The relationship between the reason for the operation and the failure of menstruation after it
Laparoscopy is performed when it is impossible to eliminate the pathology with medication. Indications for intervention:
- large size of education;
- severe symptoms;
- rupture of a cyst or ovary;
- risk of developing a malignant process;
- the likelihood of rupture of the formation or torsion of its legs.
In some cases, patients are prescribed a course of medication before surgery. If there are clear indications for laparoscopy, the intervention is performed immediately.
Most often, surgery is necessary in the presence of epithelial ovarian cysts. These types of formations have the ability to degenerate into cancerous tumors and are not eliminated by medications. Functional cysts that occur as a result of menstrual irregularities are rarely removed surgically. They usually go away on their own or under the influence of hormonal and other drugs.
In addition to general and individual factors, how long there is no period after laparoscopy and at what time the first menstruation should begin after the procedure is largely influenced by the reason for which this manipulation was performed.
Polycystic ovary syndrome
This is one of the most common diagnoses for which laparoscopic intervention is indicated. This operation is carried out as planned - on the 7th or 8th day of the menstrual cycle. During it, the membrane is removed, which interferes with the normal maturation of the follicle with the egg.
Even if such a cleansing procedure is carried out by an experienced gynecologist with “golden hands,” injury to the ovarian tissue (truncation of a small part of it) is inevitable. In turn, this causes hormonal imbalance. The magnitude of such changes is individual, and menstruation will begin when the hormonal levels are restored in the woman’s body.
In the vast majority of cases, endoscopic manipulation for polycystic disease is performed so that the woman can become pregnant. Therefore, hormonal drugs are not prescribed, and the body is forced to recover on its own. True, there are exceptions when, after laparoscopy of polycystic disease, menstruation begins on time or even earlier.
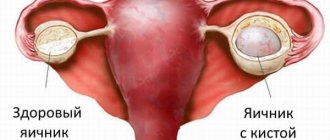
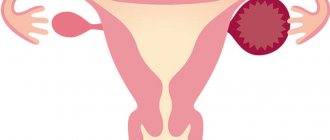
Ovarian cyst
Laparoscopic removal of an ovarian cyst is performed at the end of the menstrual cycle. Therefore, unlike endoscopic treatment of polycystic disease, the woman’s body has time to restore the imbalance of hormones, which is caused by the removal of ovarian tissue in contact with the cyst shell. This is why menstruation after laparoscopy of cysts begins according to the usual schedule or there is a slight delay of 2-4 days.
Ovarian cysts are benign formations.
After laparoscopic removal of a cyst, there may be quite heavy bleeding. If they last the same amount of time as regular critical days, then young women often mistake them for menstruation after laparoscopy.
Endometriosis
This is another pathology for which laparoscopic surgery is the “gold standard” of treatment. If endometriosis was removed from the walls of the uterus, then there will be no disruption of the cycle. If the ovarian tissue was “smoothed,” then the onset of menstruation will depend on the area of the treated surface and the day of the menstrual phase on which the operation was performed.
After laparoscopic removal of endometriosis, medications may be prescribed that can cause absence of menstruation for several months, and in some women it will look like spotting.
Sexual activity is allowed 3-4 weeks after surgery
The doctor is obliged to warn the patient about all the peculiarities that may occur in her body after laparoscopy. If discomfort, pain or unusual discharge occurs that the specialist did not talk about, then, in order to avoid complications, you should immediately seek medical help.
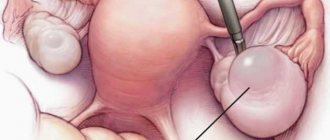
Laparoscopy as a surgical and diagnostic method
The principle of laparoscopy is the ability to conduct research or surgery without resorting to a complete opening of the abdominal cavity. This method allows for a diagnostic analysis of the presence of diseases, and, if necessary, immediate surgical treatment.
With success, this technique allows us to identify and relieve patients:
- tubal obstruction;
- uterine fibroids;
- endometriosis;
- ovarian cysts;
- adhesive process;
- ectopic pregnancy.
Thanks to the cure for such diseases, a woman’s chances of getting pregnant and becoming a happy mother increase significantly. And one of the components of complete success after using the laparoscopic method is the attentive attitude of doctors and patients themselves to the recovery process. To do this, it is recommended to scrupulously monitor all manifestations after surgery and carefully monitor the menstrual cycle.
