At 6-12 weeks, a woman registers for pregnancy and immediately receives a referral from a gynecologist for a set of diagnostic measures. The doctor’s special “interest” is the results of urine and smear tests - these indicators are used to judge how the pregnancy is progressing as a whole and whether there is a threat of any complications for the expectant mother. In most cases, it is during urine examination that pathogenic E. coli is detected in the body. The mother and child suffer from the consequences of the disease, so it is important to detect the problem as early as possible and immediately begin treatment of the disease.
General information about E. coli
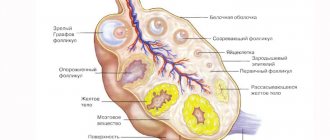
The human intestine is inhabited by a huge number of microorganisms, the vast majority of which are beneficial by participating in metabolic processes. One of the components of the microflora is Escherichia coli or Escherichia coli. It is a type of bacteria that is conventionally divided into pathogenic and non-pathogenic types.
E. coli tolerates the negative effects of external factors well, so it is able to remain viable in water, soil and even feces. It reproduces well in food, so eating contaminated food is considered a guaranteed route of infection.
Causes of appearance in urine during pregnancy
The presence of a pathogenic bacterium is very often detected in a woman’s urine, mainly during pregnancy. A common cause is considered to be a weakened immune system, but in addition to this, experts identify a number of other provoking factors.
- Failure to follow the rules when collecting biomaterial for analysis or using a non-sterile, contaminated container.
- Physiological features of the structure of the organs of the genitourinary system: a short urethra or a small distance between the rectum and the urethra.
- Failure to comply with personal hygiene rules. It is recommended to wash the genitals from front to back to prevent intestinal bacteria from entering the urethra and vagina.
- Diseases or infections transmitted through sexual contact.
- Practice anal-vaginal sex.
- Wearing tight underwear, especially made from synthetic fabrics. This leads to irritation of the skin and penetration of Escherichia into the genitourinary area.
- Pathologies of the excretory system: cystitis, urethritis, urolithiasis, pyelonephritis.
- Features of hormonal regulation during pregnancy.
Another common reason doctors call is the growth of the uterus in the second and third trimester. Increasing in size, it begins to put pressure on the pelvic organs, resulting in their displacement and deterioration in functionality. This provokes stagnation of urine - the optimal condition for the occurrence of bacteriuria.
Causes of E. coli in urine during pregnancy
Women should wash themselves towards the anus. Carelessly moving your hand in the opposite direction can cause a colony of bacteria to appear in the vagina and the appearance of E. coli in the urine. The appearance of bacteria in urine depends on the cleanliness of the sexual partner. Promiscuous sexual intercourse and sexual intercourse (oral-anal) are also ways of getting infection into the urethra. Wearing thong panties that fit tightly to the body can cause infection of the female genitourinary organs due to friction.
Chronic forms of cystitis, pyelonephritis, urethritis often recur during pregnancy. The appearance of E. coli in the urine is promoted by diseases such as diabetes, constipation, intestinal dysbiosis, genital diseases, and caries. If the concentration of bacteria in the urine is low, you will be asked to retake the tests to ensure that the microorganism does not accidentally enter the urine. If the pathogen is still sown, then it’s time to carry out gentle treatment, which will avoid the spread of infection and the use of antibiotics. Cure is 80% of cases when E. coli is detected in the first trimester of pregnancy.
During pregnancy, the urethra shortens and, under the influence of hormones, becomes more dilated. The growth of the uterus, which compresses the internal organs, provokes stagnation of urine in the kidneys and ureters, which leads to the proliferation of microorganisms. Very often, bacteriuria is asymptomatic. A woman may not even notice its presence. But the increasing load on the body during pregnancy and the urinary system, in particular, the weakening of general and local immunity, reveals health weaknesses.
Symptoms
Quite often, the presence of E. coli in the body is not characterized by clinical manifestations, so detection in the analysis comes as a surprise to a pregnant woman. The first signs of deterioration of the condition appear, as a rule, as the immune defense weakens, the fetus grows and the load on the organs of the genitourinary system increases.
