Causes of pathology
The main cause of displacement of the appendage is adhesions in the pelvis. The occurrence of an adhesive process in which the right ovary (or left) is affected is influenced by the following factors:
- Gynecological operations (abortion, cesarean section), when the integrity of the appendage is disrupted, which provokes deviations in the processes of blood clotting and cell restoration. Instead of regeneration, connective tissue is formed, gluing organs to each other.
- Concomitant pathologies of the reproductive sphere (cyst, endometritis, etc.). Due to the affected cells, the stroma of the appendages suffers, and the processes of local blood supply are disrupted. Abnormal cells begin to divide, pathological tissues grow, which leads to the appearance of scars.
- The ovary is pulled towards the uterus under the influence of the following factors:
- violation of the rules for inserting an intrauterine device;
- venereal diseases;
- endometriosis, in which the tissue of the uterine lining extends beyond its boundaries;
- ectopic pregnancy;
- use of antibacterial agents;
- ruptures during labor;
- hypothermia;
- performing hysteroscopy.
Ultrasound pulls the ovary to the rib of the uterus - About your health
If the ovary is soldered to the uterus, then this indicates the presence of an adhesive process, as a result of which the appendage fuses with the genital organ. At the same time, scars form and blood supply processes are disrupted, which prevents conception.
Causes of pathology
The main cause of displacement of the appendage is adhesions in the pelvis. The occurrence of an adhesive process in which the right ovary (or left) is affected is influenced by the following factors:
- Gynecological operations (abortion, cesarean section), when the integrity of the appendage is disrupted, which provokes deviations in the processes of blood clotting and cell restoration. Instead of regeneration, connective tissue is formed, gluing organs to each other.
- Concomitant pathologies of the reproductive sphere (cyst, endometritis, etc.). Due to the affected cells, the stroma of the appendages suffers, and the processes of local blood supply are disrupted. Abnormal cells begin to divide, pathological tissues grow, which leads to the appearance of scars.
- The ovary is pulled towards the uterus under the influence of the following factors:
- violation of the rules for inserting an intrauterine device,
- venereal diseases,
- endometriosis, in which the tissue of the uterine lining extends beyond its boundaries,
- ectopic pregnancy,
- use of antibacterial agents,
- ruptures during labor,
- hypothermia,
- performing hysteroscopy.
Symptoms that the ovary is attached to the uterus
If the left ovary (or right) is located close to the uterus, then at the initial stage of the pathology there may be no symptoms. Sometimes the clinical picture unfolds several years after the start of the process. The following symptoms occur:
- nagging pain in the lower abdomen, migrating to the lumbar region;
- disruptions of the menstrual cycle;
- discomfort during sports, intimacy;
- painful periods;
- disturbances in the functioning of the intestines;
- increased body temperature;
- bloody or yellow-green discharge.
A woman has a slight pain in the lower abdomen on the right or left. Changes in unilateral localization and increased severity of the symptom often indicate a complication - a violation of the patency of the fallopian tubes. In this case, menstruation is often delayed by 2-3 months.
Ovaries in women: location, work
The main cause of displacement of the appendage is adhesions in the pelvis. The occurrence of an adhesive process in which the right ovary (or left) is affected is influenced by the following factors:
- Gynecological operations (abortion, cesarean section), when the integrity of the appendage is disrupted, which provokes deviations in the processes of blood clotting and cell restoration. Instead of regeneration, connective tissue is formed, gluing organs to each other.
- Concomitant pathologies of the reproductive sphere (cyst, endometritis, etc.). Due to the affected cells, the stroma of the appendages suffers, and the processes of local blood supply are disrupted. Abnormal cells begin to divide, pathological tissues grow, which leads to the appearance of scars.
- The ovary is pulled towards the uterus under the influence of the following factors:
- violation of the rules for inserting an intrauterine device;
- venereal diseases;
- endometriosis, in which the tissue of the uterine lining extends beyond its boundaries;
- ectopic pregnancy;
- use of antibacterial agents;
- ruptures during labor;
- hypothermia;
- performing hysteroscopy.
Partial detachment of the ovum with the formation of a hematoma
The embryo is surrounded by several membranes that reliably protect it from negative factors of the internal and external environment. With these membranes, the unborn baby is attached to the endometrium of the uterus, through the vessels of which it receives the nutrients, oxygen and “building” material necessary for its growth and development.
For a number of reasons, at an early stage of gestation, partial detachment of the membranes may occur, followed by the formation of a retrochorial hematoma. The condition is an accumulation of a certain volume of blood behind the chorion. The prognosis in this case depends on the size of the hematoma and its progression.
