IN THIS ARTICLE:
- Group B Streptococcus - what is it?
- Why is group B streptococcus tested in pregnant women?
- Risks for a newborn with streptococcus in pregnant women in a smear
- Why is a smear for GBS taken at the end of pregnancy, but treated at birth?
- Action plan for urinary tract infections caused by GBS
- How are group B streptococci detected in a smear?
- Action plan after receiving a positive result for GBS during pregnancy
- If labor begins before the smear culture results arrive
- Risks of taking antibiotics during childbirth
- How does group B streptococcal infection manifest in newborns?
- Post-birth plan
- Can a baby catch streptococcus B bacteria after birth?
- How to prevent late-onset GBS infections?
Group B streptococcus is a type of bacteria that inhabits the digestive system of some people. In some women, they can also be detected in a vaginal smear without causing any harm to health.
However, if group B streptococci become part of the vaginal microflora during pregnancy, they can cause serious infections in the newborn baby. Read more about these bacteria, their dangers and treatment in our material.
Group B Streptococcus - what is it?
Group B Streptococcus (GBS) is a type of bacteria that lives in the intestines of many people. They can be present in the vagina and transmitted to the baby during vaginal birth. Statistics say that 10-30% of all women have group B streptococci in a smear taken from the vagina, anus or surrounding areas of the body. Keep in mind that this bacterium is different from group A streptococci - provocateurs of sore throat.
GBS can be transmitted to partners during unprotected sex, but it is not included in the list of sexually transmitted infections. It is normal if the genitals become a habitat for intestinal microflora.
What is streptococcus
Streptococci are opportunistic microorganisms that can be present in minimal quantities in healthy human microflora. The streptococcal pathogen is found in the vaginal microflora in 20% of women.
With strong immunity, bacteria are not active and do not cause dangerous diseases. But as soon as the body’s defenses weaken, as happens during pregnancy, the bacteria become active and become pathogenic.
In medicine and microbiology, streptococci are divided into 3 groups:
- Alpha-hemolytic bacteria are opportunistic bacteria that partially destroy red blood cells in their active form.
- Beta-hemolytic are the most dangerous microorganisms, leading to complete hemolysis.
- Gamma-hemolytic - not dangerous to the human body, do not cause diseases.
When the immune system is weakened, streptococcus becomes more active and becomes pathogenic.
One of the most dangerous is the gram-positive pathogen Streptococcus agalactia (GBS), belonging to group B. An opportunistic bacterium can live on the mucous membrane of the digestive system, in the rectum and vagina. Like all streptococci, Agalactia has a spherical shape, does not form spores and occurs in pairs.
People with weakened immune systems, chronic diseases, newborns, children with dystrophy, the elderly and pregnant women are most susceptible to infection.
Why is group B streptococcus tested in pregnant women?
For you, this bacterium is practically harmless, but it can cause many problems for your baby - from severe infections to stillbirth. If the test for streptococci is positive in the later stages, you will be treated with antibiotics during childbirth. This will significantly reduce the risk of infection of the baby.
The American Academy of Pediatrics, the Centers for Disease Control in the United States, and the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists strongly recommend that expectant mothers get a strep smear. The optimal period for screening is 36-37 weeks.
If there is a high risk of developing group B streptococcus, treatment is carried out during childbirth. It is mandatory in the following cases:
- the result of a smear test for group B streptococci during pregnancy was positive;
- you have urinary tract infections caused by group B streptococci, or bacteria were found in urine culture at any stage of pregnancy;
- the previous child was born with complications caused by GBS.
The introduction of mandatory testing for potential infection has reduced the number of diseases among newborns. If previously every 500th baby suffered from the consequences of GBS, now streptococci affect only 1 child out of 4 thousand.
Treatment of the disease
If streptococcus is detected in the urine during pregnancy, then treatment should be started immediately. It consists of several stages:
- Antibacterial therapy.
- Strengthening the immune system.
- Bringing intestinal microflora back to normal after antibiotic treatment.
- Detoxification of the body.
- Symptomatic therapy.
To restore intestinal microflora, the following are additionally prescribed:
During the treatment period, excessive physical activity should not be allowed. In case of high intoxication, bed rest is required.
Treatment using folk remedies is possible, but only with the permission of a specialist.
If a staphylococcal infection is not treated, a pregnant woman may experience rupture of the membranes, premature birth, or intrauterine fetal death. Prevention of streptococcus is very simple: maintaining personal hygiene, preventing colds, strengthening the immune system. With timely treatment, you can get a normal outcome and avoid unwanted complications.
Infectious diseases of the urinary system are diagnosed in expectant mothers using urine culture. Quite often, during bacteriological examination, streptococcus is detected in the urine during pregnancy, which is activated due to hormonal changes and decreased immunity.
The danger of infection is that in most cases it is asymptomatic and can cause pathologies of the placenta and infection of the baby.
Risks for a newborn with streptococcus in pregnant women in a smear
If a baby catches the bacteria immediately at birth, the consequences can be extremely dangerous:
- blood poisoning - sepsis;
- bacterial pneumonia - pneumonia;
- meningitis (observed less frequently).