Rehabilitation after discharge from hospital
In the process of recovery after laparoscopy of an ovarian cyst, a woman goes through several periods. Early rehabilitation is considered the shortest, lasting no more than 7 days. Subsequent recovery takes place at home.
On the first day after ovarian laparoscopy, the patient must be in a hospital setting. At this time she is recovering from anesthesia. The doctor monitors her condition and, if necessary, changes the treatment regimen or performs additional manipulations. This prevents many complications - uterine bleeding, suppuration of sutures, deterioration of health.
You need to get out of bed 3-5 hours after waking up. This is often problematic due to severe pain. These symptoms are normal and result from tissue damage during surgery. Rapid restoration of motor activity will improve the patient’s physical and emotional condition.
Diet
After surgery, a woman’s usual diet changes. On the first day, you are allowed to drink only mineral water, sometimes light broths. The next day you can eat slimy soups, boiled vegetables, steamed cutlets, jelly and fruit drinks. Such a diet after laparoscopy of an ovarian cyst ensures the normal functioning of the intestines and stomach, weakened after the intervention and medications taken.
Subsequently, the diet becomes more varied. In the first few weeks after surgery, the basis of the diet consists of the following dishes and products:
- baked apples;
- flax seeds;
- cereals – rice, buckwheat, oatmeal, pearl barley;
- sauerkraut;
- soups made from vegetables or with the addition of lean meat;
- hard cheese;
- steamed omelettes;
- boiled lean meat and fish;
- black bread;
- fruit juices and fruit drinks;
- herbal infusions;
- green tea;
- tomatoes;
- dry biscuits, crackers;
- vegetable salads with vegetable oil;
- low-fat kefir.
Prohibited products:
- Black tea;
- coffee;
- alcohol;
- sugar;
- mayonnaise;
- fresh wheat bread;
- spicy, fried, smoked, salted;
- spices;
- fresh cabbage, onions, radishes;
- pasta;
- grapes, pears;
- beans and peas;
- milk, cream;
- bakery;
- sweets – candies, chocolate;
- nuts.
General rules of nutrition after laparoscopy of an ovarian cyst:
- eating 5-6 times a day in small portions;
- drinking water at least one and a half liters per day;
- drinking any liquids before or an hour after meals;
- dinner - no later than 2-3 hours before bedtime;
- refusal to consume permitted foods that cause unpleasant symptoms.
With normal functioning of the digestive organs, dietary restrictions are lifted faster. What a patient with no gastrointestinal disturbances can eat after ovarian laparoscopy is decided by the doctor. The presence of problems extends the period of adherence to the diet to 2-3 months. As a preventive measure or to relieve symptoms, the doctor prescribes medications that improve the functioning of the digestive tract, eliminating heartburn, bloating, and nausea. With strict adherence to nutritional rules, such symptoms rarely occur and do not require medication.
Discharge
Immediately after surgery to remove an ovarian cyst, the patient is bothered by vaginal discharge. They consist of impurities of blood, clots, and mucus. The total duration of their presence is no more than two weeks. In this case, the largest amount of blood is observed in the first week, then its concentration decreases.
Pathological discharge has an unpleasant odor, acquires a yellowish, brownish or greenish tint, and may contain impurities of a white curd substance. This indicates the course of a genital tract infection or an inflammatory process. If they appear, you should immediately visit a doctor.
Compliance with nutritional rules is necessary to prevent failure of the digestive process. Symptoms requiring medical attention:
- constipation;
- diarrhea;
- nausea;
- bloating;
- heartburn.
To eliminate these signs, it is necessary to normalize nutrition. If discomfort occurs despite strict adherence to the doctor’s recommendations, you need to increase the amount of the following drinks in your diet:
- herbal tea – chamomile is best;
- still mineral water;
- dill decoction;
- drinks with added cinnamon, cardamom, ginger;
- kefir.
These products will speed up the digestion process and normalize the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract. To achieve the best effect, kefir for constipation should be consumed at night, 2 hours before bedtime. Herbal teas and other similar drinks are taken before meals or directly during tea drinking.
During the first 5-7 days after laparoscopy of an ovarian cyst, patients experience pain in the lower abdomen. This condition is considered natural and goes away on its own after the sutures heal. To relieve the symptoms, it is allowed to take painkillers.