In the early stages, a woman may notice a change in the color of urine, later signs of vaginitis. As the infection spreads through the urinary tract, acute inflammation begins to rapidly develop, characterized by the following symptoms:
- increased urination, cutting pain and burning sensation;
- change in the color and smell of urine, sedimentation;
- copious vaginal discharge with a strong unpleasant odor;
- pain syndrome that forms in the lumbar region or lower abdomen;
- hyperthermia, chills, fever;
- profuse sweating;
- attacks of nausea, often ending in vomiting;
- weakness, apathy, lethargy, fatigue.
The above symptoms occur if the kidneys and bladder are involved in the pathological process. Therefore, doctors recommend regular testing. In this way, pathogenic flora can be identified at the earliest stage of the disease.
Possible complications
Escherichia coli belongs to the group of opportunistic microbes. This means that in a healthy body it brings benefits, while when suitable conditions are created, it provokes the development of serious diseases. It has been proven that when the bacterium enters the urinary tract, it causes the development of inflammation, which is progressive and persistent. Its presence in the test urine sample of a pregnant woman is considered a dangerous sign requiring immediate medical intervention.
For woman
E. coli in the urine during pregnancy is a serious signal that should be responded to quickly by seeking qualified medical help. First of all, Escherichia coli negatively affects the body of the expectant mother. Doctors consider the following conditions to be among the most common complications of bacteriuria.
- Premature rupture of amniotic fluid, leading to miscarriage or early onset of labor.
- Detachment of the placenta, disrupting its normal functionality up to its complete cessation.
- The development of pneumonia or sepsis due to infection of organs.
- Ectopic bleeding.
- Damage to the mucous membranes of the gastrointestinal tract.
- Increased pressure.
- Severe forms of gestosis.
- Irreversible kidney damage, development of organ failure.
For a child
Infection of the mother poses a high threat to the fetus, primarily due to the ability of the bacterium to penetrate the systemic bloodstream, and from there, through the placenta, have a destructive effect on the child’s body. By releasing toxins, it can cause irreversible pathological processes or life-threatening diseases:
- congenital anomalies;
- inflammation of the meninges – meningitis;
- hypoxia and intrauterine fetal death.
If the fetus does not become infected during gestation, there is a risk of infection as it moves through the birth canal. As a result of the stick entering the intestines, severe damage to the digestive tract, mental retardation, and cerebral palsy can occur.
Diagnostics
The main method of medical monitoring of the condition of the woman and fetus throughout the entire pregnancy is a general clinical analysis - OAM. In obtaining reliable results, an important role is played by the correct conduct of the preparatory stage and collection of biomaterial. If the recommendations are not followed, there is a high probability of microorganisms entering the sample from outside, which distorts the data and therefore requires a repeat test.
If E. coli is detected in urine, the doctor must prescribe an additional examination, which includes a number of informative, but safe procedures during pregnancy:
- bacterial culture to confirm the presence of Escherichia;
- general blood test and study of its biochemical composition;
- smear from the urethra and vagina;
- Nechiporenko test;
- screening tests;
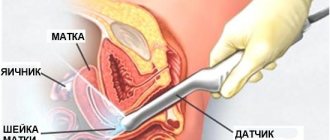
- Ultrasound of the pelvis and urinary system;
- Dopplerometry.
After carrying out diagnostic measures and receiving all the data, the doctor can assess the state of health, identify the severity of the pathology, the nature and extent of damage to the body of the mother and fetus, and only then make the correct diagnosis and select an adequate treatment regimen.
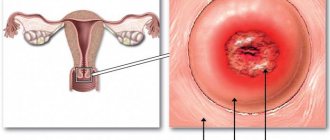
Escherichia coli in the cervical canal during pregnancy
If E. coli is localized in the cervical area, this will certainly become clear as a result of the bacterial culture procedure. This usually confirms the presence of not only E. coli, but also Klebsiella, fungi, and enterobacteria.
Before diagnosing E. coli by culture during pregnancy, a sterile smear is usually taken to determine the number of white blood cells. If the analysis shows an increase in their concentration, an indication for bacterial culture appears. With increased formation of leukocytes, the body usually reacts to various inflammatory pathologies in the pelvic organs (for example, endometritis, cervicitis, inflammation of the uterine appendages).
Treatment
If E. coli was detected in the urine based on diagnostic results, therapeutic measures must be started immediately. Treatment of bacteriuria in women during pregnancy is gentle and is based on the following principles.
- The use of pharmaceuticals that do not pose a threat to the health of the mother and fetus.
