One of the main issues for women is the issue of breast health. Every woman should know what to look for when alarming symptoms appear. The treatment, diagnosis and prevention of breast diseases must be approached with full responsibility. Breast fibrosis is a common breast disease.
Description of the disease
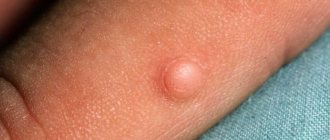
Fibroma looks like a smooth ball or knot. This disease is also called mastopathy, it is benign in nature. Fibrosis of the mammary glands is a pathological condition of fibrous tissues, in which they grow and become denser, which inevitably leads to impaired functioning of the gland. Often, fibrosis leads to a woman losing her ability to breastfeed. Quite rare, but this type of disease also occurs in men.
Unfortunately, at the beginning of the disease it is almost impossible to notice any changes. They are detected during preventive examinations and breast examinations - mammography. A pronounced fibroadenoma often causes pain and discomfort in the chest.
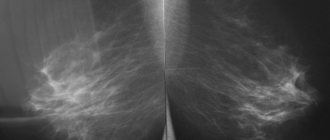
Mammography for mastopathy
Hyperplasia of the glandular component (adenosis) is easily determined by mammography. This is a multitude of uneven, finely focal shadows of irregular shape, merging with each other, with uneven, unclear contours. This is a kind of variegated zone with uneven density. Shadows are grouped in the outer quadrants, and can be scattered throughout the gland.
This happens when Cooper's ligaments become tight. What this is, we discussed above. They can merge and become like a solid compaction of the entire gland. Its triangle is wavy, polycyclic. The area where hyperplasia is present resembles a lace pattern.
Changes can be of a mixed nature. Then a chaotic mosaic pattern with pronounced density may appear. There are poorly defined focal compactions. In this case, the Cooper ligament also becomes denser.
Classification
ICD 10 code N63 for breast fibrosis.
When diagnosing fibroids, there are 2 types of pathology:
- Local (focal). A manifestation of limited fibrosis is local compaction in the mammary gland. It should be remembered that existing nodes in the mammary gland can transform into a malignant neoplasm.
- Diffuse (heterogeneous). With this type of pathology, the prognosis is more favorable. There are diffuse structures of connective tissue present here. This type of fibrosis extremely rarely develops into cancer, but it provokes many unpleasant symptoms. These include diffuse pain in the gland, when a woman cannot indicate a specific location, severe engorgement of the breasts before menstruation, the shape changes and a feeling of heaviness appears in the mammary glands.
Kinds
- Linear. During a manual examination, the doctor will feel a node or cyst, which is also clearly visible on pictures (mammography). Cysts form inside the gland ducts and in the interlobular connective tissue. If necessary, the doctor will prescribe additional tests: blood, biochemistry, hormones and ultrasound of the mammary glands.
- Periductal. Affects women during menopause. Collagen fibers form around the milk lobules in the breast. This causes compression of the vessels and capillaries that supply nutrition to the mammary gland. Both options have a favorable prognosis and do not require surgical treatment or the use of aggressive medications.
- Nodal. Develops in the form of a single node. Not much different from linear and preductal.
- Breast stromal fibrosis. Women during menopause are also affected. During menopause, involutive changes occur: the glandular tissue of the breast predominates over the connective and fatty components. Normally, this predominance should be moderate. It follows from this that stromal fibrosis is a change in tissue structure (involution), but as fibrosis grows, voids form in the chest, which can be filled with fluid. Normally, this type of fibrosis requires only preventive examinations, but drugs for its treatment are often prescribed after additional examination.
- Heavy. A rather rare type of fibrosis of breast tissue. Detected using mammography. The images show radiating fibrous tissue in the form of a ray or star. Strands formed on the mammary glands are a protective function of the body against certain types of influences on breast tissue.
Molecular iodine
Molecular iodine (I2) is the most effective form of iodine administration for the treatment of fibrocystic disease and breast cancer. Breast tissue, in addition to producing milk, exhibits low activity of the enzyme peroxidase. A decrease in enzyme activity causes a decrease in the ability to convert inorganic forms of iodine (for example, iodized salt, dietary supplements from inorganic iodine salts) into organic ones.
The use of molecular iodine does not require the participation of the peroxidase enzyme for biological use. The mammary gland is more efficient at uptake and concentration of molecular iodine (I2) than the thyroid gland, and similarly, higher amounts are concentrated in breast tissue than in thyroid tissue.