If there is severe pain after laparoscopy of an ovarian cyst, the patient is advised to remain in bed, rest more, and not make sudden movements. If you have aching muscles in your body and back, you need to walk in the fresh air. If pain worsens, activity should be stopped.
When are the stitches removed?
Sutures are removed one and a half weeks after ovarian laparoscopy. During this period, the tissues are almost completely restored and do not require additional support. Before removing the sutures, it is necessary to carry out daily procedures for their treatment. The patient herself or with the help of medical staff must replace sterile dressings and clean wounds with antiseptic solutions.
After the stitches are removed, the scars heal very quickly. The laparoscopy method involves the use of only small tissue punctures during the intervention. Therefore, traces of the surgery are practically invisible, and sometimes they heal without a trace.
After laparoscopy of an ovarian cyst, there is no need to stay in the hospital for a long time. The patient is usually discharged on days 3-5 depending on her well-being. A longer hospital stay is recommended if there are postoperative complications.
Sick leave
A certificate of incapacity for work is issued for the operation and the initial rehabilitation period. Sick leave after laparoscopy of an ovarian cyst lasts 1.5-3 weeks. If you feel unwell, have severe weakness and there are complications, it can be extended.
To quickly undergo rehabilitation after laparoscopy of an ovarian cyst, the patient must follow all recommendations of the postoperative period and at home. Her well-being depends on her lifestyle and the accuracy of following the rules specified by the doctor.
Home restoration
During the entire period of being on sick leave, the woman does not visit the attending physician. His consultation is necessary only if there are any questions about the current treatment or if the condition worsens. Therefore, she must follow the previously prescribed rules:
- daily treatment of seams;
- avoidance of active physical activity;
- refusal of sex life and sports for 1-1.5 months;
- regular ultrasound examination to obtain results on the condition of the ovary on which the cyst was removed;
- cessation of activity when pain intensifies;
- prohibition on lifting heavy objects;
- refusal to treat scars after laparoscopy of ovarian cysts using folk and other means;
- washing the body only in the shower;
- wearing a bandage immediately after ovarian laparoscopy for 1 month;
- avoiding visiting baths, saunas, swimming pools;
- prohibition on scratching an itchy seam;
- refusal of clothes that compress the lower abdomen;
- compliance with the diet established after removal of the ovarian cyst.
Removal of prohibitions is possible only after the permission of the attending physician. Neglecting the rules of the rehabilitation period after laparoscopy of an ovarian cyst is fraught with the development of complications that negatively affect the health of a woman’s reproductive system.
The total duration of the recovery period is individual for each woman. On average, full functionality of the ovaries returns after 3 months. The sutures heal in 1-1.5 months. All rehabilitation rules should be followed for 1-2 months or until they are changed by a doctor.
The patient's health returns to normal a few weeks after the operation. At this time, she may feel completely healthy and only occasionally feel pain in the lower abdomen that accompanies the healing of appendage tissue. Weakness after surgery goes away quite quickly.
Menstruation after laparoscopy usually continues as before. The first menstruation occurs according to a set schedule, individual for each woman. Bleeding may be slightly more or less profuse, long or short. This is considered normal and does not require a visit to the doctor.
Menstruation may be delayed after surgery. This is also considered normal. During surgery, the tissue of the appendage is damaged, which can lead to a temporary disruption of its functionality and, as a result, to hormonal imbalance. Menstruation comes after their work is restored. If they are absent for more than a month and a half, you should undergo diagnostics of the genital organs.
Preparing for surgery
24 hours before surgery, the patient should refrain from eating heavy foods, it is better to eat light soups. 9 hours before surgery you are allowed to drink only water. Immediately before the intervention, the woman’s intestines must be cleansed with an enema. These recommendations must be followed in order for the operation to be faster, better and without complications.
Laparotomy for ovarian cysts is carried out in the middle of a woman’s menstrual cycle; during this period it is visually possible to detect the reason that provokes the lack of ovulation, assess the functionality of the ovary, and check the condition of the endometrium.
Important! Three days before the start of menstruation, as well as during it, any surgical manipulations are prohibited, since there may be large blood loss and the risk of tissue infection.
What tests need to be taken?
At least 2 days in advance, the specialist prescribes the following types of studies to the woman:
- blood and urine tests;
- the test does not determine the blood group;
- coagulogram;
- ECG;
- MRI.
