A bluish or cyanotic cervix in gynecology is considered a likely symptom of pregnancy. The reasons for the change in color of the mucous membrane of the cervix are changes in the nature of blood circulation in the pelvic cavity.
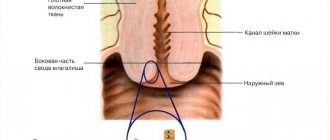
The cervix is the part of the uterus visible to the obstetrician, located in the vagina at a depth of 6-8 cm. The main task of the organ is protective. The glands of the canal epithelium produce mucus, which forms a plug that protects the uterine cavity from infection. During pregnancy, the muscular frame of the reproductive organ ensures retention of the fetus throughout the entire gestation period.
A bluish cervix is considered one of the first signs of pregnancy, and is explained by the influence of the hormone progesterone, which is intensively produced by the corpus luteum of the ovary, and then by the placenta.
Sometimes cyanosis is a sign of pathology, and not evidence of approaching motherhood. The causes of color changes can be determined after a thorough diagnosis by a gynecologist, including instrumental and laboratory methods.
Cyanosis of the cervix is not the only sign of pregnancy, therefore confirmation or exclusion of gestation must be proven by additional examinations.
Blue cervix: causes and treatment
Diseases of the reproductive system organs can manifest themselves in different ways, including being visually noticeable to the doctor during examination. Diseases of this type, for example, include cyanotic cervix. Although cyanosis, in this case, is more likely a symptom that can occur for various reasons and indicate pathologies of one type or another, both more serious and less. Why does this phenomenon occur, is it necessary to treat the causes. Who caused it, and if so, how to do it? This is discussed in this material.
How does it manifest?
Another name for this condition is cyanotic cervix. This condition should be taken literally - the vaginal part of the organ actually takes on a bluish tint. When examined by a doctor, this is noticeable on the vaginal part; in addition, this condition is visualized during colposcopy and some other instrumental studies of the cervix and uterine cavity.
Why does such a change in shade occur from a physiological point of view? The change in shade develops due to changes in the blood circulation of the pelvis in general, the uterus and its cervix in particular. But such changes can be caused by various reasons.
Changes during pregnancy
During gestation, the uterus gradually changes. For example, her neck takes on a bluish tint, with a lilac tint. But the dimensions of the cervix are also modified, it is systematically lengthened, and after childbirth it is shortened.
Early changes
If a gynecologist, when examining a pregnant patient in the early stages, discovers an opening of the cervix, then most likely the uterus is preparing to reject the embryo. The onset of a miscarriage may be indicated by a cervical canal slightly open by one finger.
Doctors can detect any modifications in the organ from the 4th week of pregnancy.
Late changes
Gynecologists, when examining women in late pregnancy, can determine by the size of the cervix when labor will begin. Starting from 37 weeks, its length will begin to decrease.
Readiness for childbirth will be indicated by a slightly open cervical canal, capable of allowing 1 finger through.
Causes
An interesting feature of this condition is that it can be both a sign of a serious pathological process and a normal symptom in certain non-pathological conditions. For example, this is normal during pregnancy. For this reason, all reasons that can cause such changes in blood circulation can be divided into pathological and non-pathological. For non-pathological processes, treatment is not required; for pathological processes, in most cases, it is necessary. What reasons can cause cyanosis of this organ?
Pregnancy
Very often, the gynecologist makes the first assumption about the presence of pregnancy based on such a symptom as a cyanotic cervix. This is considered one of the main diagnostic signs of pregnancy during a standard examination by a gynecologist. After this phenomenon is detected, the patient is prescribed ultrasound examinations and pregnancy tests to confirm this condition.
Why does this symptom appear during pregnancy? It is directly related to the action of the hormone progesterone. Moreover, it is present at all stages of pregnancy, since in the early stages progesterone is produced by the corpus luteum in the ovaries, and in later stages by the placenta.
Infections and inflammation
Pathological processes of this nature cause a fairly strong disturbance of blood circulation in the mucous membrane, as a result of which it changes its color and cyanosis of the cervix occurs. It is quite easy to diagnose such a process. Firstly, it is accompanied by characteristic symptoms, such as pain, menstrual irregularities, uncharacteristic discharge, etc. Secondly, you can take a smear from the vagina and/or uterus, which will show the presence of pathology.
The most common conditions that cause cyanosis are:
- Endometritis;
- Cervicitis;
- Inflammation of the tubes/ovaries/uterine cavity.
