Causes Symptoms Timing Diagnostics Treatment Useful tips Forecasts Prevention
A miscarriage in medicine is a spontaneous (not artificial) termination of pregnancy by the body itself, which for some reason can no longer bear a fetus. A very tragic ending, because of which families collapse, young parents become depressed and are very worried. Very rarely does this happen unexpectedly. Most often, it is possible to make a timely diagnosis, which sounds like a threat of miscarriage, and begin treatment as quickly as possible, which saves mother and baby.
Everyone wants to avoid this condition, which is why it is so important to know as much information as possible about it in order to prevent, recognize, and treat it in time.
List of effective hemostatic drugs
The regimen for taking hemostatic drugs for uterine bleeding is determined by the doctor. Patients are prescribed intravenous and intramuscular injections, IVs are placed, and pills are prescribed. The following drugs are used for treatment:
- "Dicynon." It is considered the most effective drug. Injections with the medicine take effect within 10-15 minutes. Dicinone for uterine bleeding during menstruation is taken in tablets.
- “Countrykal.” Homeostatic drug for intravenous administration.
- "Vikasol". A synthetic drug, an analogue of vitamin K, administered intramuscularly and orally.
- "Tranexam." Available in tablets and as a solution for intravenous injection. Tablets are a powerful hemostatic agent until the doctor arrives.
- Oxytocin and Methylergometrine are hemostatic agents that contract the uterus. Used in cases of postpartum pathologies.
- "Aminocaproic acid" is a homeostatic drug for intravenous administration.
- “Calcium chloride” is an intravenous drug with a “hot injection” effect.
- "Fibrinogen." Powder for injection, human blood preparation. Used with aminocaproic acid.
- Liquid extracts of nettle and yarrow are taken dropwise in the treatment of dysfunctional menorrhagia.
Cost of the drug
Depending on the form, the medicine may have different costs.
When purchasing a medication, you should take into account the region and type of pharmacy. The price category of the medicine also depends on this. Etamzilat tablets in an amount of 10 pieces cost approximately 50 rubles. However, they may have a different trade name - “Dicynon”. If you need to purchase an injection solution, then be prepared to pay 150 rubles for 10 capsules. The volume of each ampoule is 2 milliliters.
Etamsylate (Etamsylate, Etamzilat).
Indications for use:
For the prevention and treatment of bleeding during and after surgical operations in gynecology, obstetrics, otolaryngology, urology, ophthalmology, dentistry and plastic surgery;
For the prevention and treatment of capillary bleeding of various locations and origins: metrorrhagia, hematuria, primary hypermenorrhea, nosebleeds, bleeding gums, hypermenorrhea in women with intrauterine contraceptives.
Mode of application:
For menorrhagia, starting from the 5th day from the expected start of menstruation until the 5th day of the next menstrual cycle, take 3-4 tablets per day.
After surgery, until the risk of bleeding disappears, take 1-2 tablets every 6 hours.
The daily dose for children corresponds to half the dose for adults.
Side effects:
The endocrine system in very rare cases can react with acute porphyria. Back pain is rare.
All side effects are mild and transient.
Severe leukopenia was often observed in children taking Etamsylate to prevent bleeding in acute lymphatic and myeloid leukemia.
Pregnancy:
Interaction with other drugs: Taking rheopolyglucin during administration prevents the latter's antiaggregation; taking it after administration of rheopolyglucin does not have a hemostatic effect. Acceptable communication with aminocaproic acid, vikasol.
Compound:
excipients: calcium hydrogen phosphate dihydrate, sodium metabisulfite (E 223), potato starch, povidone, calcium stearate.
Additionally: The drug is used for children over 6 years of age. Do not prescribe to children with hemoblastosis.
In patients with previously recorded thrombosis or thromboembolism, use with caution. The drug is ineffective if the platelet count is low. Treatment of patients with impaired blood coagulation system parameters with Etamzilat must be supplemented with the introduction of drugs that eliminate a deficiency or defect in blood coagulation factors.
Treatment of patients with impaired blood coagulation system parameters with Etamzilat must be supplemented with the introduction of drugs that eliminate a deficiency or defect in blood coagulation factors.
Caution is required when working with vehicles or machinery, as dizziness may occur.
Manufacturer:
Attention! To make information easier to understand, these instructions for use of the drug Etamzilat have been translated and presented in free form on the basis of the official instructions for medical use of the drug. Before use, read the leaflet included directly with the medication. Expecting a baby is certainly associated with tender and pleasant feelings
During this period, every woman tries to take special responsibility for her health so that the baby develops normally and is born on time. However, sometimes pregnancy is accompanied by quite serious problems and causes a lot of anxiety in the expectant mother.
Expecting a baby is certainly associated with tender and pleasant feelings. During this period, every woman tries to take special responsibility for her health so that the baby develops normally and is born on time. However, sometimes pregnancy is accompanied by quite serious problems and causes a lot of anxiety for the expectant mother.
