Today, we will talk a little about “alpha and omega” gynecology and gynecological endocrinology - the phases of the menstrual cycle, their regulation, significance, and in particular, in our article, we will talk about the luteal phase of the cycle.
It is important to begin by understanding that a woman’s menstrual or monthly cycle is an extremely complex multicomponent system that is regulated by a number of factors - the central nervous system, hormone cascades, nervous connections, enzymes, vitamins, and microelements.
Every year, scientists discover more and more new factors regulating the cycle, for example, in recent years, vitamin D has been given great importance in hormonal relationships.
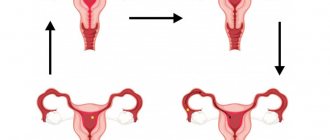
So, let's try to understand a little about this complex system. Looking at this diagram, it is clear that the normal menstrual cycle of a healthy woman, on average, consists of three main phases:
- The follicular phase is the period of time from the first day of menstruation until the dominant follicle in the ovary fully matures and its egg is released into the abdominal cavity.
- Ovulation is the actual release of an egg to meet sperm for potential conception. Some authors single out the day or three around ovulation as a separate segment, while others consider it a kind of boundary or division between the first and second phases.
- The luteal phase is the segment of the cycle immediately following the maturation and release of the egg until the beginning of the next menstruation or implantation of the embryo into the uterine mucosa.
- Menstruation - some authors distinguish the period of menstrual bleeding into a separate phase of the cycle, while the other half includes this period in the first or follicular phase.
Let's talk in more detail about what the luteal phase is in women.
What is the luteal phase in women?
Many people cannot give an exact answer: “Luteal phase - what period of the cycle is it? What phase of the menstrual cycle is this - first or second? How long does the phase last? What changes occur in the endometrium of the uterus? Which hormones predominate, depending on the phase of the menstrual cycle? " Therefore, in order to understand, you need to understand how a woman’s monthly cycle works, how many phases there are in the menstrual cycle.
Every month, certain important processes occur in the female body that accompany the possible favorable conception of a child.
Estradiol during this period
Estradiol in the female body is responsible for sleep, beautiful skin, good mood, and bone tissue development. If this hormone is not enough, then irregularities, insomnia and muscle pain may occur. To prevent this, doctors introduce complex treatment for hormonal imbalance. Monitor the intake of medications.
After all, an increased dose of estradiol can lead to pain in the back, legs, cause a decrease in muscle tissue, and an increase in fat. Also, increased estradiol causes an improvement in blood glucose levels. Ladies refuse sweets. This process is positive for women with diabetes.
The norm of estradiol in the blood during the luteal phase
Causes of elevated estradiol:
- thyroid pathology
- follicle persistence
- genital endometriosis
- excess weight
- cirrhosis
- tumors of the uterus, ovaries
- follicular ovarian cyst
- consumption of certain medications (phenytoin, clomiphene, contraceptives, cimetidine, etc.)
Luteal phase - increased estradiol
Root causes of decreased estradiol:
- heavy loads, weight loss
- restriction of protein foods, predominance of carbohydrate nutrition
- smoking, alcoholism
- pituitary disorder
- hyperprolactenemia, vegetarianism
Laboratory analysis for estradiol
IMPORTANT : An endocrinologist is involved in normalizing hormonal levels. Estradiol levels are accurately determined by laboratory tests. This test is taken in the morning on an empty stomach. The day before the procedure, give up bad habits, fats, and sexual relations.
Follicular, ovulatory, luteal phases: what are they?
The physiological feature of every woman is the presence of a menstrual cycle, which normally should take place in three stages (1st follicular phase of the menstrual cycle, ovulation and 2nd luteal phase of the menstrual cycle). Follicular, ovulatory and luteal phases are integral components of the physiological course of the menstrual cycle. The duration of the entire menstrual cycle is 21-36 days. In the normal state of affairs, monthly menstruation indicates the absence of a fertilized egg. That is, the conception of a child did not occur during ovulation and after it.
Against the background of these physiological phenomena, another (new) phase of the ovaries develops with a three-stage duration:
- Follicular phase of the cycle;
- Ovulation. The ovulation phase is normal for the middle of the cycle;
- Luteal phase of the menstrual cycle.