Once the underlying condition is treated, some children are at risk for long-term health problems. Meningitis can cause hearing or vision loss, cerebral palsy, or developmental disabilities. A small percentage of newborns are susceptible to mortality.
If group B streptococci were not detected in pregnant women and were transmitted to a baby born prematurely, he will be more susceptible to death. And if he survives, he will be at higher risk of long-term health problems due to the disease.
Why is streptococcus in urine dangerous during pregnancy?
If streptococcus agalactia is detected in the urine during the gestational period, the woman needs urgent treatment. In the absence of timely treatment, the bacterium increases the risk of pathological conditions of the mother and fetus:
- premature rupture of membranes, chorioamnionitis;
- diseases of sepsis, meningitis, pneumonia in a newborn;
- premature birth;
- intrauterine fetal death;
- the appearance of a child with cerebral palsy (CP);
- problems with learning, hearing and other pathologies in the child.
Why is a smear for GBS taken at the end of pregnancy, but treated at birth?
Streptococcus can colonize the vaginal microflora and leave it throughout pregnancy without any treatment. Therefore, a test in the first trimester cannot predict whether bacteria will be present in a smear at 36 weeks. In the early stages, the result may be negative, but positive in the later stages. Or vice versa.
Detection of group B streptococci during pregnancy allows us to make a prognosis for only 5 weeks. Therefore, if the bacterium is detected at 36-37 weeks, the woman remains infected at the time of birth.
If streptococci are detected in a smear early on, treatment will not give the desired result during pregnancy. Having eliminated the problem in the first trimester, the doctor will not be able to prevent re-colonization of the vagina with bacteria in the third and reduce the risk of infection of the newborn. For this reason, treatment is carried out during childbirth.
Streptococcus agalactia in a smear - what does this mean?
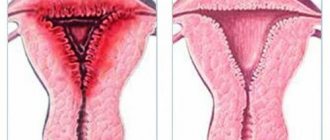
The vaginal microflora is represented by a variety of microorganisms. Depending on their relationship, the concepts of normality and pathology are distinguished. The basis of normal flora is made up of rods - lactobacilli. They are supplemented by opportunistic microorganisms, represented by streptococci, staphylococci, gardnerella, candida, urea and mycoplasma.
As long as the number of these microorganisms is insignificant, there is no large number of leukocytes, the condition of the vagina is considered satisfactory. If one of them predominates in a smear from the cervical canal, for example, streptococcus agalactia, then nonspecific inflammation is diagnosed.
A little about the pathogen
Streptococci are a large group of microorganisms that are similar in morphological characteristics. Depending on the nature of growth on nutrient media, serogroups are divided into hemolytic, greening and non-hemolytic. Groups B, D and green are present in the vagina. Normal values should not exceed 10 to 4 degrees CFU/ml.
Agalactia belongs to beta-hemolytic streptococci of group B. This means that when sown on a nutrient medium based on agar and blood, as the colony grows, a zone of complete hemolysis of red blood cells forms around it. In this case, the nutrient mixture becomes discolored.
The activity of the microorganism is accompanied by the release of various toxic substances:
- streptolysin destroys surrounding tissue;
- leukocidin destroys immune cells, allowing microbes to escape;
- necrotoxin and lethal toxin cause tissue necrosis;
- a set of enzymes that help streptococcus penetrate into surrounding tissues: hyaluronidase, proteinase, amylase, steptokinase.
The colonization of streptococci occurs with puberty and the onset of sexual activity. Possible household transmission through the use of common hygiene items.
Women can self-infect themselves if they move from back to front when washing their genitals. Microbes from the anal folds enter the vagina.
A pregnant woman can infect her baby during childbirth.
Men can become infected from women during oral or anal sex, through the intestinal walls during dysbacteriosis, or descending from the kidneys or nasopharynx.
What are the signs of infection?
Until the amount of the pathogen is at a minimum level, there are enough lactobacilli in the vagina that suppress the growth of opportunistic flora. In men, streptococcus agalactia appears after unprotected sexual intercourse. In the future, they become carriers of the infection and are able to transmit the pathogen to other partners.
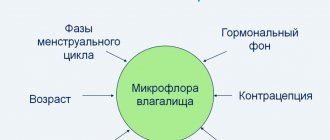
Activation of streptococcus occurs when the balance of normal microflora is disturbed. The following reasons lead to this:
- changes in hormonal levels;
- decreased immunity;
- violation of hygiene procedures;
- use of douching for personal hygiene;
- diabetes mellitus and severe pathologies.
During pregnancy, the first two factors are especially relevant. Progesterone, which gradually increases, inhibits local immunity. This process is aimed at preserving pregnancy, but it has negative consequences: latent infections of the genitourinary organs often worsen in pregnant women, and vaginitis and colpitis develop.
There are no symptoms of agalactia. These pathogens do not cause an inflammatory reaction in the vagina. Detection of a high concentration of the pathogen occurs accidentally during a routine examination. In pregnant women, signs of infection activation appear in the form of urethritis or cystitis.
Initially, the pathogen appears in the urethra, and then rises higher. Characteristic symptoms of cystitis are pain and burning when urinating, followed by a feeling of incomplete emptying of the bladder, frequent urges that are not accompanied by the release of a large amount of urine.
