The teenage years are a difficult period for both children and their parents. Physical changes during puberty often make you feel uncomfortable.
In girls, this occurs with the appearance of their first menstruation. Starting your period can be scary, especially if it comes with certain problems, such as irregular periods or premenstrual syndrome (PMS).
You may be interested in: Know your body. What is the clitoris and how to masturbate correctly Nodular uterine fibroids: treatment
What it is
Normally, menstruation lasts from 3 to 7 days . In pathological processes of the reproductive system, the amount of blood released exceeds 150 ml. In this case, the duration of menstruation is 7-14 days . This deviation indicates inflammatory or infectious processes in the pelvis. Menorrhagia is divided into two types:
- primary (develops during the first menstruation in adolescence);
- secondary (occurs in women with an established cycle).
Some women suffering from menorrhagia do not consult a doctor. They mistakenly take long periods for an individual characteristic of the body. Doctors believe that pathology requires qualified help. The main complication of menorrhagia is the development of anemia. It is accompanied by dizziness, pale skin, decreased performance and a tendency to faint. Signs of anemia have a negative impact on a woman’s condition.
Causes of heavy periods in teenagers
Too heavy menstruation
- the most common problem among teenage girls. Formally, blood loss exceeding 80 ml per cycle is considered too abundant. Although this definition is scientifically accurate, it is difficult to objectively measure blood loss during menstruation. In studies of adult women with subjective complaints of hypermenorrhea, 68% had less than 80 ml of blood loss and 42% had less than 50 ml of blood loss [Cameron].
To complaints from teenage girls
sometimes their mothers' impressions of their own menstruation influence them. Well-known comments like, “I’ve always had problems with my periods, and so will she,” must be weighed carefully.
It is still extremely important to try to determine blood loss
. If treatment has already begun, it will be impossible to convince the girl (and her mother) that her situation was within acceptable limits and did not require intervention. The patient develops a lifelong misconception about menstruation, which can subsequently lead her unnecessarily to the operating table.
A thorough survey to get an idea of your cycle time
, does not always help [Cameron], but it may be helpful to ask questions about how often the clots appear and how big they are, whether she has to get up at night to change pads, and whether the sheets or underwear get dirty. Questions about how many pads you have to use and how often you need to change them also help, but the answers depend on how much the conversation confuses the girl.
It is also important to understand to what extent menstruation interferes with the patient’s behavior.
normal lifestyle and how they affect the ability to attend school, play and have fun.
Studies should include determination of hemoglobin
and a thyroid function test. An ultrasound scan can be done, but is not necessary at this stage. No examination with anesthetics, dilators or curettes is required. Dilatation and curettage are diagnostic procedures that are needed to exclude serious disorders, and in this age group there is no severe pathology associated with the endometrium.
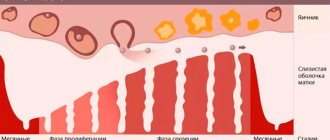
This phenomenon is based on a pathophysiological process
lack of ovulation, which is typical for the first few months after menarche. A study by Apter and Vihko showed that in the first year after menarche, only 15% of cycles are ovulatory, after 5 years this figure reaches 75%, and after 12 years - 95%. The effect of estrogen on the endometrium, not accompanied by the production of progesterone, causes constant proliferation of the endometrium for a longer time than normal, which leads to thickening of the endometrial epithelium. Detachment of such an endometrium is, for obvious reasons, associated with very heavy bleeding.
Symptoms
The main manifestation of the pathology is profuse bleeding , including clots. The girl has to change her sanitary pad every 30-60 minutes. Menorrhagia is accompanied by intense pain in the lower abdomen . Their character can be pulling, cramping or sharp. Unpleasant sensations also affect the ovarian region and lower back. On the 4-5th day of menstruation, a woman notices the following symptoms:
- general weakness;
- loss of consciousness;
- blood pressure surges;
- signs of decreased hemoglobin in the blood;
- dizziness and headaches.
In some cases, bags under the eyes , bruises and bruises on the body , and bleeding gums . In rare cases, mucus is visualized in the vaginal secretion or purulent discharge appears . In addition, vaginal itching . In complicated situations, body temperature rises .
How to get rid of heavy periods with clots
If your periods are heavy, painful, have blood clots, and are heavy, it probably means you have menorrhagia.
For such a violation of the menstrual cycle, the presence of heavy periods with clots is typical, but there may be other reasons.
Menstrual clots bother most women to varying degrees, especially in adolescence and after 40 years, although they themselves are not a pathology.
These are gel-like drops of coagulated blood that are released from the uterus during menstruation.
They resemble pieces of liver, vary in color from bright to dark red, and can be very large, but are often small in size.
It is possible to determine why you have heavy and prolonged periods with clots only after a thorough examination. A gynecologist will help you find out the causes and prescribe treatment.
What is heavy bleeding called?
When heavy bleeding during menstruation with clots can be called a pathology depends on the amount of blood released. Officially, blood loss of more than 80 ml (or 16 moistened sanitary products) during the menstrual period is considered menorrhagia.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=9gkZoYanqS4
Most women with this kind of heavy bleeding will have low hemoglobin (anemia) or signs of iron deficiency. In practice, only about a third of women are anemic. Therefore, the definition of a heavy period may be adjusted to include 9-12 regular-sized soaked sanitary products per period.
