Uterine adenomatosis is a common disease characterized as a precancerous condition. This disease is nothing more than an atypical form of dishormonal endometrial hyperplasia. If we take into account general statistics, then at least 15% of women with diagnosed adenomatosis are at risk of malignancy of the process.
This disease is characterized by uncontrolled excessive proliferation of endometrial cells. Despite the fact that uterine adenomyosis has a high potential for malignancy, with timely detection and comprehensive treatment, the disease undergoes reverse development.
Since the problem of dishormonal disorders is relevant for women mainly of reproductive age, hyperplastic processes in the mucous membrane of the uterine cavity tend to form precisely during this period of time.
Definition
Before talking about uterine adenomatosis, what it is, it is important to remember that the impetus for any hyperplastic process in the uterine cavity is always dishormonal disorders.
When a woman experiences an imbalance of sex hormones, she develops characteristic symptoms such as disruption of the ovarian-menstrual cycle, uterine bleeding during the intermenstrual period, as well as reproductive dysfunction, including infertility.
The key factor provoking the development of endometrial hyperplasia is an increase in estrogen levels (hyperestrogenism). To make diagnosis easier and formulate a treatment plan in gynecological practice, several types of endometrial hyperplasia are distinguished:
- Diffuse hyperplasia, which involves the entire endometrium, which lines the uterine cavity, in the pathological process.
- Glandular hyperplasia. With this form of the disease, polyps, cysts and additional glands can form in a woman’s uterine cavity. Compared to diffuse hyperplasia, this form of pathology is characterized by less rapid development and a low potential for malignancy.
Any condition that is accompanied by accelerated cell division and changes in their structure can be freely regarded as precancerous, but not each of these conditions can actually turn into cancer.
If a uterine adenoma is detected in women, they undergo a histological examination of tissue scrapings. Thanks to this diagnostic method, specialists evaluate the cellular composition of the biological material taken.
If no atypical cells were found during the study, then the foci of adenomatosis are benign in nature and do not pose a serious danger to women’s health.
Women of reproductive age are often diagnosed with uterine fibroadenoma, which is a benign tumor of the myometrium (muscular membrane). This condition also occurs against the background of hormonal imbalance and hyperplastic processes.
Main forms of the disease
Experts distinguish three forms of the described disease:
- Diffuse focal adenomyosis of the uterus - endometrioid cells are localized mainly on the inner surface of the uterus.
- Nodular adenomyosis - cells form nodes that contain blood or exudate. This happens because the cells in the nodes continue to perform their functions, focusing on the woman’s menstrual cycle. With this disease, single or multiple nodes can form in the uterine cavity.
- Focal adenomyosis. The growth of the endometrium in this form of the disease occurs in certain areas of the uterus, with extensive foci in the walls of the organ. The size of the lesions in this case can be very different. Focal adenomyosis of the uterus progresses, like other diseases, passing through several stages. The disease is treated with the same methods.
Causes
An increased risk of uterine adenomatosis occurs in women with a hereditary predisposition to hyperplastic conditions, as well as in those patients who have suffered from hormonal imbalance in the body for a long time. Less important predisposing factors for the development of uterine adenomatosis include:
- Previously undergone surgical interventions on the organs of the reproductive system;
- Regular exposure to stress on the female body;
- Violation of the dosage regimen or long-term use of hormonal medications;
- Diseases of the endocrine system;
- Dyshormonal disorders, which are expressed in an imbalance between gestagens and estrogens;
- Ovarian pathologies;
- Long-term regular exposure to direct sunlight, it has been clinically proven that prolonged exposure to ultraviolet radiation negatively affects the vital activity of body cells, accelerating their division;
A decrease in the body's defenses is also a reason. The immune system of any person is a key link that is capable of maintaining and regulating the process of cell division. When the immune system is in a depressed state, hyperplastic changes very often form in a woman’s body.