If no infectious agents are detected as a result of a smear, then the doctor begins to look for other reasons why a blue cervix could occur.
Tumors
The condition can develop in the presence of any neoplasms. The most pronounced cyanosis accompanies cervical cancer, since the oncological process completely changes the anatomy of the organ, including its circulatory system. For this reason, the doctor often takes tissue for a biopsy for this diagnosis - the samples are examined for the presence of atypical cancer cells.
But not only malignant tumors can cause such changes. For example, myomas and fibroids are sometimes also accompanied by the same symptom as endometriosis. Although these conditions have nothing to do with oncology, they are also associated with active tissue proliferation, and therefore affect the circulatory system in the organ.
Organ prolapse
Another fairly serious condition is significant prolapse and prolapse of the uterus. It is due to the fact that the tone of the pelvic floor muscles weakens for one reason or another, the ligaments that fix the organ stretch and lose elasticity, and under the influence of gravity the organ falls down. First, it puts pressure on the vaginal vault, and then, together with the cervix, may fall into it altogether. After this, the organ may even fall out through the genital opening.
It is clear that in this condition the blood circulation of the organ is disrupted, and this is what causes cyanosis.
This condition is quite easy to diagnose, since its signs are obvious. But prolapse in the early stages is more difficult to diagnose, since at first no characteristic symptoms are observed.
Possible deviations and their causes
Measurements and comparisons of results with existing standards raise many questions among women in the “position”. Deviations, indeed, can be indicators of trouble. Let's look at the most common anomalies and their causes.
Pregnancy in the cervix
If in the early stages the cervix is enlarged beyond normal, the doctor may suspect a so-called cervical pregnancy. This is a type of ectopic pregnancy in which the fertilized egg is implanted not into the uterine cavity, as nature intended, but into the cervix or isthmus.
There, the embryo can theoretically live and develop up to about 4-5 weeks, less often - up to 6-7 weeks. After this, the conditions become unbearable, and the fetus dies and is rejected, a miscarriage occurs, sometimes accompanied by large blood loss.
The pathology is considered quite rare; it is diagnosed less often than in 0.01% of all pregnancies. A fertilized egg can attach to the walls of the cervical canal for a number of reasons, many of which are not known for certain to medicine today.
Doctors tend to believe that this becomes possible if the conditions for implantation in the uterus do not meet the requirements, the blastocyte simply cannot gain a foothold and, in search of shelter, descends into the cervix.
The reason may be a recent abortion , after which the woman neglected the recommendations to use contraception for a certain time. A pregnancy that a young mother decides to undergo after a cesarean section can become cervical if less than 3 years have passed since the operation.
Women with previously diagnosed uterine fibroids and adhesions are also at greater risk than others.
Any interventions - surgery, trauma, inflammation of the uterus can be the cause for subsequent cervical or isthmus pregnancy. There may be no symptoms. The first thing the doctor will notice during the examination will be that the cervix is too large and the uterine cavity itself is too small. After this, ultrasound and colposcopy are prescribed.
A blood test to determine human chorionic gonadotropin, a hormone common to all pregnant women from the day of implantation, shows a too low level of hCG, uncharacteristic of the one stated by the date of the last monthly period.
On an ultrasound, the doctor will not detect a fertilized egg in the uterus, but with a careful examination of the cervical canal, he will find it there. A few decades ago there was no other way to solve this problem than to remove the uterus completely. Many women with cervical pregnancy lost the opportunity to have children in the future.
Now there are less cruel ways to help a woman and preserve her chances of motherhood in the future - vacuum aspiration and laser excision of the site where the embryo grows into the cervix. The risks of complications after such interventions are quite high, but modern medicine copes with the task quite successfully.
Short neck
A short cervix (at the very beginning of pregnancy less than 25-27 mm) can be a congenital feature of the structure of a woman’s reproductive organs, and a consequence of traumatic influences - abortion, for example, or inflammatory processes that caused shortening of the lower segment of the uterus. In any case, the insufficient length of this part of the reproductive system poses a serious danger for the child and the woman.
Normally, the cervix lengthens at the beginning of pregnancy and shortens closer to childbirth. An initially short cervix will have great difficulty coping with the load of holding a growing baby in the uterine cavity. Miscarriage, premature birth, rapid labor, or cervical rupture may occur.
A shortened cervix creates an increased risk of intrauterine infection of the fetus, since it cannot serve as reliable protection against pathogenic microorganisms and viruses.
