Painful sensations, discomfort in the lower abdomen, disruption of the menstrual rhythm, urination disorders are just some of the symptoms of the appearance of a tumor on the organ responsible for the ripening of the egg. An ovarian cyst is a cavity filled with fluid. Education tends to increase in size. Often the cyst stalk becomes twisted and the fluid-filled capsule bursts, causing peritonitis. To avoid such complications, as well as to improve the woman’s condition, minimally invasive or abdominal surgery is prescribed to remove the ovarian cyst.
Methods of surgical treatment
What method should be used to remove a tumor-like node?
Several methods are used to remove a cyst:
- Laparoscopy of an ovarian cyst is the most painless method for the patient.
- Cyst puncture. It is used only when the formation is small and there are no signs of inflammation or cancer. A nozzle is inserted through the abdominal wall under local anesthesia, with which the wall of the capsule is pierced and the contents are removed from the cavity, after which sclerosis occurs (collapse of the walls).
- Abdominal surgery or laparotomy. An open type of surgical intervention with a deep incision in the abdominal wall (up to 10–15 centimeters), performed under general anesthesia.
Discharge after laparoscopy
Bloody and mucous discharge in a small volume appears immediately after surgery and can last up to 3-4 weeks. There is no need to worry about them. If the discharge becomes brown with a greenish tint and an unpleasant odor, you should immediately consult a doctor, as this is a sign of infection and inflammatory process. The doctor will take a smear for analysis and further treatment.
The temperature after laparoscopy of an ovarian cyst can rise to 37-37.5 degrees. This is considered acceptable, since aseptic inflammation develops at the surgical site. If the patient’s temperature lasts for more than 2-3 days, an infectious complication may begin in the body.
Laparotomy of the cyst
Although laparoscopy is more often used among surgical methods, there are a number of justified indications for which abdominal surgery to remove an ovarian cyst is prescribed. In case of a complicated process, it is not always possible to carry out the required amount of treatment using laparoscopy.
Emergency indications for surgery are the following urgent cases:
- perforation (rupture) of the cyst capsule with leakage of internal exudate into the abdominal cavity;
- suppuration of the cyst tissue with further penetration of pus into adjacent organs;
- twisting of the leg-ligament, which leads to the knot suppurating;
- hemorrhage into the peritoneum.
Such cases pose a direct threat to life, as they can quickly lead to blood poisoning, shock, massive bleeding and an irreversible coma.
Indications for routine removal of an ovarian cyst by laparotomy:
- large neoplasm over 80 – 100 mm;
- active growth in a short time;
- development of a tumor-like node in the deep tissues of the gonad;
- adhesions in the area of the reproductive organs;
- suspicion of a cancer process or a confirmed diagnosis of oncology.
Do you use folk remedies?
Not really
Study of ovarian cyst. Their varieties and features
During ovulation, fluid-filled bubbles form on the surface of the ovary, necessary for better release of the egg. These bubbles do not have pathological deviations and quickly resolve. If an imbalance occurs in a woman’s body, this can lead to the formation of other forms of cystic vesicles. An ovarian cyst is a benign neoplasm. The reasons for the formation of cysts on the surface of the ovary are the following factors:
- hormonal imbalances in the body;
- obesity and diabetes;
- complications during pregnancy or infertility caused by pathogenic factors.
The disease is most often asymptomatic, and in the initial stages responds well to drug treatment.
Diagram of an ovarian cyst
Types of neoplasms
Like any other pathological neoplasm in the body, cysts have different etymologies and structures:
- Follicular formation is the most common. It is formed at the site of a follicle - a mature cell necessary for ovulation and degenerates into a cystic vesicular neoplasm. Such a cyst does not exceed five centimeters in size and is located inside the ovary. Symptoms are manifested by a decrease in basal body temperature, sharp pain in the lower abdomen, a feeling of fullness and pressing pain in the groin area.