The work of the ovaries is carried out directly under the control of the brain center - the pituitary gland. Typically, the luteal phase develops approximately two weeks before menstruation; in other words, it is the equator of the menstrual cycle.
Normally, the luteal phase of the cycle is characterized by the physiological production of progesterone in the body. The formed corpus luteum controls the process of preparing eggs, so by its condition one can judge whether a woman is able to become pregnant.
What role does the luteal phase play?
At the end of the monthly discharge, as a result of which the inner lining layer of the uterus is shed, the stage of follicular growth begins. At this time, the concentration of estrogen in the blood increases, and the endometrium gradually grows again. Before ovulation, the follicles in the ovaries mature; after they rupture, the egg moves through the fallopian tubes into the uterine cavity.
After ovulation ends, the female luteal phase of the cycle begins. The norm is the maturation of the corpus luteum. Perhaps many are interested in why yellow? In fact, the walls of the follicles contain fat and yellow lutein. The level of hormones that influence the possibility of conception increases, while in the second period of the menstrual cycle there is a decline in FSH concentration.
Even if conception has occurred, the formation of the corpus luteum will still occur after ovulation, and this is considered normal. Since this formation is responsible for the release of hormones, its presence during pregnancy is not considered a pathology. The production of hormones occurs up to a certain point.
Features of the menstrual cycle
The first phase of the cycle is follicular or menstrual. The follicular phase is counted from the first day of menstruation. During this period, the active release of hormones - follitropin and lutropin - begins in the woman’s body. Under their influence, several follicles develop in the ovary, among which only one, dominant, will subsequently remain. The phase takes about half the cycle and during this time the follicle prepares for maturation by producing estrogen. A day before ovulation, a large release of lutropin occurs and this phase ends.
The ovulatory phase lasts 24-48 hours, during which time an egg is released from the follicle. In its place a yellow body is formed. It acquires a yellow color due to the content of lipids and luteal pigment in it - therefore the next phase is called luteal. It occurs immediately after ovulation. During this period, the corpus luteum actively produces progesterone and estrogen, preparing the body for a possible pregnancy. If fertilization of the egg does not occur, then in the middle of the phase the body dies and is destroyed, the endometrium of the uterus is rejected and comes out along with menstrual blood. Follicle-stimulating hormones begin to be produced again and the cycle begins anew.
If fertilization does occur, the corpus luteum continues to produce progesterone until the developed placenta takes over this function.
Why is the luteal phase of the cycle so important? The stable functioning of the corpus luteum during this period determines how successful fertilization will be and whether the egg can attach to the uterine mucosa. During the luteinizing phase, the corpus luteum becomes the main supplier of progesterone and estrogen. Progesterone is a hormone that makes the uterine epithelium looser and more sensitive, and estrogen increases the amount of mucous secretion. If these hormones are sufficient, then the chances of getting pregnant are high.
What is the luteal phase in women, what hormones are produced?
A number of luteal phase hormones include:
- Estradiol;
- Progesterone (it is due to it that the basal temperature rises in the luteal phase);
- Androgen.
Due to these hormones during pregnancy, the likelihood of uterine contractions is reduced. They also affect the development of mammary glands for feeding the baby. If the egg has not been fertilized, the corpus luteum produces much less hormones. As a result, necrosis and detachment of the endometrium occurs. At this time, the luteal phase of ovulation stops and menstrual bleeding begins.
Norm of progesterone during LF
In addition to instrumental techniques, laboratory diagnostics are also used. The patient's blood is taken to check progesterone levels. The normal value of this hormone is 6.99 – 56.63 pmol/l. Its maximum amount is observed 7 days after the release of the egg. At this time the analysis is done. Blood is also taken for other sex hormones.
The luteal phase is important for pregnancy. It ensures normal attachment of the egg to the uterine mucosa and prevents miscarriages. With NLF, infertility develops, which requires immediate treatment.
Is it possible to determine the days of the onset of the luteal phase?
In fact, it is not difficult to calculate the days of formation of the corpus luteum if you know the features of your monthly cycle. The luteal phase always occurs after ovulation. To accurately determine this period, you need to calculate the menstrual cycle. Based on its duration, the luteal phase is calculated. The norm for women without any special deviations in the functioning of the reproductive system is the second phase of the cycle.
