To actively participate in the process of fertilization and further gestation, a woman’s uterus has a special layer of cells that lines its inner wall. Under normal conditions, the female reproductive organ is completely protected from external infection, but situations occur when inflammation of the endometrium occurs. In practical gynecology, this condition is called endometritis.
Damage to the muscular wall itself is often associated with the inflammatory process of the inner wall of the uterus, and then endomyometritis is diagnosed. Treatment is aimed at the complete destruction of bacteria and microbes in all layers of tissue.
The essence of pathology
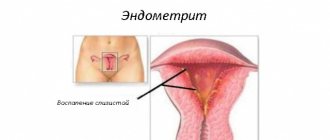
Uterine endometritis - inflammation of the uterine mucosa - endometrium.
Endometritis is a common gynecological disease. It usually occurs after surgery or abortion.
It is an inflammatory process in the endometrium - the mucous layer of the uterus. The endometrium is the inner mucous lining of the uterus, which supplies it with blood vessels .
Each menstrual cycle, the endometrium matures and grows anew, facilitating the attachment of a fertilized egg. It also protects the uterus from infections.
But if the uterus is damaged or through the ascending tract, the infection can enter the uterine cavity, which causes inflammation of its inner layer.
The cause of the disease is the penetration of various viruses, bacteria or fungi into the uterine cavity . The disease can also develop with reduced immunity.
CAREFULLY!
The pathological process initially affects only the endometrium, but if timely treatment is not provided, the inflammation quickly spreads deep into the uterus and endomyometritis develops, and adjacent organs can also be affected.
In the absence of adequate treatment, it can lead to the formation of cysts of various etiologies and adhesions in the fallopian tubes, which is accompanied by infertility. Endometritis most often affects women of childbearing age .
The disease can occur in acute, subacute and chronic forms.
What is endometritis,
Why is it combined with Metronidazole in gynecology?
Metronidazole is administered together with Ceftriaxone, since many inflammations in gynecologists are caused by anaerobic microflora, that is, a number of pathogenic bacteria can grow and multiply without access to oxygen. Ceftriaxone has little effect on such microbes, and it is also ineffective against trichomoniasis. A combination of drugs is necessary in the treatment of endometritis, complications after operations on the uterus and ovaries, and infections in the pelvic cavity.
For acute and widespread inflammation, Metronidazole is administered intravenously, 100 ml of solution 2 times a day. Ceftriaxone can be used for intramuscular injections or injections into a vein, droppers of 2 g per day, but the two drugs cannot be mixed together, the interval between injections is recommended to be about an hour. For chronic processes, it is permissible to take Metronidazole in tablets or administer suppositories.
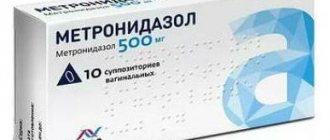
Metronidazole solution
Metronidazole tablets
Suppositories Metronidazole
Types and diagnosis of the disease
Endometritis can be:
- nonspecific - caused by infection as a result of childbirth or surgical interventions, characterized by pathological menstruation (delayed menstruation, heavy and prolonged periods), and also bothered by aching pain in the lower abdomen, discharge with an unpleasant odor, low-grade fever.
- actinomycotic - caused by fungi of various genera, the clinical picture is the same as with nonspecific endometritis.
- tuberculous - caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis (Koch's bacillus), characterized by an increase in temperature to 38 degrees, menstrual irregularities, and bleeding.
- gonorrheal - caused by gonococci, there is an increase in temperature up to 40 degrees, cramping pain in the lower abdomen, bloody-purulent discharge with an unpleasant odor.
Diagnosis of the disease includes :
- Collecting anamnesis (what concerns you, the number of abortions, births, pregnancies, operations);
- vaginal gynecological examination;
- general clinical examinations (general and biochemical blood tests, general urinalysis, scatological examination, smear for the purity of the flora);
- bacteriological studies;
- PCR studies;
- Ultrasound;
- Hysteroscopy.
IVF after recovery
In theory, the in vitro fertilization procedure can be carried out, but not a single doctor will undertake this procedure.
Endometritis is an absolute contraindication to pregnancy.
This is due to a number of factors that relate to both conception and gestation.:
- The chances of successful IVF are minimal, since the lining of the uterus is changed. This is an unfavorable factor for embryo implantation. It will be rejected;
- Even if the implantation of the embryo was successful, miscarriage will occur. This is due to increased uterine tone. A frozen pregnancy is possible due to a violation of the woman’s hormonal status.
Therefore, to carry out this procedure, you must first undergo a course of treatment, after which the likelihood of successful implantation, pregnancy and the birth of a healthy baby increases significantly.