All this data is necessary for the specialist to carry out a successful operation and avoid complications.
The effect of hysteroscopy on the menstrual cycle
After surgery to eliminate the cyst, the woman must remain in the hospital. The duration of her stay, as a rule, does not exceed a day after surgery. As soon as doctors understand that there are no threats to the health of the patient's ovaries, and the results of her ultrasound are completely satisfactory, she can be discharged.
In some cases, women's periods after ovarian laparoscopy may be accompanied by mild pain. Immediately after the operation, the patient may notice pain in the ovaries and brown discharge, which will go away in a couple of days. Sutures do not bother patients, and the likelihood of complications is reduced to nothing thanks to the professional actions of doctors. Thus, painkillers after removal of an ovarian cyst are prescribed in very rare cases.
Women should avoid any physical activity after laparoscopy; it is recommended to spend more time in the fresh air. Alcohol and heavy foods should be avoided for two weeks after cyst removal. It is necessary to observe sexual rest for about three weeks. This will protect the uterine cavity from possible infection.
Since laparoscopic intervention is considered a minimally invasive operation, negative consequences can be considered extremely rare, and the recovery period passes in a matter of days. Over time, you will notice that you no longer have two small stitches from removing the cyst. If you notice frequent increases in temperature or pain after laparoscopy, contact your gynecologist.
If you don't get your period after surgery, it may not necessarily be related to the procedure. The regularity of menstruation depends on the age, hormonal levels, and general health of the woman. Follow all the specialist’s recommendations to avoid becoming the culprit of delays. If the absence of menstrual flow is directly related to laparoscopy, then the approximate time for their recovery may be related to the professionalism of the doctor, the characteristics of the patient’s body and her age.
Medical practice shows that the onset of menstruation after surgery occurs naturally, and no cycle disturbances are observed. In some cases, some irregularities are possible, as a result of which menstruation begins earlier or later than usual. The causes of such disorders may be weak immunity, stress or depression. In this case, the woman should not give in to panic, but urgently seek advice from a specialist.
If you start menstruating, pay attention to the amount of discharge as well as any changes that occur. If you notice any deviations from the norm, doctors may recommend that you take a course of medications to strengthen the immune system and a complex of essential vitamins.
Please note: Based on the nature of menstrual flow after laparoscopy, we can conclude that recovery processes are occurring in the body. If your periods are heavy, this may indicate internal bleeding. In this case, you should not postpone your visit to the doctor.
Signs of an inflammatory process in the ovaries after surgery may be brown bloody discharge with an unpleasant odor. Another warning sign is multiple blood clots. You should not self-medicate if you have not had periods for six months after surgery. Such disorders can be eliminated with the help of hormonal therapy, carefully selected by a specialist.
But you shouldn’t wait until six months have passed. You should consult a doctor if you have not had your period for three months after surgery. Visit a gynecologist to rule out the possibility of hormonal imbalance. Also, symptoms that indicate the need to visit a specialist may be nausea, general weakness, fever, pain in the suture area.
Despite the fact that laparoscopy is a minimally invasive method in which, instead of an open operation, only three small punctures of the abdominal wall are performed, each body perceives it differently. And also surgical intervention on various organs of the female genital area can manifest itself in various variations.
One of the most important signs of normalization of the reproductive function of the female body is timely and normal periods. Based on the type and nature of menstruation after laparoscopy, it is easy for specialists to draw conclusions about the woman’s health condition and the need for further treatment.
The cyclicity must be stable.
The effect of laparoscopy on the female body is, as a rule, indifferent, but depending on which organ the operation was aimed at. In cases of diseases of the reproductive system and a favorable prognosis, menstruation most often becomes regular after laparoscopy and returns to normal.
And in some cases no changes occur. So, after laparoscopy of appendicitis, the course of menstruation does not change, and if any disruptions are observed, these may be the consequences of anxiety before the operation or the body’s reaction to the use of anesthesia.
Hysteroscopy is a microsurgical examination of the uterus, appendages and fallopian tubes, which allows you to immediately remove identified pathologies. This method is considered more narrowly targeted than laparoscopy, but no less effective. And after it, the menstrual cycle may also undergo changes.