- Dermoid or another generally accepted term is teratoma. This benign neoplasm consists of connective tissue and is no different in structure from other forms of cysts; it is a vesicle filled with purulent fluid, has an oval shape and a long stalk. Most often, this type of cyst occurs in young women (differentiation of ovarian cells during embryogenesis) and girls (during puberty, when hormonal surges provoke excessive activity). A small teratoma is poorly diagnosed; the doctor may not be able to discern its presence on an ultrasound or during a gynecological examination, so if the cyst does not cause inconvenience and there is no pain, then the patient may not know about the tumor for quite a long time.
- Endomitriotic vesicles with thin walls filled with brown liquid. They can be located both on the wall of the ovary and outside it. In diameter it reaches its maximum size of twelve centimeters. Due to the thin walls, rupture and release of cystic fluid into the abdominal cavity makes this type of neoplasm one of the most dangerous. The patient feels the endomitrioid cyst after it has ruptured and the initial stage of peritonitis begins, characterized by acute abdomen syndrome.
- Corpus luteum - this type of neoplasm of a vesicular nature is formed at the site of rupture of the follicle with an insignificant blood content. When diagnosed and treatable, the corpus luteum ranges in size from three to ten centimeters, rarely reaching a large size of up to twenty centimeters. The presence of a corpus luteum cyst on the ovary does not pose a danger even during pregnancy; rupture of this neoplasm and its subsequent degeneration into a purulent vesicular infiltrate is much more dangerous.
Corpus luteum cyst of the ovary
Diagnostics
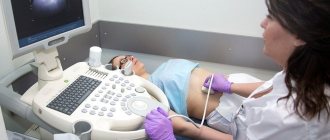
An ovarian cyst in its various stages and varieties can be diagnosed using an ultrasound examination and an initial gynecological examination. The study can only be carried out by a gynecologist. At the initial stage, during a gynecological examination, the doctor assesses the condition of the appendages and the presence of pain in them. After this, the doctor prescribes an ultrasound examination to the patient, during which it is possible to obtain a clear clinical picture of the tumor and diagnose the type of cyst and its location. Next, the doctor prescribes treatment appropriate to the type of formation.
Diagnosis of the ovaries for the presence of neoplasms is carried out in a certain sequence:
- First of all, the doctor (after an initial examination of the appendages) prescribes an ultrasound examination. It is able to give the most complete picture of the nature and structure of the neoplasm and identify the type. Ultrasound is performed using two specialized sensors, one of which is transvaginal and the other transabdominal.
- After identifying the type of neoplasm and location, the patient is required to donate blood for hormonal testing, as well as for tumor markers of a tumor nature.
- If the diagnosis requires it, the doctor will prescribe a puncture of the posterior vaginal wall, the analysis of which will help identify the presence of fluid or blood in the abdominal cavity.
Only after a high-quality and thorough diagnosis can a doctor prescribe treatment appropriate for a specific tumor.
After undergoing an ultrasound, you need to take a blood test for tumor markers
Advantages of laparotomy
Excision of a cyst on the ovary by abdominal surgery has a number of significant advantages:
- Provides wider access to all pelvic organs.
- Allows for emergency removal of a node in emergency conditions with examination of neighboring organs, and to take action if other pathologies are detected.
- Provides an opportunity for a detailed study of the reproductive organs, tissue, lymph nodes, and areas with probable cancerous changes.
- Provides the possibility of enucleation of an ovarian cyst (excision of the formation without opening the capsule), which eliminates the entry of pus or exudate into the peritoneal cavity and associated complications.
- Allows for surgical intervention of any volume and complexity, which is especially important for malignant changes, when it is impossible to determine the degree of development of the process before surgery. At any time, you can expand the surgical field for manipulation and remove the uterus, fibroids, and appendages. In this case, complete excision of the affected organs takes place without the risk of heavy bleeding.
- It is characterized by technical simplicity and does not require complex tools and equipment.
Operation process
Laparoscopy
Stages of laparoscopic cyst removal:
- The manipulation is performed under general anesthesia.
- The abdomen is treated with alcohol and iodine for disinfection.