Acute cystitis is accompanied by a deterioration in general condition, weakness, and headache. Temperature increases are rare.
What is the danger of infection?
Streptococcus agalactia is detected in 20% of women during pregnancy. Lack of timely treatment can lead to the development of the following complications:
- urinary tract infection;
- spontaneous abortion;
- postpartum endometritis;
- chorioamnionitis;
- sepsis of the neonatal period;
- pneumonia of the newborn;
- endocarditis;
- meningitis.
For a woman, in most cases, the infection will be hidden; in a newborn, it often causes complications.
In what cases is examination necessary?
There are certain risk groups for developing streptococcal infections:
- premature birth;
- long water-free period of more than 18 hours;
- rise in body temperature in a woman during childbirth;
- bacteria in urine;
- birth of a premature baby;
- low birth weight of the newborn;
- birth by caesarean section.
If a woman has had a child with streptococcus agalacia in previous pregnancies, then examination in the second birth is mandatory.
Laboratory diagnostic methods
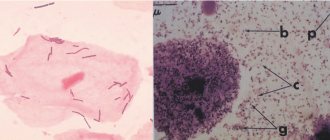
Routinely, pregnant women undergo smears from the cervical canal. This research method allows you to determine the degree of vaginal cleanliness and establish the first deviations from the norm. If coccal flora predominates in the smear, a culture test is necessary, which is the main method for diagnosing the infection.
For sowing, liquid or solid nutrient media are used. In some laboratories they add substances that inhibit the growth of other microorganisms. This increases the excretion of streptococcus by 50%.
For sowing, material is taken from the vagina and anorectal area. It is recommended to take discharge from several areas of the mucous membrane at the same time. This also increases the likelihood of identifying the pathogen. Detection of 10 to 3 CFU/ml is a normal variant.
Since the role of streptococcus agalactia in infection of a newborn is very large, a system of screening tests has been developed to detect agalactia.
To do this, they use the determination of microorganism antigens in latex agglutination, ELISA, and coagglutination. These methods are fast but have some disadvantages.
If the examination is carried out during labor, vaginal discharge may be mixed with amniotic fluid and blood. This reduces the sensitivity of the tests.
PCR diagnostics is also used. With its help, you can isolate Streptococcus agalactia in urine discharged from the vagina and from the skin of a newborn. During the study, the DNA of the pathogen is determined. Recent developments in this area make it possible to study virulence genes. Identification of such a genetic composition indicates a high probability of infection of a newborn with a severe form of the disease.
For pregnant women, the study is carried out at 35-37 weeks. The PCR method allows you to identify qualitatively and quantitatively streptococcus in the material under study. Identifying the number of microorganisms allows us to judge the contamination of the area under study. The disadvantage of this method is that it is impossible to identify living representatives of the genus and determine their resistance to antibiotics.
Related article: Gynecological smear for flora
Treatment and its basic techniques
How to treat streptococcus agalactia depends on the woman’s condition. If she does not plan to have children and there are no symptoms of the disease, then a small local treatment is sufficient.
For those planning to conceive, treatment is given only after symptoms appear.
For a pregnant woman, if streptococcus is detected long before childbirth, but there are no obvious symptoms, she needs to monitor her condition and re-test at 35 weeks.
The infection can also be isolated from a nursing mother. In this case, local treatment is prescribed until the symptoms disappear completely. Antibiotic therapy for oral administration is not carried out, because they are able to pass into breast milk.
Treatment of streptococcus agalactia in gynecology is carried out using penicillin antibiotics. There is a need for therapy when 10 to 5 degree CFU/ml is detected.
The growth and reproduction of bacteria is suppressed by the following drugs:
- penicillins;
- cephalosporins;
- macrolides.
This is the most effective treatment. The drugs are used for oral administration.
Pregnant women, even with a titer of 10 to 6 degrees in the early stages of up to 12 weeks, are not prescribed treatment. This is due to the peculiarities of the formation of the placenta. After 12 weeks, therapy can be carried out using oral medications.
In case of urethral infection and diagnosed cystitis, it is important to choose the right treatment for a pregnant woman - antibiotics of some groups are prohibited for use due to the high risk of perinatal death.
Local therapy
For local treatment, vaginal tablets and suppositories are used. Pregnant women need vaginal debridement before childbirth to reduce the risk of infection in the newborn. If sanitation was not carried out, but streptococcus 10 to 8 degrees was detected, then antibacterial therapy is necessary during childbirth.
Fluomizin vaginal tablets are used for local use. They are effective against bacterial vaginosis. It can also be used to sanitize the vagina before childbirth and gynecological operations.
Microorganisms practically do not develop resistance to the drug. The use of the drug is contraindicated in people under the age of 18, in case of an allergic reaction to one of its components, or ulcerative changes in the vaginal mucosa.
The tablet is inserted deep into the vagina in the evening before bed. The course of treatment is 6 days. When using the medicine for less than this period, resistance develops; next time the same components will be ineffective.
Terzhinan is a yellowish tablet. It contains several active ingredients that help fight bacterial and fungal infections. It also contains prednisolone, which has an anti-inflammatory effect and reduces swelling.