After hysteroscopy prescribed for polycystic ovarian disease (formation of multiple cysts), menarche will occur after taking hormonal medications. If the goal of the procedure is to restore the patency of the tubes, then you should hurry with pregnancy, since there is a high probability of progression of the disease.
When menstruation does not start for a long time, doctors prescribe medications to stimulate ovulation. Using hysteroscopy, biopsy material is taken for analysis to diagnose oncological processes in the reproductive organs, and also treat endometriosis. After the procedure, bleeding may occur, which patients often mistake for normal periods.
Also, with both procedures - laparoscopy and hysteroscopy, if there is damage to the uterus, ovaries or fallopian tubes, then menstruation may be absent for an indefinite amount of time.
In most cases, your period will return to normal after the first two to three months, and this may depend on several important factors. These include:
- hormonal status;
- general health status of the patient;
- age and physiological characteristics;
- professionalism of the surgeon performing the procedures.
If necessary, a number of drugs are selected to solve the problem
Practice shows that many operated patients have their periods on time and there are no cycle disturbances. Only in certain cases do menstruation not return to normal or come, but much later. This is often due to a weakened immune system or due to stress.
If for some reason the menstrual cycle does not improve after laparoscopy or hysteroscopy and the procedures do not bring the expected result, do not despair. First, you should visit your doctor, listen to his recommendations and follow the instructions exactly.
Most likely, a specialist will prescribe conservative treatment based on taking hormonal medications to stabilize the functions of the endocrine system, which will help smooth out the menstrual cycle and restore the reproductive capacity of the female body.
Operation laparoscopy
I’ve never written any reviews, but then I thought that suddenly it would help me mentally pull myself together and make up my mind)
I am 26 years old, I have no children or pregnancies. Due to my busy schedule and fear of doctors, I rarely went to the gynecologist. But 2 years ago, when I finally found myself at the gynecologist, I heard from him that I had a paraovarian cyst of quite large size. It does not go away on its own and can only be removed through surgery. In short, while I was gathering my courage, two years passed)) Of course, I didn’t let everything take its course, I visited the doctor once a month, did ultrasounds even more often and compared whether my cyst had grown yet. And then, during one of the regular visits, the doctor discovered that my neighbor had a cyst. Endometrioid cyst on the left ovary. I’ve already read about her on the Internet, a lot of scary things. And then I already realized that I couldn’t delay, not only did the woman’s reproductive function come into question, but on top of everything else, it was, in principle, life-threatening. I never experienced any discomfort due to these cysts, and as many girls say “they felt their cysts”... I didn’t have this, I lived as usual, the only noticeable and unpleasant moment was just hellish pain during menstruation, the first two During the day, I stupidly lived on painkillers, but over the past few months, my pain became even worse, it got to the point that I fainted, I felt terribly nauseous and my temperature rose.
I was supposed to have a laparoscopy at the perinatal center, and the day before the operation at 9:00 I was there with my things. Yes, by the way (!), thank you very much to all the girls who write in great detail about everything, describe all the details of the upcoming operation, since this is really very necessary for us, for those who still have all this ahead, according to the list of things in one of the reviews I got ready myself and realized that I took everything I needed and nothing extra!
Upon admission to the hospital, I was immediately asked to change clothes, fill out some form with questions about allergies, vaccinations, whether I had traveled anywhere during the year, and the like. Then they take blood from a vein to double-check your blood type and Rh factor and measure your blood pressure. That's all for now, and now I'm already in the elevator, which will take me to my room)
The room was double, everything was very clean and almost not scary. One thing confuses me, I see that the bed next door is occupied, but there is no “hostess” and I feel a little uneasy at the thought that she is now undergoing surgery and will soon be brought in.. So I sat there for I don’t even know how long, I think two or three hours , I had time to read, sleep, then my doctor came to me and said that later they would invite me to a chair for another examination and tell me in more detail about the operation, about another couple of hours passed) They called me in for an examination, then they asked me a bunch of questions, such as what illness you had, what time did you start having sexual intercourse, is there any disease of the reproductive system in your family, etc. Then I returned to the room again. It was time for lunch, I was told I could only have broth and only at lunch, then only water, and on the day of the operation I couldn’t even drink. After that, the anesthesiologist came, he was all in his own thoughts, scared, very quickly asked questions about allergies, asked me to tilt my head to the right, left, back and forth and stick out my tongue, and left. A minute later he returns with the phrase “Oh, I forgot to get your signature stating that you are familiar with general anesthesia.” There was a feeling that the operation was not mine, but his, I remember I thought that forgetfulness is not the best trait for an anesthesiologist) but what can I do, my eyes are afraid, and the operation is tomorrow)
Afterwards they brought my neighbor, she really didn’t look very good, there were tubes sticking out everywhere, an IV, and some other device that dosed her with painkillers. Only later did I find out that she had undergone strip surgery, which is why everything looked so scary. At night they gave me an injection and I fell asleep. They woke me up at six and told me to immediately put on compression stockings without getting up, lie down for a while and go to the post to measure my blood pressure and temperature! Oh, damn, I forgot to write about the enema!!) yes, they do it in the evening, at about 9 o’clock and in the morning at six, I experienced this “magic” for the first time, and I can say one thing, the most important thing is when you lie down and everything begins, there is no need to strain, if you relax and imagine a waterfall, it will be much better) The enema in the morning no longer seemed scary and was more gentle or something..