The days of formation and functioning of the corpus luteum are determined taking into account the presence of certain features. You need to understand that depending on age, deviations are possible.
Duration of the luteal phase
It is not difficult to understand what the luteal phase of the menstrual cycle is; it is more difficult to determine its length, since it is necessary to take into account the specific characteristics of the body. If the reproductive system works smoothly and without failures, then the duration of the luteal phase will be the last 14 days.
The days of formation of the corpus luteum can be determined using an ovulation calendar. Normally, this process should occur immediately after the release of the egg, the follicular phase. Depending on the period of your period, this will be on the 12th, 14th or 16th day of the monthly cycle.
Long follicular phase. A woman’s luteal phase can be long if the egg has been fertilized or if there are certain pathologies in the reproductive system.
What does the luteal phase mean - symptoms and signs
During this period, the woman does not experience pronounced symptoms, but the onset of the secretory phase can be monitored by paying attention to the following manifestations:
- If you carry out an analysis, you will see that the level of progesterone is increasing significantly;
- The temperature of the luteal phase exceeds 37 degrees. It can be measured rectally;
- Vaginal discharge is profuse. During the action of the corpus luteum, the secretory function increases, that is, the secretory phase of the menstrual cycle occurs at the level of the endometrium. Its nutrition increases in the luteal phase, the endometrium becomes juicy, ready for implantation of the fertilized egg.;
- Under the influence of hormones, the milk ducts in the breast expand, causing the mammary glands to enlarge.
What can be the consequences of luteal phase deficiency?
Very often, against the background of this pathology, women cannot become pregnant. This condition can develop for the following reasons:
- Frequent stressful situations, as well as injuries affecting the pituitary gland;
- Ovarian and adrenal hyperandrogenism;
- High concentration of prolactin in the body;
- Hypothyroidism, hyperthyroidism;
- Inflammation of the appendages.
These causes of luteal phase deficiency do not cause any particular symptoms in women. There is one single sign of pathology that is not difficult to notice; this is a failure of the monthly cycle. The most serious consequence is female infertility.
To normalize the luteal phase, the doctor prescribes hormonal medications. Due to the lack of symptoms, this condition is difficult to diagnose, so it is important to monitor the duration and characteristics of your menstrual cycle.
Is a short luteal phase of the cycle a defect?
Pathology such as insufficiency of the luteal phase of the cycle is quite common among women. This problem arises against the background of disturbances in the functioning of the internal organs of the reproductive system.
Insufficiency of the luteal phase of the menstrual cycle can be diagnosed not only in women suffering from infertility, but also in women who have experienced termination of pregnancy at an early stage of its development. The main reason for the development of this pathology is a sharp decrease in the concentration of progesterone, which is the main hormone for pregnancy. It is produced directly by the corpus luteum, formed during the luteal phase. Due to its insufficiency, the process of embryo implantation may be disrupted. Insufficiency of the luteal phase also occurs in premenopause.
Perspective
A woman with a short luteal phase will have difficulty becoming pregnant or may lose her baby at an early age during embryonic development.
A short luteal phase can be corrected once it has been identified, although this may not be obvious before someone tries to become pregnant.
Treatment often involves lifestyle changes, such as finding ways to reduce stress, reducing excessive exercise, or losing weight.
In other cases, treatment may require taking certain medications or hormones to help the body become pregnant.
What are the phases of NLF?
Disruption of the luteal phase of the menstrual cycle can occur in two forms:
- With the hypoprogesterone form, the following symptoms appear:
- The corpus luteum is not completely formed or is smaller than normal volumes;
- The amount of the hormone progesterone produced by the corpus luteum is reduced;
- The inner lining of the uterus in the second half of the monthly cycle has not reached the required thickness; it may be less than one centimeter.
- The pathological hyperestrogenic type is accompanied by the following characteristics:
- The corpus luteum has normal volume;
- The endometrium of the uterus has a thickness of more than 12 mm by the 21st day of the menstrual cycle;
- High concentration of estrogen in the blood;
- The level of progesterone in the blood is slightly reduced.
