed a number of techniques that solve the consequences of surgical intervention in a woman’s reproductive system.
Regardless of the type of menopause, if proper medical care is not provided, patients experience the natural onset of menopause on average 4-5 years earlier. During therapeutic and rehabilitation therapy, psychological and cardiopathic complications do not develop, tissues of the reproductive system are regenerated, and hormonal levels are maintained at the proper level.
Treatment with medications
Hormonal imbalances for each woman are individual. Medicines for menopause after removal of the uterus must be prescribed by the attending physician based on test results.
Hormonal therapy is carried out if the female body is not able to ensure the normal functioning of processes by independently producing sex hormones. In this case, ensuring the necessary hormonal levels is achieved by taking special medications containing the missing hormones. Therapy can be estrogen-based or combined. In addition to estrogen, the combination drugs also contain progesterone.
Estrogen drugs are produced in the form of tablets, pills, vaginal suppositories, patches, creams and gels, and combination products are often produced only as oral medications.
Before taking medications, you should definitely undergo a full examination, and if you are taking hormones for a long time, a medical examination is carried out annually.
Please note that taking hormonal medications is strictly prohibited for patients who have survived or are prone to cancer.
Treatment with phytoestrogens
Most cereals contain estrogens. If a patient has contraindications or allergic reactions to taking pharmacological agents, treatment of menopause after removal of the uterus can be based on taking phytoestrogens. The following grains should be included in your diet:
- wheat;
- beer malt;
- corn;
- oats;
- soy;
- lentils;
- hop;
- linen;
- yam;
- alfalfa;
- black cohosh;
- clover.
Some medications are developed based on natural estrogens contained in these crops, and can also be used if the use of hormonal drugs is contraindicated.
How to ease menopause
It is impossible to completely prevent the occurrence of menopause, since this is a physiological stage in a woman’s life. But it is quite possible to slightly delay the onset of menopause or make it easier. It should be understood that you need to start taking care of your health from reproductive age. It is important to visit a gynecologist regularly, lead an active lifestyle, exercise, and eat right.
Treatment may include several components: phytoestrogens, symptomatic treatment and hormone replacement therapy.
Some plants and foods contain phytoestrogens - plant estrogens. Taking them somewhat facilitates the course of menopausal syndrome, but phytoestrogens are not able to completely cover the body's needs. Phytoestrogens are found in flax seeds, whole grains and bran, peas, beans, and lentils.
Medications are prescribed to relieve some symptoms:
1. Antidepressants (selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors) for depressive disorders and other psycho-emotional disorders.
Psychological correction and assistance
As stated earlier, a woman’s psycho-emotional state plays an important role in the body’s adaptation during recovery after surgery. If you cannot cope with mental disorders on your own, you should pay attention to medicinal antidepressants.
Additionally, the treatment complex may include complexes of vitamins and minerals containing large amounts of magnesium and iron, dietary supplements and other auxiliary products for rapid recovery and maintenance of the normal state of the body.
If there is a deterioration in the functioning of the cardiovascular and autonomic systems, appropriate medications are indicated.
Recovery Tips
After surgery, a woman’s body is faced with severe hormonal imbalances, and the woman herself is subject to stress and prolonged depression. In addition, the postoperative period is accompanied by a long course of rehabilitation, during which the body should be supported.
To promote rapid recovery and the course of surgical menopause, you should adhere to the doctor’s recommendations issued for an individual course of treatment, as well as generally accepted advice:
- A positive environment has a positive effect on the speed of rehabilitation. It is necessary to eliminate irritants and create a positive and cozy living environment. Relatives and close people should provide moral support. If this is not possible, you can contact a psychologist or support centers.
- You should spend as much time as possible outdoors and regularly ventilate the premises. Saturation of cells with oxygen helps to normalize the psycho-emotional state and brings the functioning of the body back to normal.
- It is necessary to adhere to a balanced diet. Eliminate fatty foods from daily use and completely eliminate foods containing trans fats. These components in food can impair blood circulation and cause venous blockage of blood vessels, while exacerbating the production of hormones in the ovaries.
- Develop a balanced daily routine. Lack of sleep and overwork are eternal causes of stress and depression. An already fragile psycho-emotional state can be completely disrupted in the absence of a balanced daily routine. You should get at least eight hours of sleep a day, it is recommended to take a short lunch break, and work activity should be balanced with relaxation and entertainment.
- It is recommended to take care of your own appearance and spend more time taking care of yourself. Regardless of how long menopause lasts after removal of the uterus, a woman always wants to look beautiful, and such a useful habit will help her feel attractive and maintain her psycho-emotional state in a positive mood.
Whatever the cause of menopause, a woman in this condition needs increased care and control. You should pay attention to the fact that during menopause, exacerbations of chronic diseases, surges in blood pressure, dizziness and fainting are possible. It is not recommended to drive a car, take part in active sports or undertake physically tiring work. In addition, even after total removal (extirpation) of the uterus and its appendages, it is necessary to regularly visit a gynecologist. Lifting heavy objects is strictly prohibited, as it may cause prolapse of the bladder and subsequent involuntary urination.
Signs
Menopause without a uterus occurs with almost all the same symptoms as in the presence of this organ. A number of signs may appear:
- Hot flashes are a sharp sensation of heat in the upper part of the body, which develops as a result of a violation of thermoregulation due to a lack of estrogen. It is accompanied by other symptoms, such as increased heart rate and panic attacks. Lasts from a few seconds to several minutes. Usually replaced by chills;
- Sweating is the release of a large amount of sweat for several seconds. Moreover, this happens in many parts of the body. Usually, sweating is accompanied by hot flashes. The phenomenon is also associated with disturbances in thermoregulation;
- Dry mucous membranes and skin occur as a result of a decrease in the amount of estrogen, and it is this hormone in women that is responsible for the good condition and elasticity of the skin. Also, with a decrease in its content during menopause, the secretion of vaginal secretions decreases, and the mucous membranes become thinner and change their structure. As a result, burning, pain and a feeling of dryness in the vagina may occur;
- Disorders of urination in postmenopause have the following causes: decreased hormone levels reduce the tone of the bladder and sphincter. In this regard, urination becomes more frequent, and the portions of urine become smaller;
- From the cardiovascular system, symptoms such as jumps in blood pressure, rapid or increased heartbeat, and irregular heart rhythms appear. Sometimes there may even be pain in the heart due to a lack of oxygen in certain parts of it (which occurs due to deterioration in vascular tone);
- Psycho-emotional manifestations also have a hormonal basis. Characterized by increased anxiety, touchiness, irritability, tearfulness, sudden mood swings;
- There is a significant decrease in libido, both under the influence of hormonal and psycho-emotional factors. In addition, there are difficulties in achieving orgasm. Sex may become unpleasant due to changes in the mucous membrane;
- Osteoporosis develops, as hormonal imbalance causes a decrease in bone density;
- Memory deterioration and some depression of cognitive function are also associated with changes in the nervous system that occur under the influence of hormones.
Timely and professional treatment of this condition can significantly improve well-being and reduce the severity of symptoms.