Troubles often occur in the early stages of pregnancy. At this stage, pregnancy may be complicated by uterine bleeding, which indicates abnormalities in the development of the placenta and creates a threat of miscarriage. Etamsylate is one of the drugs that helps women save a child. How to properly use Etamzilat during pregnancy?
Are there any side effects and contraindications?
The instructions for each homeostatic drug indicate contraindications associated with hypersensitivity to components, vascular and blood pathologies:
- thrombosis;
- thrombophlebitis;
- malignant blood diseases;
- acute myocardial infarction;
- increased blood clotting.
Medicines that should not be prescribed to people with kidney disease (failure, pyelonephritis), urolithiasis:
- "Ascorutin";
- "Transcam";
- Water pepper extract.
Side effects that can be caused by hemostatic drugs during menstruation and abnormal uterine bleeding:
- heartburn;
- headache;
- allergy;
- facial redness;
- dizziness;
- nausea;
- diarrhea;
- tachycardia.
Learn how to tell the difference between periods and bleeding.
Indications for use and release form
Dicynone is indicated as a therapeutic and prophylactic agent for internal and external bleeding of various origins.
There are several ways to use it:
- oral (inside);
- intramuscular;
- intravenous;
- retrobulbar;
- local (tampons and gauze bandages).
Dicinone is prescribed in the following cases:
- to eliminate post-traumatic bleeding;
- to prevent blood loss during surgery;
- for diseases associated with bleeding (gynecological pathologies, cerebral infarction, lung and gastrointestinal diseases);
- to prevent hemorrhages in premature babies.
In pharmacies the drug is presented in the form of tablets and ampoules.
The tablets are available in two versions: the dosage for children contains 0.05 grams of ethamsylate (active substance), and the dosage for adults contains 0.25 grams.
Packaging: 100 pcs. costs about 400 rubles. Ampoules are also presented in 2 versions: 12.5% solution, 2 ml, 5% solution, 1 ml. A package of 50 ampoules costs an average of 650 rubles.
Reviews about the effectiveness of the drugs
Nadezhda, 50 years old I had an incident during my archaeological practice as a student. My periods were normal at first, but then very heavy. Nothing hurt, but it was scary. There are only men around - it’s a shame to complain. I was saved by a teacher who had with her a liquid tincture of nettle, a folk remedy for ulcers. It turned out that it also helps with bleeding.
Tatyana, 60 years old I encountered this problem during menopause. I didn’t know how to stop uterine bleeding during menopause, and generally considered it normal. She consulted a doctor when she began to lose consciousness from blood loss. They did a cleansing, put on IVs, and prescribed Vikasol. The next time, at the first sign, I took Dicinon. She never went to the hospital again.
Larisa, 28 years old I started bleeding on the first day of taking birth control pills. I immediately ran to the gynecologist. She prescribed me Dicinon and said that it is one of the best hemostatic drugs for uterine bleeding. From her I learned that you can take it for any other bleeding. I have added this medicine to my home medicine cabinet!
Attention! The information presented in the article is for informational purposes only. The materials in the article do not encourage self-treatment. Only a qualified doctor can make a diagnosis and give treatment recommendations based on the individual characteristics of a particular patient.
Hemostatic injections during pregnancy
» Nutrition » Hemostatic drugs during early pregnancy
Dicinone during pregnancy
During pregnancy, every woman is especially careful about her health and is suspicious of even the slightest suspicion that something is going wrong. All women during this period try to be as attentive as possible to what they eat, drink or do.
This is understandable, because now they are responsible not only for themselves but also for the future child, their child. But not everything can be controlled and undesirable effects may appear, and sometimes even dangerous ones, such as bleeding of various origins.
Dicinone during pregnancy is a drug that can come to the rescue in such moments.
Let us immediately draw the attention of all expectant mothers to the fact that this medication can only be used with the permission of a medical specialist who will be able to assess how harmless the use of this medication will be directly during this period of time. If the potential benefit of such treatment significantly exceeds the possible risk to the fetus in the womb, then, of course, this medication will be prescribed.
A hemostatic drug, used during pregnancy strictly as prescribed by a doctor, for bleeding, bleeding, chorion or placental abruption. It can also be used for bleeding of a different nature, for example, for very severe nosebleeds. If indicated, it is allowed from the first trimester.
In what cases can you resort to the help of this pharmaceutical?
If we talk about the period of pregnancy, then in this case Dicinon is used most often to combat bleeding, as well as in situations where chorion or placental abruption occurs.
There are also cases when Dicinon is prescribed to expectant mothers to stop nosebleeds.
If bleeding developed during lactation, then the child should be switched to artificial feeding, after which the woman will be able to resort to the help of Dicinon.
Feedback on using Dicynone during pregnancy
I will never forget all the horror that I had to experience in the first trimester of pregnancy. About a month after I found out I was pregnant, I started bleeding.
My horror knew no bounds, and all because I prepared very carefully for the conception of this child. Doctors prescribed Dicinon to me already in the seventh week of pregnancy.
