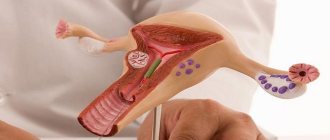
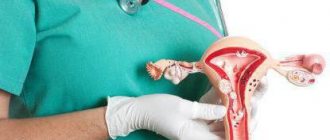
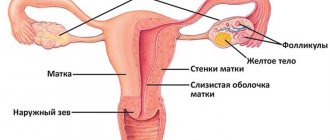
Duplication of the uterus and vagina is a congenital defect that forms during intrauterine development. At approximately the 10th week of pregnancy, paired canals are formed - subsequently they are reduced into the internal female genital organs. When the paired canals are partially connected, two isolated vaginas, two cervixes and two uteruses are formed - from each of them there is an individual fallopian tube. Along with the defect, other problems of the genitourinary system may occur. Sometimes both uteruses are fully functional due to their normal anatomical structure, but often one is less developed.
Causes of the anomaly
Duplication of the uterus and other defects of the female genitourinary organs occur in no more than 1% of women (0.3-0.9%). The reproductive and urinary system is formed in utero from one embryonic germ, which can cause the formation of several types of defects (a double uterus is often combined with a double kidney or other types of congenital pathology of the urinary system). Abnormal intrauterine development of the genitourinary organs in a girl occurs against the background of the following causative factors:
- genetic disorders;
- complicated pregnancy in the mother (threat of miscarriage, gestosis, malnutrition, intrauterine infection);
- long-term use of toxic medications during pregnancy;
- occupational hazard in a pregnant woman;
- severe diseases of internal organs in the expectant mother.
It is often impossible to accurately identify the main cause that led to the occurrence of intrauterine pathology in a girl. Therefore, in all cases when a girl or woman is found to have congenital anomalies in the reproductive system, it is necessary to conduct a full examination to identify malformations of neighboring organs. It is optimal to use the MRI method for this, with which you can obtain maximum useful information about all genitourinary organs.
Uterus doubling options
Malformation of the uterus is almost always combined with pathology of the cervix and vagina. There are several possible types of congenital uterine anomalies.
| Variant of malformation | Description |
| Full doubling | 2 uteruses and 2 vaginas are completely separated and separated from each other |
| Incomplete doubling | 2 isolated parts of the reproductive organs (uterus and vagina) in a certain area are connected by a fibromuscular septum |
| Complete doubling with one vagina | 2 uteruses, 2 cervixes and 1 vagina |
| Double organ with one cervix and vagina | 2 uteruses, but the cervix and vagina are presented in 1 version |
| Duplication of the uterus with a rudimentary horn | One half of the organ looks normal, and the second is underdeveloped and is represented by a defective cavity |
| Two-horned | The uterine cavity is deformed in the upper part, partially dividing the organ into 2 halves |
| Saddle | The fundus of the uterus is moderately deformed without dividing the organ into 2 parts |
| Internal partition | A thin fibrous septum inside the uterus separates the organ completely or partially |
It is not always the case that a young woman experiences typical symptoms and manifestations, so a congenital defect in the reproductive system is discovered by chance at the stage of preconception preparation or during an examination for infertility. The asymptomatic course of the disease is especially common with erased and unexpressed variants of doubling (bicornuate, saddle-shaped). It is much worse if the anomaly of the genital organs is combined with a delay in the outflow of menstrual blood: in this case, typical symptoms will become the basis for an accurate diagnosis.
Classification of pathology
More often than others, complete duplication of the uterus and vagina is diagnosed, in which the internal genital organs are in contact or separated from each other by the rectum or bladder. Modern medicine classifies pathology according to the following criteria:
- Duplication of the cervix and uterine body with one vagina;
- Duplication of the uterine body with one vagina and cervix.
In the latter case, it is possible to form:
- Intrauterine septum;
- Saddle uterus;
- Bicornuate uterus;
- Uterus with a rudimentary horn.
With simultaneous duplication of the uterus and vagina, the following is observed:
- Unicornuate uterus;
- Complete underdevelopment of two vaginas;
- Complete absence of two vaginas;
- Partial underdevelopment of one vagina.