Terzhinan can be used in pregnant women from the second trimester, during breastfeeding with great caution. Duration of therapy is 10 days. Before use, the tablet should be moistened with water and placed in a lying position deep into the vagina. If treatment is not carried out on a pregnant woman, then there is no need to interrupt therapy during menstruation.
Not all newborns are infected with Streptococcus agalagkia. In many cases, sanitizing the birth canal or prescribing an oral antibiotic helps reduce the infectious load and the likelihood of infection of the child to 1-2%.
Source: https://ginekolog-i-ya.ru/streptokokk-agalaktiya.html
Action plan for urinary tract infections caused by GBS
Are you experiencing symptoms of urinary tract inflammation? Contact your gynecologist as quickly as possible and take a urine test to identify the pathogen. If it turns out to be group B streptococcus in quantities above 100 thousand CFU, the doctor will prescribe oral antibiotics. An antibiotic is needed for two purposes:
- reducing the risk of premature birth, which increases with bacterial levels above 100 thousand CFU;
- treating symptoms of urinary tract infections.
Be sure to complete the full course of antibiotics, carefully adhering to the treatment regimen. After completing the course, take a repeat urine test to make sure that the treatment helped completely eliminate urinary tract infections. But keep in mind that if the antibiotic managed to destroy the bacteria that have settled in the genitourinary system, they can maintain the population on the skin of the genital organs and later attack the genitourinary system again.
If you were treated for streptococci in gynecology or urology during pregnancy, the doctor may not conduct screening at 36-37 weeks. He will automatically give you an intravenous antibiotic during labor for the welfare of your newborn.
Urine examination for streptococci
One of the most informative tests for infections of internal organs is bacteriological urine culture. This study is carried out during pregnancy registration and in the third trimester.
Using the results of the analysis, it is possible to determine the presence of an infection that can be transmitted in utero or infect the child at birth. In order for the result to be as accurate as possible, the following rules must be followed:
- Stop taking diuretics and choleretic drugs 3 days before the test.
- Eliminate heavy, salty and smoked foods from the menu one day before.
- Collect only the midstream portion of morning urine in a sterile container.
- Before collecting the analysis, it is necessary to perform genital hygiene and insert a cotton swab into the vagina.
- The test must be taken within two hours after collection.
Streptococcus agalactia in urine during pregnancy is determined by inoculating the material on a nutrient medium - a solution of 5% blood agar. In order for the bacterium to grow, it is provided with an optimal temperature for development of 37 degrees.
If streptococci are present, they form colonies of grayish plaques that are examined under a microscope. Next, the bacteria are sent to test tubes to determine their characteristics and sensitivity to antibiotics.
On average, a urine test for streptococci takes 7 days to prepare. The advantage of the study is high accuracy, exclusion of erroneous results and false reactions.
How are group B streptococci detected in a smear?
During a routine examination, your gynecologist will take a sample of the discharge from the lower part of the vagina and anus, and then send a smear to the laboratory. Taking a smear is an absolutely painless and safe procedure. In the laboratory, a bacteriological culture of the obtained material is done to find out whether group B streptococci are present in the microflora. The speed of obtaining results depends on the laboratory that carries out the analysis. Usually it takes 2-3 days.
Some hospitals have rapid tests for streptococci that provide results within an hour and can be used directly during labor. However, they are less sensitive in detecting group B streptococci during pregnancy than laboratory tests, so reputable medical organizations recommend taking a smear at 36-37 weeks.
Action plan after receiving a positive result for GBS during pregnancy
A positive test is not a death sentence. Bacteria on a smear does NOT mean you or your baby will get seriously ill, even if you don't get treatment. Streptococci in gynecology carry a low risk of infection for children, especially in cases where they are born full-term and the mother does not have a fever or her waters have not broken long before birth. Try not to worry.
However, the use of antibiotics allows you to minimize all risks. Statistics say the following: if streptococci are found in your smear and you do not receive treatment, the baby’s chance of becoming infected will be 1:200. Thanks to treatment, the chance of catching the infection will be 1:4000.
However, timely treatment will reduce not only the child’s chances of becoming infected, but also yours. If you are given an antibiotic, your chances of developing a GBS infection (such as a uterine infection) during labor or after childbirth are reduced.
During childbirth, antibiotics are administered intravenously. Often the injection is given several hours before the baby is actually born - when the water breaks or at the beginning of the active phase of labor. Caesarean section is no exception - the doctor administers a dose of the drug to prevent infection.
The ideal situation is when a woman in labor with streptococci during pregnancy receives treatment 4 hours before the birth of the child. If labor proceeds rapidly, antibiotics will bring the desired effect even in a couple of hours.
Video
hemolytic steptacocci
Attention! The information presented in the article is for informational purposes only. The materials in the article do not encourage self-treatment. Only a qualified doctor can make a diagnosis and give recommendations for treatment based on the individual characteristics of a particular patient. Found an error in the text? Select it, press Ctrl + Enter and we will fix everything! Did you like the article? Tell your friends: Advertising on the site
Article updated: 05/13/2019
Comments for the site Cackl e
Infectious diseases of the urinary system are diagnosed in expectant mothers using urine culture. Quite often, during bacteriological examination, streptococcus is detected in the urine during pregnancy, which is activated due to hormonal changes and decreased immunity.