I had to resort to using this pharmaceutical product, and it really helped me.
Use of Dicinon in case of threat of miscarriage
The threat of miscarriage is a fairly serious matter, which is why when making this type of diagnosis it is very important that the pregnant woman tries with all possible and impossible forces to ensure complete peace and comfort. This is only possible with strict bed rest. In some cases, expectant mothers are not even allowed to get out of bed.
In addition to rest, expectant mothers who are at risk of miscarriage should also take help from some pharmaceuticals. The very first thing you should do is take sedative medications such as valerian tablets. In the fight against this condition, you cannot do without antispasmodic medications, since they can significantly improve your overall well-being.
Dicynone is another pharmaceutical drug that you simply cannot do without if there is a threat of miscarriage. This medication is taken when there is a threat of miscarriage, twenty-five milligrams in the morning, afternoon and evening.
It is also important to note the fact that this pharmaceutical drug is prescribed to pregnant women in the form of tablets and not injections. Twenty-five milligrams of this product is one tablet of Dicynon.
Therefore, the expectant mother should take three tablets a day.
In conclusion of this article, it is worth noting that this type of condition can be prevented in most cases. To do this, you just need to get rid of all existing ailments even before conceiving the baby. By completing this step, you can be one hundred percent sure that the development and growth of the fetus will proceed very well. A healthy mother means a healthy fetus.
» Articles » Pregnancy » Pregnancy has occurred?! Bleeding during pregnancy in the early and late stages
Bleeding during pregnancy is the most common pathology. And this is not just a pathology, but also a serious complication, which, unfortunately, not every pregnant woman is aware of. This is primarily due to the common misconception that you can have periods during pregnancy. But in fact, there should be no bleeding normally during pregnancy.
Very rarely (in 3% of cases out of 100), some pregnant women experience slight spotting bleeding at the very beginning of pregnancy, when the woman does not yet know about her pregnancy. This occurs at the moment of attachment of the fertilized egg to the uterus, and, as a rule, corresponds to the expected period of menstruation. Only in this case is bleeding normal.
In other cases, any bleeding is regarded as a pathology
Causes of bleeding during pregnancy
Bleeding can occur both early and late in pregnancy. Depending on how early or late the bleeding occurred, we can assume the pathology that caused the bleeding.
Bleeding in early pregnancy (before 12 weeks of pregnancy) may indicate:
- about the beginning of a miscarriage; - about a hydatidiform mole.
Bleeding in late pregnancy (after 12 weeks) may be due to abruption or placenta previa.
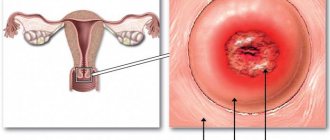
It should be noted that if bleeding occurs during pregnancy, this does not mean that it is associated specifically with fetal pathology. The reason for this may also be exacerbation of gynecological diseases in the expectant mother - cervical erosion, uterine fibroids, cervical canal polyps, and so on. Bleeding can also be caused by a banal injury to the genital organs.
Bleeding during pregnancy can be of varying intensity - spotting, moderate or heavy with clots. Quite often, bleeding is accompanied by pain. The pain can be intense and sharp, spreading throughout the entire abdomen. Often they resemble contractions, as happens, for example, with a miscarriage.
Or there may be a slightly noticeable nagging pain in the lower abdomen. In addition to pain and bleeding, a pregnant woman’s blood pressure decreases, her pulse quickens, and weakness appears. But it is impossible to make a diagnosis based on the nature and intensity of pain and bleeding, since with the same pathology these indicators differ in different women.
If the bleeding is insignificant, this does not mean that you need to lie at home and wait for it to pass. Any bleeding during pregnancy is a reason for an emergency visit to a gynecologist. Such conditions can be dangerous for both the life of the fetus and the mother.
Diagnosis of the cause of bleeding during pregnancy
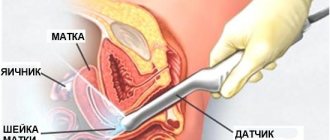
In order to identify the exact cause of bleeding, an examination by a gynecologist and a series of diagnostic studies in a hospital or maternity hospital are necessary.
During the examination, the doctor takes a smear from the vagina. A pregnant woman undergoes a general and biochemical blood test, a coagulogram, a blood test for HIV, hepatitis, and syphilis; general urine analysis. Her blood type and Rh factor are determined. An ultrasound of the pelvic organs and fetus is required.
Further, depending on the identified pathology, additional studies may be prescribed.
So, in case of a miscarriage or a non-developing pregnancy, the blood is additionally examined for hCG (human chorionic gonadotropin), hormones, and tests are taken for TORCH infections (herpes, rubella, cytomegalovirus, toxoplasmosis); smear for sexually transmitted infections. If an ectopic pregnancy is suspected, a diagnostic laparoscopy is performed. In cases of hydatidiform mole, the level of hCG is also examined.
