Authors | Last updated: 2019
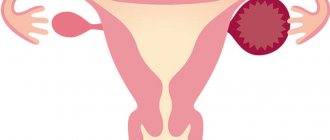
Ovarian cyst is considered one of the most common diseases occurring during reproductive age. Often the operation is prescribed for women who cannot become pregnant for a long time. After removal of the cyst, conceiving a child becomes possible. But does surgery always have a beneficial effect on reproductive health, and will surgical intervention lead to unpleasant consequences?
Is it possible to get pregnant after removing an ovarian cyst? There is no clear answer to this question. It all depends on the effect of the surgery on the woman’s reproductive system. Let's consider what factors determine the prognosis and what should be taken into account when agreeing to surgery.
Why you need to remove an ovarian cyst before planning a pregnancy
In gynecological practice, there are situations when women refuse surgical treatment of ovarian cysts, citing understandable concerns. First of all, patients are concerned about the fact that after the operation pregnancy may not occur or they will have to resort to in vitro fertilization. In some ways, these fears are justified, but you need to understand: without surgical intervention, pregnancy may not occur at all. Women with ovarian cysts are also not always accepted into the IVF program.
5 reasons to remove ovarian masses before pregnancy:
- Infertility. Endometrioid and follicular cysts disrupt the maturation of follicles, inhibit ovulation and prevent the conception of a child;
- Chronic pelvic pain. Large formations lead to constant pain in the lower abdomen, and during pregnancy the symptoms will only intensify;
- Cyst growth. During pregnancy, the formation may begin to grow uncontrollably, interfering with the normal development of the child;
- Development of complications. Pregnancy increases the risk of torsion of the cyst stalk or rupture of its capsule with profuse hemorrhage into the ovary;
Torsion of the pedicle of an ovarian cyst during pregnancy is one of the most serious complications.
- Malignization. If the cyst is a borderline formation and there is a possibility of its malignant degeneration, surgery is inevitable. During pregnancy, under the influence of hormones, it can develop into cancer.
After the operation, the chances of a successful conception, pregnancy and birth of a child increase significantly.
Expected effects after tumor removal
After the operation, the woman’s condition improved:
- Hormonal levels are normalized and ovulation is restored;
- The pressure of the cyst on the pelvic organs is eliminated;
- Unpleasant symptoms go away: bleeding, pain in the lower abdomen, difficulty urinating and defecating;
- Risks to the fetus in the early stages of pregnancy disappear (tumors located near the uterus interfere with its growth and lead to spontaneous miscarriage).
The effect of the operation will be determined by the nature of the ovarian pathology. Restoration of hormonal levels is observed after removal of endometrioma and follicular cyst. These formations affect ovulation and inhibit oocyte maturation. Other cysts (dermoid, serous, paraovarian, luteal) do not interfere with the conception of a child, but can create mechanical obstacles to fetal growth. The greatest danger is caused by formations of large sizes - from 6-8 cm in diameter.
It is important to know
When planning pregnancy, it is recommended to remove an ovarian cyst that has reached a size of 3-4 cm, regardless of its type and the presence of symptoms.
Before planning a pregnancy, it is advisable to get rid of the cyst in order to avoid potential risks to the health of the woman and the unborn child.
Factors influencing the conception of a child, as well as rehabilitation periods
Any operation is stressful for the body, and removal of an ovarian cyst is no exception. Surgical intervention affects the functioning of the reproductive organs, and sometimes it takes a long time to restore their function. The speed of rehabilitation is determined by various factors:
- Surgical access. After laparoscopy, recovery of the body occurs within 3-6 weeks. A woman can conceive a child after 3-6 months. After laparotomy (abdominal surgery), rehabilitation takes longer;
- Presence of complications. If the operation went without significant problems, the recovery time does not differ from the statistical average. As complications develop, the duration of the rehabilitation period increases;
- Character of an ovarian cyst. After removing the non-functional cyst (dermoid, paraovarian), the problem is solved, and nothing else prevents the conception of a child. In the case of endometrioma, hormonal therapy may be required after surgery;
Hormonal medications after removal of an ovarian cyst
The need to take hormonal medications in the postoperative period is due to the risk of adhesions. They may appear if there is a transition from an acute form of the inflammatory process to a chronic one. If hormonal therapy is started on time, the risk of adhesions is minimized.
