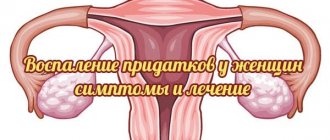
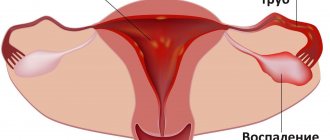
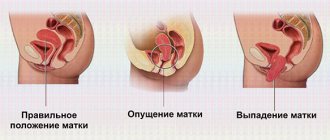
What is uterine inflammation
Inflammation of the uterus is a disease that is characterized by damage to one or more layers of the uterine cavity. There are three types of disease, depending on the depth of organ damage:
- Endometritis is a lesion of the upper mucous layer of the organ.
- Metroendometritis is an inflammation of two layers - the upper (endometrium) and middle muscular (myometrium).
- Perimetritis is an inflammation of the perimeter - the serous, outer layer of the uterus, which passes into the peritoneum and the wall of the bladder.
Most often, the disease begins with an acute form. Over time, after 5-10 days, even without treatment, the symptoms subside and it seems that the problem is solved. However, it is precisely this lull of the disease that is very dangerous - the disease transitions to a chronic, sluggish, but very dangerous stage, during which irreparable disturbances begin in the structure of the uterine tissue, changes in the structure of cells (the appearance of atypia), the formation of adhesions, cysts, and the spread of infection to each other organs and systems.
Chronic inflammation can spread not only to all tissues of the uterus, but also to nearby organs. Salpingitis (inflammation of the fallopian tubes), cervicitis (disease of the cervical canal) are some of the most common and intractable complications of the disease, leading to infertility.
Sepsis is the most terrible and life-threatening complication of chronic inflammation of the uterus.
Definition
What does the uterus look like in its normal state? During most of the menstrual cycle it is quite hard and dense. Has a light pink tint. Its surface is smooth on the outside. However, normally this condition may change in the third stage of the menstrual cycle. After ovulation, the organ becomes more loose, its throat opens slightly - this happens in order to create optimal conditions for conception and attachment of the embryo. If conception does not occur, then menstruation begins and the organ gradually returns to its normal state.
What does a loose cervix mean? This is a condition in which the density and elasticity of the tissues of this organ is slightly (or significantly) reduced. The tone of the cervix decreases, the pharynx may even open slightly. This is normal in early pregnancy and also just before giving birth. However, if this condition occurs during mid-gestation, it can lead to premature birth and miscarriage. Therefore, upon hearing such a diagnosis, many expectant mothers begin to worry. But is this justified, are such changes always associated with pathology?
Symptoms of the disease
Typically, chronic inflammation begins with the acute period of the disease. It is characterized by a period of intoxication (body temperature 38-40 degrees, weakness, chills, pain) and severe pain in the lower abdomen and back. If treatment was not carried out correctly, a chronic course of the disease begins, which is characterized by long periods of well-being and infrequent exacerbations.
Chronic inflammation in the uterus is most often asymptomatic. A woman should be wary of:
- painful critical days;
- pain during sexual intercourse;
- nagging pain in the back and in the sacral area;
- elevated temperature (around 37-37.5 degrees), rapid heartbeat and weakness;
- any changes in vaginal discharge (increased discharge, color changes, pus, blood);
- pain when urinating.
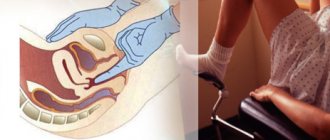
Every woman should be examined by a gynecologist at least once a year. During a simple examination, the doctor will be able to predict the presence of the disease at a very early stage and begin therapy on time.
Preventive actions
Prevention of atony consists of several points:
- A qualified doctor who will conduct the birth. Since during delivery you cannot press hard on the tummy when palpating. Also, no matter what provokes uterine atony, you should not pull the umbilical cord during labor.
- If a woman in labor is at risk for atony, then at a certain point in the labor process she is given oxytocin in order to more actively contract the uterus.
- For such a pregnant woman, even before the start of labor, the hematologist writes on a special sheet what medications to administer, as well as donor plasma if the woman experiences massive bleeding.
To avoid the development of this pathology, the woman’s body should be prepared before childbirth and timely prevention should be carried out.
Causes
The disease develops as a result of an infection that has entered the uterus. This can happen for several reasons:
- weakening of local immunity;
- surgical intervention (abortion, therapeutic or diagnostic curettage, internal examination of the uterus);
- installation of a contraceptive intrauterine device;
- frequent change of sexual partners;
- the presence of infectious diseases (streptococci, gardnerella, peptococci, gonococci, chlamydia and others);
- childbirth with complications (weak labor, large blood loss, placental remains), cesarean section;
- unprotected sex life during menstrual periods.
Chronic inflammation always develops as a result of incorrect treatment or late diagnosis of the acute period of the disease. The exception is the latent acute period of the disease while taking antimicrobial drugs. In this case, the disease almost immediately passes into the chronic stage and it is simply impossible to begin proper treatment on time.