In vitro (experimental) studies have shown that molecular iodine inhibits cancer cell division and induces apoptosis, programmed cell death, in several types of cancer cells. The introduction of I2 helps to suppress the development of both types of cancer tumors - benign and malignant.
Molecular iodine forms organic compounds on the surface of cells, so-called. Iodolactones. They are formed as a result of a reaction with unsaturated fatty acids contained in the structure of cell walls. Cell walls contain a significant amount of arachidonic acid, formed by iodolactones.
Through various experiments, it was found that cancer cells contain up to 2 times higher concentrations of arachidonic acid, the target molecule for molecular iodine. Due to their higher arachidonic acid content, cancer cells have a selectively greater ability to absorb molecular iodine and generate iodolactones.
Molecular iodine (I2) is the most effective form of iodine administration for the treatment of fibrocystic disease and breast cancer
Increased production of arachidonic acid-derived iodolactones (IL-6) causes cell cycle arrest and triggers programmed cell death, apoptosis. Understanding the mechanism explains the antitumor effects of molecular iodine and successful clinical findings.
Consistent with the results of other studies, the inorganic form of iodine in the form of salts does not have antiproliferative effects, unlike organically bound and molecular iodine. Medication therapy and proper nutrition in the early stages help to effectively cope with the pathology.
Reasons for appearance
The main factor in the appearance and growth of fibrosis is changes in the level of hormones in a woman’s body. All factors may be associated:
- hormonal changes in pregnant, nursing mothers and women during menopause
- radiotherapy - in the case of radiation therapy for cancer
- use of implants
- stress and overwork
- refusal of breastfeeding
- happy abortions
- heredity
Symptoms of diffuse pulmonary pulmonary fibrosis
The leading symptom of diffuse pulmonary fibrosis is shortness of breath. Initially, it occurs during physical activity, and as the disease develops, the condition is constantly present, regardless of physical activity.
The main clinical manifestations include:
- Cough. Initially, attacks of dry cough occur, later with sputum production;
- The occurrence of constant pain in the chest;
- Change in skin color (cyanosis);
- Decreased appetite and weight;
- Wheezing in the lungs;
- Fatigue, weakness and chronic fatigue;
- Fluctuations in temperature indicators.
Over time, with diffuse pulmonary fibrosis, symptoms appear:
- Deformation of fingers. The phalanges thicken, the nails become excessively dense;
- Hemoptysis.
Signs of breast fibrosis
To recognize a breast disease, you need to know its symptoms. The symptoms of breast fibrosis are not very varied, so it is better to remember them. After all, the number of sick women is growing every year.
The main symptom is the presence of small lumps in the breast, ranging in size from 0.2-0.3 cm, and the gland can be painful. The color above the seals may also change. There will certainly be a feeling of discomfort in the chest, heaviness and a feeling of “fullness”; there will be mild pain as during menstruation. In the cystic form of the disease, the pain when palpating the nodes will be stronger and the lumps themselves will be larger in size.
Danger of fibrosis
Breast fibrosis is dangerous because it has the ability to progress the disease. The shape of the breast looks different, which explains the severe pain. In rare cases, cysts and the contents of the ducts can rot. There is also a considerable probability that fibrosis will degenerate into a malignant formation (cancer).
Protective role of iodine
Benign fibrocystic breast diseases (breast lumps, cysts, fibrocystic breast disease) are often associated with iodine deficiency. In the course of experimental studies on animals, it was found that during the blocking of iodine absorption by perchlorates, tissue changes occurred with signs of fibrocystic breast disease, and at the same time a precancerous condition of breast tissue developed.
A two-fold risk of fibrocystic breast disease was found in a group of 90 women (23-50 years old) with elevated thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) levels and decreased thyroid function (hypothyroidism). In a series of clinical studies, researchers focused on the effects of 3 different forms of iodine supplementation in women with fibrocystic breast disease.
In the study, 233 women received sodium iodide (KI) for 2 years, and a group of 588 women received protein-bound iodide for 5 years. 70% of women given sodium iodide and 40% of women given protein-bound iodide showed improvement, but there was a high incidence of side effects (difficulty breathing, sweating, redness of the skin).
Benign fibrocystic breast diseases (breast lumps, cysts, fibrocystic breast disease) are often associated with iodine deficiency
According to a large number of specialized resources, iodine supplementation is a highly effective functional nutritional treatment for fibrocystic breast disease. The influence of iodine manifests its synergistic effect at several biological levels simultaneously.