The doctor will be able to detect shortening already at the first appointment, if it occurred before pregnancy. However, with the subsequent development of a short neck, for example, due to hormonal deficiency in the first trimester, the problem can only be detected at the 12th week of pregnancy, when the expectant mother comes for a screening examination.
Symptoms sometimes appear after this period, closer to the fourth month of pregnancy.
The growing baby begins to put more noticeable pressure on the short neck, and the woman may begin to complain that the lower abdomen hurts, and sometimes even bleeds slightly.
The discharge is bloody or bloody, sometimes mixed with mucus. If the shortening is confirmed by the results of a vaginal ultrasound, then the question of how to provide assistance is decided. In some cases, the cervix can become stronger under the influence of medications, for example, hormones, if they are not enough, but it cannot lengthen under any circumstances.
During pregnancy, such an expectant mother will be monitored more closely and, if necessary , hospitalized in order to provide treatment aimed at preserving and prolonging the pregnancy.
A pessary can be installed on the cervix - a special ring that will fix it and reduce the load of the growing reproductive organ on the short cervix.
Another method is cerclage. It is based on placing sutures on the neck, which will mechanically prevent its premature opening. It is reasonable to carry out suturing only in the early stages and up to 26-29 weeks of pregnancy; after this period, they try not to carry out cerclage.
Long neck
The cervix can be long from birth, or it can become long after undergoing operations, including abortions and curettage, inflammatory diseases of the reproductive system - the uterus, appendages, ovaries. Quite often, the first symptoms of this pathology appear precisely during pregnancy.
Elongation of the lower segment of the uterus leads to incorrect proportions of the reproductive organ, which increases the risk of pathological attachment of the placenta when this temporary organ is located in the center, too low or to the side.
The height of the placenta is of great importance, especially in the second and third trimesters; it determines how well the baby will be provided with all the necessary nutrients and oxygen.
Women with a pathologically elongated cervix are at risk during childbirth . The process of giving birth to a child is protracted; labor lasts almost 14 hours for first-time mothers, and 9-12 hours for multiparous women.
The elongated organ opens longer, slower, and more painfully.
When a child passes through such a canal, the risk of hypoxia increases, since the head and neck are in the same plane.
The difficulty lies in the fact that it is impossible to determine the pathology during a routine examination by a gynecologist. An anomaly can be suspected only during colposcopy, and confirmed or refuted only with the help of ultrasound diagnostics.
This deviation does not require special treatment, because a long neck diagnosed at an early stage can smooth out and become smaller by childbirth. If this does not happen, then doctors will probably use one of the methods of inducing labor.
Before giving birth, a woman is recommended massage , which promotes the outflow of lymph and also strengthens the muscles of the pelvic organs. Medicines are rarely prescribed , mainly in cases of post-term pregnancy in a hospital setting.
Erosion
Based on the results of biometry of this organ, as well as during manual examination, the doctor can report that the length is normal, but there is erosion. More than 60% of pregnant women experience this phenomenon. For some, changes in the mucous membrane of the cervix were observed before the onset of the “interesting” position, but it is possible that erosion can develop during pregnancy.
The reasons are varied. The mucous membrane can change under the influence of hormones if a woman took oral contraceptives before pregnancy, as well as in the case of a deficiency or excess of certain hormones during pregnancy. The cause may be previous inflammation, while erosion can sometimes manifest itself only after pregnancy.
Erosion affects women who previously had a history of sexually transmitted diseases and sexually transmitted infections, difficult childbirth that injured this organ, and multiple abortions. Even the inability to do douching correctly and extra pounds can lead to the development of such a complication.
A woman can feel the symptoms herself. At any stage of pregnancy, when erosion appears, discomfort may appear “inside” during sexual intercourse; sometimes expectant mothers complain of the appearance of scanty pink or bloody discharge. More than half of women do not experience any symptoms.
During pregnancy, erosion is not treated.
Standard methods of dealing with this unpleasant problem - cauterization and laser exposure - are contraindicated for expectant mothers due to the danger of a scar, which can cause a lot of problems and pain during childbirth, and can also create an additional threat of organ rupture. Therefore, treatment is postponed until later.
By the way, for many women, erosion goes away on its own after childbirth. This problem does not have any effect on the fetus and the course of pregnancy.
Dysplasia
Colposcopy can show another problem - cervical dysplasia. This term refers to changes in the epithelium that have precancerous conditions. Most often, the disease is detected in women aged 25 to 33-35 years. If the disease can be identified in the early stages, dysplasia is considered completely reversible, and negative consequences can be avoided.