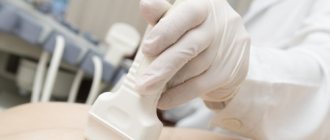
Instrumental examination methods for women
The nature of the course of LF can be determined using laboratory and instrumental diagnostic methods. Instrumental methods include ultrasound examination. The doctor looks at the condition of the ovaries and follicles. If there is NLF, the study reveals a decrease in the thickness of the uterine mucosa, underdevelopment of the corpus luteum, and decreased blood flow in the ovarian area.
A biopsy of the uterine lining is also done. It is carried out to evaluate the functioning of the receptor apparatus on which the hormone progesterone acts.
What is the short luteal phase?
Women suffering from early pregnancy loss may be diagnosed with a low luteal phase, which is when there is a low concentration of progesterone in the blood.
The luteal phase is considered abnormal if its period is less than 10 days. In such situations, it is better to consult a doctor to get qualified help. The cause of this phenomenon can only be clarified after diagnosis.
In order to establish an accurate diagnosis, the following therapeutic techniques are used:
- A week after ovulation, the woman is asked to donate blood for a test to determine the progesterone level;
- If examination of the endometrium is required, then a biopsy cannot be done;
- Rectal measurement of basal temperature. In the luteal phase it becomes more than 37 degrees. The doctor needs this information to clarify the diagnosis;
- You need to know the exact timing of ovulation. To do this, you can conduct a special test or keep an ovulation calendar for several months;
- On certain days of the menstrual cycle, a woman must undergo an ultrasound, but the exact timing of the release of the egg from the ovary must be determined in advance;
- Assessment of the condition of vaginal discharge. During the period of ovulation, cervical mucus resembles raw egg white, it is transparent and elastic;
- Through a gynecological examination, you can examine the condition of the cervix. Its level can be raised, and softness and friability are also characteristic features.
The role of progesterone and estradiol in the luteal phase
Due to these two pregnancy hormones, the process of insulin secretion is regulated, which can be disrupted under the influence of glucose.
Insulin is secreted by the pancreas after eating. This process is controlled by progesterone and estradiol, which may differ in how they perceive insulin.
Luteal phase deficiency may be due to increased concentrations of progesterone. For this reason, the perception of insulin is reduced, and the body cannot cope with the normalization of glucose levels on its own. This hormone actively affects the pancreas, causing a strong desire to eat sweet foods.
The level of this hormone increases in the blood if a woman has diabetes. This phenomenon is also considered common among pregnant women.
If the concentration of a hormone that affects the perception of insulin increases, then most likely the woman will begin to gain excess weight by eating a lot of sweet foods. Along with the kilograms, cholesterol and blood pressure levels increase. Often women with this problem suffer from heart disease or thrombosis.
Doctors very often explain the fact of increased progesterone by the patient’s overweight.
An insufficient luteal phase is considered to be an increase in estradiol in the blood. This hormone increases insulin sensitivity, which normalizes glucose levels. The desire to eat sweet foods is significantly reduced, which is important for women with diabetes.
To normalize metabolic processes in the body, the level of hormones such as progesterone and estradiol must be within optimal limits in relation to each other.
Another problem is luteal phase deficiency in premenopause. With this condition, a woman’s number of ovulations decreases. The luteal phase of the menstrual cycle becomes shorter. An accurate diagnosis can only be made after undergoing an examination prescribed by a doctor. Tests are taken at different periods of the menstrual cycle, and the exact dates of ovulation are clarified. You also cannot do without instrumental and ultrasound examinations. Sometimes the problem can be solved by taking hormonal medications.
Luteal phase deficiency is a serious disruption to the functioning of a woman’s reproductive system, so if suspicious symptoms are detected, you should seek qualified help.
Norm criteria
A normal and full luteal phase of the menstrual cycle is the key to a regular female cycle, adequate menstruation, rapid onset and successful pregnancy. Many women planning a pregnancy or concerned about irregular menstruation ask a lot of questions. Let's try to answer them.
What day of the cycle does the luteal phase begin on?