In medical practice, there is such a phenomenon as kidney aplasia on the side where the pathology of organ development is located.
Symptoms of congenital pathology
Manifestations of congenital pathology depend on the form of uterine duplication. There are 2 groups of defects possible:
No retention of menstrual blood in the uterine cavity
The vast majority of congenital anomalies of the uterus are represented by defects in which a woman has normal periods. With a regular cycle, women who do not have an intimate life will not have any symptoms or unpleasant manifestations of congenital pathology. With the onset of sexual activity, problems may arise associated with the act of love, which happens with a double vagina against the background of complete doubling. The main symptoms occur in women who want to give birth to a baby. With uterine abnormalities without menstrual problems, the following manifestations are possible:
- threat of miscarriage at any stage of pregnancy;
- spontaneous abortion in the early stages;
- late miscarriages;
- habitual miscarriage;
- premature birth;
- infertility.
In all cases of prematurity or in the absence of a desired pregnancy, it is necessary to do a full examination, starting with safe and highly informative examination methods (ultrasound and MRI).
Duplication of the uterus is an unpleasant malformation of organs
Defects with delayed blood outflow
The lack of communication between one part of the uterus and the cervix and vagina is the reason for the retention of menstrual blood and the appearance of the following symptoms:
- abdominal pain associated with menstrual periods;
- detection of a tumor-like formation gradually increasing in size in the lower abdomen.
Typically, such symptoms occur when the uterus is doubled with a functioning rudimentary horn. If the underdeveloped area of the double organ communicates with the cervix, then the following problems are possible:
- bleeding before and after menstruation;
- heavy periods;
- ectopic pregnancy.
Any types of defects can lead to the formation of genital endometriosis with typical symptoms.
Duplication of the uterus and pregnancy
Signs of duplication of internal genital organs
Clinically, a genetic defect may not manifest itself in any way until the onset of the first menstruation. Six months after its onset, concomitant diseases arise in parallel:
- Hematosalpinx . If menstrual blood does not come out naturally, it accumulates in the fallopian tube - in other words, hemorrhage occurs into the cavity of the oviduct.
- Hematometra . The pathological condition develops due to the inability to release bloody menstrual discharge. As a result, they accumulate directly in the body of the uterus.
- Hematocolpos . When the hymen becomes fused, menstrual blood begins to accumulate in the vagina.
Symptoms of duplication of the uterus and vagina are individual for each condition:
- Hematosalpinx causes “acute abdomen” syndrome, expressed in the form of paroxysmal severe pain. The disease is accompanied by fever, dysfunction of the gastrointestinal tract and genitourinary system. The skin is pale, reflex vomiting may occur, but the abdomen is soft on palpation.
- Symptoms of hematometra depend on the volume of accumulated menstrual flow and how long ago the disease developed. The pain may be minor or cramp-like. A feeling of heaviness in the lower abdomen is accompanied by cramps. Chills appear, and discomfort may occur in the tailbone or lower back.
- The only obvious symptom of hematocolpos is constant pain in the lower abdomen, reminiscent of contractions. In this case, menstruation is absent, although all the signs of its onset are expressed. The vaginal muscle groups are stretched due to incoming secretions.
In all of these pathologies, pain is weakly or not at all relieved by analgesics and antispasmodics. The bursting pain only intensifies, so under no circumstances should you put off a visit to the doctor!
Duplication of the uterus and pregnancy
The desired conception against the background of complete doubling of the reproductive organ is quite possible. Pregnancy begins on the side where the egg is released from the ovary. The beginning of pregnancy may be accompanied by the following symptoms:
- menstrual-like reaction during pregnancy (a woman experiences scanty bleeding on the days of her expected period);
- brown discharge in the first months of pregnancy (rejection of the endometrium from the part of the uterus where there is no fertilized egg);
- nagging pain in the abdomen.