To diagnose the cause of bleeding in late pregnancy, additional studies, as a rule, are not required, due to the high informativeness of ultrasound.
Treatment of bleeding during pregnancy
Treatment is prescribed depending on the pathology and stage of the disease. When a miscarriage begins, measures should be aimed at maintaining the pregnancy and stopping bleeding.
If, according to the results of an ultrasound, the fetus is viable, in the early stages of pregnancy hemostatic drugs (Ditsinon), antispasmodics to reduce the tone of the uterus (No-spa, suppositories with papaverine), hormonal drugs - gestagens (Duphaston or Utrozhestan) are prescribed until the 16th week of pregnancy to maintain progesterone levels - “pregnancy hormone”, vitamins and microelements (vitamin E, Iodomarin, folic acid, MagneB6). If the effect is good, the bleeding stops and the pregnancy continues. If a miscarriage does occur and the discharge is profuse, the uterine cavity is curetted and the remnants of the fertilized egg are removed.
When the diagnosis of a “frozen” pregnancy or hydatidiform mole is confirmed, as in the case of a miscarriage, curettage of the uterine cavity is indicated. After curettage, the hormone Oxytocin and hemostatic drugs are prescribed to contract the uterus. Bloody discharge after curettage stops after a week.
For ectopic pregnancy, treatment is surgical. A laparoscopy or laparotomy is performed and the affected fallopian tube is removed or the fertilized egg is squeezed out of the tube.
In case of placenta previa, if the discharge is insignificant, antispasmodics, magnesium drips, beta-adrenergic agonists (Ginipral), antiplatelet agents (Trental or Curantil) and vitamins are prescribed to maintain pregnancy. With placenta previa, bleeding may continue until delivery.
All this time the woman is supposed to stay in the maternity hospital. When reaching full term (38 weeks of pregnancy), a cesarean section is performed. If the bleeding is heavy, a cesarean section is performed as an emergency, even if the fetus is premature.
To compensate for blood loss, infusion therapy is performed (transfusion of fresh frozen plasma and red blood cells).
If placental abruption is suspected, an emergency cesarean section is performed, regardless of the gestational age and fetal viability. In parallel, infusion therapy is carried out.
All women with Rh-negative blood immediately after curettage, surgery for ectopic pregnancy and cesarean section are administered anti-Rhesus D-immunoglobulin to prevent Rh conflict between mother and fetus when fetal blood enters the mother's bloodstream.
All pregnant women who have experienced bleeding and managed to maintain pregnancy are advised to have sexual abstinence and emotional peace.
Many drugs that are prescribed in the hospital must be used after discharge, even if there is no bleeding, in order to protect yourself from the repeated threat of miscarriage.
If bleeding reappears, the pregnant woman should also immediately contact a gynecologist.
In the rehabilitation period, after stopping the bleeding, sedatives are used - tinctures of motherwort or valerian. Non-drug and physiotherapeutic treatment is recommended - acupuncture, endonasal galvanization, and so on.
As for traditional medicine, except for tinctures of motherwort and valerian, which have been used in obstetrics for a very long time, it is better not to use other herbs for bleeding, since in most cases they are ineffective, and in the worst case, harmful during pregnancy and can further aggravate the situation.
What is a hot shot
Hot prick is a non-medical term. This is a common injection of calcium chloride, during which heat begins to spread throughout the patient’s body, because. Due to the dilation of blood vessels, an increased volume of blood passes through the body. The skin of the face, neck and chest may become red. This condition passes very quickly, within a few minutes.
If the drug is injected quickly into a vein, some patients experience nausea, vomiting, dizziness, but the body temperature remains normal.
The most popular injections from the hot series are calcium gluconate, magnesium and calcium chloride.
Gluconate and calcium chloride have similar therapeutic effects, but chloride is more active and causes a greater irritant effect. It is injected strictly into a vein. If the product gets under the skin, tissue necrosis is possible. Calcium gluconate is administered both intramuscularly and intravenously.
Scope of application
The most commonly used is calcium chloride (calcium chloride), which has a positive and beneficial effect on the entire human body. It is able to stop the inflammatory process, increase immunity, and eliminate the negative effects of all kinds of infections.
Injections are given when:
- insufficient amount of calcium in the body;
- skin diseases;
- allergic reactions;
- for problems with the musculoskeletal system;
- intoxication of the human body with fluorine and magnesium salts;
- kidney diseases and hepatitis;
- heavy bleeding.
Surgeons resort to administering calcium chloride injections after surgery.
The drug is administered intravenously. In the hospital, IVs are used for this.
To terminate a pregnancy
A hot injection is used in gynecology to perform an abortion procedure. A hot injection during pregnancy is only permissible when the patient has contraindications to direct surgery or other methods of abortion. The manipulation is carried out under the supervision of a specialist in the gynecology department.