- The choice of medications is made taking into account the stage of pregnancy at which the infection was detected.
- Therapy is carried out under constant supervision of the attending physician and regular testing.
Medication
The basis of treatment measures is antibacterial therapy. At first glance, the task is considered difficult, since there are a lot of drugs that can negatively affect the development of the fetus. The choice of absolutely safe antibiotics and the development of a treatment regimen should be the responsibility of the attending physician. At his discretion, the following groups of drugs may be prescribed:
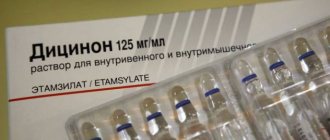
- cephalosporins - “Ceftriaxone”, “Cefoperazone”;
- penicillins – “Oxacillin”;
- amoxicillins – “Augmentin”, “Amoxiclav”;
- macrolides - Azithromycin, Vilprafen;
- anti-inflammatory drugs - Cyston, Canephron;
- antimicrobial - "Furagin".
The type of medication, duration of use and dosage should be selected by the doctor, taking into account the degree of spread of the infection and the severity of the inflammatory process. If extensive lesions are noted, the pregnant woman must be hospitalized.
Your own immunity should help speed up recovery, but since it is weakened, it requires medicinal support. In this case, immunostimulants, vitamin complexes, and medications that strengthen the defense mechanism can be prescribed. These include: “Anaferon”, “Polyoxidonium”, “Imunofan”. Taking bacteriophages is considered safe, and should also be prescribed by a specialist. After completing the course, urine culture is repeated, based on the results of which the doctor decides on further actions.
Traditional methods
Traditional medicine is often prescribed as additional therapy. Of course, pharmacological treatment remains a priority, but the use of “grandmother’s” recipes will help improve the general condition. The doctor will suggest the most effective and safe means for purifying urine from bacterial flora.
- Plantain decoction. Has an antibacterial effect. It should be taken 2-3 times a day for 10 days.
- Cranberry and lingonberry juice. Natural antiseptic and excellent diuretic. Drink a cup daily.
- Rose hip decoction. Diuretic of plant origin. Accelerates urine formation and strengthens the body's protective functions.
- Infusion of celandine. Steam in boiling water and take a quarter glass three times a day.
Hygiene procedures using decoctions of calendula flowers, chamomile, and string herbs are also recommended for pregnant women. It is imperative to take probiotics that can help quickly restore the natural flora of the vagina and intestines.
Prevention
E. coli poses a certain danger to the human body, and especially to women during pregnancy, since it can cause irreparable harm to the development and life of the fetus. To reduce the risk of developing bacteriuria or prevent re-infection, doctors advise taking the necessary preventive measures, the essence of which is as follows.
- Strictly observe the rules of personal hygiene, first wash the external genitalia and vagina (from front to back), then the anal area.
- Use hygiene products without fragrances (ideally, use baby soap).
- Refrain from douching, as this can disrupt the vaginal microflora and weaken its protective functions.
- Regulate your sex life and use barrier contraception.
- Avoid wearing tight clothes and synthetic underwear, giving preference to products made from natural fabrics.
- To avoid stagnation of urine, optimize your water load by drinking enough fluid per day, but without overloading your kidneys.
- Regularly undergo scheduled examinations, take tests and strictly follow all the gynecologist’s instructions.
- To collect biomaterial, use only sterile containers, preferably a disposable pharmaceutical container.
- Organize a proper diet, get rid of bad habits, and lead a healthy lifestyle.
Pregnancy is a difficult period in a woman’s life, therefore, she must show seriousness and responsibility. To do this, she needs to be sensitive to her health, and if there are minor changes in her state of health, she needs to notify her doctor. The measures described above will help minimize the risk of E. coli penetration and prevent the development of bacteriuria.
Source of the article: https://uromir.ru/diagnostika/issledovanija/kishechnaya-palochka-v-moche-pri-beremennosti.html
A little about E. coli
Escherichia coli is a rod-shaped, gram-negative bacteria that inhabits the lower part of the human intestine. They actively participate in metabolism; with their help, vitamin K is synthesized, which affects the permeability of vascular walls. When immunity decreases or pathologies occur, E. coli is able to penetrate internal organs.
E. coli is often found in the vaginal microflora even before pregnancy. A decrease in immunity contributes to its penetration into the woman’s urinary tract and the formation of extensive infectious foci there. A distinctive feature of Escherichia coli strains is the presence of flagella, which help the bacteria quickly spread throughout the body.
Where can the intestinal shelf be found?
To detect E. coli, you need to take a urine test and a genital swab. Subsequently, the collected materials are sent for bacteriological sowing. Such a study consists of the following: part of the material is sent into a nutrient medium, under the influence of which bacteria begin to multiply rapidly.
After a few days, doctors check the results. They depend on how many colonies of bacteria have formed. An antibiotic sensitivity test is also required to determine which medicine destroys the pathogenic microorganism.
To do this, microbes are placed in a Petri dish, and then discs with a certain type of antibiotic on the surface are placed on its surface. If the drug is effective, an empty ring appears next to the disc. This indicates that microorganisms do not multiply.
E. coli in urine
After conception, a woman must undergo a urine test for bacterial culture. It will also need to be repeated at 32 weeks of gestation.
In order for the analysis results to be accurate, the following rules must be followed when collecting urine:
- It is necessary to purchase a container at the pharmacy specifically designed for the test. These jars are sterile.
- It is necessary to collect material immediately after waking up. Then it is necessary to take him to the hospital within 2 hours. If this is not done, additional microorganisms may develop in the urine and the result may be incorrect.
- Before collecting urine, it is recommended to wash your genitals.
- You need to open the jar right before collecting urine. Otherwise, its sterility will be broken.
- First you need to urinate a little, and then pee in a jar. Avoid touching the edges of the jar with your fingers.
- At the end of the procedure, the container must be closed.
An infection in the body can be observed even before pregnancy, without being accompanied by any symptoms. But during pregnancy, it becomes more active due to decreased immunity.
The entry of a microorganism into the genitourinary system can be a consequence of improper personal hygiene and wearing thongs. Some sexual practices can also cause such negative consequences.
In a smear
If the microorganism is found in the smear, this indicates that it is contained in the vaginal area. She can get here in various ways. In this case, bacterial vaginosis develops.
If a pathogen is present here, there is a high probability of it being present within the intestines. Therefore, treatment of the disease must necessarily be comprehensive.
What is the danger of E. coli for a pregnant woman?
E. coli appears in the urine of the expectant mother when immunity decreases. Moreover, since a pathogenic bacterium provokes the occurrence of infectious diseases, the body's resistance is significantly reduced. Which serves as a favorable environment for the penetration of viruses from the external environment. What else is Escherichia coli dangerous for a pregnant woman:
- Early discharge of amniotic fluid occurs. This leads to premature birth or termination of pregnancy.
- From the vagina, the microorganism penetrates the placenta into the bloodstream of the fetus. Due to the high toxicity of the bacterium and the lack of immunity in the child, congenital pathologies occur.
- E. coli often causes meningitis, an inflammation of the membranes of the brain, in a child.
- After infection of the urinary tract, the bacterium penetrates the structural elements of the kidneys and provokes damage to the parenchyma, calyces and pelvis.
- Virulent strains, when they enter the gastrointestinal tract, cause gastritis and gastroenteritis.
- During the passage of the child through the mother's birth canal, infection will certainly occur. After the baby is born, the growth of beneficial microflora in his intestines will be suppressed, and harmful bacteria will begin to actively multiply. The child will be delayed in development or die.
The spread of E. coli throughout the body leads to sepsis and pneumonia. If pregnancy is not controlled, and a pathogenic microorganism has penetrated the placenta, then there is a high probability of fetal death in the uterine cavity.
Tank culture - Escherichia coli in a vaginal smear - how to treat, causes of appearance
Escherichia coli (Escherichia coli) multiplies uncontrollably in the vagina if the acid-base balance is disturbed. As a result, difficult-to-treat inflammation occurs, accompanied by unpleasant symptoms such as burning, itching and redness of the intimate area. .
Escherichia coli or Escherichia coli was discovered at the beginning of the 20th century by the Austrian pediatrician and bacteriologist Theodor Escherich, to whom it owes its name.
Escherichia coli is a bacterium that is part of the physiological bacterial flora of the large intestine. Escherichia coli can appear in the vagina as a result of transmission from the urethra and lower gastrointestinal tract.
This is especially dangerous for pregnant women because not treating the infection before delivery risks infecting the baby during the birth itself.