Externally, during manual examination, dysplasia can be confused with erosion, since the clinical picture is similar, but colposcopy and laboratory tests make it possible to establish the main difference. It lies in the fact that with erosion, damage to the epithelium is of a superficial mechanical nature, and with dysplasia it is cellular, that is, the destruction occurs at a deeper, cellular level.
Most often, the disease is caused by human papillomavirus types 16 and 18. They are actively “helped” by other factors that contribute to the development of the disease - smoking, weak immunity or immunodeficiency, chronic inflammatory processes in the reproductive organs that go untreated for a long time.
During pregnancy, hormonal levels that change due to natural reasons can affect the development of dysplasia. Starting sexual activity too early and giving birth too early are also risk factors.
medical and surgical —as well as constant monitoring of the further condition of the organ can prevent the development of cancer However, during pregnancy, the use of medications, and even more so surgery, is undesirable. Mild dysplasia rarely degenerates into cancer, and therefore requires only observation.
A severe form of the disease may force a woman to choose between keeping the child or having an abortion and agreeing to an emergency operation.
In each specific case, the issue is resolved individually.
Medical statistics are not very optimistic - about 30% of expectant mothers who chose pregnancy, and therefore gynecological surgery was postponed, were subsequently registered at the oncology center due to the development of cervical cancer.
Ectopia
Ectopia also resembles erosion; it is even called pseudo-erosion. With this pathology, part of the columnar epithelium is mixed into the vagina. Upon examination, the doctor sees a red spot that resembles erosive changes.
A woman may complain of copious discharge that is yellow, white, or greenish in color with an unpleasant odor. The causes of this phenomenon can be traumatic, but most often they are infectious in nature and indicate either the presence of infections or that infections have been suffered in the past.
Previous abortions, hormonal imbalances, and sexual activity started too early can increase the likelihood of ectopia. However, in most cases, doctors are quite optimistic, because ectopia also has physiological causes.
The changes that the lower segment of the uterus undergoes during pregnancy lead to changes in the tissues of the organ. After childbirth, ectopia, which is not caused by pathologies, inflammation or infections, usually goes away without a trace.
Diagnostics
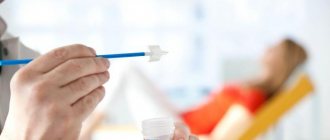
What methods are used to diagnose the condition? At the initial stage, the absence of pregnancy is established using tests and ultrasound. After this, the doctor begins to look for reasons other than pregnancy. To do this, a smear is taken from the vagina and uterine cavity - it is examined for infection in order to confirm or refute the presence of an inflammatory process in the organs. During an ultrasound to refute pregnancy, you can also see the presence or absence of tumors, neoplasms, and pathological tissue growths.
Cyanosis itself is diagnosed through a visual examination by a gynecologist using mirrors.
How is the diagnosis carried out?
It is impossible to accurately determine the cause that provokes cyanosis of the vagina and cervix during a visual examination. Only a doctor can make a correct diagnosis after receiving the results of the following manipulations:
- culture of vaginal contents for infection;
- PCR test;
- Ultrasound of the pelvic organs;
- human papillomavirus test;
- cytological examination of a smear;
- blood test for hCG;
- hormone level test;
- tumor marker test.
If the listed diagnostic methods are not enough to obtain a clear clinical picture, CT and MRI are performed. In cases where cyanosis has a pathological basis, treatment is prescribed depending on the nature of the pathology. If the change is physiological, no treatment is required.
Attention! The gynecologist always asks the woman the date of her last menstruation when visiting. This is necessary in order to determine the current phase of the cycle. The color and consistency of the cervix changes every day and this is absolutely normal.
Treatment
Treatment depends on what process caused the pathology. But in addition to the specific treatment described below, drugs are also used to improve blood circulation.
- In case of inflammatory processes, broad-spectrum antibiotics (Tsiproldet) and anti-inflammatory drugs (Diclofenac) are prescribed for a period of five to fifteen days;
- For benign pathological tissue growths, hormonal drugs (Duphaston, Utrozhestan) are used for two to six months;
- In the presence of cancer, surgery, radio wave and chemotherapy are used in various combinations or separately;
- In case of loss, only surgical intervention can help.
During pregnancy, cyanosis is normal, so it does not need to be treated.
