Preparing for analysis
No special preparation is required for a smear from the cervical canal, however, there are rules that must be followed in order for the result to be accurate:
- Before the analysis, you should wash yourself, but do not douche;
- The day before the test, you should not use lubricants or gels for the vagina;
- More than a day must pass after the last sexual intercourse;
- It is not advisable to take medications before a smear. If the use cannot be stopped, you should tell your doctor the name of the drug and its dosage;
- Before the analysis, you should not drink alcohol or energy drinks, and you should also stop smoking;
- The day before the analysis, exotic foods, as well as spicy, sour and smoked foods, should be excluded from the diet.
It should be remembered: the optimal time for taking the test is 11-14 days of the cycle, approximately 5-7 days after the end of menstrual flow.
There is no need to be afraid to take a smear from the cervix - taking it is absolutely painless and harmless to the patient.
Standard results for a smear from the cervical canal
| Index | Normal value |
| Leukocytes | 0-30 |
| Flat epithelium | 5-10 |
| Gonococci | None |
| Trichomonas | None |
| Yeast cells | None |
| Key cells | None |
| Microflora | Absent |
| Slime | Moderate amount |
If any of the analysis indicators differs from the normal value, you should definitely contact a gynecologist to prescribe treatment.
Explanation of the procedure
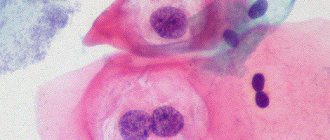
Smear bacterioscopy in women decoding : this technique is the most common procedure performed in gynecological structures. This is due to the fact that numerous diseases in the female body occur when the microflora is disturbed or an infectious process develops in the genitourinary system. If there are relevant complaints, then the procedure must be completed. Diagnostic method: the received forms with the analysis result can only be deciphered by a doctor who will tell the patient about the state of health. For diagnostic purposes, a gynecologist takes a smear to determine the flora.
Using this method, individual indicators are deciphered, which determines the informative level, as well as the method of treatment. When studying these analyzes, the reason why the pathogenic flora was formed, as well as abnormal cells, is determined. It also assesses the level of balance of hormonal levels in the female body system. Specialists do not use the writing of full diseases; they use them in abbreviated form. Designated by the first letter of the analysis parameter. To understand the normal microflora in the vagina, you need to know the letter designations.
As a rule, the zones and the collection of materials are reduced, the vagina is designated by the letter - V, the cervical area in the cervix is designated by the letter - C. The urethra is designated by the letter - U, L means a leukocyte cell, the values of which sometimes do not coincide with the norm in a pathological process. EP is translated as epithelial cell, GN is gonococci, which causes gonorrhea. Trich are translated as Trichomonas cells, in which the formation of the trichomoniasis process occurs. There are many reasons why the process of changing the level of flora in the vagina occurs.
This occurs due to the deterioration of the immune system when antibiotic therapy is used, as infection progresses, and also in diabetes mellitus. The predisposing effect is the formation of hormonal imbalance . As is known, in pregnant women, before childbirth, the production of estrogen substances stops, but the progressive formation of another hormone, progesterone, begins. Smear bacterioscopy is a very important procedure, and you need to take it seriously. If a deviation from the norm is detected, treatment is necessary.
Increased mucus content
There are many reasons why a cervical smear may have an increased content of mucus. They are divided into two main groups: physiological and pathological, that is, normal and abnormal.
The first group includes the following changes in the female body:
- Changing hormonal contraceptives;
- Pregnancy and lactation;
- Using new intimate gels or lubricants;
- Change of sexual partner;
- Taking antibiotics and antibacterial drugs;
- Stitches on the cervix, after childbirth or surgery;
- Moving to another region;
- Treatment with mud or turpentine baths, phyto-barrels.
Pathological causes include:
- STDs such as gonorrhea, chlamydia and others. In the case of these diseases, there are usually other changes in the smear;
- Vaginitis, or inflammation of the uterus. A dangerous disease that, if left untreated, can lead to consequences such as infertility and even removal of reproductive organs;
- Urethritis, or inflammation of the urethra. Quite a common occurrence, especially in the cold season. Accompanied by pain in the lower abdomen, pain when urinating. If not properly treated, it also leads to serious illnesses;
- Fibroids, cysts and other neoplasms in the uterus can cause large amounts of mucus, up to 600 ml per day;
- Dysbacteriosis, or imbalance of bacterial balance in the intestines. Rare, but can lead to increased mucus production on the cervix;
- Allergic reaction. The cause of increased mucus content in a smear from the cervical canal may be an allergy to synthetic underwear, lubricant or intimate hygiene products. Rarely, food allergies can also manifest themselves in this way.