The placenta is the organ through which nutrition, respiration and excretion of fetal metabolic products are carried out.
The formation of the placenta occurs from the overgrown chorionic villi and the decidua, its basal part. The bulk of the placenta is well-vascularized, highly branched chorionic villi.
The number of chorionic villi increases with increasing gestational age. They increase the boundary surface of contact between the blood flow of the fetus and mother. Both bloodstreams do not communicate with each other; they are separated by the placental barrier.
The placental barrier consists of:
- trophoblast basement membrane;
- trophoblast;
- basement membrane of fruit capillaries;
- stroma;
- capillary endothelium.
A continuous exchange of substances between the blood of the fetus and mother occurs through the placental barrier in the terminal villi. Oxygen and all substances necessary for its life and development enter the fetal blood from the maternal blood. Carbon dioxide and metabolic products enter the mother's blood from the fetus's blood.
Can not understand anything?
Try asking your teachers for help
The placenta performs the following functions:
- Transport. Placental enzymes are involved in nutrient transport. Gas exchange is ensured by the laws of simple diffusion.
- Depositing. The placenta contains a constantly renewed supply of blood containing nutrients necessary for the fetus.
- Hormonal. Chorionic gonadotropin is formed in the placenta, which takes part in the mechanisms of differentiation of the future sex of the fetus; placental lactogen, which supports placental function; progesterone; prolactin; estrogens causing hyperplasia and hypertrophy of the endometrium and myometrium. The placenta synthesizes corticosteroid hormones, testosterone, relaxin, serotonin and other hormones.
- Excretory. Products of fetal metabolism are excreted through the placenta.
- Barrier. The placenta serves as a barrier preventing the emergence of an immune conflict between the fetus and the maternal body. The placenta prevents the penetration of certain toxic substances into the fetus that have entered the mother's body.
What diseases cause pain in the appendage area?
Discomfort in the area where the fallopian tubes and ovaries are located, pain and severe sensations may indicate pathological processes not only in them, but also in nearby organs. This is dangerous because such diseases can lead to infertility and damage to the entire reproductive system.
So, if you feel pain in the appendages, this may indicate the development of the following diseases:
- Adnexitis is inflammation of the uterus and ovaries. This disease is dangerous because it cannot be detected immediately. In most cases it occurs without specific symptoms. Over time, the disease progresses, leading to infertility.
- Various difficult living conditions can also cause pain in the appendage area. These are obesity, diabetes, constant stress, colds. In themselves, these phenomena do not relate to the reproductive system, especially to the ovaries or fallopian tubes. But they can provoke a sharp decrease in immunity, which entails the occurrence of pathologies in a woman’s reproductive function.
The first sign indicating a malfunction in the appendages is a malfunction and disruption of the menstrual cycle. In this case, it is better to consult a specialist for advice.
Risks and consequences
Before carrying out the procedure, the expectant mother must weigh the pros and cons and take into account all the risks. Lack of information gives rise to speculation, and awareness allows you to prepare for possible consequences.
The risk of miscarriage after chorionic villus sampling is 1–2%.
All other risks are directly related to the professionalism of the medical staff. Puncture of natural barriers with a needle certainly entails rupture of capillaries. As a result, a retrochorial hematoma may form. It can again lead to miscarriage.
Source: https://gpk1.ru/bolezni/yaichnik-raspolozhen-za-matkoj.html
Diagnosis of pathology
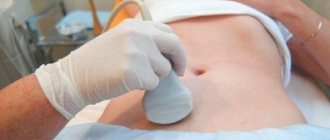
To discover that the ovary is located behind the uterus, a gynecological examination alone is not enough. An ultrasound of the pelvic organs is required. If this method does not reveal the adhesive process, then laparoscopy is performed. Additionally, MRI is used, which makes it possible to detect small changes in the reproductive system.
Ovarian displacement is also diagnosed by other methods, for example, hysterosalpingography - an x-ray examination in which a contrast agent is injected into the cavity of the reproductive organ and fallopian tubes. The procedure is performed from days 5 to 11 of the cycle . Additionally, the patient is recommended to take a vaginal smear for microflora testing.
Is one fallopian tube enough for pregnancy?
To give a detailed answer to this question, it is necessary to understand some aspects of female physiology. The fallopian tube is an organ shaped like a tube. It connects the uterine cavity with the ovary. After leaving the follicle, the female reproductive cell enters the abdominal cavity. From here, picked up by the villi, it moves into the fallopian tube, where conception occurs. Then the embryo moves into the uterine cavity, where it literally plunges into the mucous membrane, becomes overgrown with blood vessels and continues its development as an embryo. That is, the uterine appendage serves as a place for fertilization of the egg, a kind of conductor for it into the uterine cavity. The appendage does not affect the further development of the fetus.