Etamsylate solution for intravenous and intramuscular administration. 125mg/ml 2ml 10 pcs
Short description
Pharmacological action - hemostatic, angioprotective. Bleeding (intestinal, uterine and during surgical interventions), trauma, hemorrhagic diathesis, diabetic angiopathy, polymenorrhea. IV, IM/, subconjunctival, retrobulbar 0.25-0.5 g ( 2-4 ml of 12.5% solution), followed by 0.25 g (2 ml of 12.5% solution) every 4-6 hours for 5-10 days.
pharmachologic effect
Hemostatic, angioprotective. Stimulates the formation of platelets and their release from the bone marrow. Activates the formation of tissue thromboplastin (factor III) at the site of damage to small vessels, promotes adhesion and aggregation of platelets, and reduces bleeding.
Indications
Prevention and control of bleeding: parenchymal and capillary bleeding, incl. traumatic, in surgery during operations on well-vascularized organs and tissues, during surgical interventions in the dental (removal of cysts, granulomas, tooth extraction, etc.), urological (prostatectomy, etc.
), ophthalmological (keratoplasty, cataract removal, antiglaucomatous operations and other surgical interventions), otolaryngological practice (tonsillectomy, microsurgical operations on the ear, etc.
); intestinal, renal, pulmonary bleeding, metro- and menorrhagia with fibroids, secondary bleeding due to thrombocytopenia and thrombocytopathy, hypocoagulation, hematuria, intracranial hemorrhage (incl.
Directions for use and dosage
Inside, intravenously, intramuscularly. The dosage regimen is set individually depending on the indications. Orally - the average single dose for adults is 250-500 mg (if necessary, can be increased to 750 mg) 3-4 times a day.
IV or IM - the optimal daily dose for adults is 10-20 mg/kg, divided into 3-4 injections. Children are prescribed a dose of 10-15 mg/kg/day in 3-4 doses. The injection solution can be used topically (tooth extraction, etc.) - a sterile swab is soaked and applied to the wound.
In ophthalmological practice - subconjunctivally in the form of eye drops and retrobulbarly.
Side effects Contraindications
Use during pregnancy and breastfeeding During pregnancy, it is possible if the expected effect of therapy exceeds the potential risk to the fetus (the safety of using etamsylate during pregnancy has not been established). Breastfeeding should be stopped during treatment.
special instructions
Caution is required when prescribing to patients with a history of thrombosis or thromboembolism. For hemorrhagic complications associated with an overdose of anticoagulants, it is recommended to use specific antidotes
For hemorrhagic complications associated with an overdose of anticoagulants, it is recommended to use specific antidotes.
Interaction with other drugs
Pharmaceutically incompatible (in one syringe) with other drugs. Administration at a dose of 10 mg/kg 1 hour before dextrans (average molecular weight 30-40 thousand Da) prevents their antiaggregation effect (administration after dextrans does not have a hemostatic effect). A combination with aminocaproic acid, menadione sodium bisulfite is acceptable.
Storage conditions
Advantages and disadvantages
Hot injection during pregnancy has its advantages and disadvantages.
- requires minimal preliminary preparation;
- does not injure the uterine cavity;
- the procedure takes little time;
- well tolerated by patients;
- eliminates injury to the cervix;
- causes moderate uterine pain;
- does not require anesthesia,
- it is impossible to introduce an infection;
- the formation of adhesions and obstruction of the fallopian tubes is excluded.
An abortion injection is preferable for women who have not previously given birth; it does not affect the reproductive function of women in the future. Patients do not experience psychological trauma.
- general weakness, dizziness;
- nausea, vomiting, stool disorders;
- inflammation of the uterus and its appendages;
- increased body temperature and blood pressure;
- likelihood of urinary tract infection;
- the possibility of developing an allergic reaction.
Rejection of the fertilized egg may not occur or the abortion may be incomplete. Part of the embryo will remain in the uterus. It will have to be removed surgically.
Indications for the use of Dicinon in the early stages
Scarlet or brown discharge at any stage of pregnancy can cause real panic in the expectant mother. If they are caused by reasons that can lead to termination of pregnancy (threat of miscarriage), the woman is prescribed Dicinon to stop the bleeding. Its use is justified for scarlet discharge caused by partial placental abruption (no more than 1/3). In this case, the pregnancy can be maintained.
Sometimes during pregnancy, a woman may experience more than just vaginal bleeding. This condition also requires the use of hemostatic drugs. With the help of Dicinonon it is possible to stop bleeding caused by:
- surgical interventions in dentistry, ophthalmology, otolaryngology, gynecology;
- systemic blood diseases;
- emergency conditions (for pulmonary and intestinal pathologies);
- hemorrhagic diathesis.
Dicynone is prescribed only by a specialist
The drug is often prescribed to pregnant women if they have hematomas due to chorionic detachment.