At about 8 am my doctor came and said that everything would start at 10. On that day, only my operation was scheduled and the joke about the fact that I was a daredevil, the only one doing the operation on Friday the 13th was very appropriate)
But at exactly 9 o’clock they came for me and I was even glad that everything would start earlier, because when you have already gotten used to the idea that you need this operation, that this is the only effective step towards getting rid of the cyst, it becomes not so much scary as The wait for this operation is tedious and long.
They take me to the treatment room, there I take off my robe and slippers, remain in stockings, lie down on a gurney and... Attention (!) The most unpleasant thing I experienced during the entire operation was the urinary catheter. I repeat, it’s not even that painful, it’s unpleasant and incomparable to anything I’ve ever experienced, as if you want to go to the toilet and everything cuts and pricks there. They cover me with a sheet and drive me down the corridor. I remember before the operation I read all the reviews that were written here and I mentally drove along the imaginary corridor many times, lay down on a chair, looked into the lamps, and it was very unusual to feel the same thing in reality, before entering the operating room, put rag shoe covers and a hat on your head. Then you are asked to stand up, take your dog (urinary catheter) with you and go to the chair. It’s very cold inside, there are a lot of different devices around, two people are laying out things and they’re not paying attention to me. I lie down on the couch, my legs are on top, like in a gynecological chair, my chest is covered with a sheet, a device for measuring blood pressure and pulse is hung on my arm (girls no nail polish) and a catheter is inserted into a vein, an oxygen mask is put on, I remember I still had some discomfort from the urinary catheter. Two or three more people come, one of them is a male anastasiologist, they joke, talk, and I start shaking wildly, like never before, from fear, from cold, from the fact that the stomach is rubbed with something cold, it lasts about 10 minutes, then I see something dripping down the IV and the next second I stop shaking, I just lie there and don’t move, I’m not scared, with my peripheral vision I see an anastasiologist (by the way, this is not the one who came to me) and another girl looks at each other , then they look at me, I lie there, I understand what is happening and I’m not scared and I think, well, when will my eyes close) this is the last thing I remember. The next thing that happened, they woke me up, and they seemed to be screaming, but I heard everything in the distance, they gave me water to drink and said “spit!” But I can’t, the water just pours out of my mouth. They gave me water three or four more times until I couldn’t spit it out myself. Already on the chair, I managed to look at the clock; the time was 10:30. And I noticed that I no longer had a urinary catheter or anything at all except a catheter in a vein. Then they carried me on a sheet to a gurney and took me to another room, where they covered me with two blankets and gave me an injection in the butt. I fell asleep, woke up, looked at the clock, it was about one in the afternoon. She lay there a little longer and asked to be taken to the room. Oh, this sweet feeling of lightness, that the worst thing is over!) the rest of the day I either slept or just lay there, since there were no tubes in me, a few hours after the operation I went to the toilet myself. I got there fine, but on the way back I started feeling very nauseous and dizzy from the anesthesia. The next day I started walking, at first it was hard, but I was encouraged by the fact that in the evening I would need to go down to the first floor, guests would come to me)) many girls who had the same operation, but before me, lay on the crib all day long and came out only when the pressure was changed. Of course, I don’t know their whole situation, but for me, if you have the opportunity to get up and walk, you need to take advantage of it) I had a living example in front of me, my roommate. She had abdominal surgery a day before me, she began to walk later than me, this is understandable, things are not comparable. The first night after the operation she did not sleep at all because of the pain, although she was given some kind of painkiller all night, I mean, you can’t delay it, otherwise you will have no choice, they will tell you that it’s only a cavity and that’s it, it’s much more painful ! I arrived at the hospital on Thursday, on Monday morning they removed my stitches, one of which, by the way, will not be visible at all, since it was done in the navel, they said that this was a bonus from the surgeon, they also left my puncture for the piercing) was it endometriosis? We know when the histology will be ready, I’ll go see the results on Friday. For about five days after the operation, I am worried about this unfortunate gas, which everyone writes about, especially if you walk for a long time, it begins to ache in the chest and shoulders, 10 days have passed since the operation, and nothing hurts anymore, I smear the stitches with brilliant green and do not seal them with anything. I was prescribed Buserelin-Depot injections, but I really don’t want to inject them, after all, there are terrible side effects, who knows how it will affect me... But I still have to, otherwise I end up retreating halfway. The treatment is still ahead, but I am very glad that I decided to take this step, and God grant that in a few months I come here and write that everything is fine with me and we are expecting a child!) Health to you girls!!!