However, conception cannot occur in the absence of both fallopian tubes. But will just one pipe be enough? Of course yes.
If both partners are healthy, there should be no problems with conception. However, if ovulation occurs on the side where the appendage is absent, you will not be able to get pregnant. But we are talking only about the current cycle. Next month, ovulation will occur in the opposite ovary, on the side where the tube is present, and it is quite possible that pregnancy will occur. That is, pregnancy with one ovary and one fallopian tube is quite possible, but you will have to wait about twice as long.
Treatment of pathology
If the ovary is located behind the uterus, at the initial stage of the pathology it is possible to use medications:
- antibiotics;
- suppositories (for example, Longidase);
- drugs that eliminate inflammation;
- enzymes;
- vitamins and microelements.
It is useful to undergo physiotherapeutic procedures (electrophoresis with the introduction of magnesium, calcium and zinc through the skin). Thanks to this treatment, the adhesions become thinner and stretched. The patient may be prescribed sanatorium treatment (including mineral waters).
Then, when the ovary is close to the uterus, physical activity is recommended. In advanced cases, laparoscopy is performed, the purpose of which is to separate and eliminate tissues connected to each other. After the operation, a special film is applied to the appendages. In addition, a barrier fluid is used to prevent the formation of new adhesions.
During the rehabilitation period, antibiotics and medications are used, the action of which is aimed at preventing the formation of blood clots. The effectiveness of the surgical intervention is then assessed. Physiotherapeutic procedures are prescribed at the discretion of the doctor. Laparoscopy does not provide a 100% guarantee that the adhesive process will not return again and the ovary will not move again.
Other treatments:
- laser therapy based on the impact of special rays;
- electrosurgery aimed at eliminating damaged tissues with high-frequency current;
- aquadissection, in which adhesions are dissected using a water stream.
Why is the ovary soldered or located behind the uterus. Displacement of the uterus - left, right
The main cause of displacement of the appendage is adhesions in the pelvis. The occurrence of an adhesive process in which the right ovary (or left) is affected is influenced by the following factors:
- Gynecological operations (abortion, cesarean section), when the integrity of the appendage is disrupted, which provokes deviations in the processes of blood clotting and cell restoration. Instead of regeneration, connective tissue is formed, gluing organs to each other.
- Concomitant pathologies of the reproductive sphere (cyst, endometritis, etc.). Due to the affected cells, the stroma of the appendages suffers, and the processes of local blood supply are disrupted. Abnormal cells begin to divide, pathological tissues grow, which leads to the appearance of scars.
- The ovary is pulled towards the uterus under the influence of the following factors:
- violation of the rules for inserting an intrauterine device;
- venereal diseases;
- endometriosis, in which the tissue of the uterine lining extends beyond its boundaries;
- ectopic pregnancy;
- use of antibacterial agents;
- ruptures during labor;
- hypothermia;
- performing hysteroscopy.
Symptoms that the ovary is attached to the uterus
If the left ovary (or right) is located close to the uterus, then at the initial stage of the pathology there may be no symptoms. Sometimes the clinical picture unfolds several years after the start of the process. The following symptoms occur:
- nagging pain in the lower abdomen, migrating to the lumbar region;
- disruptions of the menstrual cycle;
- discomfort during sports, intimacy;
- painful periods;
- disturbances in the functioning of the intestines;
- increased body temperature;
- bloody or yellow-green discharge.
A woman has a slight pain in the lower abdomen on the right or left. Changes in unilateral localization and increased severity of the symptom often indicate a complication - a violation of the patency of the fallopian tubes. In this case, menstruation is often delayed by 2-3 months.
In some patients, during adhesions, the ovary descends to the fundus of the uterus. Sometimes an episiotomy causes a change in the position of the reproductive organ itself.
Diagnosis of pathology
To discover that the ovary is located behind the uterus, a gynecological examination alone is not enough. An ultrasound of the pelvic organs is required. If this method does not reveal the adhesive process, then laparoscopy is performed. Additionally, MRI is used, which makes it possible to detect small changes in the reproductive system.
Ovarian displacement is also diagnosed by other methods, for example, hysterosalpingography - an x-ray examination in which a contrast agent is injected into the cavity of the reproductive organ and fallopian tubes. The procedure is performed from days 5 to 11 of the cycle . Additionally, the patient is recommended to take a vaginal smear for microflora testing.
Treatment of pathology
If the ovary is located behind the uterus, at the initial stage of the pathology it is possible to use medications:
- antibiotics;
- suppositories (for example, Longidase);
- drugs that eliminate inflammation;
- enzymes;
- vitamins and microelements.