Knowing that one normal-sized soaked sanitary product contains about a teaspoon of blood (5 ml), you can calculate the approximate amount of blood you lose each day.
Another very simple way to measure bleeding is to use a menstrual cup, which has markers for 15 and 30 ml of blood loss. To measure blood loss with a menstrual cup, simply add up the estimated amounts from each bowel movement.
How to keep a menstrual diary
Keeping a menstrual diary is a useful way to estimate the amount of blood lost using the number of soaked pads, regular-sized tampons, or a menstrual measuring cup. This way, you will determine whether your periods are really heavy or within the established norm.
Only completely saturated products are counted. If the gasket was half full, count it as half.
Let's say you used three tampons and one pad a day, but they were only half full. Then you will have to multiply four by 0.5 = two to get the number of completely soaked. A "maxi" or "super" tampon or pad holds about 2 teaspoons or 10 ml of blood, so record each large soaked sanitary product as a "2".
Additionally, write a personal judgment about the amount of blood lost, where:
- “1” defines scanty discharge;
- "2" means normal flow;
- "3" is a little rich;
- “4” is very heavy with flooding.
If the number of saturated hygiene products is 16 or more, or if you write down “4”, then you should think about how to reduce heavy discharge.
Normal and abnormal clots
Sometimes heavy menstruation with clots can be considered normal. If the pieces are small—no more than a quarter of a centimeter—and only random, you don't have to worry. Unlike blood clots that form in your veins, they are not dangerous in themselves.
Normal clots:
- less than a quarter;
- found only occasionally;
- appear at the beginning of menstruation;
- bright or dark red.
Abnormal clots are larger than a quarter centimeter in size and occur more frequently. The regular occurrence of large blood clots during menstruation may signal a health condition that requires investigation.
See your doctor if you have heavy menstrual bleeding with a lot of clots larger than a quarter in size. Your period is considered heavy if you change your tampon or pad every two hours or less.
You should seek immediate medical attention if you have a period with large clots and you think you might be pregnant. This could be a sign of a miscarriage.
What Causes Menstrual Clots?
Most women of childbearing age shed the uterine lining approximately every 28 to 35 days. The endometrium grows and thickens over the course of a month in response to estrogen, a female hormone.
Its purpose is to help the fertilized egg implant in the uterus. If pregnancy does not occur, other hormonal events signal the need to shed the unwanted membrane. This is called menstruation.
When the endometrium is shed, it damages small vessels, causing bleeding.
Menstrual discharge consists of many elements:
- blood;
- blood by-products;
- slime;
- textile.
This mixture is then expelled from the uterus through the cervix from the vagina. As the mucous membrane is shed, it sinks to the fundus of the uterus, waiting for the cervix to contract and push out the contents.
To aid tissue breakdown, the body releases anticoagulants to dilute the material and allow it to pass freely.
However, when blood flow outpaces the body's ability to produce anticoagulants, period blood clots are released.
The formation of blood clots is most common with heavy discharge. For many women with normal periods, heavy flow usually occurs early in the period but is short-lived.
Menstruation is considered normal if bleeding lasts 4 to 5 days. During this time, a woman loses 2 to 3 tablespoons of blood or less.
For women with heavy periods, excessive bleeding and blood clots may be prolonged. A third of women have periods so heavy that they soak a pad or tampon every hour.
What are the causes of abnormal clots
Physical pathologies and hormonal factors can cause heavy periods with clots and disrupt the menstrual cycle. Abundant discharge in itself is a prerequisite for their appearance. And the presence of gynecological diseases increases the chances of developing abnormal blood clots.
Bend
If there is a bend in the uterus, women suffer from very heavy periods with clots. The obstruction puts additional pressure on the wall of the uterus, reducing the ability of the uterus to contract. When the uterus does not contract properly, blood accumulates and coagulates inside the uterine cavity, forming pieces that are subsequently removed through the cervix along with the blood.
Myoma
Fibroids are noncancerous, muscle tumors that grow in the wall of the uterus. In addition to heavy bleeding during periods with clots, they can also cause:
- irregular bleeding;
- lower back pain;
- pain during sex;
- protruding belly;
- problems with conception.
After age 50, many women will develop fibroids; the cause is unknown, but genetics and the female hormones estrogen and progesterone likely play a role in their occurrence.
Endometriosis
Endometriosis is a condition in which the lining of the uterus grows outside of the uterus. A clear sign of endometriosis is heavy periods with very large blood clots. During the menstrual cycle, endometriosis also causes:
- painful cramps;
- nausea, vomiting, diarrhea during menstruation;
- discomfort during sex;
- infertility;
- pain in the pelvic area;
- bleeding.
The exact cause of endometriosis is unknown, but heredity, hormones and previous pelvic surgery play a role.