- A micro-incision is made above the navel, through which carbon dioxide (CO2) is injected into the peritoneal cavity.
- When the gas pressure is sufficient, a laparoscope, a flexible optical system with a camera, is inserted through another hole. Looking at the monitor, the surgeon performs all actions inside the peritoneum.
- 3 more punctures are made in the abdominal cavity to insert clamps, manipulators and a suction device.
- The assistant fixes the affected ovary with a clamp. The surgeon excises the cyst (or the entire ovary) with a bipolar electrode and stops the bleeding.
- The removed tissue is removed through the hole, and the peritoneal cavity is washed with sterile saline.
- The instruments are removed, carbon dioxide is sucked out, and the incisions are closed with cosmetic sutures.
The duration of laparoscopy is from 1 to 3 hours. It all depends on the complexity of the placement of the neoplasm and its characteristics.
Abdominal surgery
Stages of surgery:
- The woman is given general anesthesia. The abdomen is treated with antiseptics (alcohol, iodine).
- The surgeon dissects the anterior abdominal wall layer by layer, gaining open access to the pathological area.
- The cystic tumor is excised with a scalpel, and if necessary, the entire ovary is removed.
- With an endometrioid neoplasm, the surgeon carefully examines the intestines, peritoneum, and vesicouterine fold for the presence of pathological foci and removes them.
- The bleeding stops, an anti-adhesion gel (Mesogel, Kategel) is injected into the peritoneum.
- The layers of the abdominal wall are sutured layer by layer.
Laparotomy lasts no more than 2 hours.
Preparation for laparotomy
Before surgery, the following studies must be performed:
- blood group test, general and biochemical examination, Rh factor;
- general and special urine analysis for kidney diseases;
- coagulogram or determination of blood clotting (INR, PTI);
- tests for sexually transmitted infections, HIV.
5 - 7 days before surgery, limit foods that provoke intestinal gas formation and allergies: fatty meats and smoked foods, carbonated drinks, beer, fruits, cabbage, legumes, black bread, spices, sweets made from flour and butter, milk.
The day before surgery:
- It is necessary to empty the intestines using laxatives and an enema. The less space the intestinal loops take up, the more volume remains for surgical manipulation.
- Stop eating 14 hours before surgery. A light dinner is allowed until 18:00, you can drink tea and water until 22:00.
- On the day of the operation, do not eat breakfast or drink, so that during anesthesia a gag reflex does not occur and the airways are not blocked by stomach contents.
Sex and sports after laparoscopy of ovarian cyst
are considered unacceptable loads. With regard to sexual intercourse and sports, the period of complete abstinence lasts one month. When restoring training, of course, you need to start with the least load in order to gradually master lost skills and control the limit of permissible stress. In particular, doctors prohibit lifting weights over three kilograms for the first three months after surgery, and in the next three months - no more than five.
Six months is the postoperative period, after which you need to return to your doctor for examination for complications. And if the doctor allows it, it will be possible to return to normal loads - for most women, such requirements, in principle, do not change their lifestyle, although athletes and workers in various industries or trade will have to limit themselves.
Carrying out laparotomy
How is the operation to remove a cyst performed? First, the skin is treated with antiseptics. The surgeon makes a cavity incision, for which two methods are used:
- The incision is inferomedian, which is made vertically along the line between the pubic bone and the navel area.
- Laparotomy according to Pfannenstiel. This is the main method in gynecology, in which a transverse incision is made along the fold of skin in the lower abdomen above the pubis. After healing, the scar will be invisible under the fold.
Then the surgeon opens the peritoneum layer by layer.
During laparotomy, the tumor can be removed by excision or enucleation:
- Excision is more often used for several lesions, a deep-lying node, or fusion of the cyst with the gonad. Through the incision, the gonad is pulled out from the peritoneum. The area of the ovary where the cyst has developed is excised with a “wedge” and carefully sutured.