To prevent the occurrence and development of adhesions, a specialist can prescribe hormonal and antibacterial drugs to the woman. In order to determine the need for hormonal therapy, it is important to consider a number of factors:
- Patient's age;
- Genetic predisposition to certain types of pathologies;
- The presence or absence of contraindications;
- A collection of information about the course of the disease.
However, it is important to remember that exceeding the permissible limit for taking hormonal drugs can lead to the development of serious negative consequences.
Thus, long-term therapy with progestin and estrogen can lead to the development of breast cancer. In order to avoid this, it is recommended to take breaks in the course of treatment and reduce the dosage.
The main goal of therapy is to normalize progesterone levels.
In the absence of appropriate treatment, the danger increases significantly:
- Development of diseases of the cardiovascular system;
- Decreased bone strength;
- Development of Alzheimer's disease.
The most common hormonal drugs prescribed to stabilize progesterone levels are:
- Klimen - is prescribed in case of hormonal imbalances that lead to an excess of male sex hormones. Clymene is used to prevent baldness, excess weight gain and the appearance of excess body hair;
- Klimonorm is available in the form of tablets, twenty-one per package. The course of treatment is three weeks, after this period women begin to resume menstruation, which makes it possible to stop the death of the endometrium;
- Pauzogest - the duration of therapy with this drug is a month, prescribed to women to normalize hormonal levels without accompanying menstrual discharge;
- Femoston is indicated for daily use. Its action is aimed at eliminating the symptoms of menopause, stopping the development of osteoporosis, which can develop as a result of the progression of hormonal imbalance.
Hormonal therapy after surgery to eliminate an ovarian cyst should occur under the strict supervision of doctors. Only a specialist can determine the duration of the course of treatment and medications indicated for use. Self-medication in this case is strictly prohibited, as it can lead to serious consequences.
Possible problems after surgery
The possibility of conceiving a child is greatly influenced by complications that arise after surgery. If the rehabilitation period goes smoothly, problems usually do not arise, and the woman becomes pregnant safely within the next year.
Adhesive process
This term refers to the formation of adhesions between and within the pelvic organs. Possible consequences:
- Connective tissue cords form in the lumen of the fallopian tubes, preventing the advancement of the egg and meeting the sperm. These same adhesions become the cause of ectopic pregnancy, when the fertilized egg attaches to the wall of the fallopian tube;
- Adhesions that appear on the surface of the ovary interfere with the release of the egg and inhibit ovulation;
- The adhesive process in the uterine cavity prevents the attachment of the fertilized egg and contributes to miscarriage in the early stages.
The adhesive process, as a rule, prevents the conception and bearing of a child.
The likelihood of developing adhesions increases after abdominal surgery, and there are explanations for this:
- The surgeon's instruments and hands come into contact with the ovaries and other organs;
- During the operation, the pelvic organs come into contact with air and dry out;
- Significant incisions and tissue stretching are created when creating access to the ovaries;
- There is a high probability of infection of the surgical wound.
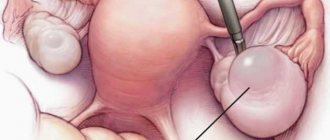
With minimally invasive laparoscopic surgery, the risk of unwanted effects on tissue is minimized. There is no contact with air or the surgeon's hands. The likelihood of developing an adhesive process is reduced. Laparoscopic surgery is recognized as the gold standard for ovarian cyst removal and is practiced in many clinics.
Laparoscopy is a minimally invasive method for treating ovarian cysts. After such an operation, a woman recovers faster.