Blue cervix
At an appointment with a gynecologist, a woman may hear that she has a cyanotic cervix; the gynecologist will definitely explain the reasons for this problem after a detailed examination. Of course, the doctor will make assumptions, but especially curious patients will want to independently figure out why the color of their mucous membrane has changed.
Normally, the shade of the cervix is closer to pink, without redness or any significant changes. In this article we will talk about the probable causes of cyanosis - blue discoloration of the mucous membrane.
Causes
During a manual examination, as well as during colposcopy, the gynecologist sees a bluish cervix in front of him. A specialist can immediately explain this by the fact that blood circulation has been disrupted. Most likely, not only in the uterus and its cervix, but also in all organs located in the pelvis.
Why did the blood supply suddenly stop properly nourishing the uterus and adjacent organs? The reasons can be both serious and pleasant.
Let's start with the last ones. We are talking about pregnancy, so there is no pathology in this case - this is a physiological process, a variant of the norm. A blue cervix allows the gynecologist to assume that pregnancy has occurred.
When interviewing the patient, there is no doubt about this if she reports that she is planning a child and is not using protection. And yet, to confirm, the doctor sends the woman for an ultrasound, and also offers to take a pregnancy test if she has not already done one.
The reason for the change in color of the mucous membrane is hormonal changes, namely, this is how an increased level of progesterone manifests itself. This picture will be observed throughout the entire period of gestation, since at the very beginning the hormone is produced by the corpus luteum of the ovary, and already in the second and third trimester - by the placenta. Now we know that during pregnancy, a blue cervix has hormonal causes.
Diseases
Now let's talk about when the cyanosis of the mucous membrane is a consequence of pathological processes.
During inflammation, blood circulation slows down very much, which is why the cervix reacts in this way. It will not be difficult for the gynecologist to make a diagnosis, because in the case of an infection that causes inflammation, the woman also has a set of unpleasant symptoms: pain, discharge, burning, cycle disruption, and the like.
To clarify his assumptions, the doctor will take a smear, which will allow him to determine the causative agent of the pathological condition.
Often the cervix becomes bluish due to the following diseases:
- Cervicitis is an inflammation affecting the cervical canal;
- Endometritis is a pathology that affects the mucous layer of the uterus;
- Adnexitis is an inflammatory process observed in the ovaries and fallopian tubes.
All these diseases can be successfully treated with modern drugs. If the disease is left unattended, then it becomes chronic and more difficult to treat.
In the case of neoplasms, the cervix is often bluish in color; the doctor will tell you in detail what this means, and we will only touch on the iceberg of the problem.
How and why measurement occurs
The parameters of the cervix are measured in two ways - on a gynecological chair using a mirror and colposcope, and using ultrasound diagnostics.
With a manual examination, the doctor can determine the condition of the external pharynx, the density of the cervix and the closure or opening of the cervical canal.
An ultrasound measures the length and also provides a more accurate idea of the condition of the internal os (the junction with the uterine cavity), which cannot be examined by other means.
When registering, the doctor conducts a manual examination, and at the same time, smears of the vaginal flora are taken for analysis. In the first trimester, a woman also undergoes colposcopy; it provides more information than a regular speculum examination.
Measuring the length of the cervix is advisable only after the 20th week of pregnancy, when the baby begins to actively grow and the load and pressure on the cervix increases.
Up to 20 weeks, the length of the cervix varies among different pregnant women, much depends on individual values. However, by week 20, the dimensions of the lower part of the uterus in different women reach common average values, and the length becomes diagnostically important.
In mid-pregnancy, ultrasound is usually done transabdominally , placing the scanner probe on the pregnant woman's abdomen, examining through the anterior abdominal wall. If there is a suspicion of lengthening or shortening of the cervix, as well as other anomalies, the doctor uses an intravaginal ultrasound method, in which a sensor is inserted into the vagina. Through the thinner vaginal wall, the cervix is clearly visible.
Control over the size and other parameters of the cervix is necessary to make sure that the child is not in danger of being born prematurely, that there is no threat of intrauterine infection, which also becomes possible if the cervical canal opens slightly or opens completely
During the entire period of bearing a baby, a healthy woman undergoes cervical examinations four times. If there is cause for concern, then diagnostics will be prescribed more often, as many times as necessary.
Diagnostics
If a woman comes to see a gynecologist, and during the examination the doctor discovers that she has a cyanotic cervix, they will discuss the reasons together. First, the doctor will rule out or confirm pregnancy. For this, as we have already said, an ultrasound and a pregnancy test will be prescribed. To confirm the result, it is better to conduct 2-3 tests. If they all show two stripes, then the woman is definitely pregnant. If the results are negative, the doctor will begin to look further.