- Enucleation of an ovarian cyst is carried out only when the benign nature of the formation is confirmed, since with this method the surrounding tissues are not affected. The process has another name – cyst desquamation. The entire capsule is removed, while care is taken to ensure that the cyst does not open and that the exudate does not leak out. Sometimes, to prevent rupture of the capsule walls, pus or exudate is drawn out of it.
If bleeding begins during surgical procedures, the vessel is doped (clamped), then bandaged or cauterized with high-frequency current (diathermocoagulation).
During laparotomy, the surrounding tissues are examined in order to:
- detecting the growth of a node into the fallopian tubes, gonads, intestines and bladder tissue;
- identifying possible cancer foci and excluding metastases.
In order to determine the nature of the tumor as quickly as possible, a biopsy of the ovarian cyst is necessary, that is, excision of a fragment of the affected tissue, and subsequent histological examination. If the formation turns out to be malignant, treatment is immediately prescribed.
Sometimes, if the doctor is concerned about the type of tissue, a biopsy and oncology analysis (histological examination) are done urgently, right during the operation.
If laparotomy is performed when there is a rupture of the cavity, a purulent process, or hemorrhage, then for 2–3 days the doctor will have to install drainage tubes so that all the fluid with pus and blood is removed from the peritoneal cavity.
How long does the surgical procedure take? The operation is classified as simple and lasts about 45 – 60 minutes.
Surgery to remove an ovarian cyst
For this disease, there are two types of surgical access - open (through an incision on the anterior abdominal wall) and laparoscopic. Each of them has its own advantages and disadvantages. Abdominal surgery to remove a cyst on the ovary is optimal for large tumors and complex anatomy of the pelvic organs. It is also chosen for the malignant nature of the process with germination into surrounding tissues and metastases into regional lymph nodes, since open access allows the surgeon to carry out manipulations freely and without any restrictions.
Preparing for surgery to remove an ovarian cyst
Before surgery, each patient undergoes a thorough general clinical examination to identify possible contraindications. The minimum set of studies includes:
- General blood test (assessment of hemoglobin level, early detection of infectious and inflammatory diseases).
- Biochemical blood test (assessment of the functions of the liver, kidneys and other internal organs).
- Coagulogram (determination of the functions of the blood coagulation and anticoagulation systems).
- Determination of blood group and Rh factor (in case of need for blood transfusion).
- Urinalysis (exclusion of renal pathology).
- Electrocardiography.
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the pelvic organs.
The patient must be consulted by a general practitioner, and in the case of extragenital pathology, by other specialists. This is necessary for the timely identification of contraindications to surgery, since if they are present, surgery can be extremely dangerous.
On the day before surgery, the patient should drink a special laxative solution to cleanse the intestines. To further empty the rectum, a cleansing enema is performed several hours before surgery.
Contraindications for surgery
There are a number of contraindications to surgical intervention for ovarian cysts. Some of them are relative, which requires the surgeon to be extremely careful, and some are absolute, that is, they categorically prohibit the operation.
It is prohibited to do this in the following cases:
- Chronic heart failure in the stage of decompensation (the heart will not be able to withstand such a load).
- Decompensated diabetes mellitus (high risk of suture dehiscence and postoperative wound suppuration with subsequent development of sepsis).
- Blood clotting disorders - thrombocytopenia, hemophilia and other coagulopathies (this is an immediate threat of fatal bleeding during surgery).
- Acute infectious diseases.
- Acute myocardial infarction.
- Stroke.
- Shock, which in gynecological practice is often caused by massive bleeding from the genital tract.
If these contraindications are present, surgery should be postponed until the patient is cured of these diseases or stabilizes her condition. For this purpose, you can contact the specialists of our clinic.
Progress of the operation
Immediately before surgery, the patient is given premedication - the administration of medications that will relieve anxiety and anxiety, as well as prevent the development of adverse events during and after the operation.
The surgery is performed under general anesthesia, which means without any sensation. The effect of anesthesia can be compared to a state of sleep. The awakening will occur in the intensive care ward, and the patient will not remember anything that happened to her during the operation.