Infectious complications
Risk factors:
- Failure to comply with the rules of asepsis and antisepsis during surgery;
- The presence of inflammatory processes in the pelvic organs;
- Immunodeficiency states.
Infectious lesions of the ovaries and fallopian tubes lead to the development of salpingoophoritis. The maturation of follicles is disrupted, and conceiving a child becomes impossible. Concomitant infection of the uterus leads to the development of endometritis. The fertilized egg does not find a place to attach, and a miscarriage occurs. But even with successful conception of a child, there remains a risk of infection of the fetus, the formation of severe defects and termination of pregnancy.
Decreased ovarian reserve
When exfoliating an ovarian cyst, the doctor tries not to touch healthy tissue, but this is not always possible. If the stroma of the organ was affected during the operation, the ovarian reserve decreases. The number of follicles decreases and the likelihood of conceiving a child decreases. The risk of infertility increases when surgery is performed on both ovaries.
Repeated operation
Repeated surgery is possible if complications develop:
- Bleeding. Occurs in the early postoperative period and is accompanied by a sharp deterioration in the woman’s condition;
Repeated surgery is performed if bleeding does not stop within several days after the intervention.
- Infection of the postoperative wound and suppuration of the sutures. Observed in the first days after surgery. Accompanied by increased pain and the appearance of purulent discharge from the wound.
After repeated surgery, the duration of the rehabilitation period increases, and the chances of conceiving a child decrease. If severe complications develop, removal of the appendages may be required.
For your information
Following the doctor's recommendations reduces the risk of complications after surgery and improves the prognosis of the disease.
Pregnancy after endometrioid cyst
After surgical removal of the cyst, pregnancy cannot occur immediately. It takes time to restore reproductive function, from 2 to 12 months, depending on the individual characteristics of the body. The patient is prescribed additional treatment with hormonal drugs. After completing the course, the chances of successful conception are high.
Complications
Any surgical intervention can provoke complications.
For example, the formation of adhesions on the fallopian tubes is an additional obstacle to conceiving a child.
Regular ultrasound examinations and being under the supervision of a specialist will help avoid consequences.
Risks
Even laparoscopy does not exclude the appearance of new cysts. Hormonal postoperative therapy will help minimize this risk.
Recommendations
In the postoperative period, it is necessary to strictly follow the recommendations of the attending physician:
- is more in motion, as this helps to avoid adhesions;
- take a course of antibiotics and immunomodulators;
- eat exclusively liquid food to normalize intestinal function;
- maintain personal hygiene and treat the wound properly;
- use hormonal therapy to quickly restore the functions of the genital organs.
Removal of an ovarian cyst during pregnancy and the effect of surgery on fetal development
When an ovarian cyst is detected during pregnancy, the prognosis is determined by the size of the formation and the rate of its growth. Small cysts do not interfere with pregnancy and do not require treatment. Large formations can lead to the development of complications:
- Spontaneous miscarriage. Termination of pregnancy most often occurs before 10-12 weeks;
- Premature birth. If the cyst begins to grow rapidly in the second half of gestation, it can cause the baby to be born prematurely;
- Torsion of the pedicle of the formation. During pregnancy, the uterus displaces the ovaries, the cyst becomes twisted, and severe pain occurs;
- Cyst rupture. It is observed more often in the second half of gestation. Accompanied by heavy bleeding.
The large size of the ovarian cyst threatens to rupture. Blood enters the abdominal cavity, which can lead to serious consequences.
Elective surgery is prescribed for large lesions and/or rapid growth of the lesion. Such a cyst should be disposed of to prevent complications from developing. The optimal time for surgery is 16-20 weeks. In an emergency, a woman can be operated on at any time.
Removal of the cyst in the first half of pregnancy is carried out laparoscopically. In the later stages, the issue of performing a cesarean section is decided. In this case, cystectomy is performed after the fetus is removed.