Physiology
During pregnancy, the uterus undergoes a number of changes - its weight increases from seventy grams to a kilogram, and its capacity increases a thousand times. These processes occur due to the stretching and growth of the mesh framework - muscle fibers, connective tissue. The organ acquires the necessary excitability and contractility. The ability to contract is transferred from muscle cells to connective tissue. The uterine wall becomes thicker and stronger.
As pregnancy progresses, the number of blood vessels and nerve receptors increases, and the muscle wall becomes thinner and softer. The growth rate of individual parts of the uterus is different; asymmetry can be traced at the placenta attachment site, in the fundus area. During pregnancy, periodic spontaneous contractions of the myometrium occur, preparing for regular labor in advance.
Despite the achievements of modern medicine, the reasons for the onset of labor are still hidden from humans by nature. The mechanism of the development of contractions has been studied quite well; it is generally accepted that the neurohumoral system takes part in it. In late pregnancy, connections are formed that enhance nerve stimuli in the ganglia of the peripheral nervous system, activating myometrial contractions.
The humoral factor is associated with the production of substances that increase the activity of muscle cells. These include serotonin, norepinephrine, oxytocin, estriol, prostaglandins, melatonin. Fetal cortisol and melatonin stimulate an increase in the hormone estriol, which is considered responsible for preparing the uterus for the process of birth of the fetus.
According to normal physiology, at this time uterine blood flow, protein synthesis, ATP increase, and all biochemical processes occur more intensely. Cell permeability to potassium, calcium, and sodium increases. The uterus is preparing for prolonged contractile stress. Alpha adrenergic receptors predominate in it, the synthesis of prostaglandins and sensitivity to oxytocin increases.
Consequences and prevention
The consequences of the disease can be very serious.
- Spread of infection to other organs – pyometra, salpingitis, oophoritis and the most dangerous – sepsis.
- Infertility is the result of irreversible changes in uterine tissue and the formation of adhesions.
- Blood poisoning is the spread of disease through the bloodstream.
- Deterioration in the quality of life - disruption of the menstrual cycle, pain during sexual intercourse, chronic pain in the lower abdomen, excessive discharge.
In order to avoid the severe and incurable consequences of chronic inflammation, you must adhere to certain rules:
- carefully observe personal hygiene;
- use barrier methods of contraception;
- refuse abortion;
- regularly undergo scheduled examinations with a gynecologist;
- have sex only with a regular partner, avoid casual relationships;
- After giving birth, visit a gynecologist as planned and have an ultrasound done.
Treatment
Before starting treatment, it is necessary to find out the cause of the disease. As part of the diagnosis, the patient is examined, an ultrasound examination of the pelvic organs is performed, an anamnesis is collected, and tests are prescribed (smears for vaginal microflora, infectious diseases, clinical blood tests). If necessary, additional diagnostic methods are used: hysteroscopy (examination of the uterine cavity), sampling of material for histological examination (biopsy), complete curettage.
Treatment of the disease always begins with the prescription of antibiotics and sulfonamides. Additionally, it is necessary to take chemicals that prevent further spread of infection (Metronidazole, Metrogyl). A complex of vitamins, immunomodulators, painkillers, homostatics to stop bleeding, probiotics, and physiotherapy (UHF, laser treatment, gynecological massage, etc.) are prescribed as necessary.
It is good if it is possible to carry out bacterial culture to determine the sensitivity of pathogenic microorganisms to a specific type of antibiotic. This will significantly save time and protect your health from useless medications.
Surgical treatment of inflammation (curettage) is carried out according to indications:
- remnants of the fertilized egg or placenta in the uterus;
- suture material;
- ingrown or incorrectly installed intrauterine device;
- the need to clean the damaged mucous layer.
An effective method of treating chronic inflammation of the uterus is the injection of drugs directly into the uterine mucosa. This approach allows you to quickly and effectively eliminate the cause of the disease.
Diagnostics
To determine the cause of inflammation, the gynecologist must conduct a thorough examination. It will allow him to understand the extent of the damage and what pathological effect it had on the organ. A cervical smear test will identify pathogens. If a more detailed examination is necessary, the woman will be recommended to use other examination methods, such as a pelvic ultrasound, biopsy, or colposcopy. Treatment of the inflammatory process in the uterus should begin immediately.
- Recipes for green tomato salads for the winter: delicious preparations
- Laser removal of papillomas
- Symptoms and treatment of intestinal colitis
Traditional methods of treatment
The use of alternative methods of treatment without consulting a physician is strictly prohibited. Only an experienced doctor can know how decoctions of medicinal herbs and serious drugs for treating infections interact with each other.
As a restorative therapy, after completion of therapy, traditional healers recommend:
- decoctions, infusions and baths with marshmallow root;
- douching and decoctions of St. John's wort;
- drink made from berries and strawberry leaves;
- compresses and douching from oak leaves.
Restoring damaged uterine tissue is a long process that requires taking hormonal medications, vitamins and immune boosters. During the entire treatment process, until complete recovery, it is necessary to exclude the development of pregnancy and re-infection. Be attentive to your health and the disease will certainly recede.