Important advice from experts
The main condition for successful recovery is sexual and physical rest. In the first case, sex immediately after removal of an ovarian cyst can provoke increased pain and slow down the healing of appendage tissue. Unprotected sexual intercourse can lead to inflammation or infections, which can lead to suppuration of the internal sutures.
You need to wear a bandage after laparoscopy of an ovarian cyst for preventive purposes. Its use is strictly indicated for women who have an increased risk of complications that may arise after surgery. A corset is also necessary when removing a large tumor or intestinal dysfunction.
Physical activity is strictly limited only in the first week of rehabilitation. Subsequently, the woman is allowed to take short walks. Light exercise is encouraged. With its help, muscles are strengthened and stagnation in tissues is prevented. Increasing pain after performing exercises with a recent laparoscopy of an ovarian cyst indicates that the body is insufficiently prepared for exercise. In such cases, physical activity should be limited for a few more days.
It is important to take all medications prescribed by your doctor:
- antibiotics – prevent suppuration of sutures and the development of infections;
- painkillers - improve a woman’s well-being;
- anticoagulants – prevent the formation of blood clots;
- hormonal – necessary to prevent hormonal imbalance after removal of an ovarian cyst or to correct the menstrual cycle;
- immunomodulators – increase immunity;
- vitamin complexes - restore the functioning of the appendages, saturate the body with useful substances.
Antibiotics and painkillers are used only 3-10 days after the intervention. Other types of drugs need to be taken for a longer period of time, which is determined individually.
Cycle changes after laparoscopy
The laparoscopic method is considered a safe and relatively painless procedure. Often, two weeks are enough for a woman to fully return to normal. And menstruation does not undergo noticeable changes - this is due to laparoscopy on certain days of the menstrual cycle.
Laparoscopy and hysteroscopy at the same time and reviews about them
Moderate amounts of blood or spotting usually occur in the first two or three days after surgery. This is considered an absolutely normal manifestation associated with a violation of the integrity of the organs: ovaries, uterus or fallopian tubes.
Later, the discharge becomes sanguineous and gradually acquires a yellowish tint. There may be a slight change in the cycle. Heavy menstruation should not be considered a pathology.
The norm after laparoscopy is considered to be: a shift in menstruation by several days, a long delay, scanty or heavy menstruation. If these manifestations are not burdened by various complications and there is no severe pain, then they should not cause concern, but a visit to the gynecologist for regular examination is mandatory.
Experts consider the first day of the new menstrual cycle to be the day of laparoscopy, so menstruation usually begins as in the patient’s standard cycle. Most likely, they will pass without visible changes, and will be accompanied by mucous discharge.
Discharge after the intervention will begin immediately and may last two to three weeks, which is considered a natural process. If the discharge begins to acquire a brownish or greenish tint and an unpleasant odor, then you should be wary - this may be a sign of infection and the onset of an inflammatory process.
Severe pain in the lower abdomen is one of the signs of the onset of the inflammatory process
A cycle delay of more than three weeks can occur due to the effects of anesthesia and stress after surgery. After surgery on the fallopian tubes or ovaries, menstruation may not begin for a long time. But if there is a long delay, there is pain in the lower abdomen and alarming discharge, you should consult a gynecologist.
