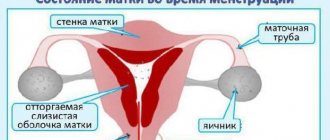
Uterus during menstruation
Quite naturally, most women are interested in how to determine the condition of their gynecological organs without visiting a doctor.
It is impossible to conduct a visual examination of the internal genitalia on your own, so the option of examination by palpation remains. Before the onset of menstruation, the uterus slightly enlarges and falls. During menstruation, the internal and external pharynx of the cervical canal of the cervix opens slightly (expands in the same way as during the ovulation process). The essence of this phenomenon lies not in readiness for conception, but in the need for free passage and removal of blood clots from the uterus.
In a woman who has given birth, the cervix no longer has a physiological bend towards the sacrum, so there is no obstacle to the passage of menstrual blood, which reduces pain during contractile movements of the uterus.
During this period, the physiological state of the reproductive organs is very vulnerable to various infections - the microflora and openness of the pathways favor the development of pathogens, so on such days it is not recommended to have unprotected sex (without condoms), take baths, swim in ponds and pools.
Critical days require certain hygiene rules, the observance of which will preserve women’s health:
- Genital hygiene should be carried out more often than usual - after defecation and before changing pads;
- Do not use heavy physical labor under any circumstances to avoid increased pain and bleeding;
- It is strictly forbidden to douche the vagina and use intimate chemicals - creams, gels, and so on.
Possible complications
In addition to discomfort and disruption of the woman’s general condition, failure to identify the cause of pain can lead to various complications. A decrease in hormonal levels disrupts the composition of normal microflora, which causes the development of pathogenic microorganisms, such as fungi of the genus Candida, streptococci, staphylococci, mycoplasma, gardnerella. Untreated pathology leads to the penetration of infection into the urinary tract and the development of genitourinary diseases (cystitis, vulvovaginitis, pyelonephritis).
When myomatous nodes are located in the submucosal layer of the uterus, the outflow of menstrual blood is disrupted. This causes increased contractions and, as a result, increased pain. Uterine fibroids also increase the risk of developing dysfunctional uterine bleeding. The disease may be accompanied by torsion of the pedicle of the node with its necrosis, impaired reproductive function (miscarriage, infertility), transformation of the node into a malignant tumor, and severe forms of anemia. Infertility and ovarian cancer are among the main complications of endometriosis.
Preparing the body for menstruation
During desquamation, the functional layer of the endometrium is rejected. The process occurs on the 28-29th day of the cycle. It lasts 5-6 days. The functional layer looks like areas of necrotic tissue, and with the arrival of menstruation, the endometrium is completely rejected in 1-2 days.
At the very beginning of menstruation, the uterus in its normal state has a smooth and tactilely dense cervix.
Its normal size in nulliparous girls is: length - 45 mm, width - 46 mm, thickness - 34 mm; and for those who gave birth: length - 53 mm, width - 50 mm, thickness - 37 mm.
During ovulation, the cervix opens a little and becomes loose. After a failed conception, the process of menstruation begins. The cervix begins to straighten and descend into the vagina.
It is the process of shedding the endometrium and leaving it from the uterus that is called menstruation. The phases of the menstrual cycle are regulated by follicle-stimulating and luteinizing hormones of the pituitary gland, due to which active substances are released: progesterone, estrogen. These hormones prepare the body for conception and regulate the menstrual cycle.
The period of menstruation usually lasts 2-7 days, and the duration of the menstrual cycle is approximately a month. However, some deviations in its duration are acceptable, but the cycle must be regular.
The pain and duration, various characteristics of menstruation, as well as the menstrual cycle are mainly influenced by heredity.
Physiological reasons
Causes of primary dysmenorrhea:
- insufficiency of the luteal phase of the menstrual cycle;
- lack of endorphins;
- excess prostaglandins.
Primary dysmenorrhea is typical for girls of asthenic physique, with an unstable nervous system. A lack of endorphins leads to a deterioration in the emotional state and the development of depression.
Prostaglandins are substances that increase vasospasm. This causes stagnation of blood in the pelvis. As a result, pain occurs during uterine contractions.
Pain tolerance depends on the level of the pain threshold. The less endogenous opiates are produced in the brain, the lower the pain threshold. Accordingly, the worse the pain is tolerated.
With primary dysmenorrhea, the pain is cramping and intense. Accompanied by weakness, malaise, fever, nausea. Dizziness and fainting are possible. Sometimes one of these symptoms becomes so severe that it overpowers the pain. Headache during menstruation reaches significant intensity, reminiscent of migraine.
The diagnosis of primary dysmenorrhea is made if the patient is young and painful periods appear a year after the first menstruation. A thorough examination should not reveal any other diseases of the reproductive organs.
Pain during menstruation
So why does the uterus hurt during menstruation? The physiological processes of rejection of the uterine mucosa cause its contractions for the speedy removal of the endometrium and unfertilized egg. These painful sensations are not associated with pathology and do not change the general condition of the woman.
A condition in which the uterus hurts during menstruation is called algodismenorrhea. It can be primary and secondary. Primary algodismenorrhea is functional in nature. The reasons for its development are the following:
- Incorrect position of the uterus, leading to stagnation of blood during menstruation.