All these manifestations are similar to typical symptoms of a threatened miscarriage, so the doctor will prescribe maintenance treatment or refer you to the hospital. If no serious problems arise in the first stages of fetal development, then the woman, with constant monitoring and treatment, carries the fetus to term and gives birth to a healthy baby.
In difficult cases of infertility associated with uterine duplication, IVF is performed. After a full examination, including MRI, the fertilized “in vitro” egg is implanted in that part of the future fetal sac where conditions for gestation are most optimal.
Fetal development with incomplete duplication of the uterus
Diagnosis of uterine duplication
The main methods for identifying various types of abnormal structure of the reproductive system are the following studies:
- transvaginal ultrasound;
- hysteroscopy;
- MRI;
- laparoscopy.
At the first stage of the examination, preference is given to non-traumatic methods - ultrasound and MRI. The doctor can easily detect a saddle-shaped and bicornuate uterus with an ultrasound scan. Endoscopic techniques are optimal when combining diagnosis and treatment.
Visual examination of the inner surface of the uterus (hysteroscopy) allows you to detect the septum and immediately remove the developmental anomaly. External examination of the uterus during laparoscopy is combined with an operation to remove a non-functioning part of the organ in the presence of a rudimentary horn.
What will a tomography show when the uterus is doubled?
MRI for double uterus
Magnetic resonance imaging allows you to obtain a three-dimensional image of the reproductive and urinary organs. MRI examination is indicated in the following cases:
- for all types of defects with a delay in the outflow of menstrual blood;
- to diagnose the causes of uterine infertility;
- at the stage of prenatal preparation after untimely termination of a desired pregnancy;
- with defects of the external genitalia that create difficulties in intimate life;
- with congenital anomalies of the urinary organs;
- in case of doubts and suspicions after ultrasound diagnostics.
The undoubted advantages of MRI are the safety and high information content of the examination: the absence of radiation exposure and the identification of precise anatomical changes in the reproductive system become the main factors for the mandatory use of magnetic resonance imaging for congenital anomalies of the genitourinary organs.
On our website you can find up-to-date information about MRI clinics, choose a place for a diagnostic study, make an appointment online or by phone, find out the exact cost and select the optimal time for the examination. You can also undergo an MRI at the price you specify yourself - details here.
Uterus division - incomplete removal
Diagnosis
It is important to make a timely and accurate diagnosis, since errors can lead to unnecessary surgical interventions. Diagnosis of duplication of the uterus and vagina, in which there is a violation of the outflow of menstrual flow, is often difficult. Pain may indicate inflammation of the appendix or ovaries, so a full examination is necessary, which includes:
- Ultrasound . This study can only detect compactions in the pelvic organs, which provokes a diagnostic error. If the gynecologist does not consider the possibility of having a vaginal septum, the patient may go to the operating table, but surgery will not bring the desired result. An ultrasound will give a correct picture of typical pathologies; in addition, the abdominal organs should be examined to confirm or exclude other anomalies.
- MRI . It is considered the most informative and accurate diagnostic method, but it must be carried out in a frontal projection. The classification of the defect, the size of the internal genital organs and the volume of accumulations of menstrual discharge at the site of pathology are established. After MRI, you can correctly formulate further therapeutic tactics and select the optimal surgical option.
- Colposcopy . It is carried out after the initial examination of the patient and allows an initial diagnosis to be made. During the examination, abnormalities in the condition of the cervix are determined, and when the organ is doubled, its location and size ratio are studied.
- Hysteroscopy . The procedure is performed under general or local anesthesia and is used in rare cases.
- Laparoscopy . It is considered a minimally invasive method and is used more in surgery than in diagnosis.
Only a doctor can decide which diagnostic method is most optimal in each specific case. To make a correct diagnosis, you must honestly answer the gynecologist’s questions without hesitation.
Treatment of uterine duplication
In the absence of problems with the outflow of menstrual blood, duplication of the uterus does not require mandatory surgical intervention. The saddle and bicornuate form of the pathology extremely rarely leads to serious consequences, being an unpleasant feature of the main reproductive organ.
If difficulties arise during intimate life, infertility and pathology with retention of menstrual blood, surgery will be required.