The chorion is the outer membrane of the fertilized egg, from which a full-fledged placenta is formed in the second trimester of pregnancy. In the first 16 weeks of pregnancy, the fetus receives nutrients through the chorion. Sometimes it happens that due to presentation (the peculiarities of the attachment of the fertilized egg in the uterine cavity), stress, high blood pressure, infection, injury, the chorion partially exfoliates. A hematoma (collection of blood) forms between it and the walls of the uterus. Gradually, the hematoma begins to resolve on its own. This is accompanied by discharge of scarlet or brown blood. With partial detachment of the chorion (placenta), pregnancy can be maintained. To stop bleeding, Dicinon is recommended, and maintenance therapy is prescribed. Treatment prognosis is positive. If the chorion (placenta) is completely detached, pregnancy cannot be maintained.
Gynecologists practicing abroad have ambivalent attitudes towards the prescriptions of their colleagues in the post-Soviet space. For example, in Canada, such medications are not used to treat this type of disorder.
Dicynone can be prescribed according to indications in any trimester of pregnancy
Since in the first three months all the organs and systems of the child are formed, the drug should be taken with extreme caution. But if the doctor recommends it for treatment, then the threat of miscarriage is higher than the potential risk of complications for the baby
In the second and third trimester, medications are taken only under the supervision of a specialist.
Hot injection abortion
A mandatory condition is an abortion under the supervision of a doctor in the gynecology department of the clinic. If necessary, he will be able to control the situation if something does not go according to plan, but there is no need to be in the hospital. You will need to visit a gynecologist in 2 days. He must confirm the success of the procedure.
Efficiency
Hot injections for miscarriage have been used for a very long time. It has proven its effectiveness with the correct selection of the drug. Has an affordable price.
When alternative drugs appeared on the pharmaceutical market, hot injections for the purpose of terminating pregnancy were no longer used, because there is a high probability of negative consequences for the patient’s body.
But during the administration of the medicine, heat begins to spread throughout the body. Sometimes redness appears on the face, neck, and chest. This is the result of the action of organic and inorganic salts injected into a vein. Solutions of calcium and magnesium salts dilate blood vessels, generating a wave of heat. But this condition passes quickly.
Can I do it at home?
The injection should be carried out only after examination and in the absence of individual contraindications. Therefore, you cannot inject yourself. Serious negative consequences can be provoked.
Useful video: how to maintain a pregnancy when there is a threat of miscarriage?
We recommend reading: Negative Rh factor during pregnancy is not a death sentence
Dicynone during pregnancy - first aid in case of threatened miscarriage - revealing secrets about pregnancy on Pitanie4Zdravie.ru
Pregnancy makes a woman truly beautiful. But during pregnancy, many questions arise that need to be answered. Especially for you, in the “Pregnancy from A to Z” section, we publish interesting and useful articles about pregnancy, so that this wonderful time for you will be as “problem-free” and joyful as possible.
You can also find here the main signs of pregnancy, how the baby’s fetus develops at different stages of pregnancy, understand what is possible and what is not possible at different stages of pregnancy. Learn more about the effect of various foods, vitamins (for example, the effect of folic acid) on pregnancy.
Indications for testing
Calcium chloride and gluconate are indispensable in the treatment of many diseases and for prevention. They have the same therapeutic effect.
Application is possible when:
- Uterine bleeding. Increase blood clotting and strengthen the walls of blood vessels.
- Lack of calcium in the body. With an increased risk of developing postmenopausal osteoporosis (bone fragility).
Calcium chloride has a strong anti-inflammatory effect, activating the activity of leukocytes. More often used in complex therapy. Prevents obstruction of the fallopian tubes and the formation of adhesions. It is prescribed after a frozen pregnancy, miscarriage, or curettage. Hot injections prevent endometritis after miscarriage.
Calcium gluconate is indicated for replenishing magnesium in the body. The need appears when taking oral contraceptives.
Symptoms
This inflammatory disease of the tonsils is caused by streptococcus. Pathology can be either acute or chronic.
Tonsillitis during pregnancy is manifested by the following symptoms:
- sore throat that increases with swallowing;
- redness and enlargement of the tonsils, sometimes accompanied by the appearance of purulent plugs and plaque;
- soreness;
- sensation of a foreign body, a lump in the tonsil area;
- enlargement and tenderness of the submandibular lymph nodes, determined by palpation (normally they have a diameter of up to 1 cm and are painless);
- increase in body temperature to subfebrile values (37.0-37.5 °C);
- asthenic syndrome - lethargy, weakness, weakness, malaise.
If a sore throat is not treated in time, it becomes chronic. In this case, the clinical picture may be erased, the symptoms are not so pronounced, the course of the disease is long with alternating periods of exacerbations and remissions.
Chronic tonsillitis and pregnancy are a dangerous combination. The pathology is dangerous due to serious complications, including the loss of the child. Exacerbation of chronic tonsillitis during pregnancy can occur with hypothermia (both general and local), prolonged and frequent exposure to stress factors, and overwork.
How they do it
A hot injection into a vein is a rather complex procedure that requires skills from a medical professional.