As we said above, the beginning of the second phase of the cycle begins from the moment of ovulation, so it would be illiterate to name a specific and only correct day. Everything will depend on the day of ovulation for each specific woman - for one it will be day 12 of the cycle, for the second it will be 15, and for the third it will be day 20-22. Previously, doctors tried to “adjust” the cycle to the same universal “lunar” cycle - 28 days, considering it the only correct one. The situation has now been reconsidered:
- If a woman is able to evaluate her menstruation as regular, even if it comes not after 28-30 days, but after 38-40, this is the norm.
- If a woman, at any cycle length, easily becomes pregnant and develops safely, this is the norm.
- If a woman is not currently planning a pregnancy, but she has proven ovulation at any cycle length and there are no gross hormonal disorders, this is the norm.
How long is the luteal phase?
The average duration of the luteal phase, in contrast to the follicular phase, is quite stable and is determined precisely by the lifetime of the corpus luteum - 10-12 days, in some cases up to 15.
If the patient has irregular menstruation, frequent delays, then the phenomenon of persistence of the corpus luteum can often be observed in the ovary - the absence of its regression outside of pregnancy - for some reason the corpus luteum does not fade, but remains, secretes progesterone and does not allow it to begin next menstruation.
How to find out the phase of the corpus luteum?
Of course, with a regular cycle and no complaints, there is absolutely no reason to specifically “look out” for the luteal phase. However, patients planning pregnancy, measuring basal temperature, and doing ultrasound examinations during the cycle can easily determine the luteal phase of the menstrual cycle:
- When measuring basal temperature, you can easily determine the day of ovulation and track the period of consistently elevated temperature after it - this will be the corpus luteum phase.
- With an ultrasound examination, it is also easy to find the corpus luteum itself in the right or left ovary, and to evaluate changes in the uterine mucosa characteristic of the second phase of the cycle.
What is the short luteal phase?
Recently, there has been a lot of conflicting information regarding the minimum length of the luteal phase. This is truly a controversial issue. It is believed that the length of the second phase of the cycle should be at least 10 days. Anything that occupies a smaller segment should be considered a short phase of the corpus luteum, which may be defective and insufficient.
In fact, it is important to rely not on some numbers, but on a specific situation. If the patient has regular, adequate menstruation, pregnancy occurs easily, a series of miscarriages does not occur - it does not matter at all whether she has a short luteal phase or not - and measuring it, in this case, is pointless.
It’s another matter if the patient has irregular menstruation, breakthrough uterine bleeding, infertility and miscarriage - then this situation requires diagnosis and the length of the second phase of the cycle, the condition of the corpus luteum and assessment of its function are really of great importance.
In such clinical situations, it makes sense to have ultrasound monitoring according to the phases of the cycle, folliculometry, measuring basal temperature, donating blood for sex hormones according to the phases of the cycle - especially the level of progesterone and luteinizing hormone, as well as assessing the condition of the endometrium in the second phase of the cycle.
Of course, such research should only be carried out by a gynecologist or gynecologist-endocrinologist who understands what, when, and at what periods of time needs to be monitored in order to prescribe this or that correction in the future.
What causes a short luteal phase?
Luteal phase defect can be caused by a number of reasons, which include:
- Disruption of the central mechanisms regulating the functions of the reproductive system. This condition can be diagnosed against the background of hyperandrogenism, hyperprolactinemia, diseases of the thyroid gland or adrenal glands;
- If the receptor apparatus of the inner layer of the uterus is changed for the worse, then a short luteal phase is possible. The reasons for this condition are explained by the presence of chronic pathologies in the genital organs caused by infection or inflammation;
- Other reasons include metabolic disorders, as well as insufficient blood supply to the corpus luteum, etc.
Features of the luteal period - the formation of the corpus luteum
When the walls of the follicle burst and release the egg, a corpus luteum appears in its place - a gland that secretes the hormone progesterone. Its activity begins from the moment the egg is released and stops 1-2 days before the new menstruation begins. The duration of this period is half the cycle.
The corpus luteum is formed from the walls of a ruptured follicle when follicular fluid leaks out of it. A small blood clot remains at the site of the rupture, the walls of the follicle shrink into folds, and the internal granular membrane begins to grow rapidly. A special yellow substance, lutein, accumulates in its cells. At the same time, the walls of the follicle are transformed into luteal cells, and a network of capillaries grows around them, which provide the resulting gland with proper nutrition.