Preparatory measures before IVF include examination.
Symptoms of pathology
Symptoms of acute endometritis:
- Sharp pain in the lower abdomen.
- Increase in body temperature to 39 degrees.
- Weakness, chills, general malaise.
- Bleeding.
- Discharge from the genital tract is green or dirty yellow in color with an unpleasant odor.
- Painful urination.
NOTE!
Signs of the disease, as a rule, begin to bother you already on the 3rd day after infection.
Symptoms of chronic endometritis:
- Nagging pain in the lower abdomen.
- Girdle pain in the lower back.
- Subfibrillary increase in temperature.
- Premenstrual and postmenstrual spotting.
- The duration of menstruation is more than 7 days.
Chronic endometritis occurs after the acute stage of endometritis and is the result of untimely or improper treatment.
The consequence of such a disease can be infertility or recurrent miscarriage.
Prevention
To avoid the occurrence of a disease, the development of causes and factors should be predicted. Treat any diseases of the genital organs in a timely manner so that they do not lead to complications.
It is recommended to avoid sexual intercourse with unverified partners and to use contraceptives during any sexual activity. Do not resort to abortion.
Early latching of the newborn to the breast will help rule out endometritis. To stimulate the body's protective properties after childbirth, it is worth taking immunomodulators.
When primary signs of the disease appear, it is not recommended to sunbathe for a long period of time in the hot sun. The process is fraught with accelerated development of emerging symptoms into a full-fledged acute form.
Diet will help in healing. Eat lean meat, as well as fish (sardine, herring, mackerel). These types of fish contain substances that alleviate the disease. On the contrary, exclude fatty fish. It is forbidden to drink tea, soda, coffee, or eat chocolate.
We recommend reading: Hydrosalpinx in women: causes, consequences, diagnosis and treatment
You need to give up tampons, they interfere with the normal movement of blood during menstrual flow. It is imperative to engage in active sports and not give up on exercise. The main thing is to establish a normal work and rest schedule.
Thus, any first symptoms should be treated immediately and lead a healthy, fulfilling lifestyle.
A doctor, an obstetrician-gynecologist, talks in detail about chronic endometritis, watch the video:
Causes
This disease can be caused by various bacteria, fungi, viruses that enter the uterine cavity due to:
- abortion;
- childbirth;
- caesarean section;
- use of intrauterine devices;
- sexual intercourse during menstruation;
- bacterial vaginosis;
- coli;
- mycoplasma;
- protozoal infection;
- streptococci;
- tuberculosis;
- diagnostic studies;
- violation of personal hygiene rules;
- ARVI;
- general infectious disease;
Pregnancy after therapy
After treatment for endometritis and the onset of a long-awaited pregnancy, you must strictly follow all the doctor’s recommendations..
To avoid adverse consequences, you should take medications that affect hormonal status, which is the prevention of miscarriage.
The recommended scheme includes:
- Folic acid preparations and iodine-containing products (Iodomarin, Folacin);
- Hormonal drugs to prevent miscarriage (Duphaston, Utrozhestan);
- Drugs that normalize blood flow in the uterus and placenta (Curantil);
- Drugs for symptomatic therapy.
Can it be cured with antibiotics?
treatment of endometritis in a timely manner and after consulting a gynecologist .
Doctors, as a rule, prescribe broad-spectrum antibiotics or taking into account the sensitivity of the pathogen to them. If endometritis develops in the postpartum period, when prescribing an antibiotic, it is taken into account that the mother is breastfeeding.
For complex treatment, multivitamins, antiallergic drugs, agents that normalize the intestinal and vaginal microflora, antifungal drugs and substances that relieve symptoms of general intoxication of the body are prescribed..
With the correct prescription of antibiotics, improvement occurs already on the 3rd day.
Expert opinion
Dmitrieva Elena Yurievna
Gynecologist-endocrinologist, 40 years of experience
Treatment of endometritis is basic therapy. Treatment of inflammation without the use of antibiotics is absolutely ineffective and pointless. Since they ensure rapid destruction of the infection, and also prevent the disease from becoming chronic. It is very important to follow all doctor’s recommendations and principles of antibiotic therapy.
Is antibiotic treatment acceptable during pregnancy?
Patients often learn about the chronic form of endometritis during pregnancy.
Treatment of the disease is allowed during pregnancy if carried out under the supervision of a doctor, and therapy uses vitamin complexes, physiotherapeutic procedures and drugs aimed at increasing immunity.
The use of antibiotics is possible only if the benefit to the patient significantly outweighs the risk of disease or disturbance in fetal development.
How to treat acute endometritis?
The acute form of the disease occurs most often.