Surgical treatment is indicated in the following cases:
- complete duplication of the uterus, in which a woman has an abnormal vaginal structure;
- the presence of a closed rudimentary uterine horn;
- an open and underdeveloped part of the double uterus, in which an ectopic pregnancy can occur;
- habitual miscarriages associated with doubling of the uterine cavity;
- septum in the uterus;
- a combination of uterine defects and gynecological diseases (endometriosis, fibroids, ovarian cysts).
The choice of surgical technique is individual and depends on the woman’s desire to bear and give birth to a child. In most cases, it is quite possible to preserve a woman’s reproductive function and ensure the absence of problems in her intimate life.
Duplication of the uterus and vagina
The most common doubling options:
- duplication of the uterus and vagina;
- duplication of the uterus and vagina with partial aplasia of one vagina;
- bicornuate uterus:
- uterus with an additional closed functioning horn;
- saddle uterus;
- uterus with a septum (complete or incomplete).
Clinic.
With complete duplication of the uterus and vagina, patients do not complain, and the malformation is discovered by chance during ultrasound or in connection with any surgical intervention. In patients with complete duplication of the uterus and vagina and partial aplasia of one of them, menstrual blood accumulates in a confined space, and therefore, on the days of menstruation, 3-6 months after the onset of menarche, severe bursting pain in the lower abdomen (algodysmenorrhea) appears, which is not relieved by painkillers and antispasmodic drugs. Sometimes there is a fistula opening in the septum between the vaginas. In these cases, menstrual blood partially enters the full vagina, but most of it is retained in a confined space. Patients who have a fistula complain of purulent discharge from the genital tract due to a secondary infection.
With a bicornuate uterus with an additional closed functioning horn, teenage girls complain of cramping pain in the lower abdomen during menstruation, and they arise with the onset of menarche and are explained by the formation of hematometra. The saddle uterus, like the uterus with a septum, usually does not have clinical symptoms in adolescence.
Diagnostics
duplication of the uterus and vagina with impaired outflow of menstrual blood often causes difficulties. Frequent diagnostic errors lead to unnecessary surgical interventions, even radical ones (appendectomy, removal of appendages, removal of one of the uteruses, etc.).
Upon objective examination, the external genitalia in patients with duplication of the uterus and vagina are not changed. With complete duplication of the uterus and vagina, vaginoscopy reveals two cervixes in each vagina. If one vagina is partially applause, then only one full vagina is available for inspection, in the dome of which one cervix is visualized. With hematocolpos of a partially aplastic vagina, one of the walls of a full vagina (left or right) bulges into its lumen. Sometimes, when the hematocolpos is large, its lower pole reaches the hymen. Rectal-abdominal examination does not always allow one to clearly identify two uteruses. Appendages are usually not identified. Hematocolpos of a partially aplastic vagina is palpated as a formation of tight-elastic consistency, immobile, slightly painful, the lower pole of which can be located at a distance of 1-5 cm from the anus. In patients with a fistulous tract, purulent discharge usually increases sharply during a rectal-abdominal examination.
Ultrasound of the pelvic organs provides reliable information for typical variants of duplication of the internal genitalia, allows you to determine the size of the uterus and the size of hematocolpos. An ultrasound of the abdominal organs and retroperitoneal space in the area of the kidneys is mandatory, since complete doubling of the uterus with partial aplasia of one of the vaginas is usually accompanied by agenesis of one kidney. In the case of atypical forms of duplication, the most valuable information that predetermines the choice of surgical intervention is provided by MRI, and the study should be carried out in the frontal projection. In some observations, in order to clarify the nature of the anomaly during duplications, it is necessary to perform hysteroscopy and laparoscopy.
Treatment.
Surgical treatment for teenage girls with duplication of the internal genitalia is indicated only when the outflow of menstrual blood is impaired, for example, with complete duplication of the uterus and vagina with partial aplasia of one of them. If there is an additional closed functioning uterine horn, its removal is indicated.
With a septum in the uterus, the issue of surgical correction is resolved only in case of reproductive dysfunction.