The danger of infection is that in most cases it is asymptomatic and can cause pathologies of the placenta and infection of the baby.
If labor begins before the smear culture results arrive
If group B streptococci in pregnant women have not been laboratory confirmed, treatment will be carried out under the following circumstances:
- labor begins prematurely or water breaks before 37 weeks;
- a lot of time passed between the moment when the waters broke and the beginning of the active phase of labor - more than 18 hours;
- During childbirth, the woman’s temperature increased – 37.7°C or more.
If you are not at risk, your midwife can do a rapid test. A positive result will be a reason to use antibiotics. If there are risk factors and the test is negative, treatment will still be given because the test may be wrong.
Another reason for using antibiotics is the experience of group B streptococcal infection during a previous pregnancy. In such a situation, the doctor may prescribe treatment even if the above risk factors are absent.
Causes of appearance and possible complications
The disease appears due to weakened immunity, infection occurs through airborne droplets. In addition, the routes of transmission of streptococcal infection can be as follows:
- During dental procedures.
- Due to bronchitis, which is chronic.
- Through the placenta.
Such bacteria enter the urine through the urethra, passing from the skin. It is not uncommon for the pathogen to enter the urethra through the anus from the colon. This route of transmission is typical for women due to the structure of their genital organs. If left untreated, streptococcus can cause serious complications.
The most common of these is urethritis, which appears only if the patient's bladder is in a weakened state. Signs of this disease are burning and severe itching in the urinary canal. As well as discharge and pain when urinating.
In addition, prostatitis, cystitis, vesiculitis, balanitis may appear, or the microflora in the vagina may be disrupted. They can occur after a prolonged sore throat, which was provoked by the appearance of streptococcal pathogens in the respiratory tract. Also, bacteria can enter the kidneys from the urinary system and cause glomerulonephritis.
Risks of taking antibiotics during childbirth
To protect the baby, you will be prescribed penicillin. The exception is if you have previously had an allergic reaction to this drug. An allergy in the form of a mild rash develops in approximately 10% of pregnant women who took penicillin. In only 1 out of 10 thousand cases, an antibiotic can provoke a severe allergic reaction requiring emergency treatment.
If you are allergic to penicillin, treatment of streptococci in gynecology is carried out with other antibiotics. They are also effective against group B streptococci and are completely harmless to newborns. Talk to your doctor about which option is best for you.
Symptoms of an increased concentration of streptococcus in the urine
The presence of increased levels of bacteria in the urine causes negative manifestations in organs and systems. When infected with streptococcus, the following symptoms are characteristic:
- frequent urge to urinate;
- increase or decrease in body temperature;
- enlarged lymph nodes in the groin area;
- rash in the form of spots on the skin;
- painful sensations, burning sensation when urinating;
- acute pain in the lower abdomen;
- discharge of cloudy urine;
- redness at the affected areas;
- pain in the throat, pharynx;
- the formation of a whitish coating in the form of flakes on the mucous membranes of the cheeks, pharynx, and tongue;
- nausea, vomiting;
- increase or decrease in blood pressure;
- aching pain in the lumbar region.
Patients develop an allergic reaction to the waste products of the pathogen. It manifests itself as a spotty rash that is covered with yellow crusts and contains pus. Infection with streptococcus often provokes autoimmune processes that cause destruction of joints, heart, and kidneys. Impaired functioning of the filtering organ leads to an increase in the level of creatinine in the patient’s blood.
In the absence of timely treatment, infection with streptococci can develop endometritis, urethritis, vaginal candidiasis, chronic inflammation of the bladder and prostate gland. Purulent discharge appears from the urethra, patients experience severe pain in the lower abdomen, lumbar region, itching, and swelling. The autoimmune disease glomerulonephritis is a late complication of infection caused by streptococcus. In the kidneys, healthy connective tissue is replaced, and the functioning of the organ is disrupted.
Children may experience symptoms of early and late infection. In the first case, the onset of the disease occurs in the first week of the baby’s life and can lead to pneumonia, sepsis, and meningitis. The disease is accompanied by increased drowsiness, fever, and problems with the respiratory system. Late infection occurs from 7 days to 3 months after the birth of a child and provokes sepsis and meningitis. The disease occurs with high body temperature, cough, nasal congestion, drowsiness, convulsions, and problems with eating.
How does group B streptococcal infection manifest in newborns?
If you are a carrier of group B streptococcus during pregnancy, it will be closely monitored by doctors after the baby is born, regardless of whether you received treatment or not.
According to research, in 90% of infected newborns who develop the disease in the earliest stages, symptoms can be replaced in the first day, these include:
- apoplectic seizures;
- inability to wake up;
- unusual lethargy;
- unusual and causeless moodiness;
- increased body temperature;
- blue skin;
- almost complete immobility;
- vomit;
- difficulty breathing;
- difficulties with feeding.
If you notice at least one of the listed symptoms while you are in the maternity hospital with your child, immediately inform the doctors.