An operation undergone during pregnancy can negatively affect the condition of the child and lead to undesirable consequences. Placental insufficiency is observed, fetal hypoxia (lack of oxygen) occurs, and its development is delayed. The likelihood of having a baby with low body weight and neurological disorders increases.
The development of severe complications can be avoided with timely treatment of ovarian cysts. If there are indications for surgery, you should not refuse surgery. It is necessary to remove the formation before the child is conceived. The risk of undesirable consequences after excision of an ovarian cyst is significantly lower than during pregnancy against the background of this pathology.
Useful video about the types of ovarian cysts and their effect on conception and pregnancy
Endometrioid ovarian cyst - what is it?
Cysts are a common condition that occurs in women between the ages of twenty and fifty. It depends on the level and concentration of hormones in the body, and begins to actively manifest itself during menstruation or pregnancy.
The appearance of this neoplasm is characterized by severe pain, heavy periods, infertility and a number of other symptoms. Treatment is carried out only through surgery, followed by drug therapy.
The cyst does not always begin to grow; in some cases it can remain unchanged throughout life. Often the disease passes without obvious signs and is detected only when planning a pregnancy.
Possible causes of the formation and development of an endometrioid cyst are:
- Frequent abortions;
- Rapid weight gain;
- Long-term use of intrauterine contraceptives;
- Long-term effects of stress;
- Artificial birth;
- Heredity;
- Formation and spread of inflammatory processes in the abdominal cavity;
- Surgeries on the organs of the reproductive system, which resulted in a violation of the integrity of the uterus;
- Pathologies in the menstrual cycle;
- Increased estrogen levels;
- Decreased immune defense;
- Malfunction of the thyroid gland or its removal.
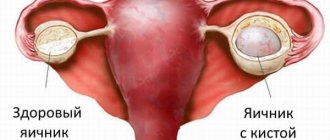
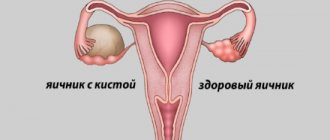
Modern medicine identifies several main types of cysts, according to their location:
- Endometrioid cyst of the right ovary - manifests itself in disruptions of the menstrual cycle, which may be accompanied by malfunctions or the development of inflammatory processes in the intestines and bladder;
- Endometrioid cyst of the left ovary - symptoms correspond to the previous type. Dimensions can range from a couple of millimeters to several tens of centimeters. In appearance it looks like a bubble filled with blood. Determined using ultrasound diagnostics;
- Endometrioid cyst of two ovaries is the most common form of the disease. Most often it is a consequence of hormonal imbalance in the body.
- To determine each type of cyst, a thorough examination is necessary.
One of the main symptoms of a neoplasm is partial or absolute infertility. Often this symptom is not only the main one, but also the only one.
Other signs of an endometrioid ovarian cyst are:
- Pain in the lower abdomen of varying strength, which manifests itself during intimacy;
- Slight increase in body temperature;
- Attacks of dizziness, nausea and vomiting;
- Disorders of the gastrointestinal tract and bladder, which is caused by an increase in the amount of acid produced;
- Disruptions to the normal course of the menstrual cycle. Too much discharge, which is accompanied by severe pain and lasts for more than a week.
The severity of symptoms directly depends on the size of the cyst. Self-medication can reduce the intensity of symptoms, but it cannot be completely cured. It is important to understand that only a specialist can draw up a treatment plan.
In addition, the disease is divided into stages:
- Initial - the size of the cyst is less than one centimeter. The lesion extends to only one ovary;
- Moderate level of severity - cyst size up to six centimeters. The lesion also extends to only one ovary;
- Heavy - size exceeds six centimeters. Both ovaries are already affected, the disease begins to spread to adjacent organs;
- Heavy - the size of the neoplasm is more than ten centimeters. The lesion covers not only the ovaries, but also nearby organs.
An ovarian cyst is a serious disease of the female reproductive system that requires close attention. One of the main problems that accompany cysts is infertility. It is not recommended to delay treatment and abuse self-medication.