Molecular iodine is the most effective form of treatment for severe conditions where relatively high doses must be administered to achieve maximum therapeutic effect. Organically bound iodine is useful for effective long-term prevention. Compared with iodide, the use of organically bound and molecular iodine provides a lower incidence of side effects affecting the thyroid gland.
Diagnostics
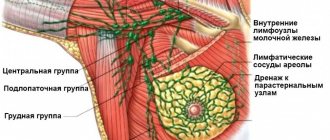
To begin with, the doctor (mammologist) examines the nearest lymph nodes and area of the breast, palpating for the presence of lumps. If they are detected, the woman must undergo additional diagnostics.
Mammography and ultrasound are prescribed; in advanced cases or when mammography is not informative, CT and MRI are prescribed. Additional examination also helps to determine the degree of fibrosis development. An examination of the blood vessels of the breast and milk ducts (chropoductography) may also be prescribed. A contrast agent is injected into the ducts, with the help of which their condition is determined. If a malignancy is suspected, a biopsy is performed (tumor tissue is removed for examination). Blood is donated to determine hormone levels.
Which doctor should I contact? A mammologist or gynecologist can help you examine your breasts for breast fibrosis.
Types of treatment
Treatment of breast fibrosis is selected individually for each woman. It will also depend on the causes of the disease, the location of the tumor and the type. Attention should be paid to age and the presence of other inflammatory diseases, endocrine disorders and other diseases. In most cases, conservative therapy is used, in others surgical intervention is required.
Conservative treatment. Used for all types of fibrosis at the initial stage of development. This is the best treatment for breast fibrosis. For this type of treatment, the following groups of drugs are prescribed:
- analgesics (pain relief)
- sedatives (calming)
- vitamin complexes for maintaining health
- diuretics for edema (if necessary)
- homeopathy
- hormonal drugs
Drug therapy
In some cases, hormones are prescribed for the treatment of fibroids, since the organ is directly dependent on them. Let's look at some medications that help cure breast fibroids:
- Parlodel. The drug is made from ergot. As a result of the action of the drug, the hormone prolactin and somatotropic hormone are released into the blood.
- Tamoxifen. This drug suppresses ovarian function. As a result, the compaction in the glands decreases and their pain stops.
- Bromocriptine. Corrects excess prolactin levels in the blood.
- Tibolone. Suppresses ovulation and has an antiestrogenic effect.
Oral contraceptives are also often prescribed. Duphaston, Norethiseron and others. There are contraindications. Before use, you should consult your doctor.
Proper nutrition plays an important role in the conservative treatment of fibrosis. This is used to improve the effect of medications, to remove estrogen from the body and unload it while fighting the disease. Some foods should be limited, such as:
- strong brewed tea
- coffee
- cocoa
- smoked meats
- bold
- fried food
The use of tobacco and alcohol is strictly not recommended. Smoking with any type of fibroids can provoke the development of cancer.
A woman should get a good night's sleep (at least 8 hours), organize a work and rest schedule. Don't overload yourself with exercise.
Surgical treatment
Surgeries are used quite rarely: in advanced cases of breast fibrosis or in the presence of large lumps that cause pain. It is necessary to remove the nodes themselves of any size: small and large, and a postoperative cosmetic defect will be observed.
ethnoscience
In the treatment of fibroids, folk remedies are used not so much for treatment, but to alleviate the symptoms of the disease: pain is reduced, hormone balance is observed, immunity is increased and a sedative effect is observed. But this does not mean that you should not pay attention to this type of treatment; it supports the body and helps fight the disease. You need to be treated with folk remedies correctly.
It is best to use the traditional type of treatment in a comprehensive manner. Locally treat the breast (tumor) with ointments and compresses and use general therapy with herbs and herbal tablets.
To choose this type of treatment as primary or secondary, you must consult a doctor. Folk remedies will not cure chest nodes, but will help in the fight against fibroids.
Prevention
For early detection of an existing disease, it is necessary to undergo preventive examinations 1-2 times a year. A visit to a mammologist and mammography are a prerequisite for healthy breasts.
A woman should avoid stress and have proper rest. Timely pregnancy and breastfeeding are also the main condition for the prevention of fibrosis.
You should always consult your doctor before using oral contraceptives.
The prognosis of the disease is almost always favorable, with the exception of some cases (as a consequence of degeneration into cancer). Those women who have been diagnosed with this need to carefully monitor their breast health and undergo examination by a gynecologist.