What is the corpus luteum of the ovary?
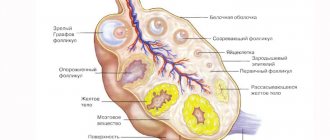
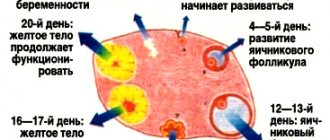
The corpus luteum of the ovary is a special temporary endocrine organ that normally appears in women in the ovary every menstrual cycle at the site of a burst follicle. After ovulation - the release of an egg from a ruptured follicle - the cells of its walls actively divide and are filled with a yellow substance called “lutein”. This substance gave its name to the corpus luteum.
The main function of the corpus luteum is to produce progesterone, a hormone that supports the development of pregnancy. If conception has occurred and the egg has implanted into the endometrium, the corpus luteum continues to develop and produces more and more progesterone. If there was no fertilization, then the corpus luteum dies, and a scar appears in its place (the so-called white body). In the new menstrual cycle the situation repeats itself.
At the peak of its development, the corpus luteum reaches 3 cm in diameter. If its size exceeds 4 cm, this means that a cyst has appeared inside it. As a rule, cysts less than 7 cm in size, like the corpus luteum itself, produce progesterone. The larger size of the cyst indicates that the corpus luteum has ceased to fully perform its functions.
The course of menstruation after a burst cyst
Various surgical interventions, including removal of a benign tumor, have a small effect on the onset of menstruation . It happens that after surgical removal, instead of the usual discharge, red-brown mucus appears . If the secretion turns yellowish or greenish, it can be said that there is an infection in the body.
Such disorders are accompanied by certain symptoms:
- drowsiness;
- weakness;
- constant low-grade fever.
Sometimes after a cyst, menstruation occurs with white discharge , which indicates thrush.
This situation requires prompt consultation with a doctor. You should undergo comprehensive treatment in a specialized institution.
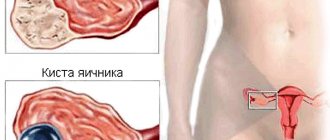
Why do luteal cysts form?
The mechanism of formation of corpus luteum cysts is that after ovulation, follicle cells do not grow and are not filled with lutein. In this case, the follicular walls are stretched and filled with serous fluid. The exact causes of corpus luteum cysts are unknown. The most likely factors predisposing to their occurrence are:
- disturbances of blood and lymph flow in the corpus luteum;
- inflammatory diseases of the pelvic organs;
- hormonal imbalance;
- severe stress;
- taking medications to stimulate the ovaries for infertility;
- taking emergency contraception medications;
- poor nutrition;
- abortions.
Luteal cysts occur exclusively in two-phase menstrual cycles and most often in only one of the ovaries. They are often detected during a multiple pregnancy. It should be noted that corpus luteum cysts never become malignant.
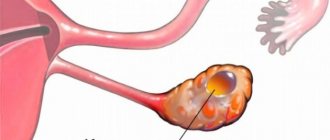
The base of the cyst ruptures
How can you tell if an ovarian cyst has burst? If a cyst on the ovary bursts, symptoms of the disease are most often observed due to:
- Thin capsule walls that have formed due to weakened follicles and an inflamed ovary. This form of the disease is more susceptible to blood pressure during the period of ovulation and can provoke signs of rupture of the ovarian cyst just a few months after the appearance and beginning of formation.
- “Wrong” hormonal levels. Hormonal levels also directly affect the nature of development and the likelihood of symptoms appearing with a burst ovarian cyst. If, during the growth of a tumor, hormones are released at an increased rate or, on the contrary, their concentration level decreases, the ovaries react to this, stopping the process of producing follicles. Due to hormonal imbalance, blood pressure in the reproductive system changes, which directly leads to symptoms of ovarian cyst rupture.
- Disturbances in the circulatory system. The tumor can rupture and provoke symptoms of a ruptured cyst on the ovary if the woman has been diagnosed with problems with circulation or blood clotting. Any disturbances and disruptions in blood circulation during the growth of the disease can cause rupture of the capsule, the appearance of signs of a burst ovarian cyst, symptoms and fluid entering the abdominal cavity or genitourinary system.
- Physical influence. The capsule can burst even with normal, everyday physical activity, sports or sexual contact. Mechanical influence can lead not only to the detachment of tumor tissue and the fact that a cyst on the ovary bursts; symptoms. Physical impact is fraught with twisting of the cyst stalk, which in turn entails multiple inflammation and aggravation of the pathology.
Symptoms of a corpus luteum cyst
The symptoms of their appearance are not always expressed - in rare cases, women develop:
pain during sexual intercourse and physical activity;
- heaviness in the lower abdomen (from the side of the cyst);
- disruptions in the rhythm of the menstrual cycle (in non-pregnant women).
In most cases, these tumor-like formations gradually decrease in size and disappear towards the end of pregnancy, and in non-pregnant women - within 2-3 cycles. Pain from a corpus luteum cyst goes away as it decreases.
However, in rare cases, luteal cysts cause serious complications. These include:
- violation of the integrity of the follicle walls - rupture of the corpus luteum cyst (in this case, the contents spill into the abdominal cavity);
- torsion of the leg, which results in necrosis of surrounding tissues;
- internal bleeding (rupture of a cyst with hemorrhage into the ovary).
These conditions may be accompanied by acute pain in the lower abdomen, nausea, dizziness, and general weakness. Torsion of the cyst stalk and its rupture can cause bleeding, lead to the development of an infectious and inflammatory process in the pelvis, peritonitis, etc. In addition, when the legs are torsed, necrosis and inflammation of the surrounding ovarian tissues are possible.