The main reasons for the appearance
Researchers have not yet fully studied the diffuse-focal form of adenomyosis and have not identified all the reasons that provoke its appearance. At the same time, doctors note that such a lesion is most often detected in patients whose hormonal background is experiencing serious and long-term disruptions. Such women are at particular risk, so they must carefully monitor their health and, when the first signs of damage appear, immediately seek help from a specialist.
The main factors that lead to the appearance of focal adenomyosis of the uterus include: frequent pregnancies, certain surgical interventions, installation of a spiral, frequent curettage or abortions.
In addition, the following factors can be considered as provoking factors:
- Susceptibility to the disease at the genetic level. In this case, a woman may experience not only focal adenomyosis, but also other forms of endometriosis.
- Problems with the amount of hormones in the body: too much estrogen or lack of progesterone.
- Regular stress, worries, emotional outbursts, irregular rhythm of life, excessive stress of both a mental and physical nature.
- Intensive sports activities.
- The presence of bad habits, as well as uncontrolled use of medications that were not prescribed by the treating specialist, and failure to follow the dosage.
Symptoms
It is not possible to independently diagnose uterine adenomatosis at home. To make a diagnosis, a woman will need a comprehensive medical examination. Despite this, there is a list of clinical symptoms that may suggest the development of adenomatosis. These symptoms include:
- Frequent episodes of nagging pain in the lower abdomen;
- Bloody discharge during the intermenstrual period;
- Painful sensations during intimacy;
- Irregular menstrual cycle;
- Reproductive dysfunction (infertility);
- Disorder of psycho-emotional activity (apathy, emotional lability);
- Frequent episodes of headaches.
Women with a similar diagnosis develop metabolic syndrome. This syndrome is characterized by excess body weight, male-pattern body hair growth, voice changes, and an increase in the concentration of insulin in the blood.
Uterine adenoma, what kind of tumor is it and how is it dangerous for a woman?
Uterine adenoma is a benign tumor formed from glandular cells of the uterine endometrium. Externally, they are growths of regular shape, located on a thick base or thin stalk. If the leg is long, the adenoma may prolapse into the vagina.
After an adenoma occurs, a woman does not experience symptoms of the disease for a long time, so neoplasms are discovered when they reach a large size. The larger the size of the adenoma, the more the woman’s condition worsens and the higher the risk of carcinoma formation.
Despite their benign quality, adenomas can cause complications:
- menstrual irregularities;
- miscarriages, missed pregnancies;
- infertility;
- uterine bleeding;
- severe anemia;
- transition to cancer.
Adenoma in pregnant women can cause placental abruption, bleeding, and disrupt uteroplacental bleeding. This leads to oxygen starvation of the fetus and the development of fetoplacental insufficiency.
Diagnostics
One of the most informative ways to accurately detect uterine adenomatosis is transvaginal ultrasound. Using this instrumental diagnostic method, it is possible to assess the condition of the endometrium, its thickness, the presence of focal or diffuse hyperplastic changes.
In order to assess the potential for malignant degeneration, a woman undergoes a histological examination of scrapings from the uterine cavity. In order to identify metabolic syndrome and assess its severity, the diagnostic plan includes a general clinical blood test, a blood test for sugar, and a laboratory analysis for the level of sex hormones.
Uterine adenomatosis and cancer
Any changes in the uterus (proliferation of cells and tissues, changes in cell structures, the appearance of neoplasms, etc.) should cause a certain concern, because there is a risk of developing cancer. However, they are not really malignant very often.
Focal adenomatosis is considered a precancerous condition, but the main evidence of its danger is a histological examination of scraping tissue from the uterine cavity. The term “without atypia” as a result of the study indicates the benign nature of the process and the minimal risk of developing uterine cancer in the near future. And the detection of atypical cells based on histology results indicates a precancerous condition.
Regardless of the research results, hyperplastic processes in the uterus must be treated.
Treatment
If the uterine adenoma is in the initial stage of its development, then the woman is prescribed complex conservative treatment, which includes long-term use of hormonal medications.
Drugs from the group of gestagens, combined oral contraceptives, gonadotropin-releasing hormone antagonists, estrogen-gestagen drugs, and androgens help stop the development of hyperplastic changes.