Difficulty breathing
If you are at home and your baby has difficulty breathing or turns blue, call emergency medical services. If you have other symptoms, contact your doctor promptly.
How to treat agalactia before conception and during pregnancy
The vaginal microflora includes a variety of microorganisms, including pathological ones. They do not affect the condition of a healthy woman, but can be activated in conditions of reduced immunity.
The composition of the microflora determines the state of normal and pathological conditions. When a large amount of opportunistic flora is detected in a smear from the cervical canal, this indicates the development of an inflammatory process.
This flora includes Streptococcus agalactia.
Streptococcus in the vaginal microflora
Most of the normal vaginal flora is lactobacilli. Opportunistic flora include streptococci, staphylococci, candida, gardnerella, ureaplasma and mycoplasma. If the number of these microorganisms does not exceed the norm, the condition of the vagina will be satisfactory.
One of the causative agents of nonspecific inflammation is Streptococcus agalactia. The group of streptococci includes a large number of different microorganisms with similar morphological characteristics. Based on the type of growth on a nutrient medium, hemolytic, non-hemolytic and greening microorganisms are distinguished.
Streptococci of groups B and D, as well as viridans, are found in the vaginal environment. Agalactia is a beta-hemolytic streptococcus from group B. The norm for streptococci is 10 to 4 CFU/ml.
The colonization of streptococci in the vaginal environment occurs during puberty, especially at the beginning of sexual activity. Self-infection from the anal folds is also possible if, while washing, you direct movements away from the anus.
At-risk groups:
- women who have suffered premature birth;
- increased temperature during childbirth;
- anhydrous period of more than 18 hours;
- birth of a premature baby;
- underweight infants;
- C-section;
- the presence of bacteria in the urine.
During childbirth, a woman can infect her newborn. Streptococci are also transmitted through household means through shared hygiene items. A man can become infected during oral or anal intercourse.
When the balance of vaginal microflora is disturbed
While there are few streptococci in the vaginal environment, lactobacilli predominate. In large quantities, they can suppress the growth of opportunistic flora and protect against inflammation. Streptococcus is activated when there is an imbalance in the vaginal microflora.
Causes of microflora imbalance:
- hormonal changes;
- weakened immunity;
- failure to comply with personal hygiene rules;
- douching;
- severe systemic pathologies (diabetes mellitus).
During pregnancy, inflammation develops due to two factors at once (immunity and hormones). An increase in progesterone levels negatively affects local immunity, which is necessary to maintain pregnancy. However, against this background, latent infections of the genitourinary system often worsen.
A man becomes infected during unprotected sexual intercourse. He becomes a carrier and transmits streptococcus to his sexual partners.
Symptoms of streptococcus agalactia
Agalactia does not cause severe symptoms, there is no inflammatory reaction in the vagina. The pathogen begins to act in the urethra, rising higher through the genitourinary organs.
Symptoms of cystitis occur: pain and burning during urination, frequent urge with the release of a small volume of urine, a feeling of incomplete emptying.
In acute cystitis, the general condition also worsens, the patient feels weakness and headaches.
How to treat streptococcus before and during pregnancy
The treatment regimen for streptococcus agalactia is selected depending on the patient’s condition. If the disease is latent and the woman does not plan to have children, local therapy can be limited. When a patient is planning a pregnancy, treatment for streptococcus begins only after symptoms appear.
Pregnant women who do not have significant symptoms should be seen by a doctor and re-examined at 35 weeks. During lactation, local treatment is prescribed until symptoms disappear. Oral antibiotics are not prescribed because they pass into breast milk.
Treatment tactics:
- A woman is planning a pregnancy. Therapy is prescribed only for vaginal discomfort. If there are no obvious symptoms of infection, conception and pregnancy are not prohibited.
- The woman is not planning a pregnancy and has symptoms. If urine culture does not contain pathogens, local treatment is prescribed to eliminate symptoms.
- A pregnant woman with streptococcus detected in a smear or bacterial culture.
If streptococcus is detected early and there are no signs of inflammation, a re-examination is prescribed at 34-35 weeks. Therapy is carried out before labor or during labor (at least 4 hours before delivery). The woman is given penicillin antibiotics, cephalosporins or macrolides. It is not advisable to carry out therapy several weeks before birth: streptococcus will colonize the vaginal mucosa after treatment is completed. - Lactation period.
During feeding, treatment with antibiotics can be dangerous for the child, so local effects are preferred. Typically, Hexicon suppositories with chlorhexidine are used, 1-2 per day for a week. After some vaginal preparation with lactobacilli to restore the microflora.
Treatment usually begins with Nitrofurantoin, which has a universal effect. If group B streptococci are present, Ampicillin is prescribed, as it accumulates in the vaginal mucosa. This makes it possible to prevent infection of the newborn.
Streptococcal therapy is carried out using penicillin antibiotics when a concentration of 10 to 5 CFU/ml is detected. Cephalosporins and macrolides also help stop the proliferation of microorganisms. The most effective are oral medications.
To treat streptococcus, you can use antibiotics Doxycycline, Levofloxacin, Vancomycin, Ceftriaxone, Benzylpenicillin, Fosfomycin, Linezolid. Self-medication is not recommended, since improper use of antibiotics can lead to the development of resistance and imbalance of the intestinal microflora.