When the egg is fertilized and enters the uterus, the corpus luteum continues to grow and secrete the hormones estradiol and androgen, which prepare the mammary glands for milk production and reduce the possibility of uterine contractions. Another hormone, gonadotropin, maintains the viability of the corpus luteum and does not allow termination of pregnancy. The resulting gland functions until the placenta is completely formed.
If pregnancy does not occur for some reason, the corpus luteum develops in the reverse order, luteal cells die, and the level of hormones produced quickly decreases. The menstrual cycle ends with the disappearance of the corpus luteum and the appearance of new follicles.
Luteal phase deficiency - possible symptoms
In frequent cases, women are faced with a pathology - luteal phase deficiency. The symptoms of this pathological condition are not pronounced, so it is difficult to immediately identify NLF. A woman should be alert to the following symptoms:
- Frequent menstrual irregularities and pain during ovulation or discharge;
- Slight spotting before menstruation;
- Inability to get pregnant for a long time;
- Habitual miscarriage.
With the help of a special examination, the doctor can confirm the condition of “luteal phase insufficiency”. Signs can be supported by the following data:
- Insignificant difference in basal temperature in two cycles, shorter duration of the second half of the monthly cycle;
- Ultrasound diagnostics describing the dynamics of follicle maturation, the thickness of the inner layer of the uterus, as well as the nature of blood flow in the ovaries. An ultrasound on the appointed day of the cycle may show a violation of the dimensional parameters of the corpus luteum, as well as the condition of the endometrium. The abnormal structure of the corpus luteum and its improper blood supply are also revealed;
- Taking tests to determine hormonal status;
- Taking a biopsy of the endometrium of the uterus.
If necessary, the doctor may prescribe additional diagnostic procedures.
Therapy
What drugs, other than hormonal ones, can cure the pathology? If the cause of the deviations is immune deficiency or genetic prerequisites, non-hormonal drugs duphaston and others are used. If there is an excess of progesterone, only hormonal therapy is indicated. Hormones are also used in the case of hyperandrogenism and hyperprolactinemia.
You can get rid of hormonal deficiency by using contraceptives in tablet form. Oral contraceptives help regulate the production of hormones and establish their balance in the body.
In the absence of ovulation, medications are prescribed to stimulate the ovaries. For endometrial pathology, antibiotics, anti-inflammatory drugs and immunomodulators are prescribed. To improve the immune status, the gynecologist prescribes vitamin complexes, acupuncture and physiotherapy.
If the pathology was caused by a nervous breakdown or an acute mental reaction to stress, patients are prescribed sedatives. If the medications do not work enough, a consultation with a psychologist or psychotherapist is necessary.
Physiotherapy and vitamins
Vitamins and spa treatment are prescribed as auxiliary therapy during treatment. For hormonal drugs to work, it is important to stabilize the emotional background and avoid increased physical activity. Vitamins are prescribed along with the diet.
Doctors advise using special multivitamin complexes for women, such as Vitrum, Vitrum Beauty and others. In addition to normalizing the hormonal cycle, they help improve the overall tone of the body, the condition of hair, skin, and nails.
Correction of hormonal levels
Is it possible to get pregnant during the luteal phase?
This depends on the previous, follicular phase and the state of hormonal levels in the future.
Insufficiency is a consequence of reduced function of the corpus luteum, in such cases support of the luteal phase is required. It is carried out using progesterone drugs Duphaston and Utrozhestan. Most often they are prescribed from the 14th day of the cycle to the 25th. The use of hormones does not affect fertilization. Correcting hormone levels only allows you to change the condition of the endometrium and ensure implantation of the fertilized egg if conception has occurred.
But there are certain difficulties with prescribing the drug:
- Dose selection. It must be prescribed individually. Each woman's progesterone level is at a certain level, and it is impossible to say for sure that the same dose of the hormone will be required with the same blood test results.
- Withdrawal bleeding. After the end of taking progesterone, bleeding appears, which corresponds in time to menstrual bleeding. But if a woman did not use protection during treatment, then there may be an embryo in the uterine cavity. Bleeding will lead to detachment of the ovum and miscarriage. Pregnancy tests during this period are not yet effective. Therefore, those undergoing treatment need to be protected from pregnancy.