It is useful to undergo physiotherapeutic procedures (electrophoresis with the introduction of magnesium, calcium and zinc through the skin). Thanks to this treatment, the adhesions become thinner and stretched. The patient may be prescribed sanatorium treatment (including mineral waters).
Then, when the ovary is close to the uterus, physical activity is recommended. In advanced cases, laparoscopy is performed, the purpose of which is to separate and eliminate tissues connected to each other. After the operation, a special film is applied to the appendages. In addition, a barrier fluid is used to prevent the formation of new adhesions.
During the rehabilitation period, antibiotics and medications are used, the action of which is aimed at preventing the formation of blood clots. The effectiveness of the surgical intervention is then assessed. Physiotherapeutic procedures are prescribed at the discretion of the doctor. Laparoscopy does not provide a 100% guarantee that the adhesive process will not return again and the ovary will not move again.
Other treatments:
- laser therapy based on the impact of special rays;
- electrosurgery aimed at eliminating damaged tissues with high-frequency current;
- aquadissection, in which adhesions are dissected using a water stream.
If the ovary has gone behind the uterus, then gymnastics aimed at eliminating the adhesive process is advisable. Since the pathology is quite serious, it is better to use the methods of official medicine, and use exercises in combination with them.
Chances of pregnancy
As mentioned earlier, the bending of the ovary behind the uterus (left or right) is often a manifestation of the adhesive process. Difficulties in getting pregnant are caused by a violation of the anatomically correct location of the reproductive organs.
A woman who finds out that her ovary has gone behind the uterus, of course, doubts the possibility of conception. To normalize the condition of the reproductive organs, the help of a qualified gynecologist is required.
To get pregnant, you need to undergo treatment. If it is not effective, then IVF is performed. Since adhesions increase the risk of attachment of the fertilized egg outside the reproductive organ, it is necessary to direct all efforts to eliminate it.
Possible complications
First of all, the gynecologist must assess how mobile the ovaries are and identify the true cause of the displacement. Once a definitive diagnosis is made, treatment is required. Otherwise, the following complications may occur:
- transition of the adhesive process to neighboring organs, which is fraught with their displacement;
- disruption of the relationship between the uterus and appendages;
- deterioration of fallopian tube patency;
- ectopic pregnancy;
- problems with ovulation;
- bend of the uterus;
- infertility.
Source: https://pro-acne.ru/venerologiya/yaichnik-pripayan-k-matke-chto-eto-znachit-prichiny.html
Chances of pregnancy
As mentioned earlier, the bending of the ovary behind the uterus (left or right) is often a manifestation of the adhesive process. Difficulties in getting pregnant are caused by a violation of the anatomically correct location of the reproductive organs.
A woman who finds out that her ovary has gone behind the uterus, of course, doubts the possibility of conception. To normalize the condition of the reproductive organs, the help of a qualified gynecologist is required.
To get pregnant, you need to undergo treatment. If it is not effective, then IVF is performed. Since adhesions increase the risk of attachment of the fertilized egg outside the reproductive organ, it is necessary to direct all efforts to eliminate it.
Possible complications
First of all, the gynecologist must assess how mobile the ovaries are and identify the true cause of the displacement. Once a definitive diagnosis is made, treatment is required. Otherwise, the following complications may occur:
- transition of the adhesive process to neighboring organs, which is fraught with their displacement;
- disruption of the relationship between the uterus and appendages;
- deterioration of fallopian tube patency;
- ectopic pregnancy;
- problems with ovulation;
- bend of the uterus;
- infertility.
In addition, if the ovary is close to the uterus, this can lead to its prolapse. With timely initiation of therapy, serious consequences can usually be avoided, so every woman is recommended to undergo preventive examinations by a gynecologist and not delay a visit to the doctor if there are suspicious symptoms.
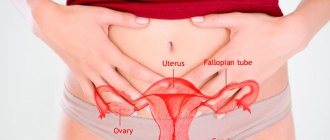
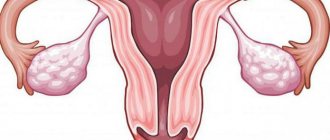
This paired female organ, part of the reproductive system, performs reproductive and secretory functions. The location of the ovaries in women is the same - on the sides of the uterus. The outer side of the glands is attached by a neurovascular ligament to the surface of the pelvis, in the area of the ovarian fossa. The fallopian tubes depart from the ovaries, which actually connect the uterus and glands. In gynecology, the collection of ovaries and fallopian tubes is usually called appendages.