Hormones
Proper growth and thickening of the uterine lining depends on the balance of estrogen and progesterone. If there is too much or too little of one or the other, you may experience heavy menstrual bleeding. What can cause hormonal imbalance:
- menopause;
- stress;
- weight gain or loss.
The main symptom of hormonal imbalance is irregular menstruation. For example, your period may be later or longer than usual, or you may miss it entirely.
Miscarriage
About half of all pregnancies end in miscarriage. Many pregnancy losses occur before a woman even knows she is pregnant. When an early pregnancy is lost, it can result in heavy bleeding, cramping, and clotting of blood clots.
von Willebrand disease
Heavy menstrual flow can also be caused by von Willebrand disease. Between 5 and 24 percent of women with chronic heavy menstrual bleeding have this condition.
Von Willebrand disease may be the cause of your heavy periods and period clots. You also bleed easily after a minor cut or your gums bleed after every brushing.
Contact your doctor if you suspect this is causing heavy bleeding.
What complications can there be?
One of the main complications of heavy menstrual bleeding is iron deficiency anemia. Anemia is a condition that occurs when there is not enough iron in the blood to produce healthy red blood cells. Symptoms include:
- fatigue;
- weakness;
- pallor;
- shortness of breath;
- chest pain.
To determine the underlying cause, your doctor will ask you about what might be affecting your period. For example, you have had previous pelvic surgery, used contraception, or were pregnant.
In addition, your doctor may order blood tests to look for hormonal imbalances.
Imaging tests, such as an MRI or ultrasound, may be used to check for fibroids, endometriosis, or other conditions that are obstructing blood flow.
How are menstrual clots treated?
When it comes to how to stop heavy periods and what can be done about clots, the best answer is to control your bleeding with medications and taking care of your health. In rare cases, when it is necessary to remove fibroids, surgical procedures are resorted to. Talk to your doctor about the pros and cons of all your options for stopping period bleeding.
Hormonal contraceptives
Hormonal contraceptives suppress the growth of the uterine lining. A progestin-releasing IUD can reduce menstrual blood flow by 90 percent, while birth control pills can reduce menstrual blood flow by 50 percent.
Hormonal contraceptives may also be useful in slowing the growth of uterine fibroids and adhesions.
For women who cannot or do not want to use hormones, the drug tranexamic acid, which affects blood clotting, is prescribed. Medications that stop heavy period bleeding, such as Ibuprofen, may be sufficient.
Surgical intervention
Sometimes you may need surgery to get rid of conditions that are causing clots during your period. The cervix is dilated, followed by scraping of the uterine mucosa. This is usually done in an outpatient setting under sedation. Although curettage will not cure heavy bleeding, it does provide a respite for several months as the endometrium then thickens again.
For women with uterine tumors, such as fibroids, that do not respond well to medications, surgery may be necessary to remove them. The type of surgery will depend on the size and location of the lesions.
If the size is large, you will need a myomectomy, which involves a large incision in the abdomen to access the uterus. If the tumor is small, laparoscopic surgery is performed. Laparoscopy also involves making incisions in the abdomen, but they are smaller.
Recovery diet
Treat blood loss with extra fluids and salt. Any time you feel dizzy or have a racing heart when you get out of bed, it's a sign that your blood volume is too low. Drink more salty liquids, such as tomato or other vegetable juices, salty broths. Drink four to six cups (1-1.5 liters) of fluid per day.
Nourish your body with iron to replace what is lost during heavy bleeding.
Start taking one iron tablet (eg 35 mg ferrous gluconate) a day. You should also increase the amount of iron you get from foods - red meat, liver, egg yolks, dark green vegetables and dried fruits such as raisins and prunes are good sources of iron.
Causes
In most cases, heavy bleeding during menstruation is caused by abnormalities in the reproductive system.
In the postpartum period, such discharge is considered a normal physiological process. But their occurrence is not associated with the work of the appendages. Bloody discharge that appears after labor is completed is called lochia. They are caused by intense contractions of the uterus after the birth of the baby. In other cases, among the reasons for heavy periods are:
- Hormonal disorders. The intensity and duration of menstruation depend on the thickness of the endometrium, which lines the inside of the uterus. It is he who is rejected at the onset of critical days. Its formation occurs under the influence of estrogens produced in the first half of the cycle. In case of hormonal disorders, their number exceeds the established norms. Thick endometrium increases the intensity of menstruation.
- Deviations in the functioning of the circulatory system. If blood clotting is poor, heavy discharge is especially dangerous. In this case, the woman notices bleeding from minor injuries.
- Consequences of using contraceptives. Menorrhagia may be the result of an individual reaction of the body to a method of protection. This happens both while taking the pills and after installing the fallopian device. In this case, intermenstrual bleeding is also observed.
- Neoplasms. Bleeding can be caused by the presence of tumors of malignant or benign origin. They tend to grow actively. When mechanically damaged, the tumors bleed and cause discomfort. These include fibroids, cysts, polyps and papillomas.
- Wrong lifestyle. Sometimes heavy bleeding is caused by intense physical activity, drinking alcohol or eating excessively spicy foods.
- Heredity. In rare cases, heavy menstruation is associated with characteristics that are passed down through the female line. Then the pathology is not temporary, but permanent.