It is necessary to exclude the inflammatory process. To do this, the doctor will take swabs to see if there is an infection in the vagina or cervix. An ultrasound examination is also performed to ensure that there are no tumors. When the doctor has determined why your cervix is bluish, he proceeds to therapy, if necessary.
Cervix during pregnancy: length norms by week in the table and reasons for deviations
- What it is
- How and why measurement occurs
- Changes during pregnancy
- In the early stages
- In the later stages
- Pregnancy in the cervix
Examination of the cervix is an important diagnostic tool for an obstetrician-gynecologist. The condition of this part of the main reproductive female organ can indicate the well-being or disadvantage of the developing pregnancy, the timing of gestation, and allows one to make predictions regarding the upcoming birth. We will talk about what the cervix should be like during pregnancy and why deviations may occur in this material.
Treatment
Each disease has its own treatment regimen. In many cases, medications that affect circulation may be prescribed. If the tests reveal inflammation, then the gynecologist will prescribe an antibiotic and medications that relieve inflammation.
If we are talking about endometriosis, then hormonal medications may be prescribed. The duration of their use is up to six months. In case of cancer, the doctor assesses the situation and decides what to do with the tumor - remove it or carry out chemotherapy first. It all depends on the specific case. Unfortunately, the treatment will be long and difficult.
When the uterus prolapses, only surgery is indicated. In old age, when the situation is advanced, it is completely removed. Young women may be offered a so-called suturing, in which the uterus is surgically returned to its place.
Consequences
A blue cervix is only a visual symptom that does not cause the woman any discomfort. It is important to find the cause and eliminate it, otherwise not only health, but also life may be at risk. Inflammation is fraught with further development of infection, which can cause peritonitis or abscess.
Cancerous tumors tend to metastasize and then it is quite difficult to fight them. If benign tumors are not controlled, they can degenerate or grow excessively, disrupting the functioning of surrounding organs.
With uterine prolapse, there is a high probability of infection. Over time, urinary or fecal incontinence may develop, since all the pelvic organs are closely interconnected. At the initial stage, you can avoid surgical treatment by regularly performing a set of exercises that your doctor will tell you about.
Prevention
To prevent pathological blueness of the cervix, it is necessary:
- Be sure to visit a gynecologist every six months for a preventive examination;
- In the morning and evening, especially during menstruation, observe the rules of personal hygiene;
- When having sexual intercourse, use a condom if you do not know your partner well;
- Regularly monitor your hormone levels if you have ever experienced a hormonal imbalance.
Do as much exercise as you can and keep your muscles toned, avoid casual sex, eat well and support your immune system with healthy sleep and vitamin supplements. Forget about alcohol and cigarettes. And then you may never hear the doctor’s verdict - a cyanotic cervix. Only if you are planning a pregnancy will this symptom become a joyful sign of a long-awaited event for you!
Disease Prevention
The following rules will help prevent the development and spread of infectious processes:
- Regular preventive examinations with a gynecologist.
- Timely treatment of various inflammatory processes localized in the pelvic organs.
- An unscheduled visit to the doctor if changes in well-being are detected.
- Related examination and treatment of the sexual partner.
- Using condoms to protect against unwanted pregnancy, avoiding taking COCs and IUDs.
- Elimination of physical inactivity.
- Compliance with the rules of a healthy diet, additional intake of vitamin and mineral complexes in the autumn-spring period.
Most often, the cervix becomes blue during pregnancy, so the discovery of such a change during a gynecological examination is not a cause for concern, but this does not always happen. In some cases, cyanosis of the vagina and cervix signals the development of dangerous changes in the girl’s body and indicates pathological progress. The diagnostic process should begin immediately after identifying the problem.
This article is posted for educational purposes only and does not constitute scientific material or professional medical advice. Always trust your doctor first!
Causes of a cyanotic cervix
A bluish or cyanotic cervix in gynecology is considered a likely symptom of pregnancy. The reasons for the change in color of the mucous membrane of the cervix are changes in the nature of blood circulation in the pelvic cavity.
The cervix is the part of the uterus visible to the obstetrician, located in the vagina at a depth of 6-8 cm. The main task of the organ is protective. The glands of the canal epithelium produce mucus, which forms a plug that protects the uterine cavity from infection. During pregnancy, the muscular frame of the reproductive organ ensures retention of the fetus throughout the entire gestation period.