Upon presentation, the patient is examined and a vaginal culture is prescribed to determine the sensitivity of the microflora to antimicrobial drugs.
Treatment is carried out immediately by prescribing cephalosporins, namely Cefazolin intramuscularly.
For complex treatment it is prescribed :
- Gentamicin (an aminoglycoside antibiotic that is effective against gram-negative bacteria).
- Metrogyl (antimicrobial drug, used to combat protozoan microorganisms and anaerobic bacteria).
- Ceftriaxone (a parenteral cephalosporin antibiotic of the third generation with prolonged action).
For emergency use it is prescribed intramuscularly:
- Ampicillin (bactericidal drug).
- Sulbactam (has an inhibitory effect on beta-lactamase and has an antimicrobial effect).
The dosage and duration of treatment is prescribed only by a doctor..
After receiving the results of the flora culture tank, the doctor, if necessary, prescribes other antibiotics in accordance with the causative agent of the infection.
For example, Doxycyline is prescribed if the cause of endometritis is chlamydia . It stops protein synthesis and bacterial growth.
Clindamycin (a drug from the lincosamide group) is used to detect staphylococci and streptococci in tests.
Treatment of endometritis depending on the form
The fight against inflammation of the endometrium of the muscular layer of the uterus is currently carried out in a comprehensive manner, and it is based on antibiotics. It should be noted that the prescription of such serious drugs depends entirely on whether the process is acute or chronic.
Antibiotics for acute endometritis
Most often, specialists are faced with an acute form of the disease. In this case, timing is everything. The patient is advised to undergo examinations to exclude acute surgical pathology and determine the sensitivity of the uterine flora to antimicrobial agents.
The process of differential diagnosis between gynecological and surgical problems does not take much time. It is worth noting that the duration of establishing the degree of sensitivity of pathological flora to antibiotics in a woman is usually 2 - 5 days.
Therefore, doctors begin treating the inflammatory process in the patient immediately, using standard complexes of drugs:
- Women are prescribed second-generation cephalosporins, in particular Cefazolin, 1 gram 3 times a day. The drug must be administered intramuscularly, and it is recommended to combine these injections with a similar injection of 80 mg of Gentamicin. The complex regimen also includes intravenous administration of Metrogyl three times a day at a dosage of 0.5 grams per dose.
- An interesting combination of banal penicillins and beta-lactam antibiotics is widely used for emergency treatment of endometritis. An example would be the simultaneous administration of the drug Unazin in a dosage of 1.5 grams up to 5 times a day and the usual, widely used Agumentin up to 5 grams in the same time period. Medicines are recommended to be injected exclusively into the patient’s muscle to achieve a higher concentration of the drug and prolong the duration of action of the antibiotic.
- Many experts emphasize the need to sanitize the uterine cavity with a solution of 1st and 2nd generation cephalosporins to remove purulent plaque from the walls. Such recommendations can be treated differently, but unnecessary forceful penetration into the uterus can stimulate an existing inflammatory process. Most gynecologists recommend not to perform instrumental revision of the uterus unless absolutely necessary.
In modern medicine, there are quite a lot of regimens for the use of antibiotics for acute endometritis, and all of them have the right to life. The main condition for any medical prescription is the speedy relief of inflammation and complete safety of treatment for the patient.
Antibiotics for chronic endometritis
When treating a chronic form of inflammation of the uterine walls, the time factor is no longer particularly important, so doctors have enough time to determine the reaction of the pathological flora of the woman’s reproductive organ to the main groups of antibacterial agents. Before prescribing specific treatment for chronic endometritis, a special study is carried out - an antibiogram. It is this analysis that allows doctors to choose the correct regimen for using antibiotics.
Most often, when treating the chronic form of the disease, the same drugs are used that give a proven effect in acute cases. Experts recommend prescribing cephalosporin medications, and to enhance their effect, therapy is supported by the use of fluoroquinolones.
Most often, gynecologists choose a combination of Kefzol or Cefotaxime with Clindamycin. Most experts advise maintaining treatment with the drug Metronidazole, which actively suppresses the growth of anaerobic flora in the patient’s vagina and uterus.
However, in the chronic period of the disease, refusal of antibacterial drugs plays a leading role. The basis of treatment is the restoration of the woman’s immune system, for which immunomodulators, complexes of vitamins with microelements and stimulants for the restoration of damaged tissues, in particular Actovegin, are prescribed in large doses.
Watch the video about endometritis:
Therapy for chronic endometritis
To treat the chronic form , the same drugs are used as for the treatment of the acute form .
However, many doctors advise patients to undergo an antibiogram to determine the effectiveness of the prescribed drugs.