What to do if a teenager has heavy bleeding during menstruation
During adolescence, the menstrual cycle is quite unstable, since the hormonal system is just beginning to function. In this regard, the break between menstruation can be 2 months, and sometimes more. However, what to do if a teenager is diagnosed with menorrhagia?
Menorrhagia is a condition that involves severe blood loss during menstruation. In addition, menstruation lasts more than 7 days, which can lead to iron deficiency anemia.
Heavy periods in a 13-year-old teenager are determined by these criteria:
- the duration of menstruation exceeds a week;
- blood comes out of the genital tract in large quantities;
- the presence of large blood clots;
- the lost blood volume requires the use of a large number of pads:
- you have to change the gasket every hour;
- menstrual cycle less than 21 days;
- blood spotting can also be observed in the middle of the menstrual cycle;
- During menstruation, the girl feels severe, sharp pain, requiring the use of painkillers.
Why does a teenager experience the first heavy periods with blood clots? Menorrhagia can occur due to the development of psycho-emotional, chronic, endocrine, gynecological and other diseases. In medicine, the most common causes of heavy periods are:
- Hormonal disbalance. During adolescence, sex hormones are just beginning to be produced, so severe disruptions in their functioning may occur.
- Gynecological ailments: fibroids, polyps, tumor, hyperplasia.
- The presence of inflammatory processes in the area of the uterus and its appendages.
- Blood clotting disorder.
- Taking certain medications, in particular anticoagulants or antiplatelet agents.
- Lack of vitamins and minerals that are involved in blood clotting.
- Predisposition to menorrhagia at the genetic level.
- Stressful situations or severe depression.
- Physical or emotional stress.
- Poor nutrition, including various diets.
- Development of pathological processes in the liver, thyroid gland,
- Cardiovascular system or urinary system.
- Consuming only fermented milk products, under the influence of which the synthesis of enzymes that inhibit blood clotting occurs.
- Uncontrolled use of hormonal drugs.
Teenagers have heavy periods quite often. This process can be observed within three years after the onset of menstruation. Heavy menstruation is often observed against the background of:
- severe obesity or, conversely, underweight;
- psychotraumatic situations related to studies and relationships in the team;
- intellectual overload.
As a rule, menorrhagia leads to rapid fatigue, rapid heartbeat, constant weakness and blood clotting disorders, which significantly affects the quality of life of a teenager, reducing academic performance and even more negatively affecting the psychological state, resulting in a vicious circle.
What to do if a teenager experiences heavy periods? Therapeutic measures are prescribed only when it turns out that hormonal imbalances cannot be eliminated on their own.
Only in this case will a specialist prescribe hormonal therapy aimed at restoring hormone production. Most teenage girls respond well to hormonal therapy, which produces positive results within a year.
However, therapeutic measures of a hormonal nature are used quite rarely, since menorrhagia can be cured through a number of these measures:
- prescribing the correct physiotherapeutic therapy: physical therapy, swimming pool, active recreation, galvanization, mud therapy, EHF therapy, etc.;
- elimination of anemia through the use of iron-containing drugs;
- a diet that includes a full range of nutrients, trace elements, minerals and vitamins;
- psychotherapeutic measures aimed at stabilizing the psychological state of a teenager, reducing stress and eliminating depression.
When prescribing therapeutic measures, much attention is paid to the pain of menstruation. Severe pain during this period often indicates inflammatory processes in the genital area or endometriosis.
During treatment, traditional medicine is no less useful. As therapy, infusions of nettle, yarrow or corn silk should be used. Infusions of these herbs are used a few days before the start, as well as during menstruation.
Heavy periods in teenagers happen quite often, especially in the first few years, so you shouldn’t panic right away. If a teenager is very worried about menorrhagia, it is imperative to consult a specialist who can make the correct diagnosis and prescribe appropriate treatment.
source
The most common and severe forms of dysfunction of the reproductive system during puberty in girls include juvenile uterine bleeding. This term refers to dysfunctional bleeding at the age of 10-18 years from the beginning of the first menstruation until adulthood.
This gynecological pathology occurs in approximately 10-20% of all girls in this age category. Heavy and frequent bleeding can cause a significant decrease in the level of hemoglobin in the blood, aggravate hormonal disorders, and in the future cause infertility. In addition, uterine bleeding in adolescents negatively affects the psychological state of children, causing isolation, self-doubt, fear for their health and even life.
The main reason is disturbances in the functioning of the hypothalamic-pituitary system. Hormonal imbalance provokes a single-phase ovarian cycle with a delay in menstruation and further bleeding. Most often, dysfunctional uterine bleeding of puberty occurs during the first two years after menarche.
There is no direct connection between this pathology and the development of other secondary sexual characteristics. In general, the girl’s puberty proceeds without disturbances. In more than a third of patients, the disease can be complicated by the appearance of acne and oily seborrhea.
The appearance of uterine bleeding in older girls is noted at early menarche (7-12 years). It is diagnosed in more than 60% of patients. With the late appearance of the first menstruation (after 15-16 years), this pathology occurs rarely - no more than 2% of cases.
