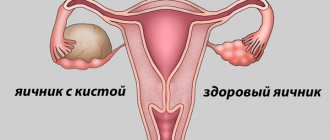
Women of any age are susceptible to gynecological diseases; for example, an ovarian cyst in a teenage girl raises a lot of questions and concerns. A benign formation is a cavity filled with fluid that appears during the reproductive period of life.
Girls whose menstrual cycle is irregular are especially susceptible to the occurrence of ovarian cysts, but the presence or absence of sexual activity does not play a significant role in the appearance of the formation.
Causes and symptoms of cysts
The body of a teenage girl has distinctive features from the physiology and body structure of an adult woman; at a young age, the uterus is small in size, and the ovaries are in a high position. Despite the fact that the causes of formations in young girls have not been thoroughly studied, doctors identify factors that contribute to the development of ovarian formation:
- increased body weight;
- hormonal disbalance;
- unreasonable use of hormonal drugs;
- stress.
Additionally, such phenomena as infectious processes in the genital area and earlier onset of menstruation increase the risk of a benign formation.
Every year, doctors register cases where ovarian cysts are detected in newborn girls. Doctors suggest that an unfavorable environmental situation and viral and bacterial diseases suffered by a woman affect the health of the developing fetus. So, it is possible that a child may have an ovarian cyst in the womb.
The likelihood of giving birth to a girl with a pathology of the reproductive system is high in pregnant patients who have bad habits and take hormonal medications during this period.
As a rule, cystic formation in a teenage girl goes unnoticed and there are no pronounced symptoms. Thus, the body temperature remains at the normal level, the tests do not raise the doctor’s suspicions, so the formation is noticed only during a comprehensive examination.
Prevention
Unfortunately, there are no preventive measures to prevent the appearance of ovarian cysts in girls. Parents should carefully monitor the regularity of the menstrual cycle, ensure the child has a calm psycho-emotional state, reduce physical activity and visit a gynecologist every six months. Mom needs to talk to her daughter about sex life, tell her that pain during sex is an alarming symptom. It is also necessary to try to limit the child from bad habits and trips to the solarium. Following these precautions will reduce the risk of ovarian cysts in children.
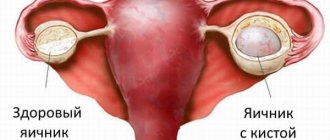
Types of ovarian cysts
The right ovary is most often affected, but ovarian cysts differ in etiology and symptoms. Gynecologists identify the following types of formations in the body of teenage girls:
- follicular;
- corpus luteum cyst;
- mucinous.
The cause of a follicular cyst is the concentration of fluid in unruptured follicles, while the egg dies, and the duration of menstruation increases, making them painful. This type can reach impressive sizes - up to 10 cm.
A corpus luteum cyst is characterized by the appearance of fluid mixed with blood in the so-called corpus luteum; most often this formation is a consequence of hypothermia and excessive physical activity. Less commonly, doctors identify a mucinous cyst, characterized by abundant mucus secretion, as well as polycystic ovaries.
Possible complications during the development of cysts
A cyst on an ovary in a teenage girl can lead to possible complications, including torsion and rupture of the formation. In the case of the latter damage, pain occurs in the lower abdomen, radiating to the perineum, and the functioning of the urinary system is disrupted and an increase in body temperature, dizziness and vomiting are observed.
Often the asymptomatic course of the disease ends after injury, strenuous exercise, and sexual intercourse can also cause complications.
Diagnostic measures
For timely detection of formation and confirmation of diagnosis, a gynecological examination is necessary.
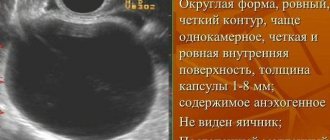
Palpation of the pelvic organs can detect compactions, and the pain of the neoplasm indicates its large size, but in any case it is important to undergo an ultrasound examination. It will show not only the shape of the cyst, but also its exact size and characteristics. If malignancy is suspected, the doctor will prescribe additional tests for the patient. During an examination of infants, the size of the formation is determined in a newborn child with a detected cyst.