If the pathological process is at a stage that is not amenable to conservative treatment, then the woman is prescribed surgical methods to eliminate foci of hyperplasia. For uterine adenomatosis, the following surgical treatment options are used:
Hysteroscopy. This procedure is a minimally invasive surgical technique. Removal of pathologically altered tissue is carried out under video control, which minimizes the risk of traumatic damage to healthy uterine tissue. The only drawback of the hysteroscopic technique is the high risk of recurrence of focal endometrial hyperplasia.
Scraping. This method involves manually removing the pathologically altered mucous membrane of the uterine cavity using a metal curette. Curettage is a therapeutic and diagnostic intervention that is carried out under general anesthesia, and the resulting biological material is sent for histological examination to the laboratory.
Complete or partial removal of the uterus (hysterectomy). This radical surgical intervention is performed only if there are specific indications. Hysterectomy may be recommended for postmenopausal patients, subject to frequent recurrence of adenomatosis. In addition, partial or complete removal of the uterus is prescribed if there is a high risk of cancer formation.
After a woman has undergone one of the surgical treatment options, she is prescribed a course of hormonal therapy, which is aimed at restoring hormonal levels, strengthening the body's defenses, and stimulating regenerative processes in the uterine cavity.
Endometrial adenomatosis is an atypical (diffuse or focal) endometrial hyperplasia, which has the nature of a precancerous disease.
Precancerous is a pathological process that has varying degrees of probability of developing into cancer. Precancerous hyperplastic processes can often undergo reverse development and in only 10% of patients transform into cancer. The presence of such a possibility requires doctors and patients to take this pathology very seriously.
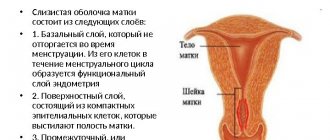
All hyperplastic processes in the endometrium arise with the participation of hormonal dysfunction and are manifested by uterine bleeding and infertility. The decisive role in their appearance belongs to hyperestrogenism. Under the influence of excess estrogen, quantitative and qualitative structural changes occur in the endometrium, leading to uncontrolled growth and thickening of its internal structures. Depending on what type of cells this process is realized, several types of hyperplastic processes are distinguished. If the proportion of glandular structures increases, we speak of glandular endometrial hyperplasia. In some cases, cystic-enlarged formations appear in the lumens of the glands, and hyperplasia is called glandular-cystic. Adenomatosis is characterized by the appearance and growth of atypical cells in the endometrium.
If the hyperplastic process covers the entire surface of the endometrium, hyperplasia is diffuse in nature. Diffuse adenomatosis develops against the background of a diffuse hyperplastic process. In the focal form of hyperplasia, endometrioid tissue grows in a limited area and over time begins to “bulge” into the uterine cavity, taking on the appearance of a polyp. Focal adenomatosis is an endometrial polyp with elements of atypia.
For endometrial adenomatosis, surgical treatment is used. The prognosis of the disease is influenced by the patient’s age, the nature of hormonal disorders, concomitant neuro-endocrine diseases and the state of the immune system.
Main stages
Experts divide focal adenomyosis of the uterine body into the following stages:
- At this stage of development, the depth of growth of endometrial foci into the muscular layers of the uterus reaches 1/3. If a dangerous formation in the cavity of the said organ is detected in a timely manner, it can be easily and quickly treated without complications.
- The endometrium in the uterus extends to 1/2 part, so the gynecologist prescribes the patient a course of hormonal medications, as well as appropriate physiotherapeutic procedures.
- In this case, the endometrium is widely distributed in several areas of the uterus, localized in the area of the outer walls of its muscular layer, leading to more serious complications and problems in the patient’s body.
- What is stage 4 diffuse focal adenomyosis? In this case, the endometrium begins to actively damage tissues located outside the uterine cavity. Neoplasms begin to form on neighboring organs. As a rule, the doctor prescribes mandatory surgical intervention for the patient.
Causes of endometrial adenomatosis
The causes of endometrial adenomatosis are similar to the causes of the hyperplastic process in the endometrium, against the background of which atypical cellular transformation occurs. There are no reliable causes of endometrial adenomatosis. None of the studied causes of hyperplastic processes is a guaranteed trigger for the development of an atypical process in the endometrium, but a combination of unfavorable factors increases the risk of its occurrence.
There is no doubt that the leading role in the development of the hyperplastic process in the uterus belongs to hormonal disorders, affecting all parts of the neurohumoral regulation of the body. Physiological cyclic changes in the uterus occur with the participation of estrogens and gestagens. Under the influence of estrogens, the inner mucous layer of the uterus (endometrium) increases in volume, and gestagens prevent it from growing excessively and contribute to its timely rejection. If there is too much estrogen, the growth of the endometrium becomes uncontrolled.
The causes of hyperestrogenism can be disturbances in the hormonal function of the ovaries, leading to anovulation. The absence of ovulation makes the cycle single-phase and provokes pathological endometrial hyperplasia.
Polycystic ovary syndrome is accompanied by chronic anovulation and can serve as a favorable reason for the development of hyperplasia in the endometrium.
Uncontrolled use of hormonal drugs can provoke hormonal disorders, leading to endometrial hyperplasia.
The combination of hyperestrogenism, extragenital pathology and neuroendocrine disorders in the body increases the likelihood of developing endometrial adenomatosis. For example, severe obesity in combination with hypertension increases the risk of endometrial cancer by 10 times.
The liver is responsible for the utilization of estrogens, therefore, with diseases of the liver and/or biliary tract, hyperestrogenism sometimes occurs.
Against the background of uncontrolled growth of the inner layer of the uterus, atypical cells may appear, which form the basis of endometrial adenomatosis. Cells that are not similar to the cells of the surrounding tissue are called atypical.
Modern methods of treatment
In medicine, new methods have been developed for the treatment of focal adenomyosis of the uterus:
- Electrocoagulation. In this case, pathological formations in the body are affected by an electric discharge, which destroys focal formations in a mild form.
- Embolization. This method of treatment is based on blocking the blood flow that flows to all formations. Due to the lack of oxygen, the formations begin to quickly collapse.
- Ablation helps destroy the lining of the uterus.
All the described treatment methods have their own advantages; with the help of them, many patients were able to eliminate adenomyosis without dangerous health consequences.
In addition, doctors advise leading an active lifestyle, maintaining proper nutrition, exercising regularly and maintaining a healthy sex life. If you have regular problems with the menstrual cycle, it is important to immediately see a doctor and conduct a comprehensive examination to diagnose the pathology in a timely manner.
Symptoms of endometrial adenomatosis
Since endometrial adenomatosis is characterized by the appearance of atypical cells, it does not have distinctive symptoms, the presence of cellular atypia cannot be confirmed without laboratory testing.
At the initial diagnostic stages, the presence of a hyperplastic process is established, after which its nature is clarified.
Ultrasound scanning using a transvaginal sensor helps to identify changes in the thickness and structure of the endometrium of a diffuse or focal nature.
Diffuse endometrial adenomatosis has no distinctive ultrasound signs and is visualized similarly to diffuse hyperplasia.
Focal endometrial adenomatosis is a polyp with atypical cellular changes; ultrasound examination reveals the presence of a polyp, but cannot determine the nature of the cellular changes.
Priority in the diagnosis of endometrial adenomatosis is histological examination of a complete scraping of the mucous layer of the uterus. In laboratory conditions, the cellular composition and nature of structural changes are studied, the degree of atypia and its severity are determined. Curettage of the uterine cavity allows you to provide material for subsequent laboratory testing. Since total evacuation of the uterine mucosa is possible only under visual control, curettage is performed with the participation of hysteroscopy.
Rehabilitation and postoperative care after removal of gastric adenoma
After removal of an adenoma, a woman needs high-quality care to restore the endometrium of the uterus and prevent the development of complications.
Immediately after surgery, the woman is prescribed bed rest, antibiotics, anti-inflammatory drugs and drugs to normalize hormonal levels. In the absence of complications, discharge from the hospital is carried out 7-10 days after surgery.
Prevention of complications in the first month:
- take hot baths.
- visit the pool, swim in ponds.
- lift weights.
- be sexually active.
- use suppositories, tampons, douching.
For a speedy recovery, a woman needs to eat well, take vitamins, control her weight and monitor her condition. For the first year after removal of an adenoma, you need to visit a gynecologist once every three months, then you can reduce the number of examinations to twice a year.
Attention! You can plan pregnancy after removal of the adenoma after 4 cycles, unless the doctor finds other contraindications.
About the disease
Often, during a preventive ultrasound, women find out that they have endometrial adenomatosis. However, they begin to claim that they did not feel any symptoms of the onset of the disease.
Adenomatosis of the uterine mucosa is a benign neoplasm that manifests itself as a violation of the base of the cells that make up the uterine cavity.
If focal adenomatosis develops quickly, benign polyps can quickly degenerate into malignant ones, which causes significant harm to health.
As a rule, this disease is characterized by an overgrown neoplasm or the appearance of growths on the walls of the uterus. This is what is considered the initial stage of the onset of the disease, since polyps gradually begin to form from such growths. Important: the outcome of treatment and the patient’s condition do not depend on how long the polyp is in the uterine cavity, since they can cause the same harm to human health.
Today, focal adenomatosis is mainly encountered by women whose age varies between 30-50 years, but sometimes the pathology also occurs in young representatives of the fairer sex.
The shape of the resulting polyp is similar to an ordinary mushroom:
- The neoplasm has a thin stalk attached to the lining of the uterus.
- The polyp has a body that resembles a mushroom cap.
Treatment with drugs
Treatment with drugs can be carried out in conjunction with non-traditional drugs. This may include hirudotherapy, or treatment with leeches, homeopathy and medication. This set of procedures always brings a positive effect.
But doctors prohibit patients from self-medicating and purchasing medications without a prescription, as this is extremely dangerous for the health and condition of the woman herself. Moreover, with the right choice, homeopathic medicines will help enhance the effect of taking other medications.
Many women have tried leech treatment on themselves. It helps accelerate blood flow and eliminate the process of inflammation inside the organ.
Signs and causes of the disease
Treatment of the disease should be carried out after identifying the causes of adenomatosis, because the preparation of a treatment regimen depends on them.
The causes of the disease include:
- disturbances in the functioning of the immune system;
- performing an abortion or cleaning the uterine cavity;
- “jumps” of hormonal levels;
- frequent stress and depression;
- development of miscarriage in the first weeks of pregnancy;
- untreated inflammatory diseases occurring in the genitals;
- endocrine problems in women;
- untreated fibroids.
These are the main reasons for the development of pathology, but endometrial polyp also often occurs due to heredity. Doctors, first of all, pay attention to this reason, after which they prescribe additional tests.
Symptoms of this pathology include:
- problems with conceiving a child;
- copious vaginal discharge of the blood type, which cannot be associated with menstruation;
- constant bleeding after PA;
- pain in the lower abdomen, which often intensifies after sex or heavy exercise.
Causes
There are several opinions of doctors about the origin of adenomas, some attribute them to true tumors, others believe that they are the result of hormonal dysfunctions, and still others attribute the adenoma to a consequence of an inflammatory process, as a result of which endometrial cells penetrate into deeper layers.
Experts identify several provoking factors:
- physical inactivity;
- overweight;
- hereditary predisposition;
- irregular sex life;
- taking combined contraceptives;
- chronic genital infections;
- inflammatory diseases of the uterus (adnexitis, endometritis);
- previous operations on the uterus;
- inflammatory processes of the ovaries;
- age over 30 years;
- age-related changes - premenopause;
- early onset of menstruation (before 12 years);
- severe nervous shock.
Uterine adenoma can be provoked by dysfunction of the pituitary gland and thyroid gland, which affect the overall hormonal balance of the body. If it is not possible to identify the causes of adenoma formation during an examination by a gynecologist, an examination of the endocrine system should be performed.