Reasons for deviation from the norm
The following factors can provoke an abnormal condition:
- suffered stress;
- tissue dysplasia;
- abortions/miscarriages;
- difficult childbirth;
- large fruit;
- polyhydramnios;
- conception that occurred immediately after childbirth;
- injury;
- hormonal imbalances;
- surgical or medical procedures.
Pregnancy in the cervix
If the fertilized egg attaches in this place, then its development will not occur. The embryo will remain viable for a maximum of 5 weeks, after which it will be rejected. With this pathology, women experience severe bleeding, which can be stopped with the intervention of doctors.
Attention! The cause of pregnancy in the cervix is most often an early abortion or surgical manipulation in the uterine cavity. The abnormality is diagnosed during an ultrasound, after which the patient is referred to a gynecologist or surgeon.
Short neck
With a shortened cervix, women undergo special manipulations, during which sutures are placed (up to 28 weeks). Refusal to timely cerclage will lead to the following consequences:
- spontaneous abortion;
- infection of the fetus (intrauterine);
- gap;
- rapid birth.
Long neck
The disease can be congenital, caused by an abortion, surgery, or gynecological diseases. A long cervix opens slowly and poorly during childbirth, which increases the risk of fetal hypoxia.
Erosion
In almost 70% of examined patients, erosion is detected. The reasons lie in trauma to the mucous membranes, hormonal imbalance, sexually transmitted diseases, etc. During pregnancy, the pathology is not treated, as it often goes away on its own after delivery.
Dysplasia
With this form of the disease, epithelial changes occur. In the absence of timely treatment, an oncological process may develop. The reason lies in low immunity, bad habits, chronic inflammation, and the HPV virus.
Attention! Most often, the disease is detected in women under 35 years of age. The pathology has a negative impact on the pregnancy process and often provokes premature birth.
Possible causes of a bluish tint
The shape of the cervical region is like a cylinder with a narrow lumen - the cervical canal. It contains a special mucus that protects the gynecological tract from the spread of germs, such as sexually transmitted diseases. But the integrity of the barrier can be compromised with concomitant gynecological diseases, both infectious and hormonal. A number of infectious and inflammatory diseases may be asymptomatic, but the color of the mucous membrane will be changed due to venous congestion.
A regular annual examination by a gynecologist will allow timely diagnosis of changes in color, consistency, and discharge in the presence of inflammation.
The cervix may be bluish for several reasons:
- pregnancy;
- infectious-inflammatory process;
- uterine prolapse and elongation;
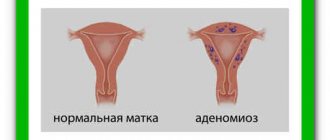
- endometrosis;
- tumors.
The cervix reflects the state of a woman's reproductive system.
Pregnancy
One of the likely signs of fertilization and normal development of the embryo is a change in the pink color of the mucous membrane to bluish. As a rule, the cervix acquires this shade at 6-8 obstetric weeks of pregnancy.
The reason for this phenomenon is a change in blood supply under the influence of the hormone progesterone, which is otherwise called the pregnancy hormone. In addition to cyanosis, the doctor diagnoses an increase in the size of the uterine body, its softening and increased mobility.
Infectious and inflammatory processes
The causes of a cyanotic cervix may lie in an active infectious process occurring in the tissues of the cervical canal, the integumentary epithelium of the cervix, and the uterine cavity. Infections such as chlamydia, urea and mycoplasmosis, herpes simplex viruses, diseases caused by opportunistic flora can cause venous congestion of the lower gynecological tract.
The reason for the change in the color of the cervix from pink to bluish are pronounced infectious processes - endometritis, cervicitis, as well as inflammation of all parts - the ovaries, tubes and uterine cavity.
The vaginal mucosa also becomes bluish.
Factors contributing to the development of inflammatory processes:
- decreased resistance;
- genetic predisposition;
- moderate to severe anemia;
- chronic diseases of the genitourinary system;
- sedentary lifestyle, unhealthy diet;
- hormonal therapy with corticosteroids and oral contraceptives;
- intrauterine contraception.
Warning signs regarding hidden diseases of the genital organs are infertility, menstrual irregularities, periodic aching pain, spotting and acyclic bleeding, and pathological discharge.