Otherwise, additional therapy may be required to eliminate the consequences. Such injections can only be given intravenously. If the product gets under the skin, it will cause necrosis of the subcutaneous fat. The injection syringe must have a small diameter.
Preparation
No preparatory procedures are required before disposing of the fetus using medications. The only condition is to limit food intake on the day of the procedure.
Abortion by injection is carried out only after the patient has undergone examination and in the absence of individual contraindications.
Giving an injection
The main condition when administering an injection is to administer the drug very slowly, otherwise you can injure the vein wall.
You can administer the product in 3 ways:
- Jet (regular injection).
- Drip (classic drip).
- Electrophoresis (the product enters due to current discharges).
If the injection is given quickly, fainting is possible. If the patient suffers from hypotension (low blood pressure) and a tendency to lose consciousness, then the healthcare worker should be warned about this. In this case, the medicine will be administered within 4-5 minutes.
After interruption
The rehabilitation period plays a serious role. Not only the patient’s health, but also her reproductive ability in the future depends on recovery.
Chemical abortion has few complications compared to surgical abortion, but it is advisable to minimize them.
- avoid sexual intercourse for 30 days to prevent infection of the uterine cavity;
- avoid physical overexertion, postpone sports activities;
- strictly observe hygiene requirements, wash yourself 3 times a day with a light solution of potassium permanganate;
- Change underwear daily and sanitary pads several times during the day.
After a miscarriage, you need to visit a gynecologist for a preventive examination. Do an ultrasound of the pelvic organs within six months.
If a woman experiences mood swings or depression, a psychologist will help. You can take a light herbal sedative.
How to get rid of tonsillitis during pregnancy and why it is dangerous
MAKE AN APPOINTMENT WITH AN ENT DOCTOR ONLINE
Tonsillitis during pregnancy is a rather unpleasant throat disease, which is fraught with its consequences. Each of us has had a sore throat (an acute form of tonsillitis) at least once in our lives. If the inflammatory process is not completely defeated, the cold becomes chronic and causes troubles for a person throughout his life.
Statistics show that 20% of the world's inhabitants suffer from chronic tonsillitis. The disease can take anyone by surprise, including pregnant women. The situation is complicated by the fact that an ordinary person can undergo full-fledged drug treatment, including antibiotics. A pregnant woman has many restrictions, and even more dangers.
Side effects
When administering a hot injection, side effects may develop.
Most often it occurs:
- headache;
- bradycardia;
- difficulty breathing;
- general weakness;
- gagging;
- increased sweating;
- anxiety disorders;
- arrhythmia;
- fatigue.
Cardiac conduction disturbances, uterine atony, and asthenia are rarely observed. Side effects usually develop with an overdose.
During a non-surgical abortion, a concentrate of a special drug is injected into the woman's body. Side effects or lack of effect after injection can only be explained by non-compliance with the doctor’s recommendations or the omission of existing contraindications.
Treatment
How to treat tonsillitis during pregnancy? Firstly, using methods that are safe for mother and fetus. Secondly, in the shortest possible period of time.
Drug treatment
Treatment of chronic tonsillitis during pregnancy is possible with the help of drugs such as Tantum Verde spray or sublingual tablets Lizobakt, Doctor MOM lozenges, Strepsils. They have no toxic effects and are safe for women and fetuses. If you have normal iodine tolerance, you can lubricate your tonsils with Lugol's solution.
Physiotherapeutic methods of treatment include magnetic therapy, ultrasound, and EF on the tonsil area.
You can gargle with mineral water, solutions of furatsilin, baking soda, sea salt, and potassium permanganate. Rinsing is harmless and has a local anti-inflammatory and antibacterial effect. In addition, pathogenic bacteria are mechanically washed away from the tonsils.
Such procedures for chronic tonsillitis should be carried out as often as possible. It is better to alternate different rinsing solutions. In this case, microbial resistance will not develop. Solutions prepared from decoctions and tinctures of medicinal plants (Chlorophyllipt, Rotacan) are well suited for rinsing.
Miramistin is an antiseptic with anti-inflammatory, antibacterial, antiviral, and antifungal effects. It can be used both for rinsing and for irrigating the tonsils and oral cavity. Aerosols Kameton, Ingalipt, Hexoral are also used topically.
In extreme cases, antibiotics are used. During pregnancy, the use of penicillin drugs is permitted. Amoxicillin and Flemoxin are usually prescribed. They do not have a harmful effect on the embryo and have a wide range of effects.
Folk remedies
Treatment of chronic tonsillitis during pregnancy using traditional methods should be agreed with a doctor.
The most common means:
- propolis, honey in the absence of allergies;
- gargling with herbal decoctions - horsetail, chamomile, eucalyptus, St. John's wort, mint, sage;
- lubricating the tonsils with horsetail juice;
- the use of juice of medicinal plants - aloe, Kalanchoe;
- steam inhalations with soda, mineral water, herbal decoctions.