Escherichia coli in a smear is a cause of infection in women
Escherichia coli bacteria are native to the colon, where they help break down food and produce B vitamins and vitamin K. Although they are beneficial in the colon, they are harmful in other parts of the body.
Their presence in the vagina is likely due to transmission of microorganisms from the lower gastrointestinal tract. The source of genital tract infection may be the passage of pathogens from the urinary tract .
This is especially true for women who have a shorter urethra and its exit close to the vagina and anus, increasing the likelihood of transmitting bacteria between these structures.
Escherichia coli is one of the aerobic bacteria that causes inflammation in the vagina. E. coli in the vagina multiplies uncontrollably, especially as a result of quantitative and qualitative disruption of the natural vaginal microflora.
Physiological microflora provides resistance to bacterial colonization and is an important factor that naturally protects mucous membranes from the formation of potentially pathogenic bacteria and fungi. A decrease in the number of lactic acid bacteria from the genus Lactobacillus occurs mainly during a decrease in general immunity.
Thus, Escherichia coli in the vagina is often a problem for pregnant women. Hormonal changes that occur in expectant mothers change the vaginal pH to alkaline, which promotes the active proliferation of pathogenic microorganisms in the vagina, such as E. coli.
Scientists also report that their presence may be due to hormonal changes after menopause and estrogen deficiency, which ensure normal vaginal microflora.
Escherichia coli in the vagina - symptoms and consequences
Escherichia coli can cause the following symptoms in the vagina: persistent itching, burning, irritation and pain in the intimate area, which increases during urination .
The prerequisites for taking a vaginal smear for Escherichia coli are the presence of white or gray vaginal discharge combined with a fishy odor.
Sometimes there may be complaints about the gastrointestinal tract (nausea, abdominal pain, vomiting and diarrhea) and symptoms from the urinary system (pollakiuria, urination in portions and a feeling of an unemptied bladder).
Untreated E. coli bacteria in the vagina during pregnancy can lead to serious complications for the expectant mother and fetus. There is a risk of miscarriage, premature birth, premature rupture of membranes and perinatal infection in newborns.
How to treat Escherichia coli in the vagina in women?
Treatment of Escherichia coli in the vagina is determined by the gynecologist based on the results of a smear taken from the vagina. Before the examination, sexual abstinence and non-use of vaginal medications for several days are recommended.
Antibacterial cleansers should not be used on the day of the smear test. Vaginal culture for E. coli bacteria is positive if the presence of E. coli bacteria is detected, and a poor physiological flora represented by lactobacilli.
then usually prescribe metronidazole or clindamycin. After completion of therapy, it is necessary to take a control smear from the vagina to assess the effectiveness of treatment.
In addition, gynecological probiotics are used, which, thanks to the content of lactic acid bacteria from the genus Lactobacillus, restore the microbiological balance of the vagina. There are many probiotics on the market, both oral and vaginal in globule form.
It is estimated that these bacteria should make up more than 95% of the total vaginal flora. By achieving the desired low pH, a low pH level provides an additional effect that inhibits further proliferation of pathogens.
How to get rid of E. coli in a smear? Maintaining hygiene
You must practice strict hygiene - wash your hands often, especially after using the toilet and before preparing food.
Intimate hygiene is of great importance. For intimate hygiene, you should use special preparations in the form of a gel or regular glycerin soap, which are hypoallergenic, do not cause irritation and do not affect the natural pH.
It is not recommended to use sponges and washcloths, which are an excellent breeding ground for bacteria. You must remember the correct direction of washing movements during intimate hygiene - from the front to the back . It is necessary to use a separate towel for drying intimate areas.
You should wear breathable cotton underwear and change it frequently. You should beware of tight or tight clothing, which prevents free air ventilation in intimate areas, thereby creating a warm and humid environment, ideal for the growth and reproduction of bacteria. Maintain sexual abstinence until complete recovery.
During therapy, abundant hydration of the body is required. It is recommended to drink boiled or still mineral water and cranberry juice.