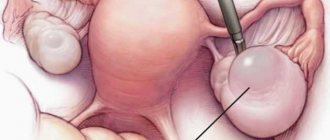
Cyst surgery
Surgery to remove the cyst should be performed using laparoscopy and laparotomy. If the disease has complications, then the following may be prescribed:
- cystectomy (a tumor near the ovary is removed to preserve healthy tissue);
- oophorectomy (the cyst is removed together with the ovary);
- adnexectomy (appendages are completely removed; such removal is prescribed only in exceptional situations).
Surgical removal is not so common, but laparoscopy is often used, and it allows you to preserve reproductive function.
Treatment methods for ovarian cysts in teenage girls
In some cases, an ovarian cyst in a child goes away independently, and the gynecologist also recommends observing asymptomatic and small formations for at least 3 months. Nevertheless, many patients require medical care and the prescription of hormonal drugs and surgical intervention.
Drug therapy
If the cyst is actively growing, doctors prescribe therapy to get rid of the formation. The treatment regimen is carefully selected based on the age, personal characteristics of the girl’s body and chronic diseases, thanks to this it is possible to preserve the full reproductive function of the ovaries.
Specialists select a suitable hormonal agent; during therapy, young girls undergo complex treatment for ovarian cysts, remain in bed or refuse physical activity.
Surgery
If a teenage girl has a torsion of the pedicle of the cyst, then doctors resort to surgical treatment - laparoscopy, this method allows preserving reproductive function. Most often, the formation is removed, while healthy tissue and the ovary itself remain undamaged; less often, oophorectomy is performed, which involves removing the cystic formation along with the ovary.
If you consult a doctor in a timely manner, even in emergency situations, it is possible to avoid unpleasant consequences and completely restore the health of patients.
Non-traditional methods as auxiliary treatment
The use of folk remedies must be agreed with a doctor. The body of a teenage girl is highly sensitive to drugs, so treatment methods must be safe and effective. Thus, a pharmaceutical tincture of peony helps to stop the growth of formation, which should be taken for 10 days, 1 teaspoon with the addition of water, 2 times a day.
Follicular cysts can be treated at home with viburnum juice and honey; a healthy mixture of these products strengthens the immune system and promotes the resorption of ovarian formation. To obtain a therapeutic effect, mix 1 tablespoon of berry juice with the same amount of honey and take for 30 days.
Causes of occurrence in adolescence
The risk group for developing ovarian cysts includes girls with the following conditions:
- premature puberty;
- hormonal disorders;
- inflammatory diseases of the vulva and vagina with a recurrent course.
The incidence of neoplasm increases as puberty approaches. In girls aged 9-12 years, it is observed in 16.9% of cases, and up to 55% of the pathology occurs in girls aged 13-15 years. This indicates the stimulating role of the pituitary gland and sex hormones in the development of the cyst.
Malignant tumors in the pelvis are rare in adolescents. Ovarian cysts are often benign in origin, associated with follicular growth or the formation of the corpus luteum. After menarche, 1-2 years pass until a regular menstrual cycle is established. For some girls, this process ends after 17 years. Delays in menstruation may be periodically observed, and there is no ovulation. At the same time, the follicle continues to grow and a cyst forms.
If the egg is mature, a temporary endocrine gland is formed in the ovary - the corpus luteum. Her condition is negatively affected by:
- malnutrition;
- physical exercise;
- inflammatory diseases;
- stress;
- abortion.
Under their influence, a cyst is formed, which can resolve on its own.
At the age of 13, it is already possible to develop endometriosis. Its origin has not been precisely established, but it is noted that endometrial foci in atypical places may be a consequence of a violation of embryogenesis, the result of the introduction of menstrual blood. A tumor gradually forms on the surface of the ovary, which has hormonal activity and itself responds to cyclic changes. The rejected endometrium does not come out, but accumulates under the capsule, forming a “chocolate cyst”.