Tumors and uterine prolapse
Changes in hormonal levels in a woman’s body can cause the growth of fibroids, which are localized both in the body of the uterus and in the cervical region. The growth of a benign tumor leads to impaired blood circulation in the cervix. Obstruction of the outflow of venous blood leads to a change in the color of the mucous membrane from pink to bluish.
The reasons for the bluish tint of the cervical region with growing fibroids are excessive production of estrogen or disruption of the perception of this hormone by the uterine receptors.
Conditions such as elongation (lengthening and drooping) of the cervix and its prolapse cause the bluish color of the mucous membrane. Signs of the disease include the sensation of a foreign body in the vagina, pain during sexual intercourse, and discomfort.
A malignant tumor completely changes the anatomy of the organ, causing a change in color.
In addition to tumors, the cervical region can acquire a blue color due to endometriosis. The cause of the bluish tint in this case is endometriotic lesions.
Changes during pregnancy
In a non-pregnant woman, the length of the cervix is approximately 3-4 cm with a width of 2.5 centimeters. These values are not absolute and there may be some individual variations.
If a woman is not pregnant, but is just planning to conceive a baby, her cervix is pink, smooth, and when examined with a mirror, it looks somewhat shiny.
In the early stages
When pregnancy occurs, the cervix undergoes great internal and external changes. Due to the increased blood supply, the delicate pink color is replaced by purple, bluish, and cyanotic.
The process of “maturation” begins, which will last all nine months, because the small neck will have to thicken, grow, become thicker and more elastic in order to ensure the baby’s passage through the birth process.
In the first trimester, based on the condition of the cervix, doctors can judge the possibility of spontaneous termination of pregnancy or miscarriage . If the cervix is loose and the gynecologist’s finger misses during examination, then such unfavorable events are very likely.
Normally, in the early stages, the cervix should deviate slightly towards the anus and be tightly closed.
A loosely closed cervical canal creates not only the threat of miscarriage, but also the threat of penetration of pathogenic microbes, fungi, and viruses into the uterine cavity, which can damage the membranes and lead to fetal death.
Sometimes intrauterine infection results in anomalies and malformations of the baby, congenital diseases.
The first changes in the cervix begin around the 4th week of pregnancy , when the growing fertilized egg begins to slightly protrude the wall of the uterus to which it is attached. This creates a slight asymmetry.
The cervix changes its position in space; if during ovulation it rose higher in order to increase the chances of sperm penetration, now the main task is not to miss the fertilized egg; for this, the lower segment of the uterus has to descend and lean back.
Many women who want to quickly find out whether pregnancy has occurred are interested in what the cervix should feel like to the touch, because it is no secret that many planning a pregnancy carry out palpation at home on their own. Approximately 8-10 days after conception, under the influence of the hormone progesterone, the cervix becomes softer. The cervical canal, on the contrary, closes more tightly.
A rigid cervix in the early stages may indicate a threat associated with increased tone of the uterus itself. This can happen, for example, with autoimmune diseases or with a lack of progesterone.
In the later stages
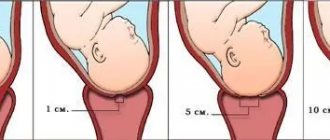
In the third trimester, doctors judge the timing of the impending birth based on the condition of the cervix. This part of the uterus becomes softer. The length of the cervix gradually decreases by about half; on an ultrasound, you can see how the internal os expands, preparing for the upcoming birth.
This process is slow, gradual, taking several months. Changes occur under the influence of hormones - estrogens.
At 38-39 weeks, the doctor can begin to check the readiness of the cervix for childbirth . Such readiness can be judged by the ability of the cervical canal to pass the examining doctor’s finger through it.
Carrying out such palpation on your own is strictly prohibited, and technically, fortunately, this is quite difficult to do.
Sometimes a week or a few days before giving birth, a woman may notice the release of a mucous plug, the same one that served as an obstacle to pathogenic microbes throughout pregnancy. The cervix gradually smoothes out and begins to expand. For some women, such cervical preparation “starts” only at 40 weeks, and for some – even later.
If a woman gives birth to her first child, then it is possible that the cervix may begin to change in advance, and it will do this rather slowly. In multiparous women, preparation begins later and proceeds faster. Their neck “remembers” how to behave in the current circumstances.
If the cervix is not in a hurry, doctors may prescribe preparatory treatment that will help the cervix “ripen” faster. The appropriateness of such stimulation by modern gynecologists is considered controversial.
Some doctors are sure that there is a need for stimulation, others believe that you should wait and trust nature, which knows better than any doctor when it is time for a child to be born.