In pregnant women up to 12 weeks, therapy is not carried out, this is due to the peculiarities of the formation of the placenta (with a titer of 10 to 6 degrees CFU/ml). From 4 months, oral medications are prescribed. Oral antibiotics must be prescribed when streptococcus is detected in the urine of a pregnant woman. Self-medication for cystitis in pregnant women can be dangerous. Some antibiotics increase the risk of perinatal death.
Preparations:
- Antibacterial local treatment: Metromicon-neo (1 suppository in the morning or before bed for a week).
- Complex treatment for the 1st-2nd trimester: Amoxiclav (375 mg every 8 hours, suppositories), Hexicon (1 suppository at night for 7 days).
- Combination therapy: Azithromycin (1 g once), Diflucan (one time), Vetadine No. 10, Trichopolum (1 tablet three times a day).
- Sanitation of the vagina: Fluomizin (1 vaginal tablet per day for 6 days).
Prevention of complications plays an important role. If one of the partners is diagnosed with a streptococcal infection, the other is recommended to take a smear (women from the vagina, men from the nasopharynx).
Local therapy for streptococcus
Local therapy includes vaginal tablets and suppositories. Before childbirth, it is imperative to sanitize the vagina to reduce the chances of infection of the child. If the concentration of streptococcus exceeds 10 to the 8th degree and sanitation was not carried out, antibacterial therapy is required during childbirth. Sanitation of the birth canal and antibiotics help reduce the likelihood of infection of the child to 1-2%.
Recommended drugs:
- Fluomizin.
Vaginal tablets effective for bacterial vaginosis. The tablet should be inserted into the vagina before bedtime (6 days). Microorganisms rarely develop resistance to the drug, but using the drug for less than 6 days leads to its ineffectiveness the next time. Contraindications to Fluomizin: allergies to components, ulcers of the vaginal mucosa, age under 18 years. - Terzhinan.
The drug is used in the treatment of bacterial and fungal infections. Thanks to prednisolone in its composition, Terzhinan has anti-inflammatory properties and reduces swelling of the mucous membrane. Pregnant women can use Terzhinan from the second trimester, during lactation only with the permission of a doctor. Before use, the tablet is moistened. During menstruation, therapy is not stopped. The course of treatment is 10 days. - Hexicon.
The suppositories contain chlorhexidine bigluconate, due to which they have an antimicrobial and antiseptic effect. Hexicon is effective for vaginosis and colpitis. Can be used during pregnancy and breastfeeding. To treat streptococcus, use 1 suppository 1-2 times a day for 7-10 days (for pregnant women 5-10 days).
The danger of streptococcus
During pregnancy, Streptococcus agalactia can be suspected due to frequent urethritis and cystitis, but even healthy women are recommended to get tested.
The fact is that agalactia is detected in 20% of pregnant women. If the patient has given birth to an infected child, examination in subsequent births is mandatory.
In a woman, the infection spreads latently, but in a baby, streptococcus can cause complications.
Complications of streptococcus in mother and child:
- urinary tract infections;
- postpartum endometritis (inflammation in the surface layer of the endometrium of the uterus);
- chorioamnionitis (inflammation of the membranes of the fetus);
- spontaneous abortion;
- infant pneumonia;
- sepsis of the neonatal period;
- endocarditis (inflammation of the inner lining of the heart);
- meningitis (inflammation of the membranes of the brain).
When treating streptococcus agalactia, preference is given to complex therapy with penicillins or cephalosporins. Individual drugs are chosen depending on the specific situation. A timely visit to a doctor will help avoid complications not only for the woman herself, but also for her child.
- Gonal 33%, 35073507 33%3507 - 33% of all
- Clostilbegit 25%, 2623 votes2623 votes 25%2623 votes - 25% of all
- Menopur 16%, 1704 votes1704 votes 16%1704 votes - 16% of all
- Puregon 14%, 1523 votes1523 votes 14%1523 votes - 14% of all
- Pregnyl 9%, 910910 9%910 - 9% of all
- Menogon 3%, 323 votes323 votes 3%323 votes - 3% of all
Source: https://BornInVitro.ru/infekcii-i-bolezni/agalaktiya/
Post-birth plan
If there is streptococcus in a smear in pregnant women and there is concern that the baby has become infected during childbirth (the mother developed an infection during childbirth or the baby has an elevated temperature), immediately after birth, doctors:
- will treat the newborn with antibiotics;
- They will conduct a full examination, including blood tests.
If there are breathing difficulties, the baby will be sent for an x-ray. If the temperature does not subside, a spinal tap test may be performed.
A baby without symptoms of infection can be taken home 1-2 days after birth. Discharge after the first day is possible if:
- you received antibiotics 4 hours before the baby was born;
- there were no signs of infection at the time of delivery;
- the baby was born full-term, he feels well and has no other health problems;
- you have received detailed instructions from your doctor on how to properly monitor your newborn’s symptoms at home;
- you have the opportunity to quickly receive medical care.
If the above points cannot be followed, the child must remain in the hospital for a full 48 hours.