The surgical procedure is as follows:
- First, the surgeon will treat the surgical field - the lower abdomen - with an antiseptic solution to prevent pathogenic bacteria from entering the abdominal cavity.
- Then, layer by layer, step by step, the skin, subcutaneous fat, muscles with fascia and peritoneum are dissected. More often, a lower median laparotomy is performed - a longitudinal incision along the midline running from the navel to the pubis. Less commonly, a transverse Pfannenstiel incision is used above the pubic region, where the natural fold of the abdomen is located (the same incision is made, for example, during a caesarean section).
- After spreading the edges of the wound, the surgeon examines the pelvic organs for the presence or absence of pathological processes that might not be visible during ultrasound examination.
- The main stage of the operation is removal of the ovarian cyst. If the size of the formation is small, ovarian resection is performed - removal of the organ fragment affected by the cyst. If the pathological process is pronounced, and the ovary is almost completely replaced by a cyst, then oophorectomy is indicated - complete removal of the ovary.
- The final stage of the operation is layer-by-layer suturing of the wound with the obligatory installation of temporary drainage.
As a rule, surgery lasts no more than 2 hours. However, if a malignant nature of the cyst is suspected, an extended operation may be required, including removal of the fallopian tube on the affected side, as well as regional lymph nodes. The doctor determines surgical tactics in each individual case.
Postoperative period after removal of an ovarian cyst
The postoperative period lasts on average 1-2 weeks. The patient spends the first 2-3 days in the intensive care unit, since at this time there is always a risk of developing early complications, such as:
- Internal bleeding.
- Seams coming apart.
- Suppuration of a postoperative wound.
- Pulmonary embolism.
Fortunately, this happens extremely rarely thanks to the use of the most modern equipment and drugs with proven effectiveness.
On the first day, the patient may experience unpleasant sensations such as pain in the area of the surgical wound, discomfort in the throat, and chills. This is absolutely normal and does not require any special treatment. It is very important after abdominal surgery to remain calm and not make unnecessary movements for at least 1-2 days so that the edges of the wound can heal a little.
Sutures require careful and regular care to prevent inflammation and even suppuration. Every day, the surgeon examines the postoperative wound, and the nurse changes the bandages and treats the wound with antiseptics. These simple steps provide reliable protection against dangerous complications.
After the patient is transferred to the general ward, a rehabilitation period begins. You should gradually increase the load on the abdominal muscles, but in no case overdo it. This is fraught with the development of a postoperative hernia, which will require repeated surgery.
Types of laparotomy and extent of surgery
How is an ovarian cyst removed and what methods are used? When removing cystic nodes, several surgical techniques are used, which differ in the depth of surgical intervention and the volume of tissue removed.
Which surgical technique the surgeon will choose is determined by the type of ovarian cyst, size, location, degree of damage to the gonad, the nature of the nodular formation and the likelihood of cancerous degeneration.
Surgical techniques:
- Ovarian cystectomy - removal of only the cyst by enucleation while preserving adjacent tissue. The scar on the ovary heals quickly and the gonad is quickly restored. Cystectomy during laparotomy, like laparoscopic cystectomy, allows you to preserve normal ovarian function and fertility. It is possible if the ovary is not affected by a pathological process and the neoplasm is benign.
- Ovarian cyst resection - removal of the formation by excision of a triangular (wedge-shaped) section of ovarian tissue. It is more often performed for large lesions, cysts that have grown deeply into the tissue of the reproductive gland. This treatment allows you to preserve the gonad, which is restored within a few months and menstrual function is completely stabilized.
- Ovariectomy - complete excision of the gonad along with the cyst and adnexectomy - excision of the cyst, diseased ovary and fallopian tube. These techniques are used in cases of significant destruction of the ovarian structure, ruptures, suppuration, and suspected cancerous transformation of cells. If only one ovary is removed, fertility is preserved and the woman is able to conceive.