Escherichia coli (Escherichia coli) in a smear
Source: https://easytip.ru/escherichia-coli-%D0%B2%D0%BE-%D0%B2%D0%BB%D0%B0%D0%B3%D0%B0%D0%BB%D0% B8%D1%89%D0%B5-%D1%81%D0%B8%D0%BC%D0%BF%D1%82%D0%BE%D0%BC%D1%8B/
How to properly prepare for the test
E. coli quickly develops resistance to antimicrobials and antibiotics. Therefore, she is treated with powerful antibiotics that are unsafe for a pregnant woman. In order not to harm the health of the mother and unborn child without a good reason, gynecologists prescribe a repeat urine test while observing all sterility standards:
- Urine should be collected only in a sterile container. When purchasing containers at a pharmacy, you should pay the pharmacist’s attention to this, since the range of products also includes non-sterile containers.
- You should not eat before collecting urine.
- It is very important to wash your genitals with hypoallergenic soap or shower gel before collecting urine. Then you should blot them with a clean cotton towel.
- The vaginal opening must be closed with a sterile tampon.
- Urine collection should be carried out no earlier than an hour and a half before delivery to the laboratory.
- The container should contain an average portion of urine.
- When collecting, the stream of urine should not come into contact with the labia.
After filling the container, you must quickly cover the container with a screw cap, being careful not to touch the inner surface. If necessary, biological fluid is collected by medical personnel using a sterile catheter.
Why is E. coli found in the urine of a pregnant woman?
It is extremely rare that the cause of the appearance of escherichia coli in the urine during pregnancy is an actively growing uterus. In this case, compression of the lower pelvic organs occurs and their slight displacement, leading to stagnation of urine. Such conditions are favorable for the proliferation of pathogenic bacillus.
Most often, factors for the penetration of E. coli into the body include:
- Sexually transmitted infections, STDs.
- A persistent decrease in the body's resistance to infectious agents.
- Disturbances of the endocrine system, provoking relapses of chronic diseases.
- Untreated pathologies of the urinary system before conception: pyelonephritis, urolithiasis, glomerulonephritis, hemorrhagic cystitis.
- Frequent change of sexual partners before and after pregnancy.
- Anal-vaginal sex.
- Constantly wearing underwear made of synthetic fabrics.
- Wearing thongs increases the likelihood of E. coli strains from the anus entering the vagina, provoking their active reproduction.
And the most important reason for the appearance of Escherichia coli in the urine is neglect of personal hygiene rules, especially infrequent changes of underwear. When washing, you must act in a certain direction. The hygienic procedure should be carried out from the vagina to the anus, and not vice versa. Otherwise, the pathogenic bacterium will easily penetrate the vagina with fecal particles.
E. coli in urine during pregnancy
The expectant mother regularly undergoes a general urine test from the moment of registration until the birth. This is a kind of precautionary measure, thanks to which the inflammatory process can be detected in time. When the pathology is confirmed, the pregnant woman must undergo a bacterial culture procedure (bacterial analysis of urine flora). This will allow you to identify the microorganism that caused the inflammation, find out the degree of its sensitivity to antibacterial drugs and, accordingly, determine the most appropriate treatment tactics.
There are several sources of E. coli entering the urine during pregnancy:
- insufficient or improper hygiene of the genital organs (for example, washing from the anus to the vagina);
- mixed sexual contact (penetration into both the vagina and rectum);
- constant wearing of thongs;
- congestion in the pelvis caused by rapid growth of the uterus.
The norm of E. coli in urine during pregnancy is 105 coli per 1 ml of urine. If an expectant mother comes to see a doctor with complaints characteristic of an inflammatory reaction (general malaise, strong smell of urine, nagging pain in the lumbar region and frequent urination), the threshold normal values are reduced to 104 sticks per 1 ml of urine.
Clinical picture
In the acute course of the inflammatory process, the following symptoms may occur:
- Sharp pain when urinating, incontinence and urine leakage.
- The appearance of an amorphous sediment or drops of urine in the urine.
- Unpleasant smell of urine, change in color. Painful sensations in the lumbar region and (or) abdomen.
- Hyperthermia followed by chills. Increased sweating.
- The appearance of greenish mucus with a pungent odor from the vagina.
- Increased fatigue, lack of appetite.
- Drowsiness, emotional inhibition.
If the kidneys are not involved in the pathological process, then most symptoms will be absent. At the initial stage, only signs of bacterial vaginitis appear.
Treatment of a pregnant woman who detects E. coli in her urine
In addition to the fact that the bacterium causes numerous complications, it can only be gotten rid of with the help of antibiotics. Pregnant women are horrified by this development of events, because everyone knows about the teratogenic effect of antimicrobial drugs. Perhaps the first generation of antibiotics had similar properties, but they have long been replaced by modern drugs that can be used when carrying a child.
Gynecologists always select the safest types of antibiotics for pregnant women, without side effects and with minimal contraindications. In addition, gentle doses of medications will be selected that cannot harm the mother and baby. What drugs to inject during pregnancy should only be selected by a doctor; self-medication can cause serious harm to the child.
Treatment of a pathogenic microorganism during pregnancy is carried out with the following antibiotics:
- Amoxicillin and clavulanic acid (Augumentin, Amoxiclav).
- Penicillins.
- Cephalosporins. During treatment, not the entire range of antibiotics is used, but only some of them, depending on the stage of pregnancy.
These drugs do not have a teratogenic effect or a cumulative effect. Furagin, an antimicrobial drug, has proven itself well in therapy. This is the only nitrofuran derivative that can be used during pregnancy, but only up to 35 weeks. For symptomatic treatment, gynecologists recommend Canephron, a herbal anti-inflammatory drug. Cyston has the same properties, but doctors stopped prescribing it to women due to the risk of allergic reactions to medicinal herbs.
If you notice one of the symptoms of E. coli, you should notify your gynecologist. After passing the tests, gentle treatment can be prescribed. A pregnant woman should wash herself daily with infusions of medicinal herbs:
- Chamomile.
- A series.
- Calendula.
They have disinfectant and antimicrobial properties. Sometimes gynecologists recommend antimicrobial suppositories, especially during short periods of pregnancy.
The rays of ultraviolet light kill all microorganisms, and Escherichia coli is no exception. Physiotherapeutic procedures using radiation are used in conjunction with drug therapy. Antibiotic therapy lasts about two weeks, and then new laboratory tests of the urine are carried out. If E. coli is detected again, differential treatment is carried out to identify effective antimicrobial agents.
To strengthen the body, it is necessary to consume special vitamins, but only those recommended during pregnancy. Conventional complexes contain vitamin A, which, if in excess, can negatively affect the development of the fetus. Immunomodulators and immunostimulants during pregnancy can only be used with the permission of the treating gynecologist.
Escherichia coli in a smear during pregnancy
A woman, having learned about her “interesting situation,” must immediately register and undergo a full medical examination in order to know that her child is not in danger. Significant indicators of the health of the expectant mother are smear and urine analysis. Based on these results, existing pathologies can be identified and immediate measures can be taken to eliminate them.
This study is often the only opportunity to identify a digestive infection in a pregnant woman’s body. The consequences of this disease can be dangerous for both the mother and the unborn baby. Therefore, E. coli detected in a smear during pregnancy is the first signal to think about your health and the future development of the child.
Symptoms:
- malaise, general weakness;
- frequent loose stools;
- nausea accompanied by vomiting. The vomit may contain a greenish tint;
- decreased appetite.
These are the first symptoms that E. coli is present in the body. As a rule, they appear after one day or even a week. If treatment was started quickly, without naive assumptions that it will go away on its own, the symptoms will disappear in a couple of days. Otherwise, the situation may worsen.
It is important to know that if symptoms do not go away for more than two days, be sure to seek qualified help from doctors. And do not self-medicate, taking information from the public domain as a basis. In the case of pregnancy, such actions can lead to disappointing consequences. Therefore, for treatment, contact your obstetrician-gynecologist strictly!
How does intestinal infection affect pregnancy?
Because when carrying a child, the mother’s immune defenses are weakened, this leads to the appearance of various types of infections.
The worst thing that can happen is the breaking of water or premature birth. This, in turn, will lead to infection of the fetus, and there is also a risk of developing pathologies.
They can affect not only his health or appearance, but also lead to death.
There is a certain percentage of probability that E. coli during pregnancy in a smear can penetrate through the vagina into the placenta, and from there into the blood of the fetus. This can lead to the development of a disease such as meningitis.
When this infection enters the urinary tract, it is not eliminated from the body, but, on the contrary, contributes to the development of the pathogenic process.
As a result, the immune defense of a pregnant woman’s body decreases, which makes her most vulnerable to other diseases.
It may be that the infection entered the body before the woman became pregnant and did not manifest itself until certain moments. Therefore, when taking a urine test for flora and undergoing a medical examination, it is successfully detected. Then the doctor begins to think about what medications can be used to cure it. As a rule, antibiotics are prescribed.