If streptococci were detected in a smear in a pregnant woman and her baby was born prematurely, hospitalization may last even without signs of infection. Doctors will also conduct additional diagnostics, since in the presence of GBS, premature babies are more likely to become infected and become more seriously ill.
Diagnosis and treatment
The sooner streptococcus is detected in the urine, the more effective treatment measures will be. To find the causative agents of this disease, special tests have been developed that can show results for the presence of bacteria within half an hour. As a rule, in medical institutions, in addition to tests, they use analysis of a selected sample.
If streptococcus is detected, doctors will refer the patient for testing for nephritis and urethritis. In children, such infections can be detected both early and late. In the first case, they will experience breathing problems, fever and drowsiness. As for the late stage, it is characterized by the appearance of convulsions, fever, lack of appetite, cough and nasal congestion.
But sometimes streptococcus does not produce such pronounced symptoms, so experts recommend diagnostics in a laboratory to detect bacteria.
In a urine test for such an infection, a large amount of hemoglobin and creatinine will be present.
Doctors use antibiotics to treat streptococcal infections. To ensure that such therapy does not harm the patient’s body, the treatment is supplemented with drugs that restore the microflora. If, as a result of exposure to streptococcus, the patient develops severe poisoning of the body, the medical institution will prescribe him to refuse any physical activity and adhere to bed rest.
When prescribing medications, the doctor will take into account the fact that urine is very sensitive to antibiotic drugs. Therefore, as a rule, complex measures are used in the treatment of such a disease. The course of antibiotic treatment ranges from 10 to 14 days. As preventive measures, experts advise paying close attention to your health, paying attention to your immune system and maintaining personal hygiene. Also, it should be remembered that it is possible to get rid of a streptococcal infection and avoid subsequent complications only if the patient consults a doctor in time.
The microflora of the human body is inhabited by a huge mass of different bacteria. Streptococcus actively multiplies in the urine in conditions of weakened immunity or during hypothermia, infecting the urinary tract. In an environment favorable to infection, the inflammatory process begins to develop.
Can a baby catch streptococcus B bacteria after birth?
Yes, this is possible. Group B streptococci in a mother's smear can cause symptoms of infection in the baby a week after birth. The risk remains for the first three months of a toddler’s life. According to statistics for the United States, the development of late infection caused by group B streptococci is recorded more often than early infection.
Late-onset GBS infection can cause the same problems as early onset. Children born prematurely are at higher risk. With late onset, meningitis is more common.
The reason for calling the doctor should be:
- inability to wake up;
- inexplicable moodiness;
- unusual lethargy;
- increased body temperature;
- almost complete immobility;
- vomit;
- feeding difficulties;
- epileptic seizures.
Call emergency services immediately if your child has difficulty breathing and their skin turns blue.
How to prevent late-onset GBS infections?
Using antibiotics during labor if you have been diagnosed with group B streptococcal infection during pregnancy will not prevent later onset of the disease. Only half of the children with late-onset infection had their mother as the source of the bacteria. In other cases, the sources of infection remain unknown, so it is difficult to take any preventive measures.
Conclusion
You should not be afraid of group B streptococci in the smear. If you are diagnosed with this bacterium at 36-37 weeks of pregnancy, your doctor will definitely give you an antibiotic injection during childbirth to minimize the risk of infection of the newborn.
But keep in mind that even without treatment of streptococci in gynecology, not all children become infected with this infection. The most important thing is to do the analysis in a timely manner. Also, do not forget to monitor the behavior of the little one after birth, so as not to miss the symptoms of the disease caused by streptococcal bacteria.
Causes of streptococcal infection in pregnant women
Streptococcal infection during pregnancy is detected quite often in a smear. In some regions this figure is significantly higher than the statistical average of 30%. This is explained by the transmission of the disease. Streptococcus isolated in smears of a pregnant woman could enter the woman’s body through one of the following routes:
- From person to person, for example, when shaking hands, kissing.
- Sexually.
- Use of personal hygiene items by several people, one of whom is a carrier of a bacterial infection. This applies not only to towels, but even soap.
During pregnancy, women's immunity is significantly reduced. This is due to certain changes in the body.
Infection can occur both at the beginning of pregnancy and in the last weeks. Therefore, significant attention should be paid to the safety of the expectant mother. In some cases, it is even useful to limit your social circle.
At risk are women who have addictions that further suppress the functioning of the immune system. Also, negative consequences are more often recorded in those who suffer from diabetes.
In addition to its unsystematic occurrence in a latent form, detected streptococcus in the urine of a pregnant woman can lead to the development of various skin rashes. We are talking about the following diseases:
- Superficial streptoderma. They come in the following varieties - Tilbury Fox, folds, annular, periungual, slit-like, bullous, lips, mucous membranes, including the oral cavity and throat.
- Deep streptoderma has one form. The disease is called ecthyma.
- Atypical streptoderma is lichen simplex, acute diffuse streptoderma. Papular syphiloid impetigo occurs only in children under 1 year of age in the absence of proper hygienic care. Its second name is diaper dermatitis.
Often, pregnant women confuse the first manifestations of streptococcal infection with other ailments. Therefore, it is important to know what symptoms are characteristic of this disease.