The main causes of the pathological condition in adolescents:
p, blockquote 9,0,0,0,0 —>
- pathologies of the blood coagulation system;
- formation of ovarian tumors of hormonal origin;
- acute and chronic infectious diseases (ARVI, pneumonia, chronic tonsillitis, chicken pox, rubella);
- diseases of the endocrine system (pancreas, adrenal glands);
- tuberculosis of the genital organs;
- malignant neoplasms of the body and cervix;
- living in unfavorable conditions, excessive physical and psychological stress;
- poor nutrition that does not provide the body with necessary vitamins and microelements.
The most significant provoking factor is chronic tonsillitis with regular periods of exacerbation. There is a definite connection between the disease in girls and how her mother’s pregnancy proceeded. Provoking factors could be late toxicosis, chronic intrauterine fetal hypoxia, premature aging or placental abruption, and asphyxia of the child at birth.
For many girls, the regular monthly cycle is not restored immediately after menarche, but only over the course of six months to two years. Menstruation may be delayed by two to three months, and sometimes even six months. Uterine bleeding most often occurs after a delay of menstruation of up to 2 weeks or a month and a half.
In some cases, dysfunctional bleeding may occur a week or two after menarche or occur during the intermenstrual period. The main symptoms of the pathology include:
p, blockquote 13,0,0,0,0 —>
- copious (more than 100 ml per day) and prolonged (over 7 days) bleeding;
- discharge that occurs 2-3 days after the end of menstruation;
- menstruation that recurs at intervals of less than 21 days;
- dizziness, drowsiness, nausea as a result of anemia;
- pale skin, dry mouth;
- pathological desire to eat inedible foods (for example, chalk);
- depressed state, irritability, rapid physical fatigue.
Very often, a girl and even her more experienced mother cannot identify the disorder and regard it as normal menstruation. The girl can continue to lead her usual lifestyle, thereby delaying treatment, which should begin immediately, and aggravating the problem. It should be remembered that any heavy discharge, especially with clots, requires close attention. Menstruation is considered heavy when a pad or tampon has to be changed at least every hour.
Since pathology can be caused by various reasons, in addition to a mandatory examination by a pediatric gynecologist, consultation with an endocrinologist, neurologist, or oncologist is necessary.
For diagnosis, general and special methods for studying the disorder are used. General ones include a gynecological and general examination of the patient, examination of the condition of internal organs, analysis of the physique and height-to-weight ratio, and the presence of secondary sexual characteristics. From the conversation, the gynecologist will learn about the date of the first period, the regularity of the menstrual cycle, previous diseases and general health.
Patients are prescribed a number of laboratory tests: general urine and blood tests, biochemical blood test, sugar test and hormonal screening to determine hormonal levels. To clarify the diagnosis, ultrasound and MRI of the pelvic organs are performed.
Abnormal uterine bleeding during puberty should be differentiated from other pathological conditions that may be accompanied by bleeding, namely:
p, blockquote 20,0,0,0,0 —>
- diseases of the blood system;
- hormone-producing ovarian tumors, endometriosis, cervical cancer;
- inflammatory diseases of the genital organs;
- injuries of the vagina and external genitalia;
- beginning abortion during pregnancy;
- polycystic ovary syndrome.
With diseases of the blood system, patients often experience nosebleeds and the appearance of hematomas on the body. Unlike inflammatory diseases of the genital organs, dysfunctional uterine bleeding is rarely accompanied by cramping pain in the lower abdomen. If tumors of various types are suspected, their presence will be determined after ultrasound and other specific diagnostic methods.
If there is heavy bleeding and the girl is not feeling well, it is necessary to call an ambulance. Before her arrival, the child is put to bed, given complete rest and an ice pack is applied to the stomach. The patient should be given a lot of sweet drinks, preferably tea. Even if the bleeding was stopped on its own, this should not be a reason for complacency, since such pathologies are prone to relapse.
The main goal of therapy is the complete cessation of discharge and normalization of the menstrual cycle in the future. When choosing methods and drugs for treatment, the intensity of bleeding, the severity of anemia, laboratory test data, and the general physical and sexual development of the patient are taken into account.
Curettage of the uterine cavity to treat and stop discharge in adolescents is carried out in exceptional cases. They are indicated only when the pathology threatens the patient’s life. In other cases, they are limited to drug therapy.
Drugs used for uterine bleeding in adolescents
If the girl’s general condition is satisfactory and there are no signs of severe anemia, treatment can be carried out at home using hemostatic drugs, sedatives and vitamins.
If the patient's condition is severe and there are all signs of anemia (low hemoglobin, dizziness, pale skin), hospitalization is necessary.
To stop bleeding and normalize the menstrual cycle, the following drugs are prescribed:
p, blockquote 28,0,0,0,0 —>
- uterine contractants - Oxytocin, Ergotal, water pepper extract;
- hemostatic drugs - Vikasol, Tranexam, Ascorutin, Dicinone, Aminocaproic acid;
- combined oral contraceptives - Rugulon, Non-ovlon, Janine;
- sedatives - bromine or valerian preparations, motherwort tincture, Seduxen, Tazepam;
- drugs to regulate the menstrual cycle - Utrozhestan, Duphaston, which are taken from the 16th to the 25th day of the cycle;
- vitamins – group B, including folic acid, C, E, K.