But if corpus luteum deficiency is observed already during a diagnosed pregnancy, with existing signs of a threatened miscarriage, then prescribing Duphaston or Utrozhestan makes sense to preserve it. In this case, hormones are taken until the placenta is formed, and in severe cases even until 21 weeks of gestation.
Insufficiency of the second period of the menstrual cycle can be observed periodically in completely healthy women. Therefore, observation and diagnosis of only one month is not as important as two or three month studies. For example, you need to measure your basal temperature yourself and draw up a chart for it.
In the absence of ovulation, one cannot speak of luteal phase deficiency; in this case, the follicle does not mature, so cyclical changes do not appear. Such forms of hormonal disorders require searching for the cause and eliminating it, rather than blindly prescribing hormones.
A woman is the guardian of the clan, since the main goal of her life is to bear and give life to a child. An egg can only be fertilized during a certain phase of the menstrual cycle - the ovulatory phase, after which the luteal phase begins (progesterone phase, corpus luteum phase).
In this topic, we want to tell you in detail what the luteal phase is in women, what day of the cycle it comes on and how long it lasts. In addition, we will look at luteal phase deficiency, its symptoms and treatment.
Possible complications and consequences
Hormonal drugs that change progesterone levels can only be purchased with a prescription. Self-use is dangerous to health and can lead to bleeding, hormonal imbalances with serious consequences, including death. Therefore, you can independently use only folk remedies, follow a diet and provide rest to the body, if necessary.
Luteal phase deficiency - treatment with Duphaston
Luteal phase deficiency can be caused not only by hormonal imbalance, but also by other reasons, which include genetic or immune abnormalities. If the problem is not detected in a timely manner, it can result in miscarriage and infertility. To eliminate such risks, a woman must undergo comprehensive treatment, the main goal of which will be to eliminate the cause of NLF. Duphaston is used for luteal phase deficiency, and utrogestan, and oil solutions of progesterone.
Treatment of NLF with medications
If, after taking the test, low progesterone is detected in the luteal phase, treatment will be carried out with the help of hormonal drugs. In addition to taking hormones, it is necessary to regulate the follicular phase, which is important for the normal maturation of the egg and the growth of the inner layer of the uterus.
If a woman has luteal phase deficiency, treatment with Duphaston will be effective after consulting a doctor. For hyperprolactinemia or hyperandrogenism, Duphaston alone is not enough for treatment. In such cases, the use of drugs that regulate the concentration of prolactin and androgens is required.
Hormonal deficiency in the first or second phase is often treated with oral contraceptives. If anovulation is observed, then taking medications to stimulate the ovaries is indicated. If NLF is associated with impaired endometrial receptivity, then the doctor prescribes drugs to eliminate inflammatory reactions, as well as antibiotics and immunomodulators.
Progesterone level
In the luteal phase, the level of this hormone is considered normal if it reaches the readings: 6.99-56.64 nmol/liter. An analysis to determine the concentration of this hormone is taken in the laboratory. This happens on days 4-5 of the cycle. According to the rules, it should be done after an 8-hour break between meals. Preferably in the morning. If there is not enough progesterone in the body , then the fetus experiences:
- Addison's disease
- abnormal development of the genital organs in boys
With increased progesterone, it happens:
- menstrual cycle disorders
- excessive hair growth in women
- polycystic disease
- acne
- miscarriage
Laboratory analysis for hormones
Luteal phase support - preventive methods
Luteal phase support is required if irregularities in the menstrual cycle are detected. You can identify the problem as early as possible using the following methods:
- Regular maintenance of the menstruation calendar. A woman can independently determine the presence of a problem if the duration of the cycle has become shorter or longer;
- Visit a gynecologist twice a year.
To prevent the development of NDF, you need to:
- Timely treatment of gynecological and chronic diseases, pathologies of internal organs and organs of the endocrine system;
- Maintain a balanced diet;
- Exercise;
- Eliminate psycho-emotional stress.
LF support is necessary not only when planning a physiological pregnancy, but also the luteal phase and ecology are also carried out with the prescription of a progesterone series of drugs.