- Endocrine pathology, caused by an increase or decrease in the synthesis of prostaglandins, leads to hormonal imbalances in the body.
- A woman’s emotional instability leads to a decrease in the threshold of pain sensitivity.
- The constitutional characteristics of a woman play an important role. Thus, with infantilism, due to the small size and insufficient development of the muscles of the uterus, its ability to stretch is impaired. This causes irritation of the nerve endings, which is accompanied by pain.
Secondary algodismenorrhea occurs against the background of damage to the organs of the genitourinary system. The uterus can hurt during menstruation with the development of inflammatory processes, fibroids, endometriosis, ovarian apoplexy, and abnormal development of the genital organs. Installation of an intrauterine device can also cause increased pain, which is associated with stimulation of the release of prostaglandins.
Spasms due to uterine fibroids
Spasms and pain also occur after fibroids appear in the uterus. This happens because the organ tries to get rid of it in the same way as with an ectopic pregnancy. He actively contracts the walls in order to expel it. Fibroids appear from the wall of the uterus, usually near the cervix. This is accompanied by severe cutting pain and frequent spasms. There is also copious discharge of blood from the vagina. The pain spreads to the entire lower abdomen and can radiate to the sacrum.
In this case, there is only one way to relieve cervical spasm. To do this, it is necessary to surgically remove the fibroid. This will also relieve uterine spasms and prevent the development of complications. In order to avoid its occurrence in the future, it is necessary to regularly conduct examinations and visit a doctor.
You can independently determine the onset of the disease by certain signs. These include:
- Heavy menstruation with copious discharge.
- Spasms and pain in the lower abdomen appear periodically.
- Frequent urge to urinate begins.
- Constipation occurs.
But it happens that not all people may notice the symptoms. They are not felt by people who tolerate pain well and do not notice it.
Women who are at risk and susceptible to the manifestation of the disease should pay special attention to their health. These include women and girls:
- nulliparous at the age of about 30 years;
- having excess body weight;
- who have a hereditary predisposition;
- with hormonal imbalances in the body;
- with weakened immunity.
Ovulatory abdominal pain in women after menstruation
Not all women experience ovulatory pain, but most of the fair sex are familiar with it. Painful sensations appear approximately two weeks before the onset of menstruation, the pain is felt directly inside the pelvic bone.
During ovulation, slight bleeding occurs from the ovary, it causes irritation on the wall of the abdominal cavity, and as a result, the woman experiences pain. The intensity of pain depends on the individual characteristics of the body and the degree of bleeding.
If a woman has a stomach ache after menstruation during ovulation, then this is a feature of the woman’s reproductive system, and not some kind of pathology; painful ovulation cannot provoke other gynecological diseases.
Since during the cycle the right and left ovaries often work in turn, pain during menstruation can be observed either on the right or on the left. The pain is concentrated in the lower abdomen and appears about two weeks before the start of menstruation. The pain does not last long, depending on the individual it can last several minutes or several hours, although some women complain of a dull ache that torments them throughout the day.
The nature of the pain - it can be sharp or dull, its intensity is low. In general, everything related to menstrual pain is difficult to fit into the overall picture. Each woman’s body is individual, and therefore pain sensations can manifest themselves in completely different ways and have different intensities. Some women endure everything on the go, while others simply need bed rest and painkillers.
Features of the treatment of ovulatory abdominal pain
If you experience pain in the middle of the menstrual cycle, go to a gynecologist for prevention; only after an examination can you be sure that the pain is really related to ovulation. A woman should keep an ovulation diary and mark on the calendar the beginning and end of menstruation, as well as the day when pain appears, this will also help the doctor in establishing the correct diagnosis.
If the issue of contraception is relevant for a woman, then the option of using oral contraceptives, the effect of which is aimed at suppressing ovulation, is possible. This solves two problems at once: control of unwanted pregnancy and relief from pain after menstruation and during ovulation.
Pregnancy symptoms
In addition to delayed menstruation, pregnancy can manifest itself with a number of other symptoms:
- Constant fatigue can be caused by hormonal changes in the body, which are among the first signs of conception.
- The breast reaction may become aggravated. All touches to it become painful, and sometimes there is an increase in volume.
- Cramps and pain in the lower abdomen, which happens before menstruation, can be one of the signs of pregnancy before the delay.
- Small vaginal discharge, which is a sign of attachment of the egg to the uterus.
- Nausea may appear along with a delay in menstruation and go away fairly quickly or accompany the woman throughout pregnancy.
- The constant urge to urinate is associated with a gradual increase in blood in the body, as well as other fluids that ensure the vital functions of the mother and the unborn baby. The longer you are pregnant, the more often you will have to visit the toilet. However, this symptom should not be confused with a possible manifestation of inflammatory diseases, for example, cystitis.
- Glitches in the schedule. If previously menstruation appeared on a clearly designated day, but now even after PMS there are no periods, then fertilization may have occurred.
- Sensitivity to odors is an early sign of pregnancy and is caused by a sharp increase in estrogen levels in the blood.