You can simply chew propolis or gargle with a solution (1 tsp of propolis tincture for 1 glass of water). Honey has an antipyretic and anti-inflammatory effect. It can be added to tea or simply dissolved in your mouth.
The simplest steam inhalation is to inhale the steam of boiled potatoes over a saucepan. Such procedures can be carried out with a solution of baking soda or salt. You can add a small amount of “Star” balm to the water, containing extracts of herbs and essential oils.
But prolonged exposure to steam is undesirable during pregnancy. Therefore, inhalation using a nebulizer with mineral water or saline solution is best. Read more about inhalations during pregnancy →
Contraindications
There is a certain list of contraindications for medical abortion using injections.
- bleeding disorders, taking heparin and other anticoagulants;
- the presence of scars on the uterus can lead to its rupture and severe internal bleeding when large doses of oxytocin are administered;
- the presence of an installed spiral in the uterus, in which case early abortion is possible only by vacuum aspiration.
With caution, injections to stimulate miscarriage should be administered to women with chronic renal or liver failure, diseases of the cardiovascular system, if artificial valves are implanted in the heart.
Diagnostics
Diagnosing the threat of early miscarriage is not difficult. The diagnosis is made after a thorough collection of anamnesis and complaints, general and gynecological examination
. During a gynecological examination, the doctor assesses the condition of the cervix (whether it is shortened and smooth, the external os is closed), the presence or absence of blood discharge, and palpates the uterus (whether it corresponds to the gestational age or contracts in response to palpation).
An ultrasound is also required to evaluate the tone of the uterus, whether there is a fetus in the uterus and whether its heartbeat is determined, whether it corresponds to the gestational age, and the presence/absence of a retroplacental hematoma.
Laboratory methods used:
- Hormonal studies
Determination of the level of progesterone, hCG, 17-ketosteroids, thyroid hormones according to indications.
- Colpocytological examination
The karyopyknotic index (KPI) is calculated, on the basis of which a threat can be suspected in the early stages even before the clinic appears (an increase in the KPI is the first sign of a threatening miscarriage).
- Vaginal smears
This item also includes testing for hidden sexually transmitted infections.
- Blood type and Rh factor
To exclude Rh-conflict pregnancy.
- Blood clotting
Necessary for suspected thrombophilic conditions.
Alternative methods of abortion
An alternative method to hot injection is contraction of the uterus using medications. The most commonly used drug is Mifepristone. It can only be used for up to 6 weeks.
The female sex hormone (progesterone) that supports pregnancy is blocked. The uterus contracts and the embryo comes out.
The drug Oxytocin is also used for abortion. But this injection for abortion in the early stages is especially dangerous. With a significant increase in dosage, rupture of the reproductive organ is possible. It is most often used for up to 16 weeks if the fetus has a developmental defect that is incompatible with life.
The artificial drug resembles human hormones. Stimulates smooth muscles, which leads to uterine contractions. The dose of oxytocin is calculated individually by the gynecologist. Growth is taken into account
Causes
There are a variety of reasons for the threat of miscarriage: they are usually dictated by the characteristics of the fetus, the state of the mother’s health, or some external factors. While carrying a baby, a woman faces many dangers, each of which at a certain moment can provoke termination of pregnancy. The most common are:
lack of progesterone necessary to continue pregnancy; excess androgens (these are male hormones that actively suppress female ones); rejection of the fetus by the mother’s body due to incompatibility with a man at the genetic level; mismatch of Rh factors: negative - in the mother, positive - in the father; abnormal blood clotting (increased); pathological structure of the uterus: defects in its development, non-standard shape (saddle-shaped, bicornuate) prevent the implantation of the fertilized egg; fetal genetic mutations; infectious diseases: rubella, chlamydia, syphilis, pyelonephritis, pneumonia and even sore throat during pregnancy; gynecological diseases: uterine fibroids, endometritis, inflammation, sutures in the uterus; previous abortions and miscarriages with curettage, as it damages the endometrium; endocrine diseases: thyroid problems, diabetes; taking certain medications that are contraindicated for bearing a child; herbal medicine: for example, active use of parsley, nettle, St. John's wort, tansy in any form - and the threat of miscarriage in the early stages is guaranteed; a common cause of threatened miscarriage in the later stages is pathology of the cervix or placenta; emotional state of a pregnant woman: constant stress, nervousness, resentment, anxiety, discontent; work until the deadline; questionable lifestyle: drugs, strong coffee and other harmful products, smoking, alcohol; falling, jumping, blows to the stomach, heavy physical activity; aging of the egg: according to statistics, in women over 35 years of age, the threat of miscarriage is diagnosed 2 times more often.
There may be only one reason, or a combination of them may work. In this matter, everything happens very individually. It is very important to identify a dangerous factor in time and exclude it from the life of the expectant mother, if possible. In order not to be late with treatment, you need to know the main signs of a threatened miscarriage, which will become an alarm signal notifying you of an urgent visit to the gynecologist.
Stubborn statistics. According to data, 20% of all pregnancies end in miscarriage.