With elevated estrogen levels, girls are prescribed Turinal, Norkolut for three cycles with a three-month break, with further repetition of the drug regimen. If the level is low, sex hormones are prescribed in a cyclic manner. Hormone therapy is not the main method of preventing new bleeding.
Physiotherapy is used as auxiliary treatment methods - electrophoresis with novocaine or vitamin B1 and acupuncture. The second procedure is prescribed for blood loss without the threat of anemia, in the absence of pronounced hormonal imbalance.
If bleeding is caused by diseases of the endocrine system, appropriate specific treatment and iodine preparations are prescribed.
For the purpose of sedation and normalization of the processes of excitation and inhibition of the central structures of the brain, Nootropil, Veroshpiron, Asparkam, Glycine can be prescribed. Comprehensive treatment and measures to restore the menstrual cycle include performing physical therapy exercises and psychocorrective sessions with a psychologist.
Clinical recommendations for uterine bleeding during puberty include bed rest during treatment, applying cold to the lower abdomen, and drinking plenty of fluids to replenish fluid loss from the body. Do not apply a warm heating pad, take a hot bath, douche, or take hemostatic agents without consulting a doctor.
Of great importance is the elimination of the symptoms of iron deficiency anemia, which is most often a complication of uterine bleeding. For treatment, iron preparations such as Ferrum Lek, Maltofer, Hematogen, Totema, Sorbifer Durules are prescribed. The drugs are taken in tablet form; injections are more effective. In the future, the girl should follow a diet that includes foods rich in iron: red meat, liver, poultry, seafood, spinach, beans, pomegranates, brown rice, dried fruits, peanut butter.
After discharge from the hospital, the girl must be registered with a pediatric gynecologist.
Traditional medicine knows many herbs, infusions and decoctions of which have a hemostatic effect. However, they cannot completely replace drug treatment. Herbal decoctions and infusions can be used as an additional treatment method.
Among the most effective plants are:
p, blockquote 39,0,0,0,0 —>
- knotweed - contains acetic and malic acids, tannin, vitamins K and C, strengthens the walls of blood vessels, increases blood viscosity;
- water pepper - tannin, organic acids, vitamin K in the composition stabilize the activity of the smooth muscles of the uterus, increase blood clotting;
- shepherd's purse - contains alkaloids, organic acids, vitamin C, tannin, riboflavin, which help reduce blood secretions;
- Nettle is the most famous plant for stopping bleeding, regulates the menstrual cycle, and saturates the body with vitamins K, C, A, B.
To prepare decoctions, plant herbs are crushed, poured with boiling water and kept in a water bath for 15-20 minutes. After straining, take several times a day. The duration of use and dosage should be checked with your doctor.
Since juvenile bleeding occurs mainly due to hormonal disorders, there are no specific preventive measures. However, following certain recommendations will help reduce the risk of their occurrence:
p, blockquote 42,0,0,0,0 —>
- Timely treatment of infectious and viral diseases, especially those that become chronic (tonsillitis, bronchitis, ARVI).
- Regular observation of pregnant women by an obstetrician-gynecologist, starting from early gestation, in order to identify and correct early and late toxicosis, edema of pregnant women, intrauterine disorders of fetal development, premature birth, fetal hypoxia.
- The teenage girl’s adherence to the principles of proper nutrition - eating foods rich in vitamins, excluding fast food, avoiding “diets” that involve prolonged fasting.
- Maintaining a menstrual calendar, which will help you pay attention to deviations when they first appear.
- Taking sedative medications to strengthen blood vessels and the nervous system (as prescribed by a doctor).
- Giving up bad habits, following a daily routine, getting enough sleep, regular physical activity, and playing sports.
- Notifying girls about the dangers of early sexual intercourse.
p, blockquote 43,0,0,0,1 —>
Separately, it should be said about the need to visit a pediatric gynecologist. Many mothers consider this unnecessary until the girl becomes sexually active. A visit to a pediatric gynecologist for preventive purposes, especially after the onset of menstruation, should become the same norm as visits to other doctors.
source
Heavy periods are normal for some women. Severe bleeding is considered a feature of physiology, the structure of the genital organs and blood vessels. But most often they occur in pathologies due to metabolic or hormonal imbalances. Even if there are no painful sensations, and the cycle is regular, it is advisable to visit a doctor to understand how serious the deviation is and how you can make blood loss during menstruation less noticeable.
- Hormonal disbalance
It is considered normal if menstruation appears no earlier than 11 and no later than 16 years, lasts 3-7 days, and its total volume is 40-100 ml. The color and consistency of menstrual blood also matter. Usually it is dark red, mucous, and does not contain large clots.
A convenient way to determine blood loss and whether it is normal is to count the number of absorbent sanitary pads that a woman has to use every day during her period. By summing up the number of pads used per day, you can find out approximately how much blood is lost over all days:
- Blood loss is considered “very light” if pads need to be changed 1-2 times a day (this corresponds to 6-9 g of discharge containing blood and mucus).