Heavy periods
Knowing that internal organs take much longer to heal than the skin, you also don’t have to worry about having heavy periods. The first and even second periods after laparoscopic surgery can be bright and quite heavy. This is due to the healing process of damage to internal organs, and again, if there are no signs of inflammation, then such a process is considered normal.
How is laparotomy performed?
The operation is performed under general anesthesia. The surgeon treats the skin at the intended incision site with disinfectants, then horizontally cuts the lower part of the peritoneum. Then he moves the tissue apart, gaining access to the affected area, and excises the tumor.
Without fail, the neoplasm is submitted for histology, and the doctor examines nearby tissues and organs to detect abnormal changes. If other pathologies are found during the operation, complete removal of the ovaries may be required.
Important! If during a histological examination it turns out that the cyst is cancerous, an ovarian resection operation is performed on an emergency basis.
To avoid bleeding, the vessels are ligated or cauterized during surgery. Since the ovarian tissue is very thin, the sutures on the cut are applied carefully. If laparotomy is performed due to rupture of a tumor or a purulent process in it, drainage tubes are left in place for a couple of days so that the fluid with pus is drained out.
Possible complications
Complications after laparoscopy to remove an ovarian cyst can occur both in the first days after surgery and several months later. The early development of negative consequences is often associated with incorrect surgical procedures. Possible complications:
- uterine bleeding;
- injury to neighboring organs and vessels;
- an allergic reaction to anesthesia or gas injected into the abdominal cavity;
- increased body temperature;
- development of infectious diseases.
Symptoms such as nausea, vomiting and dizziness are considered normal in the first hours of recovery from anesthesia. This condition does not require urgent medical attention unless the woman’s well-being worsens. Normal body temperature can rise to 37-38 degrees 1-2 days after the intervention.
During late rehabilitation or after complete recovery of the body, the following consequences may be detected:
- periodic uterine bleeding after laparoscopy of an ovarian cyst, manifested during the intermenstrual period;
- formation of adhesions in the pelvis;
- absence of menstruation is a sign of dysfunction of the appendages;
- pain in the ovary after laparoscopy - often indicates an inflammatory process;
- re-formation of an ovarian cyst;
- lack of conception for 6-12 months;
- hormonal imbalance.
To reduce the risk of complications, it is necessary to regularly see your doctor. This will allow diseases to be detected in the early stages, which increases the chance of their complete elimination. It is recommended to visit a specialist monthly in the first three months after surgery. In the future, it is enough to carry out an examination 3-4 times a year, and one and a half years after the operation - every 6 months.
When can you get pregnant after laparotomy?
Are you planning a pregnancy?
Not really
The answer to this question depends on a large number of factors, including the complexity of the pathology, the presence of complications during the rehabilitation period, and so on.
If the operation was performed on only one ovary, and the other functions normally, producing the hormones necessary for the maturation of the egg, then conception is possible almost immediately. However, it is undesirable to become pregnant in the first months after surgery, so doctors recommend using barrier contraception so as not to disrupt the restoring hormonal balance with oral contraceptives.
The likelihood of conception is directly proportional to how much organ tissue was preserved during the operation.
Reference! Doctors recommend planning a pregnancy no earlier than after 4 months. But in each specific case this period may shift in one direction or another.
Only the attending physician can tell the patient exactly when she can become pregnant. It is important to understand that the ovaries should recover after the intervention, and the hormonal levels should stabilize. If after the operation the woman cannot become pregnant within six months, a thorough examination is necessary. Often the cause of infertility after laparotomy is adhesions, as well as complications that interfere with the ability of the egg to properly mature.
Symptoms that require consultation with a doctor
The occurrence of complications is most often accompanied by obvious symptoms. Signs that require visiting a specialist:
- persistent postoperative pain lasting more than a week;
- redness of the skin near the stitches;
- vaginal discharge with an unpleasant odor;
- uterine bleeding;
- high body temperature lasting more than 2-3 days after laparoscopy of an ovarian cyst;
- severe weakness in the late rehabilitation period;
- nausea, vomiting and diarrhea;
- prolonged absence of menstruation.
These symptoms indicate a malfunction in the body. An independent attempt to stop their manifestations can worsen the state of health or lead to the progression of the pathology.