An increased content of mucus in a smear is not a disease, but a consequence of the disease. The exact cause of its appearance can only be determined by a doctor after a comprehensive examination.
Clinical manifestations
The first thing that begins to bother a woman is discomfort in the area of the external genitalia and the appearance of discharge. The discharge is homogeneous, whitish-gray, with a specific unpleasant fishy odor, which intensifies during and after sexual intercourse, after menstruation and hygiene procedures.
Sexual intercourse is accompanied by dyspareunia - unpleasant sensations, sometimes pain in the vaginal area. Burning and itching with BV are rare, but if they are present, vaginosis cannot be ruled out in any case. Dysuria—painful urination with itching and burning—is possible.
If any vaginal symptoms appear, a woman should be thoroughly examined, since other infections may be hidden under the guise of bacterial vaginosis: gonorrhea, trichomoniasis, chlamydia, mycoplasmosis, candidiasis, ureaplasmosis, etc.
Upon examination, the gynecologist will find thick white-gray discharge that is evenly distributed throughout the mucous membrane of the vulva and vagina. The doctor will not see symptoms of inflammation - swelling, hyperemia - since the disease belongs to the group of non-inflammatory ones.
Slime function
In the female body, mucus performs important functions:
- Protective. Mucus prevents bacteria and foreign substances from entering the uterine cavity;
- Lysing. Mucus can destroy bacteria and foreign substances that enter the vagina;
- Regenerating. Mucus takes part in the restoration of damaged tissue areas, so after childbirth and operations the amount of mucus increases;
- Participates in fertilization. With the help of mucus, sperm enters the uterine cavity for subsequent fertilization of the egg.
Mucus is produced by special cells under the influence of female sex hormones - estrogens. She is alkaline and alkaline, whereas the vagina is acidic. The mucus contains lactobacilli, plasma and some blood cells, and epithelial cells.
Depending on the day of the menstrual cycle, the composition and amount of mucus changes. From days 1 to 5 it is released in small quantities and has a watery consistency; from days 6 to 10 it becomes thicker and is released in larger quantities. From 10 to 15 days, during the period of ovulation, mucus reaches its maximum quantity and thickness. After the 15th day of the cycle, if fertilization has not occurred, the amount of mucus gradually decreases, and if pregnancy occurs, it increases.
Degrees of definition
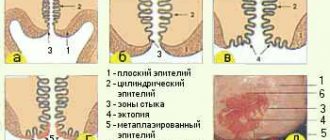
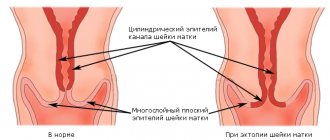
Vaginal cleanliness is determined using several grade forms. Based on what data is revealed by examination in a general smear, four degrees are distinguished. With the first degree of determination, this fact means that the patient is healthy. In this case, the state of the vaginal microflora is optimal. But, according to medical data, such identification of the form is very rare. When the second degree is detected, a slight deviation in the level of flora occurs. This form is the most common degree in healthy patients. In the third degree, it is discovered that there has been a deviation from the norm of the indicator, opportunistic bacteria are growing.
In the fourth degree, significant deviations from the norm are determined, which means that bacterial vaginosis and other sexually transmitted infections have progressed. When the amount of lactobacilli decreases, this means that there has been a violation of the acid-base balance of the vaginal microflora level. This manifestation occurs in women with an active sex life. The level of the indicator in the vagina is significantly influenced by pathogenic and opportunistic microorganisms. Coccus is a type of bacterium with a spherical shape.
This bacterium is found in the system both as a norm and as a deviation from the indicator when various inflammatory diseases occur. The norm is the detection of single cocci in the analysis. When a decrease in immune defense occurs, the level of coccobacillary forms in the flora begins to increase. Coccus happens:
- gram positive;
- gram negative.
To determine the type of coccus using a laboratory test, staining is carried out using a special technique. During which the so-called gram staining is revealed.
Those types of microorganisms that remain colored after the smear is washed are considered gram-positive. And those that are discolored are considered gram-negative. Gram-positive indicators are streptococcus and staphyloccus cells. Gram-cell cocci are the cells of gonococcus, Proteus, and Escherichia coli. When the number of epithelium and leukocyte levels increase, this means that acute or chronic forms of the inflammatory process are developing in the body.
When should you worry?
Normally, mucus does not cause discomfort in a woman. But if:
- There is too much vaginal discharge;
- The discharge is yellowish or greenish in color;
- The discharge has an unpleasant odor;
- Discharge with a cheesy consistency;
- The discharge contains blood clots or brown spots (outside of menstruation);
- Discharge causes discomfort;
- Itching appears in the vagina;
- Redness, spots or acne appear in the perineum;
- Pain appears in the lower abdomen.