- For “light discharge”, it is necessary to use 3-4 pads per day (change every 6-8 hours, which corresponds to approximately 10-12 g).
- With “moderate” blood loss, pads need to be replaced once every 4 hours (13-15 g/day is released).
- “Heavy” discharge is considered to be such that the pads need to be changed every 3 hours (up to 18 g of blood is lost per day).
“Very large” blood loss is when the pad leaks every 1-2 hours. In this case, medical attention is already required, since obvious pathology is observed.
The amount and consistency of discharge is individual for each woman. They depend on hereditary and congenital features of the structure of the uterus, blood clotting, metabolism, temperament, lifestyle, nutritional system, physique, age. The following factors can affect the nature of the discharge:
- Use of hormonal contraceptives. They are taken to suppress egg maturation and ovulation according to a strictly defined pattern. Violation of the dosage regimen leads to the appearance of heavier than usual menstruation.
- Installation of an intrauterine device. In the first 3 months, periods may be longer and more abundant until the body gets used to the new hormonal levels.
- Use of duphaston and other hormonal medications. Stopping their use leads to a sharp increase in progesterone levels and the onset of copious bleeding after a few days.
- Taking anticoagulants and other medications that can reduce blood clotting.
The intensity increases if during their course the body is subjected to increased physical stress, if the woman experiences emotional stress.
Menstrual bleeding increases after an abortion or uterine surgery, as well as after childbirth. This is to blame not only for changes in hormonal levels, but also for disruption of the internal surface, which stimulates more intensive development of the endometrium. The occurrence of adhesions or scars in the uterine cavity leads to the appearance of clots of coagulated blood in the menstrual flow, resulting from its stagnation.
In adolescents within 2 years after the onset of puberty, as well as in women during the onset of the first menopausal changes, as a result of hormonal instability, heavy bleeding alternates with scanty bleeding during menstruation. Menstruation comes late or, conversely, too often.
https://youtu.be/NLd0QAh3348
Severe bleeding with clots can occur during menstruation if a woman has hormonal imbalances in her body or diseases of the uterus and appendages.
An increased content of estrogen leads to excessive growth of the endometrium and increased bleeding during menstruation. The cause of hyperestrogenism is a violation of the production of hormones of the pituitary gland, thyroid gland and other endocrine organs, the use of contraceptives and hormonal drugs, metabolic disorders and other factors.
Sometimes during pregnancy, due to a lack of progesterone, menstruation does not disappear. If your period comes with a slight delay, and the bleeding afterwards is heavy and painful, this may mean that a miscarriage has occurred at a very early stage.
Menstrual-like bleeding can also be heavy when an ectopic pregnancy occurs.
Increased abundance and pain of blood discharge occurs with endometriosis, the presence of uterine tumors (fibroids and cancer), the appearance of tumors in the ovaries, polyps in the endometrium or cervix. Inflammation of the endometrium also causes changes in its structure and increased bleeding during menstruation.
Often, with diseases and hormonal disorders, menstruation turns into uterine bleeding, which also appears between them. The danger of excessive blood loss is that the hemoglobin level decreases due to loss of iron. Sometimes, to stop bleeding, urgent medical attention is required, even complete removal of the endometrium (uterine curettage).
Signs of anemia are nausea, vomiting, weakness, dizziness, headache, fainting, and drop in blood pressure.
If there is excessive bleeding, leading to a deterioration in general health and loss of ability to work, it is necessary, first of all, to consult a doctor and find out the cause of this anomaly. An examination is carried out using ultrasound and hysteroscopy to study the condition of the endometrium and detect diseases of the uterus and ovaries. A blood test can reveal hormonal disorders and the presence of inflammatory processes.
Based on the examination results, treatment is prescribed and general recommendations are given on how to reduce the amount of menstrual bleeding. In case of hormonal disorders, oral contraceptives (Mersilon, Rigevidon) or progesterone preparations (Duphaston, Utrozhestan), drugs that suppress the production of estrogen in the ovaries (Pregnil) are prescribed. Homeopathic remedies (mastodinon, remens) are used to regulate hormonal levels.
Hemostatic medications are used that regulate blood clotting and strengthen the walls of blood vessels, such as etamsylate, dicinone, vikasol (a synthetic analogue of vitamin K, a natural coagulant). To strengthen blood vessels, it is necessary to take vitamin preparations containing vitamins C, K and group B.
Drugs that enhance uterine contractions (oxytocin, pituitrin) are used. They help make your periods shorter. To increase hemoglobin levels, iron supplements (maltofer) are prescribed.
Warning: All these products are used only as prescribed by a doctor. Failure to comply with the dose leads to vascular thrombosis. Instead, you can take decoctions of nettle, shepherd's purse, water pepper (1 tablespoon of herb is infused in 1 glass of boiling water). They are consumed 3 times a day, 50 ml.