In such cases, emergency surgery is required, since delay can be fatal. For intra-abdominal bleeding, depending on the amount of blood loss and the woman’s condition, both conservative and surgical treatment are possible.
Definition and specificity of pathology
The signs of a rupture or if an ovarian cyst has burst are the detachment of tumor tissue of the reproductive organ, which occurs for a number of reasons. When considering the question of what are the symptoms when an ovarian cyst bursts, it is worth knowing that regardless of the size and nature of its functioning, every foreign mass that affects the ovary, when ruptured, leads to fluid from its capsule flowing into the area of the organs of the reproductive system and gastrointestinal tract. - intestinal tract. Because of this, the patient may experience severe pain, suffer from infection and death of healthy tissue.
Cystic formations of small sizes and signs, symptoms of rupture of an ovarian cyst for a long time, as a rule, are invisible to a sick woman. They are usually found during routine examinations of the reproductive system or during an ultrasound examination of the abdominal or gastrointestinal tract. At the same time, regardless of the stage of development and characteristics of formation, any benign tumor affecting ovarian tissue is a pathology. This means that it must be cured, and highly preferably before ovarian cyst rupture symptoms show.
Diagnosis and treatment of corpus luteum cyst
A corpus luteum cyst is usually detected during routine ultrasound as an incidental finding. In non-pregnant women, it is also possible to detect cysts during laparoscopy. Quite often, a corpus luteum cyst is difficult to differentiate from other ovarian tumors, so color Doppler sonography is used to confirm the diagnosis, showing the absence of blood vessels inside the tumor.
If within several months the cyst has not undergone reverse development, and the patient feels worse, oral contraceptives are prescribed outside of pregnancy, which accelerate the process of resorption of the tumor.
Also widely used:
- balneotherapy and mud therapy;
- physiotherapy (magnetic and laser therapy, ultraphonophoresis).
In emergency cases, surgical intervention is performed - the cyst is removed within healthy tissue using laparoscopic access (rarely using a cavity incision).
Can an ovarian cyst come out during menstruation?
Often girls do not even suspect that such formation comes out with menstruation on their own. There is a theory that the cyst not only resolves, but also leaves the body during menstruation . A benign tumor has a close relationship with the menstrual cycle. Before the onset of the critical days, the neoplasm can provoke pain and heaviness.
The release of a cyst during menstruation occurs provided that it arose due to organ malfunction and lack of ovulation. Its disappearance may be due to atrophy.
How does a corpus luteum cyst affect the course of pregnancy?
In most cases, it does not pose any threat to the child and mother, but as already mentioned, sometimes complications may develop that require surgical intervention.
In addition, if the cyst is large, then the level of hormones necessary for the development of pregnancy (especially progesterone) may decrease. Therefore, pregnant women are additionally prescribed drugs that contain progesterone until the placenta is formed (16-20 weeks of gestation).
In case of emergency complications, the pregnant woman is treated only surgically. In the vast majority of cases in this situation, with timely treatment, the prognosis for the child and mother is favorable.
Rupture of ovarian cyst ICD 10
Hemorrhagic cyst of the corpus luteum
ICD-10 alphabetical indexes
External Causes of Injury - The terms in this section are not medical diagnoses, but rather a description of the circumstances under which the event occurred (Class XX. External Causes of Morbidity and Mortality. Heading Codes V01-Y98).
Medicines and chemicals - table of medicines and chemicals that have caused poisoning or other adverse reactions.
In Russia, the International Classification of Diseases
10th revision (
ICD-10
) was adopted as a single normative document for recording morbidity, reasons for the population’s visits to medical institutions of all departments, and causes of death.
ICD-10
introduced into healthcare practice throughout the Russian Federation in 1999 by order of the Russian Ministry of Health dated May 27, 1997 No. 170
The release of the new revision (ICD-11) is planned by WHO in 2022.
Abbreviations and symbols in the International Classification of Diseases, 10th Revision
NOS
- without other instructions.
NEC
— not classified in other categories.
†
— code of the main disease. The main code in the dual coding system contains information about the underlying generalized disease.
*
- optional code. An additional code in the double coding system contains information about the manifestation of the main generalized disease in a separate organ or area of the body.
Apoplexy or rupture is one of the most common complications of ovarian cysts. Typically, the tumor capsule bursts in functional formations, which, due to the possibility of spontaneous resorption, are observed and treated conservatively.
Rupture of an ovarian cyst, the symptoms of which every patient with growths on the appendages should know, is considered a gynecological emergency. In rare cases, it is possible to manage with drug therapy; more often, patients require immediate hospitalization and surgical intervention.
How to cure the disease?
Are there signs of a corpus luteum cyst? You have the opportunity to get rid of unwanted symptoms and protect yourself from dangerous complications. Experienced doctors work at the On Clinic medical center in Almaty. The gynecologist will conduct an examination. Based on its results, you will be prescribed treatment. It is developed individually.
The therapeutic course is aimed at:
- elimination of symptoms;
- suppression of the inflammatory process;
- resorption of cystic formation;
- normalization of hormonal levels;
- increasing the body's defenses.
In cases where the luteal cyst is large and does not respond to conservative treatment, the patient is prescribed surgery. Any disease at an early stage is better treated, so you should consult a doctor at the first signs.
Many gynecological diseases are asymptomatic. In order to detect them early and promptly treat them, it is recommended to visit a gynecologist at least once every 6 months.