You should consult a doctor immediately.
Gn smear: where to go
Where should you go if you suspect an infection?
In large cities there are budgetary medical organizations - skin and venereal disease clinics. They are focused on the diagnosis and treatment of infections that are predominantly sexually transmitted.
Also, private clinics of the same specialization can provide diagnosis and treatment of sexually transmitted diseases anonymously and in more comfortable conditions.
To undergo a smear test, please contact the author of this article, a venereologist in Moscow with many years of experience.
Drug treatment of increased mucus content in the smear
It is used depending on the cause of the disease:
- Antibacterial therapy. It is used in case of damage to the body by bacteria or viruses. The antibiotic is selected depending on the sensitivity of the foreign agent. Both general and local drugs are used;
- Antifungal therapy. It is used when the body is infected with fungi (most often the Candida type). Medicines are used both locally and internally;
- Douching. Used for large amounts of mucus. It is carried out with boiled water at room temperature or decoctions of herbs, such as sage and chamomile;
- Hormonal therapy. It is carried out under the supervision of a gynecologist (often in a hospital) in case of hormonal imbalances in the body;
- Treatment of cystitis and urethritis. It is carried out using diuretics and antibacterial drugs;
- Antiallergic therapy. It is carried out with the help of antihistamines (for example, Suprastin, Zodak) and adsorbents (Polysorb, activated carbon).
Surgical treatment
Surgical treatment is carried out in the presence of neoplasms in the uterus or its appendages according to indications.
Treatment with folk remedies
The experience of past generations has accumulated many treatment methods that are still relevant today:
- For infectious diseases, a decoction of elecampane, celandine or fenugreek will help;
- For hormonal imbalances, a decoction of boron uterus, an infusion of rowan in alcohol, and tea from white rose leaves are effective;
- For allergies, a decoction of chamomile and dandelion root will help;
- A decoction of oats and wormwood is effective against dysbiosis;
- To treat urethritis and cystitis, lingonberry leaves and kidney tea will help;
- It will strengthen the immune system and help you cope with any disease more quickly: a decoction of rose hips, echinacea, honey water.
It should be remembered that traditional medicine works individually for each person. You should not use them without consulting your doctor.
Treatment regimens for bacterial vaginosis
Before starting treatment, the gynecologist sets the following goals:
- complete recovery with no clinical manifestations of BV;
- return to normal indices of additional studies: laboratory, microscopic;
- eliminating the possibility of developing infectious complications during pregnancy or childbirth, in the postoperative period.
Bacterial vaginosis is treated on an outpatient basis; such conditions are not subject to hospitalization. The main means of treating this disease according to modern recommendations are drugs of the 5-nitroimidazole group (Metronidazole) and Clindamycin. The use of the latter is preferable, since it has virtually no side effects. During treatment, it is necessary to refrain from drinking alcohol during the entire course of therapy and for 24 hours after - the combination of these drugs with alcohol causes severe adverse reactions. Medicines are usually prescribed intravaginally, in the form of a cream or vaginal suppositories. Various treatment regimens are recommended:
- Clindamycin cream 2% is inserted into the vagina, 5 g at night for one week;
- Metronidazole gel 0.75% is used 5 g intravaginally before bedtime for 5 days;
- Metronidazole tablets are taken 500 mg with water, twice a day - morning and evening, the course of treatment is a week;
- Tinidazole tablets are taken 2 grams with water, once a day for 3 days.
If the recommended treatment regimens are ineffective or intolerable, alternative treatment is prescribed:
- Ovulate with clindamycin 100 mg intravaginally at night for 3 days.
- Clindamycin capsules 300 mg orally twice daily for 7 days.
- Metronidazole tablets 2 grams once (high loading dose).
- Tinidazole tablets for a course of 5 days, 1 gram once a day.
Treatment of pregnant women is carried out only with tablet forms of Metronidazole and Clindamycin. Prescription of Metronidazole is possible only after the end of the first trimester of pregnancy, and Clindamycin is not contraindicated in the early stages. The drugs are prescribed in a course of one week.
If bacterial vaginosis is diagnosed in a girl who is not sexually active, then Metronidazole tablets are used in therapy at the rate of 10 mg/kg body weight 3 times a day with a course duration of no more than 5 days.
Complex therapy for BV must necessarily include preparations of ascorbic and lactic acid to restore the acidity of the internal environment of the vagina (normal pH = 4.5). These are drugs such as Vagilak and Vaginorm S. They are prescribed after antibacterial therapy, when foreign microorganisms have been removed and it is necessary to restore normal flora from scratch.