- Increasing the temperature a few notches can tell you a lot, but you'll have to keep a temperature log to do that.
- Positive test response. Pharmacy tests can rarely detect pregnancy before your period is missed. If you notice other signs of pregnancy and the test shows a negative result, it is worth repeating the test in a few days.
Algomenorrhea as the most common cause of painful menstruation
Algomenorrhea is a common gynecological disorder characterized by menstrual dysfunction and painful menstruation. Algomenorrhea occurs in almost every second woman.
This disorder manifests itself as periodic pain in the lower abdomen before the onset of menstruation. Pain in the lower abdomen can vary in intensity and duration. The woman has a feeling that pain is spreading through the intestines. Algomenorrhea in most cases begins a week before the onset of menstruation and can continue throughout the menstrual cycle. The nature of the pain characteristic of algomenorrhea can be described as cramping, pulling, aching.
There are primary and secondary algomenorrhea:
- Primary algomenorrhea occurs as a result of impaired outflow of menstrual blood and spasmodic contractions of the uterus. The question of why primary algomenorrhea appears can be answered as follows: incorrect position of the uterus (for example, its posterior deviation), endocrine diseases, intrauterine contraception (coils, etc.), increased amount of prostaglandins.
- Secondary algomenorrhea often appears as a result of inflammatory processes in the pelvic organs or after gynecological operations (including abortions). With secondary algomenorrhea, fever, lower back pain, and bloating may occur.
In addition to pain in the lower abdomen, a woman may experience weakness, nausea, headache, and depressed mood. The intensity of pain during algomenorrhea, as a rule, negatively affects a woman’s performance, well-being, and mood.
In this regard, it is important to know why algomenorrhea occurs. The causes of this menstrual dysfunction vary.
In the vast majority of cases, algomenorrhea is a concomitant disease that occurs with other gynecological diseases - such as endometritis, inflammatory processes in the uterine cavity, inflammation of the uterine appendages, and infectious diseases of the genitourinary tract.
Treatment should be aimed at eliminating the underlying cause. After this, it will be possible to reduce the manifestations of algomenorrhea.
Why does the organ get bigger?
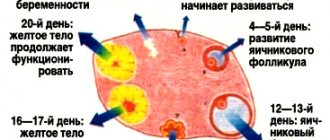
The female organs begin preparing for the possible conception of a child; this happens during the period of ovulation, especially in adolescence, since the body is still young. The restoration of the uterus is observed, against the background of which the development of dominant follicles occurs. In the middle of the cycle, about two weeks after the onset of menstruation, the egg is warm and ready to conceive a baby. Due to an increase in progesterone levels, an accumulation of nutrients necessary for the nutrition of the fetus is observed in the uterus. All these actions are necessary to nourish and strengthen the egg. Provided that pregnancy does not occur, then the excess accumulation is thrown out.
Unfortunately, not only natural factors can cause the uterus to increase in size; this phenomenon often occurs as a result of a number of diseases.
If intrauterine contraception is used for a long time, an increase in the size of this organ may be detected upon examination by a gynecologist. After the birth of a baby, especially in adolescence, the size of the uterus remains enlarged throughout the year. Formations of a benign and malignant nature can cause uterine enlargement after and before menstruation
With any diseases of this organ, there is a possibility of a delay in menstruation, so it is very important to consult a doctor in a timely manner. You should be wary if the volume of menstruation is more than usual
It is especially important to regularly monitor the stability of menstruation during adolescence. This phenomenon may indicate not only pregnancy, but also other more serious problems.
If everything is fine with the uterus, then after menstruation it recovers. The cervix returns to its usual size, the walls become hard again, the uterus rises, and dryness is observed in the vagina. Conception and fetal development become possible with the production of endometrium. Already in the middle of the menstrual cycle, an increase in the size of the uterus is observed, it becomes soft again. The uterus actively contracts, the amount of discharge increases.
During this period it should be of normal shape. If its size is larger than normal, then this indicates illness or pregnancy. In some cases, menstruation occurs even if you are pregnant; the main thing is not to worry, but to get all the relevant tests. This phenomenon occurs mainly in adolescents, since the uterus has not yet fully formed and is not ready to bear a child. By the way, pregnancy can occur even during menstruation.
the uterus does not contract after menstruation
Hi all! Here is the situation. My period started 5 days earlier, but it went on for 2 days and just stopped for a day and it wasn’t even masolo, then another day it went on for maybe 6 hours, and now I don’t have my period, it ended abruptly, it’s just clear and that’s it .usually I decrease and the cabbage soup ends, but here it’s not like that. And now the uterus doesn’t contract, what is it? At the same time, the nausea is very strong, I can’t stand the smells and I eat like an animal. Usually I’m in control, I could even abstain from food, for the sake of my figure. I feel heaviness in stomach.
Girls, thank you in advance for your advice! I took the test immediately after my period and showed one line.