- Hysterectomy - removal of the uterus. The cyst, ovaries and uterus are removed if a cancerous process is confirmed or there are serious reasons to believe that the likelihood of cancer is very high.
A qualified specialist is always concerned with the question of how to remove a cyst on an ovary, so as to affect as little tissue as possible and not have to cut out the ovary.
Indications for surgery
Ovarian cyst is a pathology that most often affects women of reproductive age. As the size of the tumor increases, there may be pain or pulling in the lower abdomen, and pressure may be felt from the inside. Removal of a cyst can be urgent (emergency) or planned.
Emergency surgery
Surgery is performed urgently when:
- cyst rupture;
- purulent inflammation;
- twisting of the cystic “leg”.
Such phenomena are extremely dangerous and need to be diagnosed in time. You should immediately consult a doctor if a woman experiences the following symptoms:
- acute pain in the lower abdomen, radiating to the legs and rectum;
- nausea, vomiting;
- general weakness or faintness;
- temperature jump (38°C or more);
- bleeding or abnormal vaginal discharge.
Observing all of the above phenomena, you must not hesitate, you need to call an ambulance. Attempting to treat the disease at home will lead to death.
Planned surgery
If drug therapy does not give the desired result, then the woman is indicated for surgical excision of the cyst. The procedure takes place as planned with preliminary tests and preparation.
Indications for surgical intervention:
- the size of the cystic tumor reaches 6 or more centimeters;
- the neoplasm appeared during menopause;
- if you suspect cancer.
Recovery after laparotomy of an ovarian cyst
After removal of the ovarian cyst by laparotomy, the patient will have to stay in the hospital for 7 to 10 days under the supervision of specialists.
Within 30 – 60 days after suture removal:
- Any physical exertion and lifting weights exceeding 1 kg are strictly prohibited;
- taking a bath, visiting a bathhouse, sauna, swimming pool;
- It is necessary to abstain from sexual activity after removal of an ovarian cyst for 2 months.
During this period, it is absolutely necessary to take vitamins. Depending on the type of cyst, as prescribed by the doctor, continue treatment with hormonal drugs and immunomodulators.
Methods
In medicine, three key methods are used to remove ovarian tumors:
- laparotomy;
- laparoscopy;
- laser surgery.
To get a detailed consultation, you need to make an appointment at a clinic in Moscow. The price of the operation depends on the chosen method and complexity.
Laparotomy
Abdominal surgery is a classic option for excision of an ovarian cyst. In gynecological emergencies, only this method is used. Surgery is also indicated if the presence of malignant cells in the tumor is suspected.
The operation is performed by making an incision in the anterior wall of the peritoneum to gain open access to the problem area. If necessary, the surgeon decides to remove the ovary along with the cyst - in whole or in part.
Recovery after abdominal surgery is long – at least 2 weeks. The length of stay in the hospital depends on the patient’s condition; they are discharged after 5-7 days. Lifting heavy objects and undergoing excessive physical activity is prohibited for a month.
Laparoscopy
This method is the least traumatic for organs and is aesthetically pleasing, since only small incisions are made on the skin (up to 1 cm). As a result, the woman quickly goes through the rehabilitation period without loss of performance.
Surgical instruments and a laparoscope with a video camera are inserted into the peritoneum through punctures. The doctor is guided by the image on the monitor, which is magnified up to 40 times. This allows you to see even the smallest neoplasms that are difficult to distinguish during open abdominal surgery.
After laparoscopy, the recovery period is easy. The woman can get out of bed on the same day, and discharge from the clinic occurs on the 3rd day. There are practically no restrictions during this period. However, she does not experience any pain in the operated area.
Laser surgery
Removing a cyst using a laser is the fastest and most accurate treatment method. The role of a scalpel is performed by a laser beam, which also cauterizes the incision sites, eliminating the possibility of bleeding.
The cost of laser surgery is higher than other methods.
Pregnancy after cyst laparotomy
If only a cyst on the ovary or only one sex gland was removed, then a healthy ovary is capable of producing hormones and eggs. Therefore, the probability of conception after surgery for an ovarian cyst remains very high. Reproductive function will finally stabilize after at least 2 to 5 months have passed.