As a rule, cephalosporin drugs (Kefazol, Cefotaxime) are also prescribed, and fluoroquinols are added for better effect.
A prominent representative of fluoroquinols is Levofloxacin. It is a broad-spectrum antibiotic with high efficiency and has a bactericidal effect.
You can also add Metranidazole to the list of antibiotics. It is an antiprotozoal and antibacterial agent .
IMPORTANT!
To obtain the expected result, you must strictly follow all doctor’s instructions in taking all medications, otherwise the treatment will be ineffective.
Interaction with other drugs
The most dangerous combination of Ceftriaxone is simultaneous injection into a vein with solutions containing calcium. With this drug interaction, insoluble salts are formed, which settle in the bile ducts, kidneys and lungs.
The result may be asymptomatic darkening on ultrasound, which spontaneously disappears after cessation of treatment. But development is also possible:
- renal failure;
- blockage of the gallbladder with jaundice;
- pancreatic lesions.
Therefore, for 2 days after the administration of the antibiotic, calcium-containing drugs for intravenous administration are prohibited , including feeding droppers.
The combination of Ceftriaxone and Levomycetin is considered an unfavorable combination , since the toxicity of the drugs increases and they mutually weaken the antimicrobial effect of each other. You cannot combine this medication with Vancomycin. Ceftriaxone disrupts the contraceptive effect of hormonal pills, because of this, gynecologists recommend using suppositories and a condom during the therapy period and 1 more cycle after.
Other treatments
For effective treatment, in addition to antibiotics, they are prescribed:
- antipyretic and painkillers (to relieve general symptoms);
- hemostatic agents;
- immunomodulators;
- multivitamins;
- restorative drugs;
- hormones;
- physiotherapy (UHF, electrophoresis, pulsed ultrasound to improve blood circulation in the pelvis).
Any inflammation in the body leads to a deterioration in health and knocks you out of your usual way of life..
Every woman between the ages of 15 and 50 can face this disease.
CAREFULLY!
When the first symptoms appear, even the most “harmless” ones, you should immediately consult a physician or gynecologist.
Only an experienced doctor can easily diagnose inflammation of the uterus and prescribe all the necessary tests and studies.
It should be noted the importance of timely contact with a specialist to prevent the development of complications such as peritonitis, inflammation of the uterine appendages, parametric phlegmon, pelvic abscess, pelvic hematoma and thrombophlebitis, various uterine cysts and infertility.
With timely and correct treatment with antibiotics, as well as following all doctor’s recommendations, endometritis of the uterus can go away without any special consequences for the woman.
Treatment regimen with Ceftriaxone for inflammation of the appendages
For inflammation of the uterine appendages, Ceftriaxone is administered at a dose of 2 g for at least 1 week. The doctor may additionally include Gentamicin and Metrogyl in the treatment regimen. Treatment with the drug helps relieve pain and temperature reactions, general weakness, and nausea for 2-3 days. The menstrual cycle gradually normalizes.
The antibiotic prevents the transition of the acute phase to the chronic phase and the formation of adhesions (adhesions) in the pelvis, which then becomes the cause of ectopic pregnancy or infertility.
How many days to inject
In case of an acute inflammatory process, Ceftriaxone can be injected for 5-7 days, then a follow-up examination and tests are necessary, after which the doctor either extends the injections for another 3-5 days or transfers the woman to another antibiotic tablet (for example, Suprax).
In case of chronic processes in the appendages, it is very important to achieve complete destruction of the infectious agent, so the drug is administered before laboratory confirmation of cure. The average course of therapy is 10-14 days.
Is it necessary and with what to dilute for inflammation of the ovaries and other pathologies?
For inflammation of the ovaries, as for any other indication, Ceftriaxone powder for injections into the buttock is diluted with a 1% lidocaine solution. To do this, for 1 g of antibiotic (one bottle) you need to take 1 ampoule (2 ml) of water for injection and 2% Lidocaine.
They are drawn into a syringe and then released into the bottle by piercing the rubber stopper. It is necessary to shake it until the powder is completely dissolved, and then draw the antibiotic back into the syringe. The resulting solution is injected immediately after preparation into the upper outer quadrant of the buttock.
In the treatment of gynecological diseases, 2 g of Ceftriaxone is most often prescribed. That is, you need to dissolve 2 bottles of the drug. Injections can be given immediately, but in different buttocks (1 g in each direction) or at intervals of 12 hours. In the hospital, both intramuscular and intravenous injections are used. For the latter, take only water or sterile saline solution in ampoules of 10 ml per time.
If droppers are recommended, 40 ml of 0.9% sodium chloride, 5% glucose or Voluven will be required.
Watch this video on how to dilute Ceftriaxone before administration: