All about uterine fibrosis: etiology, clinical picture and treatment
Fibrosis is a layer of connective tissue that forms on a woman's reproductive organ. As a result of layering, fibroids begin to form, characterized by a benign course. The disease affects 10 to 20% of women, most often suffering from this pathology at the age of 30 years. About 25% of patients do not know about the presence of the disease, since uterine fibrosis goes unnoticed for a long time.
Main reasons
Scientists have not yet figured out the exact cause of the disease. They suggest that the female hormone estrogen plays an important role in the development of this disease. That is, the main cause of the disease is hormonal changes. There are several factors that can influence the formation of fibrosis in the uterus:
- genetic predisposition;
- development of inflammatory diseases in the female reproductive organs;
- excess body weight;
- frequent stressful situations at work and at home;
- pregnancy increases the production of estrogen and progesterone, fibroids develop and grow rapidly during this period;
- secondary immunodeficiency states.
Cervical fibrosis is provoked by frequent abortions and cleaning during abortion. Poor nutrition and abuse of bad habits contribute to the development of pathology. The main predisposing risk factors are wearing an intrauterine device, injury to the organs of the reproductive system, and forced cesarean section. Knowing all the risk factors and causes of fibrosis, the doctor will be able to reduce the likelihood of the appearance of nodes to a minimum.
Clinical picture
Fibromatosis of the uterine body is of two types: diffuse, focal. Changes in connective tissue and the appearance of compaction most often do not go away without leaving a trace. It is impossible to independently detect fibrosis, especially when the pathology is at the initial stage of development. Symptoms depend on the location and size of benign tumors, as well as their number. Fibroids may decrease in size during and after menopause. The main signs of fibrosis:
- pain during intercourse;
- enlargement of the lower abdomen;
- feeling of pressure or fullness in the lower abdomen;
- frequent urination;
- pain in the pelvis and lumbar spine;
- menstruation lasting longer than usual.
Fibrous formation causes increased and prolonged menstruation (menorrhagia), as well as intermenstrual bleeding outside the menstrual cycle (metrorrhagia). Benign nodes provoke constipation (obstipation) if they put pressure on the rectum.
As a result of a violation of general and local immunity, focal fibrosis of the endometrial stroma forms in the cervical canal. It leads to the fact that a woman cannot bear a child, possibly infertility or inflammation of the uterine appendages. If left untreated for a long time, the disease leads to menstrual irregularities.
You can avoid such complications if you visit a gynecologist in a timely manner. Endometrial fibrosis is characterized by bloody discharge from a woman’s genital tract between menstruation, a discrepancy between the thickness of the mucous membrane of the uterine cavity and the day of the menstrual cycle, most often the endometrium becomes thinner.
Folk remedies
If cholecystitis is diagnosed along with bile reflux, folk remedies are used along with the main treatment for gastritis:
- eat 2 pears daily on an empty stomach;
- take a decoction of oats before meals - 500 ml, pour 1 liter of boiling water and leave for 40 minutes;
- drink ¼ glass of rowan juice 30 minutes before meals.
To eliminate heartburn when the contents of the duodenum are released into the stomach, celery root is used. Drink a tablespoon of juice before meals.
An effective remedy for the treatment of reflux gastritis is flaxseed. It can be purchased at a pharmacy. Pour 2 tablespoons of the product into a glass of boiling water and leave for 10 minutes. Drink 100 ml of decoction before meals.
To prevent food from moving in the opposite direction, you need to sleep on high pillows and do not lift heavy objects.
Research and diagnostics
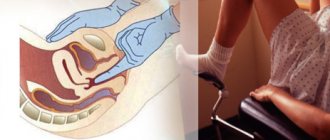
Most often, fibrosis is discovered completely by accident, for example, when the patient came for a routine examination, which should be carried out every six months. If a woman seeks help with complaints characterizing fibrosis, the doctor first performs a gynecological palpation examination (through the vagina, rectum and abdominal wall).
- Having discovered a tissue compaction, the gynecologist sends the patient to undergo a pelvic ultrasound. An ultrasound examination allows the doctor to see the internal structures of a woman's reproductive organs. Ultrasound detects nodes. Sometimes a transvaginal ultrasound is required, in which an ultrasound probe is inserted into the vagina and provides clearer images because it is closer to the uterus.
- It is advisable to use magnetic resonance imaging or computed tomography.
- If fibroids are pressing on the ureter, you will need to check the kidneys and urinary tract using ultrasound and x-rays using a contrast agent.
- If necessary, a blood test is taken from the patient (if anemia is suspected), as well as to measure hormone levels.
Existing treatments
The doctor develops a treatment plan depending on the patient’s age, the size of the benign node and general health. Conservative treatment of the disease includes the use of the following drugs:
- nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (Ibuprofen);
- birth control pills (Marvelon, Femoden, Logest, Microgynon);
- hormonal contraceptives (Zhanin, Yarina);
- gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonists (Triptorelin, Goserelin, Buserelin).
If fibromatous nodes are combined with endometrial hyperplasia, the doctor will prescribe gestagens. Be sure to use vitamins B, A, E. Vitamin therapy has an effect similar to gestagens. Their continued use improves menstrual function and reduces the manifestations of the disease.
Attention! Self-administration of drugs is prohibited. You can use medications only after medical consultation. Each drug has contraindications; before use, you should read the instructions.
Large formations must be removed. Surgery occurs with minimal damage to the uterus. Healing after myomectomy does not last long, but the recovery period depends on the competence and professionalism of the attending physician. Myomectomy can be hysteroscopic or embolization. The choice of type of surgical intervention depends on the clinic, the size and weight of the benign tumor, as well as the location of the fibroma.
Types of myomectomy
There are several types of surgery. Treatment depends on the clinical picture, the size and weight of the formation and the location of uterine fibrosis.
The presented technique is suitable for the treatment of submucosal nodes. Using a hysteroscope, the doctor inserts a special instrument into the uterine cavity to remove the fibroid.
Embolization
A catheter is inserted through the femoral artery, which reaches the uterus through the artery. A special contrast agent is injected into the place where branches into separate small channels begin. Next, an element is introduced through the catheter, which is carried through the arteries and fills the fibroids. Thus, the formed node is separated from the blood supply.
Definition of disease. Causes of the disease
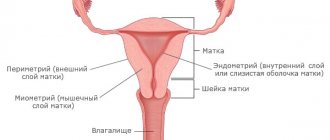
Uterine fibroid is a hormone-dependent benign neoplasm that develops from the cells of the myometrium (the muscular wall of the uterus). At its core, fibroma is a type of uterine fibroid. A distinctive feature of uterine fibroids is the predominant content of connective tissue in the tumor tissue.
Fibroma is a round formation, the structure of which contains connective tissue components, myocytes, blood vessels, plasma cells and mast cells. [1]
According to studies, the peak incidence occurs in the premenopausal period (46-55 years), in some cases this pathology occurs in women of late reproductive age (35-40 years), but in recent years the disease has also been diagnosed in younger patients (25-30 years ). Uterine fibroids can grow, regress and even disappear in postmenopause, but in 10-15% of women the formation increases in the first 10 years of the menopausal period, combined with hyperplastic processes of the endometrium and proliferative diseases of the ovaries. [3]
General information
Benign tumors of the uterine (fallopian) tubes are a rare gynecological pathology, detected mainly in postmenopause. According to the observations of specialists in the field of oncology, obstetrics and gynecology, in the structure of neoplasia of the female genitalia, benign tubal formations occupy up to 0.5-3%. However, taking into account the asymptomatic course, low progression and small size, their prevalence in the population may be higher. The most common benign neoplasms are adenomatoid tumors measuring 1-2 cm and teratomas. The relevance of timely diagnosis of DOMT is due to the risk of their malignancy with spread to the ovaries, peritoneum, and greater omentum.
Symptoms of uterine fibroids
Three main features can be distinguished:
- bleeding and other various menstrual irregularities;
- presence of pain;
- dysfunction of adjacent organs.
Deformation of the uterine cavity by submucosal nodes leads to bleeding and other menstrual dysfunction; patients complain of an increase in the intensity and duration of menstruation, and the appearance of bloody intermenstrual discharge. Simply enlargement of the uterus due to fibroids can also lead to various uterine bleeding.
As the fibromatous node enlarges, complaints of various pains in the lower abdomen may occur. Most often these are pains of a pulling or aching nature. The growth of fibroids may be accompanied by a feeling of heaviness and discomfort, and an increase in the size of the abdomen may occur.
Dysuric phenomena and defecation disorders may be symptoms of subserous localization of fibroma. Acute pain syndrome, increased body temperature and symptoms of intoxication are characteristic of tumor necrosis and torsion of the stalk of subserous fibroma. The severity of clinical manifestations depends on the degree of disruption of the blood supply to the fibromatous node.
Benign fallopian tube tumors
Benign fallopian tube tumors
- These are slowly growing non-invasive volumetric formations originating from the epithelial, muscular, serous tubular membranes or surrounding tissues. Usually not clinically manifested. With volumetric neoplasia, complaints of discomfort, pain in the lower abdomen, signs of compression of surrounding organs, and infertility are possible. Diagnosed using gynecological examination, ultrasound, CT, MRI of the pelvic organs, hysterosalpingography, ultrasonography, laparoscopy. They are treated surgically with laparoscopic or laparotomic adnexectomy, tubectomy, extirpation or supravaginal amputation of the uterus and appendages.
Pathogenesis of uterine fibroids
So why does fibroma appear? Despite a number of clinical studies, science cannot give a clear answer to this question. In the development of fibromatous nodes, disturbances in the hypothalamic-pituitary system, changes in the state of the body’s immune system, hereditary predisposition, and the presence of chronic infections in the patient play an important role. Various changes in the blood supply to the pelvis, which often occur in patients with fibroids, are a favorable factor for the development of the tumor. [4]
In addition, there are risk factors for developing uterine fibroids:
- age;
- early menarche;
- no history of childbirth;
- obesity;
- long-term use of contraceptives.
Often the onset of the disease is asymptomatic, and women learn about their diagnosis during a routine examination with a gynecologist. The manifestation of the clinical picture of uterine fibroids largely depends on its size and location. A growing fibromatous node can become one of the causes of infertility and miscarriage. [3]
The pathogenesis of uterine fibroids is still a subject of heated debate. According to the classic works of K.P. Ulezko-Stroganova, conducted on the morphology of the female reproductive system, the formation of the rudiments of fibromatous areas occurs at the embryonic stage.
Scientific literature data on the importance of sex hormones in the development of uterine fibroids is currently very contradictory, however, numerous clinical and laboratory studies confirm that disruption of estrogen metabolism in a woman’s body leads to mitotic activity, which contributes to the formation of fibromatous nodes. An increase in fibrometry occurs due to hyperplasia of smooth muscle cells and their proliferative changes.
Focal fibrosis of the endometrial stroma
Tumors in the internal organs of a benign nature form unnoticed by patients and often remain asymptomatic for a long time.
The first signs appear when the changed tissue grows, the growth is compressed, and it degenerates into cancer. Endometrial polyps, including glandular fibrous ones, are often found in women.
The disease requires adequate treatment, otherwise the risk of complications will increase.
General characteristics of the pathology
A glandular-fibrous endometrial polyp is a tumor-like formation that forms on the uterine mucosa and consists of glandular cells and connective tissue. The disease is not dangerous, but if there is no treatment and the symptoms are ignored, it leads to consequences. It can occur at any age, but more often women during menopause encounter pathologies.
The growths are small in size (but can grow greatly). It is a smooth pink substance. Has stroma and body. Situated on a thin stem or on a wide base. The second type is more prone to malignancy. The stalk has many blood vessels that supply it for growth. Polyps with a glandular-fibrous structure can be single or multiple.
Causes
The reason for the formation of formations in the organs of the female reproductive system is an imbalance of hormones. The likelihood of polyps, including those with a mixed fibrous and glandular structure, increases with excessive estrogen concentration and progesterone deficiency. Because of this, focal changes occur in the mucosa.
The disease may be caused by:
- Chronic infections and inflammation of the appendages and uterus. They are accompanied by impaired blood circulation in the endometrium, which creates a favorable environment for tumor growth.
- Genetic predisposition. A woman whose relatives (grandmother, mother) suffered from pathology are at risk.
- Having excess weight, obesity.
- Long-term use of hormones, use of an intrauterine device.
- Artificial termination of pregnancy.
- Injury to mucous membranes.
- Diseases of the thyroid gland.
Polyposis can also be provoked by hypertension, diabetes, decreased immunity, frequent stress, and metabolic disorders.
Classification
The uterine cavity is lined with two types of tissues, which, according to histology, correspond to the types of polyps: functional and basal. The first is considered hormone-dependent, cyclically replaced. The second does not depend on hormones. This is the basis during menstruation. Based on this, glandular fibrous polyps are basal and functional.
Functional type
The appearance of a growth is provoked by the action of hormones. Due to the lack of progesterone and excess estrogen, fertile soil is created for the formation of a polyp. The tumor grows directly from the endometrium.
When fertilization does not occur during active ovulation, the cells of the functional layer of the endometrium are released along with menstrual blood. If there is insufficient exfoliation, the remnants of the endometrium form the basis for a future tumor. In this way, a polyp is gradually formed. With each cycle, the growth changes along with the functional layer.
Glandular fibrous formations of this type do not reach large sizes, but they quickly spread and are often localized in groups. The pathology is very rarely accompanied by any manifestations. Fibrous tumors of the functional type are often detected during ultrasound.
Basal type
The growths from the cells of the basal layer are located on a thin stalk. A characteristic feature of a polyp is the presence of blood vessels. Consists of glandular tissue and muscle fibers. Fibrous tumors of this type are distinguished by a mature structure and a variety of morphological variants. Localized unevenly, chaotically.
Pathology often occurs against the background of stable mucosa in healthy women. Often diagnosed during menopause.
It is distinguished by the non-functionality of epithelial cells and the absence of hormonal dependence on menstruation. There are polyps:
- Indifferent. Characterized by an increase in the number of neutral cells.
- Proliferative. Accompanied by endometrial hyperplasia. They often become inflamed.
- Hyperplastic. They are characterized by the proliferation of internal cells and the formation of a “substratum” of the basal stroma.
Symptoms
Manifestations of fibroglandular endometrial polyp do not always occur. Often the course of the disease is hidden. Only when the growth increases in size, is squeezed or is injured, signs may appear. The intensity of symptoms depends on the diameter and location of the tumor. The pathology is accompanied by:
- menstrual disorder;
- heavy bleeding during menstruation;
- pain during intimacy;
- discomfort in the lower abdomen;
- early termination of pregnancy;
- mucous secretions.
The occurrence of severe pain that radiates to the legs and back may indicate the transformation of the polyp into cancer. Malignancy of cells along with ingrowth into the mucous membranes signals that the formation is metastasizing.
Possible complications
If alarming signs of the disease appear, you must go to the hospital, undergo examination and therapy. Even the slightest delay in treatment (especially with a severe clinical course), refusal to undergo surgery or take medications is fraught with:
- Degeneration of a benign fibrous growth into cancer. With endometrial atypia, a threat to the patient’s health arises.
- Deterioration in the quality of intimate life. With an enlarged formation, a woman experiences pain during and after sexual intercourse. There is a loss of interest in sex (the girl is trying to avoid discomfort).
- Inability to conceive a baby. Due to the strong enlargement, glandular fibrous polyps cover the cervix. Against the background of changes in the endometrium, the egg will not be able to attach to the mucosa.
- Miscarriage. The tissue deformed by the fibrous tumor is not able to support the growing baby. The pathology is accompanied by bleeding, which leads to detachment of the child's place.
- Menstrual cycle disorders. Due to hormonal imbalance, menstruation fails. They become irregular and are accompanied by severe pain. Bleeding with fibrous growth is profuse.
- Anemia. Due to blood loss, a woman experiences malaise and a decrease in the body’s protective properties.
Glandular fibrous formations that follow a functional type can grow. Multiple growths are more difficult to treat.
Diagnostics
When symptoms of a fibrous polyp appear, you need to consult a doctor. Pathology, if you delay its treatment, leads to unpleasant complications. To prescribe the correct therapy, it is necessary to differentiate polyposis from other diseases. During diagnosis, the doctor, in addition to collecting complaints and anamnesis, and also examining in a chair, prescribes:
- Ultrasound. A safe method that allows timely detection of any changes in the membrane (thickening, expansion). Additionally, you can study the condition of the fallopian tubes and ovaries.
- Hysterosonography. A more accurate ultrasound examination technique involves injecting a saline solution into the uterus.
- Colposcopy. Thanks to imaging, any abnormalities in the endometrium are detected.
- Metrography. The growth can be seen under the influence of x-rays.
- Hysteroscopy. The most informative method. The procedure is often carried out in combination with curettage. To study the polyp, a biopsy is performed.
- Laboratory tests - smear for flora, bacteriological culture from the cervical canal, tests for sexually transmitted infections.
- Blood test to determine hormone concentrations.
Similar article – How to remove a callus on the foot
Treatment methods
Treatment of pathology can be conservative or radical. Often, a glandular fibrous polyp is treated in a comprehensive manner, first the growth is removed, and then medications are prescribed to restore the body and heal tissue, and also prevent relapse.
Medication
If the polyp is small and does not cause pain or other symptoms, surgery is not required. If there is a hormonal imbalance, steroids are prescribed.
There are cases when excision of a polyp is contraindicated. One of these is childhood. Pathology can occur even in a 10-year-old girl, for whom surgery is undesirable.
For women under 35, the use of oral contraceptives is indicated. The scheme and duration of the course is determined by the doctor.
Table - Drug therapy for fibrous polyps
Drugs
Effect/properties
When no positive dynamics are visible after drug therapy, surgery is prescribed.
Surgical
If fibrous polyps are large, multiple and accompanied by severe symptoms, they are removed. The most harmless and effective methods of excision of growth:
- Hysteroscopy. Low-traumatic method. The operation is performed using light anesthesia on the third day after menstruation. The duration of the intervention is on average 30 minutes. It consists of inserting a hysteroscope through the dilated cervix (to examine the cavity, determine the size and number of formations). Then the tumor is cut off with a surgical loop or forceps and the remains are scraped out.
- Laparoscopy. This method is preferred if there is a high risk of cancer. It involves removing the polyp along with the uterus. The procedure is performed using general anesthesia. During the operation, several incisions are made in the abdomen through which a device with a camera is inserted. After examining the organ, it is excised.
- Laser treatment. Removal of glandular fibrous polyps with a laser beam is a non-traumatic method. After the operation, no scars remain, and reproductive function is still preserved.
For rapid tissue healing and restoration of the body after the intervention, the use of antispasmodics (Papaverine, No-shpa), antibiotics (Ceftriaxone, Sumamed), gestagens (Marvelon, Triquilar), and vitamins is prescribed.
After excision of a polyp, you cannot take a bath, visit a bathhouse, sauna, have sex, or swim in ponds.
Features of pathology during menopause
Changes in hormonal levels during menopause can provoke the appearance of fibrous polyps in the uterus. Small growths are treated with hormones, and in case of severe growth, with surgical methods.
During menopause, it is not easy to identify pathology. One of the manifestations is disruptions in the menstrual cycle, which, in principle, are normal during the onset of menopause.
Glandular fibrous polyp and pregnancy
Growths in the uterus interfere with conception, but even with their presence, fertilization is possible. However, education left unattended by a doctor can lead to the inability to get pregnant in the future. This is one of the reasons why doctors advise removing the tumor as soon as it is discovered. Fibrous growths are dangerous during pregnancy, as they increase the likelihood of miscarriage.
Prevention
After removal, polyps may appear again. Reducing the risk of relapse helps:
- treatment of concomitant diseases;
- regular examinations by a gynecologist;
- leading an active, healthy life;
- rejection of bad habits;
- exclusion of casual sex.
conclusions
Glandular fibrous tumor in the endometrium is an unpleasant disease that every girl can face. With adequate therapy, the prognosis is favorable - women's health is preserved. Ignoring the manifestations of pathology or refusing treatment is fraught with complications, including infertility and cancer.
Questions and answers on: endometrial stromal fibrosis
Hello! I am 31 years old and gave birth to a 13 year old child. I want more children. There was one eco protocol; the histology conclusion was unsuccessful; scraps of cervical epithelium of a typical structure, a small polypoid fragment with endometrial glands of the proliferative type and stromal fibrosis; scraping from the uterine cavity; endometrium with glands of the early and middle stages of the proliferation phase , in the stroma there is diffuse pronounced lymphoplasmacytic infiltration, perivascular and periglanudular fibrosis. Conclusion: chronic endometritis. glandular fibrous polyp of the endometrium. What does this mean? Is it possible to treat such a diagnosis? Do they do eco thanks!
Hello. At 10.5 weeks, an ultrasound scan was taken. First pregnancy, planned, all previous tests are good, 39 years old.
The result of histology is as follows: “During histological examination, the presence of tissues of the decidua and villous chorion with chorionic plate is noted. The decidua is infiltrated with lymphocytes and plasma cells, with foci of edema, fibrinoid necrosis, and necrobiosis.
In the basal part of the decidua there is focal, superficial invasion of interstitial trophoblast, spiral arteries without signs of gestational restructuring. The chorion is represented by mesenchymal type villi, which are covered with trophoblast of varying thickness with proliferation phenomena.
Most villi have an avascular stroma without signs of angiogenesis, often with signs of fibrosis. Single villi contain fetal capillaries, in the lumen of which nuclear erythrocytes of the fetus are visible. Large foci of villi with symptoms of necrobiosis are also found, as well as villi “embedded” in fibrinoid.
Diagnosis: impaired development of pregnancy in early gestation 6-7 weeks; anomaly in the development of the villous chorion: impaired vascularization and maturation; decreased invasion of the interstitial trophoblast into the endometrium with impaired decidualization.”
Analysis of fetal genetics.
Conclusion: 46,XY nuc ish (DXZ1x1,DYZ3x1,D18Z1x2)x/(RB1,D21S341)x2/(D16Z3,D15Z3,BCR)x2
Source: https://lechenie-nog.info/ochagovyj-fibroz-stromy-jendometrija/
Classification and stages of development of uterine fibroids
Classifications of uterine fibroids are based on the location and direction of growth of the formation, as well as on clinical manifestations.
1. By localization and direction of growth:
- subserous - growth of a fibromatous node towards the abdominal cavity (intra-abdominal location, intraligamentous location). In this case, the fibroma is located under the serosa of the uterus;
- submucosal - growth of a fibromatous node towards the uterine cavity, under its mucous membrane (endometrium);
- interstitial - the growth of fibroids inside the wall of the uterus, in the thickness of the muscle layer.
2. According to clinical manifestations:
- asymptomatic uterine fibroma (occurs in 70-80% of cases) - fibroma that does not manifest itself in any way. Typically, the early stage of fibroid development is asymptomatic.
- symptomatic uterine fibroid (occurs in 20-30% of cases) - in this case there are various symptoms caused by the tumor. As already mentioned, clinical manifestations of symptomatic uterine fibroids can be: menstrual irregularities - menometrorrhagia; pain syndrome of varying severity and nature (pulling, cramping, dysmenorrhea); various signs of compression and/or dysfunction of the pelvic organs that are located next to the uterus; infertility; habitual miscarriage.
Depending on the number of nodular formations, single and multiple uterine fibroids are distinguished. Multiple uterine fibroids are more common.
Chronic antral gastritis
Chronic antral gastritis can occur in active and inactive forms. Not to be confused with reactive type. This is called reflux gastritis or chemical gastritis.
The degree of inflammation (mild, moderate, severe gastritis) and activity (low degree of activity or grade 1, moderately active or grade 2, high degree of activity or activity 3) is determined by the results of FGDS and histological analysis.
These criteria depend on the characteristics of the life activity of Helicobacter pylori and are identified by the degree of penetration of such cells into the gastric mucosa:
- lymphocytes;
- plasma cells;
- neutrophil granulocytes.
Complications of uterine fibroids
A risk factor for the health of patients with fibroids is an increase in the tumor with characteristic signs of pathology - bleeding; pressure of the node on neighboring organs.
The most common complications of uterine fibroids include:
- anemia: due to prolonged and heavy uterine bleeding, the concentration of hemoglobin in the blood decreases. The main symptoms are weakness, fatigue, headaches, dizziness, the appearance of trophic changes;
- infertility: large uterine fibroids significantly reduce the chances of pregnancy. This is due to a number of reasons: the uterine cavity changes and implantation of a fertilized egg becomes difficult; large fibromatous formations can block the mouths of the fallopian tubes, preventing sperm from entering them;
- the birth of a fibromatous node: this complication occurs when the node is submucosal on a stalk, when it exits into the vagina. The onset is always acute and requires immediate hospitalization! If left untreated, it can lead to serious consequences, such as infectious inflammation, peritonitis;
- torsion of the tumor stalk, malnutrition of the formation, leading to subsequent necrosis: uterine fibroids can deform the vessels that provide its blood supply, and thereby cause tissue necrosis. Necrosis can be provoked by physical activity, sexual intercourse, and pregnancy. It is one of the most dangerous complications and requires immediate hospitalization!
- disturbances in the functioning of internal organs , which occur due to excessive pressure on the pelvic organs, which causes the development of chronic diseases (constipation, colitis, cystitis, pyelonephritis, hydronephrosis).
Diagnosis of uterine fibroids
As a rule, diagnosing uterine fibroids in most cases is not difficult. First of all, it is necessary to correctly identify the medical history and take into account all risk factors for the occurrence of uterine fibroids, and conduct a gynecological examination. The easiest way to diagnose uterine fibroids is a gynecological examination on a chair . During this examination, subserous fibromatous nodes may be palpated separately from the uterus. Most often in the form of separate formations of a round shape, dense, with varying degrees of mobility. The uterus itself can be of various sizes, but more often it is enlarged, and can be of enormous size. The surface of the uterus is palpable with a tuberous, fibromatous nodes of a denser structure. If blood circulation in fibromatous nodes is impaired, palpation becomes painful. In women with interstitial fibroma, an enlarged uterus can be felt, the consistency of which will be dense, the surface may be smooth or lumpy. Malnutrition of the interstitial nodes usually does not occur, so palpation of such a uterus is most often painless.
Ultrasound examination (ultrasound) of the pelvic organs is the gold standard not only for diagnosing primary uterine fibroids, but also for their dynamic monitoring. [1] The advantage of the method is its information content, accessibility, and safety. However, it is worth considering the fact that ultrasound is a rather subjective diagnostic method, because the reliability of the results largely depends not only on the qualifications of the specialist, but also on the patient’s preparation for the study.
Ultrasound diagnostics makes it possible to assess the size of the uterus, establish the number of pathological foci and their location, the nature of the shape and contours, size, structure and density; during dynamic observation, compare the data with the results of the previous study, assess the dynamics of the pathological process. To clarify the location of fibromatous nodes, you can use ultrasound tomographs that provide a three-dimensional ultrasound image. Significant diagnostic data can be revealed by color Doppler mapping (CDC) . Using it, you can evaluate not only the echographic picture of the structure of the fibroma, but also evaluate its blood flow.
Along with ultrasound diagnostics, methods such as computed and magnetic resonance imaging . However, methods of radiological diagnosis in women of reproductive age are resorted to under strict clinical indications.
In case of menstrual irregularities, patients are advised to undergo diagnostic hysteroscopy - a highly informative method that allows assessing not only the condition of the uterine cavity, pathological processes of the endometrium, the type of node and its location, but also deciding on the possibility of performing transcervical fibromectomy with endoscopic control. [1] Such a procedure is possible only in patients with fibroids with an enlarged uterus of no more than 12-13 weeks of pregnancy.
In addition, to assess the condition of the endometrium for diagnostic purposes, endometrial curettage with histological examination is used. The results of histological examination can significantly affect the management of the patient. Carrying out diagnostic curettage allows you to decide on the continuation of conservative therapy or the extent of surgical intervention.
In special cases, if it is necessary to differentiate between fibroma and giant ovarian and retroperitoneal tumors, diagnostic laparoscopy is used.
Treatment of uterine fibroids
There are two main tactics for treating uterine fibroids - conservative and surgical. The only way to completely get rid of the tumor is through surgery.
Conservative treatment methods involve influencing pathogenetic changes to slow the growth of uterine fibroids. This can be achieved by prescribing hormonal therapy. The main drugs here can be gestogens, gonadotropin releasing hormone agonists, androgens, gonadotropin antagonists. Correction of metabolic disorders such as obesity and diabetes mellitus, normalization of immune processes, restoration of menstrual function, prevention of inflammatory diseases can also have a beneficial effect on the disease. [5] [6]
Despite the positive results of conservative therapy, surgical treatment remains the leading method in the treatment of uterine fibroids. [1] The extent of the operation largely depends on the age of the patient and her desire to maintain the ability to become pregnant, on the location and size of fibromatous nodes, the rate and nature of their growth.
Indications for surgical treatment are:
- symptomatic uterine fibroid (presence of pain, pathological uterine bleeding, signs of anemia);
- submucous location of uterine fibroids;
- subserous node of uterine fibroid on a stalk;
- rapid growth of fibroma and its large size;
- cervical and cervical-isthmus localization of fibroma;
- acute malnutrition of fibroid nodes, severe ischemic and degenerative changes;
- the presence of a fibromatous node in the area of the tubal angle of the uterus;
- compression of pelvic organs by fibroids - bladder, ureters, rectum. Especially if this leads to disruption of their functions.
Previously, the only treatment for fibroids was radical surgery - hysterectomy, that is, removal of the uterus. The modern approach is to remove fibromatous nodes using laparoscopic technologies, which allows preserving not only menstrual function, but also the woman’s ability to bear a child. Minimally invasive organ-preserving operations include uterine artery embolization, which is both an independent procedure and one of the stages of preparation for surgery. Due to the decrease in blood flow after UAE, the nutrition of the nodes is disrupted, which leads to their reduction and prevents further growth. [5] [6]
With timely diagnosis and treatment, uterine fibroids have a fairly favorable prognosis. Malignization of fibroids, that is, malignancy of the tumor, occurs extremely rarely, in only 2-5% of cases.
Therapeutic measures
The choice of treatment method depends on the stage of the disease. If uterine fibrosis is asymptomatic, then sometimes the doctor suggests monitoring the progression of the disease. The patient should visit the doctor regularly to monitor changes. And in the period between visits, a woman should follow the following recommendations:
- if necessary, reduce body weight to normal;
- take vitamins and microelements, eat well;
- avoid visiting saunas and steam baths;
- do not sunbathe;
- get rid of bad habits.
In case of negative dynamics of the disease, the doctor prescribes drug or surgical treatment depending on the age of the patient. In nulliparous women of reproductive age, surgical intervention is used only in extreme cases.
Drug treatment
Hormonal therapy with drugs from different pharmacological groups is the basis of drug treatment in the presence of fibroid nodes. Androgens (Danazol, Gestrinone) are used to reduce the production of steroids. To reduce tumors, they are taken over a long course (up to 8 months).
For endometrial hyperplasia, the use of gestagens is indicated (Dydrogesterone 10 mg 2-3 times a day or Norethisterone 5 mg per day). These drugs are taken with 5 mg from days 5 to 25 of the MC. Such treatment is justified only if the fibroid tumor is small and accompanied by endometrial hyperplasia. The standard course of gestagen therapy is 8 months.
Excellent results in treating the disease using the Mirena system have been recorded. Its action is based on the gradual release of a certain dose of levonorgestrel. This treatment stops the growth of fibroids and provides additional contraception. The use of COCs containing ethinyl estradiol and dienogest/drospirenone inhibits the growth of small nodes. Contraceptive therapy according to the usual regimen is carried out over a three-month course.
GnRH agonists (Buserelin, Goserelin) suppress the action of the ovaries and pituitary gland, reduce blood flow to the uterus and thus disrupt the nutrition of fibroid nodes. As a result of long-term use, a decrease in estrogen levels and a reduction in the size of the formation is achieved. The effect of therapy is temporary; after stopping the use of GnRH agonists, fibrous nodes return to their original size after 4-6 months.
Studies have shown that if you take the drug at 100 mg/day for 2 months, the effect persists even when using a smaller amount of agonist (from 5-20 mg/day) for 4.5 months. GnRH agonists are used preoperatively to reduce fibroids.
Surgery
Removal of uterine fibroids is indicated for pain, bleeding, compression of adjacent organs and submucous growth. Surgical treatment is also necessary for large tumors, concomitant diseases (ovarian tumors, endometriosis) or node necrosis.
Types of myomectomy
Surgeries that preserve the integrity of the organ and reproductive function in case of uterine fibroids include hysteroscopic, laparoscopic and abdominal myomectomy. What is myomectomy and how is it performed? During the operation, the fibroid node is removed, while the uterus is preserved. For submucosal localization of the fibrous node, hysteroscopic myomectomy is used.
Before surgery, carbon dioxide is injected into the abdominal cavity to provide free space for manipulation. The operating doctor inserts a resectoscope through the vagina into the uterine cavity and removes the node under visual control. The operation is low-traumatic and has a short recovery period.
Laparoscopic myomectomy is performed if subserous or intramural nodes are present. The laparoscope is inserted into the cavity through small incisions in the umbilical area. Punctures are made in the lower abdomen through which instruments are inserted.
An abdominal myomectomy is performed through incisions in the abdomen and uterus. The recovery period after such an operation is longer, but this method allows you to preserve the organ and the ability to bear children. For mature patients who do not plan or cannot have children, radical surgical methods are used: complete hysterectomy or supravaginal amputation of the uterus.
Embolization of fibroids or uterine arteries
UAE is a method that makes it possible to fight fibroids without active surgical intervention, while the patient still has the opportunity to give birth to a child. It consists of occlusion (blocking) of the vessels feeding the neoplasm, while the blood supply to the fibrous nodes is blocked, followed by their regression.
Uterine artery embolization
FUS ablation is a technique of high-frequency ultrasound evaporation of tumors under MRI control. Tumor tissues are heated to 65-85 degrees, resulting in thermal necrosis. Sound waves do not cause damage to healthy tissue. The method allows you to remove the fibromatous node without surgery, preserving the woman’s uterus and reproductive function.
Nature and causes of the disease
Over the past decade, the number of cases of uterine fibrosis has increased several times. Doctors explain this trend by the fact that, under the influence of various unfavorable factors, the process of tissue proliferation begins in the female body. Naturally, unfavorable ecology plays a major role in this. Fibrosis consists of the appearance of a series of connective tissue compactions that lead to the formation of scars. In medical practice, there are known cases of this disease affecting the lungs, liver, mammary glands and other organs. Sometimes the fibers can completely cover the mucous membranes, increasing their size several times.
Pathological processes, as a rule, begin with increased production of collagen in a woman’s body. This substance is the main component of connective tissue. If the level of collagen gradually increases, exceeding the permissible level, then normal cells begin to be displaced. Over time, this leads to the fact that the work of the organ affected by fibrosis is disrupted or completely stops.
The following reasons for the appearance of this disease can be identified:
- Inflammatory process in the reproductive organs.
- Excess weight.
- Hormonal imbalances.
- Artificial termination of pregnancy.
- Genetic predisposition.
- Stress.
- Poor nutrition.
- Bad habits.
Most often, uterine fibrosis is diagnosed in women who have had an artificial abortion. Caesarean section, installation of coils, cleaning after a miscarriage, injuries to the organs of the reproductive system - all these mechanical effects can also cause the development of the disease. Therefore, the gynecologist must review the patient’s medical history over the past few years.
Often people with second or third stages of obesity suffer from fibrosis. Therefore, before starting therapy, the doctor may prescribe a special diet for weight loss and mild physical activity. Otherwise, the treatment will not bring any effect, since hormonal drugs will not be able to slow down the development of the disease due to the patient’s high weight. Surgery for obesity has too high a risk of death.
Signs of illness
The clinical picture of uterine fibrosis depends on the patient’s age, the stage of development of the disease, the location of the tumor, and hormonal levels. Often the reason for a woman to see a doctor is concomitant genital pathologies. During the examination, the presence of benign neoplasms in the patient’s reproductive system is determined.
Main symptoms of the disease:
- Uterine bleeding.
- Painful sensations in the lower abdomen and lower back.
- Problems with urination and constipation.
Often, uterine fibrosis does not manifest itself in any way. But this applies only to the initial stage of development of the disease, when the fibrous tumor is still small in size. Without treatment for this disease, tissue begins to grow inside the uterus, completely filling its cavity. In addition, the nature of menstrual flow changes. They can be both abundant and meager. Medical practice knows cases of complete absence of menstruation.
Often the tissue grows so much that it begins to fill the fallopian tubes and damage the cervical mucosa. In most cases, this leads to infertility. Naturally, treatment of the disease in young nulliparous women excludes surgical intervention, since not individual areas are removed, but the entire damaged organ. This eliminates the possibility of getting pregnant in the future. Therefore, the doctor prescribes a complex of hormonal drugs.
In the case of an advanced form of the disease, tissues can grow in other organs. Often, with fibrosis of the uterus, a woman is bothered by pain in the liver or pancreas. This indicates the rapid spread of the disease in the body.
In such cases, surgery is prohibited because there is a high risk of death due to bleeding in the damaged organs. Therefore, your doctor may recommend taking a course of medication. In addition, a strict diet must be observed, in which spicy, fatty and fried foods should be excluded.
Diet
Treatment will not bring the expected effect without following a special diet. The diet includes gentle dishes that reduce and normalize the level of acidity in the stomach. Nutrition rules for reflux gastritis:
- during an exacerbation, follow diet No. 1;
- exclude spicy, fried foods from the diet;
- do not eat 3 hours before bedtime;
- eat 5-6 times a day in small portions;
- exclude cold and too hot dishes - take food only warm.
table No. 1 (click on the picture to enlarge) Compliance with the regime promotes recovery. It is advisable that meals be taken without haste, at certain hours. If you have reflux gastritis, you can eat:
- viscous porridges - buckwheat and oatmeal are especially useful;
- soups with minced meat;
- steam cutlets;
- low-fat fish;
- well-cooked vegetable stew;
- low-fat dairy products;
- eggs (no more than 2 times a week);
- yesterday's bread (fresh increases acidity);
- crackers;
- butter, olive oil;
- jelly;
- herbal tea;
- for dessert - marmalade, soufflé, pastille, baked apples.
Nutrition for gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD)
During the period of remission, it is recommended to drink medicinal mineral water. Tonic drinks, seasonings, rich broths, and gas-forming products are excluded from the diet.
Treatment and preventive measures
Often, the course of treatment for uterine fibrosis includes the following measures:
- Taking vitamins B, A, E and C.
- Taking antioxidant drugs.
- Lack of strong physical activity.
- Avoiding overheating of the body.
- Healthy lifestyle.
- Rejection of bad habits.
- Losing excess weight.
- Healthy eating.
- Full sleep.
The inflammatory process should be avoided, since fibrosis that has formed in the uterus tends to develop in the tissues of other organs.
The disease can affect the lungs with frequent smoking or the liver with an unhealthy diet. Therefore, it is imperative to lead a healthy lifestyle, which also includes exercise, but in moderation.
If fibrosis was diagnosed in time, but continues to progress, the doctor prescribes hormone therapy. Its main goal is to slow down and further stop the growth of the tumor. But often the disease is discovered only when surgical intervention is unavoidable.
Uterine fibrosis is usually removed in order to reduce the risk of its degeneration into cancer. However, following all recommendations and a correctly prescribed course of therapy will help stop the increase in tumor size.
But it is worth remembering that the disease requires constant monitoring, so it is necessary to undergo ultrasound examination as often as possible.