Ovaries in women
Normally, each ovary is located on the side of the uterus. When viewed from the abdomen, these organs are located in the lower part of the abdominal cavity, directly under the inguinal folds. They are attached to the surface of the small pelvis by a ligament of nerves and blood vessels. This area is called the ovarian fossa.
From there the fallopian tubes go to the uterus. The reproductive organs in question have their own peculiarity of location, namely that they are located asymmetrically in relation to each other - one is located slightly higher than the other. Also, the size of the organs is slightly different. Usually the right ovary is larger and heavier than the one on the left. In shape and color they are absolutely identical.
Normally, the reproductive organ is equal to the following dimensions: length - 20-50 mm, width, thickness - 15-30 mm. If there are minor discrepancies, within a few millimeters, then most likely this indicates the individual characteristics of the woman. If the size is much higher than normal, then there is a reason to visit a doctor.
The left ovary is close to the uterus, adhesions
My husband and I have been planning to have a baby for a year, but it doesn’t work out. The spermogram is good. Hormone tests are normal, except for androstenedione, which is twice as high. I decided that this was the reason. A month ago I had an ultrasound, and as a result, both ovaries are multifollicular, but this is all being corrected. And today I was prompted to do another ultrasound and in conclusion: a multifollicular right ovary is a “rosary” symptom and an adhesive process on the left cannot be ruled out, the left ovary is close to the uterus “underlying”, the uterus is tilted back. The ultrasound specialist told me to collect documents for IVF. I was shocked by this diagnosis and what was said. There have never been any inflammations, which is where the adhesions come from. My gynecologist quit, another one will be released only on September 15th.
Girls, I didn’t check the pipes, but how do they check them?
Ovaries close to the uterus
This is a sign of an adhesive process. Have you checked the pipes?
My right ovary is also adjacent to the uterus. This is due to adhesions. But the doctors did not say anything that this could interfere with getting pregnant.
I have it too, is it really adhesions on top of everything?
and I have one just on a short leg, that’s close!! :)))
and my left one is adjacent to the fundus of the uterus. When I'm on my period, the left side always hurts. Maybe it really is something that is interfering with pregnancy..
Girls, I didn’t check the pipes, but how do they check them?
My ovary (right) was also soldered to the corner of the uterus due to adhesions, the uterus was pulled accordingly to the right, I had painful periods, my right side always ached, I had a laparoscopy, the adhesions were cut, the ovary was detached, the uterus was pulled into place, the tube is now tortuous but passable. My G said that this was one of the reasons for infertility (not counting endometriosis) now during menstruation there is no such tension in the side
Good afternoon The lower abdomen hurts very much, often on the left side. I went for a pelvic ultrasound and they said that the left ovary had moved very close to the uterus. Please tell me what the dangers of this are? what could this be from? Will your side always hurt? and will there be problems getting pregnant? Is this normal? Patient age: 24 years
Consultation with a doctor on the topic “The left ovary is adjacent to the uterus”
- 1
Write
question to the doctor 2 Click
ask a question 3 Wait
Get your consultation. To do this, simply ask your question in the box below and we will try to help you.
We need to know your opinion. Leave a review about our service
Hello. I'm 3 weeks pregnant. An ultrasound showed that there was an inflammatory process and the ovaries are adjacent to the uterus and now there are adhesions. They told me to take tests for progesterone and hCG to find out if there was a threat. Tell me how bad it is and what are the chances of a successful pregnancy? Thanks in advance.
The ovaries are attached to the uterus.
Hello. I'm 3 weeks pregnant. An ultrasound showed that there was an inflammatory process and the ovaries are adjacent to the uterus and now there are adhesions. They told me to take tests for progesterone and hCG to find out if there was a threat. Tell me how bad it is and what are the chances of a successful pregnancy? Thanks in advance.
So put the nonsense out of your head and enjoy your pregnancy!! Congratulations.
Yes, and these tests must be taken if there have been miscarriages - they are needed to find out whether you need hormonal support.
2 Registration mark for goods and services of Kimberly-Clark Worldwide Inc., USA. Children's disposable diapers Huggs Ultra Comfort for girls/boys. Virobnik: “Kimberly-Clark s.r.o.”, Czech Republic. Renewal of the state sanitary and epidemiological examination No. 602-123-20-3/6357 dated December 23, 2016, issued by the State Food and Product Service of Ukraine. Children's hygienic diapers-panties HUGGIES® (Haggis) for girls/boys. Renewal of the state sanitary and epidemiological examination No. 602-123-20-3/6356 dated December 23, 2016, issued by the State Food and Product Service of Ukraine. Virobnik: “Kimberly-Clark s.r.o.”, Czech Republic. Haggis Classic.