Rules for donating urine:
- Buy a special sterile container for analysis. It opens before collecting urine and closes at the end of this procedure. Thus, it will be possible to prevent the entry of various “garbage”.
- Before collecting urine, wash your anus and vagina well. For this, it is recommended to use baby soap because it does not contain fragrances or chemical additives.
- Collect samples no more than an average portion. In this case, you need to make sure not to touch the top layers of the container.
If these three points are observed, you can be completely confident in the reliability of the results.
How can an infection enter the body?
There are several main reasons for this:
- Wearing a thong. Such panties create a rubbing effect, which provokes the penetration of this infection into the urinary system.
- Washing from anus to vagina.
- A sexual act in which a mixture of the flora of the genitourinary and intestinal systems occurs.
In a pregnant woman, an infection of this kind can occur due to intense enlargement of the uterus. But since there are not very many reasons listed, if you take them seriously, this will help protect yourself from infection.
What to do if intestinal bacteria are found in the vagina?
In science, this disease is called “Bacterial vaginosis,” which is characterized by copious discharge.
Medical specialists say that the detected problems in the vaginal microflora indicate possible disorders in the intestines.
The presence of the bacilli in the body of a pregnant woman can lead to serious problems. Therefore, they recommend using complex treatment.
Causes of inflammation:
- improper genital hygiene. First you need to wash the front part, then the anus, and not the other way around;
- constantly wearing thongs. Doctors recommend wearing cotton underwear;
- an intrauterine device is installed;
- indiscriminate change of sexual partners, combined intercourse;
- heatwave;
- diabetes;
- weakened immune defense of the body;
- Frequent douching helps wash out beneficial microorganisms.
Not everyone can guess that E. coli is present in the body. To do this, you need to undergo a medical examination and tests. But, however, there are several signs that suggest the occurrence of such a problem.
For example, there may be copious discharge with an unpleasant odor and pain during sexual intercourse. This also includes itching and burning in the genitals.
These symptoms are very similar to thrush; if you don’t neglect your health, you will be able to avoid its appearance too.
Preventive measures:
- Wash your genitals after urination, bowel movements and sexual intercourse. The main thing in this hygiene is its correct implementation (this was already mentioned a minute earlier).
- If possible, do not use deodorized toilet paper and sanitary pads; they provoke irritation of the mucous membranes.
- If you frequently change sexual partners, it is recommended to use contraceptives (condoms).
- Do not douche frequently. This negatively affects the condition of the vagina. Gynecologists recommend doing this only when seriously necessary. In general, it would be very useful for teenage girls to listen to such lectures from their parents or from the specialists themselves. Unfortunately, most girls do not know how to wash themselves properly, use sanitary pads, and so on. Not to mention the age when they become mothers. Therefore, it is possible that such infections arise against the background of illiteracy.
- After using the drug with the applicator, it is necessary to thoroughly disinfect it.
In order to protect yourself from the occurrence of this disease, it is important to follow these recommendations. Moreover, there are not so many of them that you can’t remember them, and besides, they are quite basic.
Prevention
After treatment, care must be taken to ensure that E. coli does not reappear in the urine:
- Have sex with a condom.
- Observe personal hygiene rules.
- Avoid douching.
- Drink about 2 liters of clean water every day.
- Do not use scented hygiene products.
You should wash yourself after each visit to the toilet and be sure to wash your hands. And it is extremely important during pregnancy to regularly test urine for possible detection of E. coli. The sooner treatment begins, the fewer unpleasant complications will arise.
Source of the article: https://sksochi.ru/prochee/opasno-poyavlenie-kishechnoy-palochki-moche-beremennosti
Escherichia coli
Escherichia coli is a conditionally pathogenic flora. It must be in the intestines. The appearance of E. coli in the urine (Escherichia coli) is not normal. Urine should ideally be sterile. Bacteriuria occurs quite often in pregnant women. Microorganisms are detected in the urine after a bacterial culture test, which is basic when registering a pregnant woman. It is especially important to conduct this study when the norm for leukocytes in a general urine test is exceeded. Then there is an inflammatory process of the urinary tract, which may be caused by bacteria. When analyzing urine for bacterial culture, an antibiogram is drawn up to determine the sensitivity of E. coli to a specific type of antibiotic.