But conception within six months is undesirable, since incomplete restoration of ovarian function can lead to early miscarriage or tissue rupture in the suture area when the uterus enlarges. Therefore, it is advisable to plan a pregnancy no earlier than five to six months after laparotomy of the ovarian cyst.
Methods for treating ovarian cysts without surgery are disclosed in our separate work.
Types of ovarian cysts
In modern medicine, the following types of ovarian cysts are distinguished:
- Follicular;
- Corpus luteum cyst;
- Mucinous;
- Paraovarian;
- Dermoid;
- Endometrioid;
- Hemorrhagic.
Follicular cyst and corpus luteum cyst
Follicular cyst and corpus luteum cyst
Such cysts are formed during the normal functioning of the ovaries of a healthy woman. That is why cysts of this type are called functional. In young girls and women, in 90% of cases when a cyst is detected, it is the functional form that is diagnosed.
Functional cysts, as a rule, form on the left or right ovary and disappear on their own within a period of several weeks to several months. No treatment required. Follicular cysts and corpus luteum cysts can reach sizes of 5 cm or more.
Mucinous cyst
most often consists of several chambers filled with mucous fluid. In some cases, they can reach large sizes and degenerate into a malignant ovarian tumor.
Paraovarian cyst
appears from the appendage, located above the ovary and representing a single-chamber formation of a round or oval shape, which is filled with a clear liquid. Quite often, this tumor is diagnosed in women aged 20 to 40 years. In most cases, the ovary is not related to the pathological process.
Dermoid cyst
contains various derivatives of connective tissue (fat, nails, hair, teeth, etc.), parts of embryonic layers.
Endometrioid cyst (endometriotic)
is a blister filled with blood that forms on the ovary during endometriosis. In addition to the formation of ovarian cysts, endometriosis can also manifest itself as prolonged nagging or aching pain in the lower abdomen, extremely painful periods, and infertility.
Hemorrhagic cyst
formed through hemorrhage into a functional cyst. The main symptom by which this type of cyst is distinguished is a nagging, dull pain in the lower abdomen. If the cyst is in the left ovary, then the pain in the lower abdomen on the left side is more pronounced
Complications after surgery
When laparoscopy is performed by a professional, the development of complications is negligible. But the possibility cannot be ruled out 100%. Possible complications include the following: bleeding, vascular damage, thrombophlebitis, damage to nearby organs, infectious disease of the abdominal cavity, infertility, recurrence of the cyst.
It should also be noted that complications after laparoscopy of ovarian cysts are individual and depend on certain factors:
- pregnancy;
- abortions;
- hormonal imbalances;
- overweight;
- chronic diseases;
- alcohol or drug abuse;
- smoking;
- hypothermia;
- non-compliance with medical recommendations.
The reappearance of an ovarian cyst is a postoperative complication and occurs quite often. The cyst may reoccur after laparoscopy due to hormonal imbalances and the risk factors described above. After laparoscopy, the doctor prescribes the necessary course of drugs that stimulate the production of male hormones. Very often, such treatment methods are used after removal of the endometrioid cyst.
To prevent the recurrence of a cyst, be sure to follow your doctor’s recommendations, do not neglect the prescribed treatment, be sure to periodically visit your gynecologist, eat right and avoid stress.
Ovarian adhesions - a possible risk of infertility
Adhesions are a pathology due to prolonged inflammatory processes, operations, endometriosis, which is an fusion of tissue in places of inflammation.
If the onset of postoperative inflammation in a woman is not treated on time, it develops into chronic inflammation, resulting in an adhesive process of tissue fusion in the female genital organs. Women often suffer from constant pain in the lower abdomen, which cannot be treated with painkillers, as it is caused by anatomical disorders. Among the consequences of the disease are kinks in the fallopian tube, difficulty in fertilization, ectopic pregnancies, and infertility.