Pain in other diseases of the female organs
There are a number of situations when discomfort in the uterus occurs as a result of damage to neighboring organs. Such pain is called radiating pain. Among the most common causes of discomfort in the lower abdomen are:
- gastrointestinal diseases - in this case, a woman feels a slight tingling or sharp stabbing pain during menstruation;
- hemorrhoids - unpleasant sensations occur in the form of spasms;
- lesions of the musculoskeletal system and spine - sensations can be pulling or sharp and radiate to the lumbar region during menstruation;
- diseases of the genitourinary system;
- congenital or acquired disorders in the pelvis.
Pain in the uterus and the menstrual cycle
Algomenorrhea is what scientific medicine calls pain before the onset of menstruation. Every second out of three women suffers from spasms, accompanied by additional symptoms:
In some cases, this is just a signal about the onset of menstruation, in others it is the first sign of pathologies in the body.
Why does the uterus hurt before menstruation?
Characteristic cramps in the uterus before menstruation occur for one reason: the endometrium, if pregnancy does not occur, is torn away from the walls of the uterus. In this case, a large amount of prostaglandins are released, which are responsible for strong muscle contraction, causing discomfort. It is almost impossible to avoid this feeling. In some women it is strongly expressed, in others it is tolerated.
If the uterus hurts several days before menstruation, most likely this is not a deviation from the norm. This sign will be a characteristic symptom of approaching menstruation.
Several reasons why the uterus hurts before menstruation a week before:
- adhesions of the pelvic organs;
- damage to the digestive tract;
- menstrual irregularities;
- late ovulation;
- pregnancy;
- inflammation of the genital organs.
Why does the uterus hurt during menstruation?
The occurrence of pain directly during menstruation is considered normal: the body tries to remove the rejected endometrium along with the unfertilized egg as quickly as possible.
Most women don't think about it and stock up on painkillers in advance to relieve discomfort. The same thing happens when the uterus hurts a week before menstruation. Naively believing that these are harbingers of discharge, girls block the unpleasant sensations with pills.
The reasons for this phenomenon are:
- Young age - the girl has just entered reproductive age, the menstrual cycle has not yet been established.
- Excessive physical activity causes pain in the uterus during menstruation, as well as the cause of uterine tone before menstruation.
- Sexual contact - when menstruation has already arrived and sexual intercourse has occurred, cramps may also occur.
Why does the uterus hurt after menstruation?
A woman is most alarmed by tingling in the uterus after menstruation, when pain is observed a couple of days after the end of the discharge. If the situation repeats itself every time, gynecologists attribute this to a slight increase in hormones. Besides this, there are several other reasons:
- taking certain medications;
- acute inflammation of appendicitis;
- poisoning;
- cystitis;
- inflammation of the ovaries;
- inflammation of other genital organs;
- muscle strain or injury.
All of these problems can cause pain in the uterus, because the discomfort is concentrated in the lower abdomen, which is easily confused with cramps.
Why does the uterus hurt in the middle of the cycle?
Another strange phenomenon that frightens girls is pain in the uterus in the middle of the cycle. The most common reason is the onset of ovulation - it is observed in women of reproductive age. Other prerequisites for the occurrence of pain will be:
- Implantation of the fertilized egg - when conception occurs, the fertilized egg descends into the uterine cavity and attaches to the mucous membrane.
- Gynecological pathologies: inflammation of the appendages, adenomyosis, ovarian cysts, rupture of ovarian cysts.
If the examination shows that pregnancy has not occurred and there has been no ovulation, then it is urgently recommended to consult a doctor. Such a dangerous symptom as tingling in the uterus on the 22nd day of the cycle may indicate serious problems.
Pathological causes
Pain may occur due to infection of the reproductive organs. More often, women who are promiscuous and do not use barrier contraceptives suffer from this. Infections cause inflammation of the mucous membranes, and without treatment, pathogens penetrate into the tissues, which leads to serious complications. Inflammatory processes affect nearby organs and can affect the entire pelvic cavity.
Pain in the uterus often occurs due to inflammation.
The uterus also hurts in the following conditions:
- Neoplasms – fibroids, ovarian cysts. If the latter leg is torsioned, the discomfort intensifies and radiates to the lower back.
- Adhesive process. Pain sensations appear in waves, radiating to the anus and lumbar region.
- Endometriosis. Characterized by the development of cells of the uterine mucosa outside its normal location. If you do not respond to pain, they will begin to grow into the abdominal cavity and even penetrate other organs. Surgery will be required to get rid of endometriotic lesions.
An ectopic pregnancy, in which a fertilized egg is implanted outside the uterine cavity (mainly in the fallopian tubes), is accompanied by a gradual increase in pain. At first it is nagging in nature, but after a few days the intensity of the symptoms intensifies, the pain increases, and radiates to the lower back. The temperature may rise. In this condition, urgent surgery is required; you need to call an ambulance.
Helps increase the amount of sleep
During menstruation, it is advisable to sleep 9 hours. You definitely need to eat light food, give up fast food and smoked foods. Buckwheat, cottage cheese, dried apricots, vegetable juices, herbal teas are useful. It is worth limiting physical activity. Try reflexology.
When to sound the alarm about painful periods? Pay attention to these signs:
- Heavy periods.
- Heat.
- Chills.
- Fainting.
All these troubles can be eliminated by proper treatment. For example, antibiotics can help if the cause of the listed symptoms is some hidden infectious process. Visit swimming pools and saunas carefully, maintain personal hygiene, and then this factor will be eliminated. Infections cannot be ignored, because... they lead to the formation of adhesions and scars.
If the pain is on one side, this should alert you. The cause may be a condition such as ovarian torsion. This is a dangerous condition, and if not noticed in time, it can be life-threatening. It is treated surgically. If ovarian torsion is suspected, the doctor immediately takes the patient to an ultrasound scan and then to the operating room. Most often the ovary has to be removed.
To prevent this from happening, do not exercise or lift heavy objects during your period. Otherwise, there is no specific prevention of torsion. An additional factor may be the presence of an ovarian cyst in a woman. If the cause of the pain is endometriosis - a condition where endometrial cells grow outside the uterus - then pain can also occur during sex.
Additionally, bloody discharge may appear as the endometrium continues to function as usual. It reacts to the amount of hormones, and during menstruation it bleeds. Laparoscopy helps confirm the diagnosis. Sometimes the endometrium can be found in the ovaries, intestines, and kidneys. The disease is quite serious, and both conservative and surgical approaches to its treatment are possible. Hormonal therapy is used more often, but if it does not help, then pathological foci are removed from the affected peritoneal organs using minimally invasive methods.
Read also: What you need to know about HPV in women and what test to take to detect it
If you have an IUD (intrauterine device), monitor your condition. The fact is that at first there may be discomfort, but later adaptation occurs. If the pain continues, this indicates a possible displacement of the spiral. An ultrasound will clear everything up. The best recommendation is to have the IUD installed by a trusted gynecologist, and in case of severe discomfort, give preference to other methods of contraception. There are frequent cases of not only displacement, but also ingrowth of the IUD into the uterus.
Sometimes, over time, painful periods can go away spontaneously on their own, but you shouldn’t rely too much on this. Symptomatic treatment of such a problem is possible only if other causes of algodismenorrhea are found and eliminated or excluded. If you have a question about what to do during painful critical days, whether you need to endure the pain, the answer is this: if the pain cannot be endured, then it is a sign of pathology. You need to go for a consultation with a gynecologist you trust.
The following studies may be prescribed:
- Flora smear.
- Blood chemistry.
- Tests for the level of estrogen and progesterone, and other hormones if necessary.
Ultrasound has great diagnostic value. The study allows you to evaluate the structure of the reproductive organs. With its help, you can find out why blood cannot flow freely from the uterus to the vagina. For example, the cause may be fibroids. While it is small, the woman has no idea what is in her uterus. Sometimes the nodes can reach the size of a pregnant uterus. The disease has become extremely widespread due to the fact that women began to give birth to fewer children, and the first birth was postponed until the age of 30-35. The uterus is not designed for such a large number of periods.
Attention! Mild pain during menstruation, even more likely just discomfort - a variant of the norm
What causes
Pain in the lower abdomen occurs due to many etiological factors. For convenience, they are usually divided into several groups depending on when the woman first noticed pain: before, during or after the end of menstruation.
Before your period
About half of women regularly visit a gynecologist with complaints of pain that manifests itself 2-3 days before their expected period. Pain in the pelvic area is not a deviation if the pain does not interfere with the patient’s usual rhythm of life and is of a muted pulling, cramping or aching nature. The reason for their occurrence is simple: changes occur in the body due to the active activity of hormones. The level of progesterone and estrogen decreases sharply, which provokes a natural decrease in the amount of endorphins for the secretion of which they are responsible. In the absence of these natural painkillers, the girl becomes sensitive and susceptible even to uterine contractions that are barely noticeable at first. In addition, the potassium-magnesium balance is disrupted, which leads to cramps and pain. All this negatively affects the central nervous system, malfunctions of which cause changes in physical and emotional state.
Before the onset of menstruation, the intestines begin to work more actively, which also negatively affects the patient’s well-being. In this situation, pain in the lower abdomen can be caused by constipation, flatulence and cramps.
If unpleasant sensations bring severe discomfort to a girl, forcing her to take analgesics and give up active life, one of the pathological conditions can be suspected:
- growth of polyps and malignant tumors;
- the occurrence of an infectious-inflammatory process (cystitis, salpingitis, etc.);
- development of hormonal imbalance;
- formation of fibromatous nodes.
Severe pain can also bother the patient if the luteal phase of the cycle is insufficient. This occurs due to disruption of the activity of higher brain structures or ovarian dysfunction.
During your period
Pain during menstruation is called algomenorrhea syndrome. It occurs due to a number of reasons, the main of which is a violation of the synthesis of prostaglandins, which are responsible for increasing the susceptibility of receptors to pain. Their excess quantity is incorrectly perceived by the brain, and therefore intense uterine spasms are interpreted as a pathology and are accompanied by burning, unbearable pain.
Fibroids (benign tumors) also cause cutting cramps during menstruation. In addition, women complain to the specialist about prolonged and heavy discharge, often leading to dangerous bleeding, as well as the occurrence of spotting in the middle of the cycle. As the myomatous nodes grow, the patient's condition worsens.
Cysts bother girls throughout their entire cycle, but during menstrual periods the pain becomes especially noticeable, intensifying with fast walking and jumping.
An incorrectly installed intrauterine device can also serve as a trigger for pain during menstruation. The foreign body compresses the uterus, squeezing the vessels and interfering with the normal contraction of the organ.
After critical days
If the patient suffers from severe algomenorrhea, pain may persist even after menstruation has stopped for 3-4 days.
Polycystic disease (endocrine gynecological disease) causes the patient to suffer from girdle pain of a pulsating nature, intensifying after menstruation. In addition, a woman suffers from constant fluctuations in body weight, increased oily skin and male-pattern hair growth.
You should not try to cope with severe pain on your own, turning to traditional medicine and dubious advice from friends for help. You can get rid of them if the diagnosis is correct and the correct therapy is selected.
Inflammation of the cervix (cervicitis)
Cervicitis is a very dangerous disease of the pelvic organs of the fairer sex, which is characterized by an inflammatory process of an infectious nature. Inflammation develops in the mucous membrane of the cervix, and such an unpleasant symptom appears as a tugging of the uterus.
shutterstock
The causes of cervicitis are similar to the causes of ovarian inflammation. Infectious pathogens of this disease can have different etymologies:
- bacterial: both pathogenic (Trichomonas, chlamydia, mycoplasma, gonococci) and opportunistic (Escherichia coli, staphylococcus, streptococcus);
- viral (genital herpes, human papillomavirus);
- fungal (candida).
You should not let inflammation of the cervix take its course, as this can lead to irreparable consequences in the future. If the disease becomes chronic, it will cause serious complications:
- cervical erosion (and then dysplasia);
- thickening (hypertrophy) or thinning (erythroplaxia) of the walls of the uterus itself;
- development of the risk of spontaneous miscarriages and even infertility if the infection spreads through the genital tract.
In addition, the reasons for the development of cervical inflammation can be:
- injuries resulting from abortions (the uterus is weakened after cleaning), the use of contraceptives installed intrauterine, hysteroscopy;
- weak immunity (the body’s inability to fight bacterial infections);
- hormonal imbalances;
- improper douching;
- promiscuous sexual intercourse.
Treatment of cervicitis (inflammation of the cervix)
Acute cervicitis, caused by the appearance of bacteria in the body, involves the use of antibiotics for treatment, to which certain bacteria are sensitive, which is determined on the basis of tests. In addition, UHF or physiotherapy may be prescribed, but strictly after the exacerbation of inflammation has been relieved. And since this disease is often provoked by sexually transmitted diseases, it is imperative to check the sexual partner for the presence of the causative agent of inflammation and, if infected, carry out treatment.
If you do not start an intensive fight against the disease in a timely manner, acute cervicitis acquires a chronic form, when pronounced symptoms may disappear altogether, and then determining the disease becomes much more difficult without examination by a doctor.
Chronic cervicitis poses a great danger to a woman’s body, since with it the infection penetrates into the deep layers of the cervix and provokes the appearance of dysplasia, the next stage after which is uterine cancer. In addition to antibiotics, suppositories are also prescribed to relieve inflammation. Chronic inflammation of the cervix is quite difficult to treat. That is why, in the absence of positive results from drug treatment, it is worth resorting to the following surgical methods to solve the problem:
- laser therapy;
- cryotherapy;
- diathermocoagulation;
- radio wave radiation.
It is important to note that during the treatment of inflammation it is necessary to additionally use drugs whose action is aimed at restoring the natural balance of the vaginal microflora
shutterstock
Diagnostics
Pain rarely occurs in isolation. Much more often it is accompanied by a host of other symptoms.
- Scanty or copious discharge. Including during the intermenstrual period. The nature of the exudation is different: we can talk about a small amount of leucorrhoea, serous type or purulent in nature. It is necessary to distinguish diseases of the described profile from sexually transmitted pathologies. For these purposes, PCR, ELISA tests and some others are prescribed.
- Menstrual irregularities. By type of delay, opsomenorrhea (too long period of menstruation), dysmenorrhea (intense pain), oligomenorrhea (small amount of discharge).
- Changes in fertility patterns. A woman loses the opportunity to have children. However, this is not an axiom. The possibility of natural conception remains, although the probability of such an outcome is not higher than 25%.
- Increased body temperature. Hyperthermia is at the level of 37.5-38 degrees and slightly higher.
- Intense pain in the lower abdomen. Pulling character. It differs in localization from typical pain in the uterus.
- Nausea, vomiting, dizziness, weakness, drowsiness and symptoms of general intoxication of the body are possible.
Diagnostic measures begin at an appointment with a specialist. At the first suspicion of ovarian pathology, you should contact a gynecologist. You cannot delay the examination, complications are possible.
At the initial consultation, the doctor interviews the patient about complaints and records information for further analysis.
It is important to collect anamnesis. This will allow us to identify diseases that the patient has suffered or is suffering from.
Recent unprotected sexual intercourse and the presence of other pathological processes in the gynecologist’s opinion play a huge role.
In the future, the following studies are prescribed to establish and verify the diagnosis:
- Complete blood count (aka CBC). Shows a picture of a classic inflammatory process with high values of ESR and leukocytes. But not always. With menstrual pain there is no inflammation.
- Examination using a gynecological speculum. It is carried out to determine the condition of the patient’s reproductive tract.
- Bimanual examination.
- Colposcopy. Allows you to examine the cervix under a microscope.
- Ultrasound examination of the uterus and ovaries (pelvic organs).
- Biopsy of tumors using puncture or laparoscopic access.
- Histological evaluation of tissues. Prescribed in the presence of tumors. Allows you to determine the structure of neoplasia.
- In extreme cases, contrast-enhanced MRI is indicated to distinguish tumors from cysts and from each other.
- PCR test for suspected sexually transmitted infections.
- A smear from the vagina and cervical canal.
- ELISA study.
- Ultrasound of the pelvis.
If all indicators are normal, they speak of menstrual, physiological pain. This condition is identified by the method of exclusion.
Stomach hurts after menstruation
In this section we will talk about why your stomach hurts after your period.
During menstruation, the uterus rhythmically contracts in order to expel everything that has served its purpose and is unnecessary. Some women have very sensitive pain receptors in the abdominal cavity, and they respond with pain to every contraction. And for some, the uterus is located in a non-standard way, tilted back, and then it puts pressure on the nerve centers, which causes a feeling of heaviness in the lower abdomen, aching in the sacrum and lower back.
The activity of the uterus and our sensitivity are highly dependent on hormonal levels. With an increased amount of the hormone estrogen, which is more often observed in women after 30 years, periods are not only painful, but also very heavy and long. If all the hormones are jumping, then the woman suffers from both PMS and algodysmenorrhea.
If your stomach hurts after menstruation, this may also be due to a violation of the natural balance in the body between sex hormones (primarily progesterone) and prostaglandins, towards the predominance of the latter. Prostaglandins are specific chemicals that play a key role in causing most of the symptoms associated with menstrual discomfort. They are produced by the tissue of the uterus and stimulate its contraction. The higher the level of prostaglandins in the body, the stronger the force of contraction of the uterine muscle and, consequently, the strength of pain. Excess prostaglandins can cause other accompanying manifestations: nausea, vomiting, headache, sweating, chills, tachycardia.
Heavy periods plus insomnia and weight loss sometimes occur when the thyroid gland, which regulates the production of all our hormones, is overactive.
Menstruation with a noticeable pain syndrome also occurs with an incorrect position of the uterus, its underdevelopment (sexual infantilism), inflammation in the genital organs, endometriosis and other diseases, as well as increased excitability of the central nervous system. Painful periods are more common in young nulliparous women and can also be a symptom of infertility.
In addition, painful periods are observed with intrauterine contraception (IUC), which is associated not only with the presence of a foreign body in the uterus, but also with the activation of prostaglandin synthesis due to the IUD.
If you have a stomach ache, a lot of time has passed since your period, and the pain does not stop, consult a doctor immediately!
When pain speaks of illness
It is possible to distinguish physiological manifestations of menstruation from pathological ones by the nature of their manifestation, as well as by accompanying symptoms. You should seek urgent medical help if:
- sharp pain occurs suddenly. In this case, it may indicate a bend of the uterus during menstruation;
- there is an increase in body temperature. This condition is typical for purulent and inflammatory processes;
- a woman discovers the presence of purulent discharge;
- bleeding develops.
In the cases listed above, you need to seek specialized help.
Palpation of the uterus at home: recommendations and precautions
If something is bothering you, it is easier to conduct a preliminary examination at home than to be nervous before going to the gynecologist. It is better to cut the nails on the index and middle fingers of your right hand and put on a sterile glove before starting palpation. The easiest way to feel the uterus is while sitting on the toilet, squatting or placing one foot on the sofa, the edge of the bathtub, etc. You can try to take a position similar to the one you take in the gynecological chair.
So, insert two fingers into the vagina and feel the tubercle. This is quite easy, the main thing is not to make sudden movements to avoid injury to the organ. But determining the consistency of the cervix is not so easy if you are not a professional. Only the comparison method will help the amateur. And yet, you can find out something on your own - if the middle finger literally rests on the cervix, it means that it is located quite low, as before menstruation. If you can barely reach it, then the uterus has contracted, as it should after menstruation. Remember, before starting and especially during menstrual periods, it is not recommended to palpate the organ.
What are the risks of self-examination?
If you are used to constantly palpating the cervix, refrain from manipulation at least 2-3 days before menstruation. Even the doctor will prefer to postpone the examination until the end of menstruation and here’s why:
- At this time, the cervix begins to partially dilate, so it is easy to get infected and get inflammation of the ovaries or fallopian tubes. Against this background, adhesions can form, leading to infertility.
- Even if you use sterile gloves, there is a risk of damaging the cervix. Typically, such injuries heal quickly, unless, of course, an infection occurs.
- For the most part, independent palpation of the organ does not give anything, and only a doctor can identify the pathology. After all, the gynecologist not only feels the cervix, but also examines it with a mirror.
These warnings do not directly prohibit self-palpation, but suggest that in case of any suspicious symptoms, it is better to consult a doctor and clarify the diagnosis professionally.
Is a self-examination necessary?
The female body itself creates all the conditions in order to monitor the regularity of the cycle, identify the most favorable time for conception or, conversely, protect itself from unwanted pregnancy.
Recently, many women prefer to visit the gynecologist less often and conduct diagnostics themselves, at home. Knowing exactly how the cervix feels to the touch before menstruation, with such an examination you can understand whether pregnancy has occurred. If there is no opportunity to contact a specialist at the moment, palpation can be done at home. However, you should always remember that the slightest carelessness can lead to accidental injury or infection.
What a woman should always pay attention to
Not everyone experiences toxicosis in the first months of pregnancy, and one pregnancy can be very different from another. However, in some cases, women note the appearance of irritating odors, a feeling of rejection of specific products, or, conversely, strange taste preferences. which had not been observed before. Any of these signs may indicate pregnancy.
It is already clear that the symptoms of menstruation and pregnancy are extremely similar. However, if you feel unusual pain in the lower abdomen, you should consult a specialist for advice.
A slight increase in temperature can tell a woman about the onset of pregnancy or the appearance of a sluggish inflammatory process.
Scanty flow: if you have not previously noticed the appearance of light periods, and during your cycle you had unprotected sexual intercourse, then you should consult a gynecologist, since scanty bleeding can be a sign of an ectopic pregnancy.
Pain in the mammary glands, increase in volume and swelling may indicate both menstruation and pregnancy. The appearance of colostrum secreted from the nipples will tilt the diagnosis in favor of the latter. However, breast pain in a specific area, combined with discharge from the nipples, against the background of excluding pregnancy, is a reason for an urgent visit to a mammologist, since such symptoms may indicate oncology.
All of the above has one big amendment: each organism has its own individuality. If you cannot determine exactly what signs are bothering you, buy a pharmacy test. If your schedule is delayed and you suspect you are pregnant, you can contact a gynecologist who will examine you and prescribe the appropriate tests. However, in most cases, a woman intuitively determines the presence of pregnancy better than any tests or analyses.
When the uterus hurts before menstruation, a woman does not experience the most pleasant sensations. In addition to discomfort and cramps in the lower abdomen, girls are tormented by guesses: what was the cause of such ailment. Often this symptom indicates the approaching onset of menstruation or possible pathologies of the reproductive system.
What is PMS
Rarely lucky women note that the onset of “critical days” goes smoothly for them: before menstruation there is no pulling in the lower abdomen, no rashes appear on the face, the general condition is cheerful and active. Much more often, 3-4 days, or even 10 days before the arrival of the next monthly cycle, a woman experiences ailments:
- chest pain;
- there is bloating;
- pulls the lower back;
- mood changes frequently;
- Libido decreases.
The chest seems to fill up, swell and hurt so much that it is impossible to touch it. The abdomen increases in volume, it is impossible to retract it, so you have to wear loose clothes. Aching pain occurs periodically. The face is covered in dust, as some people note: on the eve of menstruation, acne appears.
There is little energy, you want to sleep, the woman notices irritability or tearfulness. This is a strong premenstrual syndrome, that is, changes in the body that signal the imminent arrival of menstruation. To one degree or another, its signs are familiar to most women. They are caused by an increase in the concentration of progesterone and prolactin. Regardless of how the cycle ends - menstruation or conception, the body is preparing for pregnancy.
The role of the uterus in a woman’s life
The uterus performs the following functions:
- Protection of the higher genital organs and peritoneum from infections penetrating from the vagina - in this case, the cervical canal takes on this role.
- Regular, spontaneous cleansing of the uterine cavity and cervical canal, vaginal cavity - we are talking about regular menstruation.
- Participation in sexual intercourse and creation of favorable conditions for the movement of sperm through the cervical canal into the uterus and its cavity, fallopian tubes.
- Implantation of the fertilized egg into the uterine cavity and the creation of favorable conditions for the development of the fetus throughout the entire period of pregnancy, participation in the process of natural childbirth.
- Due to the ligamentous apparatus itself, it forms and strengthens the pelvic floor, supporting the internal organs located above it.
But as noted earlier, its most important function is reproductive, creating favorable conditions for bearing and giving birth to a child.
Premature placental abruption
Symptoms of premature placental abruption are:
- Bleeding. Depending on the location of the source of bleeding and how long ago the placenta was separated, scarlet, dark or brown blood may appear from the genital tract. Bleeding can be external, internal or internal-external.
- Pain in the uterine area, radiating to the thigh, womb, or without clear localization, dull or paroxysmal;
- In severe cases of placental abruption, weakness, dizziness, severe abdominal pain and even fainting are observed;
- Asymmetry and unilateral pain of the uterus;
- Hypoxia is observed on the part of the fetus. Due to incomplete adhesion of the placenta to the uterus, the blood supply to the fetus deteriorates and it develops oxygen deficiency. If the detachment is more than 1/3-1/2 of the area of the placenta, intrauterine fetal death occurs.
If such symptoms occur, the pregnant woman should limit physical activity and immediately contact an ambulance. Treatment of this condition is possible only in a hospital setting.