A large group of benign ovarian tumors consists of cystadenomas. They develop from the germinal epithelium lining the surface of the organ. Histologically, it is serous and mucinous. It is impossible to differentiate a cyst from a functional formation before surgery.
Germ cell tumors account for half of all benign ovarian tumors. They consist of germinal tissues and are a consequence of improper embryogenesis. But in little girls they are rare, the frequency increases at 10 years. The process always occurs on both sides. Therefore, after removal of a dermoid cyst on the right, it is necessary to be observed by a gynecologist in order to identify it on the left in time.
Malignant tumors may have a cystic structure. They can be primary or metastatic and require careful diagnosis.
Risk to reproductive health if left untreated
Some girls try to get rid of severe symptoms by taking painkillers, which can lead to a number of pathologies. Thus, the tumor suppurates - its structure changes, the volume of accumulated fluid increases, and pressure is also noted on nearby pelvic organs.
The appearance of adhesions threatens the development of infertility in the future, but the most serious thing is the rupture of an ovarian cyst. The release of contents is fraught with peritonitis and death.
Memo for parents
Parents should supervise their child's timely and regular visits to the doctor.
- It is necessary to provide the teenager with a positive psycho-emotional atmosphere and eliminate situations that provoke stress.
- If you have any infectious diseases, treat them.
- If a girl smokes, she should be persuaded to give up this habit.
To prevent the recurrence of a cyst or its growth during the treatment period, the child must adhere to certain rules:
- do not lift heavy objects;
- avoid prolonged exposure to the sun or solarium;
- avoid sudden movements;
- reduce the intensity of physical activity.
Compliance with preventive measures and careful attitude towards your health will ensure successful conception and happy motherhood in the future. Be healthy!
Experience in treating ovarian cysts – a patient’s story
Preventive measures
Parents should pay attention to the health status of the teenage girl, monitor her daily routine and psycho-emotional mood. Gynecologists warn that bad habits, passion for solariums and uncontrolled use of hormonal drugs negatively affect women's health and increase the risk of diseases.
The parent’s task is also educational work, since after the appearance of a cyst, its development is facilitated by the causes of formation. They need to be eliminated and the girl’s treatment must be taken responsibly.
Pain at the end of the menstrual cycle often indicates the approach of menstruation, but if suspicious symptoms appear, it is necessary to undergo an ultrasound examination. It is much more correct to detect the formation in time, get tested and determine the nature of the tumor, since complications can appear unexpectedly. Girls should visit a gynecologist at least once a year in order to protect themselves from failure of the reproductive system.
Symptoms
Cysts can be complicated or uncomplicated.
In the latter case, the disease is most often asymptomatic and is therefore detected by chance.
For example, a follicular cyst, even with a large volume, may not manifest itself clinically.
In this case, the child’s condition is stable, the blood test is normal, and there is no increase in temperature.
Very rarely, a cyst can provoke slight delays in the cycle; also, between menstruation, there may be spotting, an increase in body temperature, pain that radiates from the lower part of the peritoneum to the leg or lower back, and impaired bowel movements.
Signs of a complicated course of the disease
But a complicated cyst can lead to the following:
- Torsion of the legs. Occurs when lifting heavy objects, sudden body movements, and frequent constipation. The clinical picture resembles signs of acute appendicitis, so careful diagnosis is needed.
- Bleeding into the ovary , corpus luteum, or abdominal cavity. Occurs with significant physical exertion, inflammation, and also with strong pressure from neighboring organs.
- Rupture of the cyst wall. This is the most dangerous complication, which can also occur during severe physical exertion. In this case, the organ becomes infected, which can lead to infertility.
With polycystic ovary syndrome, severe abdominal pain, vomiting, and hemorrhagic shock are observed. There may also be a fever and extreme fatigue.
Important! Any type of pathology causes disruptions in the menstrual cycle and intermenstrual spotting.