If there is heavy bleeding during menstruation, it is recommended to avoid drinking strong tea and coffee and staying in the hot rays of the sun. To ease bleeding and pain, a cold heating pad is briefly applied to the lower abdomen.
https://youtu.be/unWtItWztNQ
source
Menorrhagia is a form of menstrual irregularity. It is characterized by an increase in the abundance and duration of bleeding during menstrual periods. Menorrhagia is considered a symptom of serious gynecological diseases. It requires immediate diagnosis and careful treatment, since ignoring the situation leads to the development of iron deficiency anemia.
Normally, menstruation lasts from 3 to 7 days . In pathological processes of the reproductive system, the amount of blood released exceeds 150 ml. In this case, the duration of menstruation is 7-14 days . This deviation indicates inflammatory or infectious processes in the pelvis. Menorrhagia is divided into two types:
- primary (develops during the first menstruation in adolescence);
- secondary (occurs in women with an established cycle).
Some women suffering from menorrhagia do not consult a doctor. They mistakenly take long periods for an individual characteristic of the body. Doctors believe that pathology requires qualified help. The main complication of menorrhagia is the development of anemia. It is accompanied by dizziness, pale skin, decreased performance and a tendency to faint. Signs of anemia have a negative impact on a woman’s condition.
The main manifestation of the pathology is profuse bleeding , including clots. The girl has to change her sanitary pad every 30-60 minutes. Menorrhagia is accompanied by intense pain in the lower abdomen . Their character can be pulling, cramping or sharp. Unpleasant sensations also affect the ovarian region and lower back. On the 4-5th day of menstruation, a woman notices the following symptoms:
- general weakness;
- loss of consciousness;
- blood pressure surges;
- signs of decreased hemoglobin in the blood;
- dizziness and headaches.
In some cases, bags under the eyes , bruises and bruises on the body , and bleeding gums . In rare cases, mucus is visualized in the vaginal secretion or purulent discharge appears . In addition, vaginal itching . In complicated situations, body temperature rises .
In the postpartum period, such discharge is considered a normal physiological process. But their occurrence is not associated with the work of the appendages. Bloody discharge that appears after labor is completed is called lochia. They are caused by intense contractions of the uterus after the birth of the baby. In other cases, among the reasons for heavy periods are:
- Hormonal disorders. The intensity and duration of menstruation depend on the thickness of the endometrium, which lines the inside of the uterus. It is he who is rejected at the onset of critical days. Its formation occurs under the influence of estrogens produced in the first half of the cycle. In case of hormonal disorders, their number exceeds the established norms. Thick endometrium increases the intensity of menstruation.
- Deviations in the functioning of the circulatory system. If blood clotting is poor, heavy discharge is especially dangerous. In this case, the woman notices bleeding from minor injuries.
- Consequences of using contraceptives. Menorrhagia may be the result of an individual reaction of the body to a method of protection. This happens both while taking the pills and after installing the fallopian device. In this case, intermenstrual bleeding is also observed.
- Neoplasms. Bleeding can be caused by the presence of tumors of malignant or benign origin. They tend to grow actively. When mechanically damaged, the tumors bleed and cause discomfort. These include fibroids, cysts, polyps and papillomas.
- Wrong lifestyle. Sometimes heavy bleeding is caused by intense physical activity, drinking alcohol or eating excessively spicy foods.
- Heredity. In rare cases, heavy menstruation is associated with characteristics that are passed down through the female line. Then the pathology is not temporary, but permanent.
Diagnostics
To find out the cause of abnormal periods, certain manipulations are carried out. First of all, the possibility of pregnancy is excluded. A woman needs to do a test to determine the level of hCG in her urine. If the result is in doubt, a blood sample is additionally examined for the presence of human chorionic gonadotropin. A blood fluid test will show pregnancy before the test.
To identify structural changes in the appendages and uterus, ultrasound monitoring . As part of its implementation, the size and position of the organs are determined. Using ultrasound, you can detect various neoplasms in the pelvic area. During a gynecological examination, a visual analysis of the vagina is performed to check for damage.
To obtain an expanded picture of the state of the reproductive system, hysteroscopy and biopsy . These studies evaluate endometrial, ovarian, and cervical tissue. In order to exclude cancerous tumors, a cytological examination of a vaginal smear . A biochemical blood test allows you to determine concomitant diseases or an inflammatory process in the body. Donating blood fluid for hormones is necessary to diagnose pathologies of the endocrine system.
Serious menstrual problems
Although most menstrual problems are not serious, a few conditions do require medical attention. These include:
Amenorrhea (lack of menstruation)
Girls who have not started menstruating by age 15 or 3 years after the first signs of puberty have primary amenorrhea. Amenorrhea can be caused by genetic problems, hormone imbalances, or problems with the development of the reproductive organs.
Hormonal imbalance can lead to secondary amenorrhea, when a girl with a regular menstrual cycle suddenly stops menstruating.
Since pregnancy is the most common cause of secondary amenorrhea, taking a pregnancy test is recommended. Besides hormonal imbalance and pregnancy, other factors that can cause both primary and secondary amenorrhea include:
- Stress
- Weight loss or gain
- Anorexia
- Stopping birth control pills
- Thyroid diseases
Intense training, especially in ballet, figure skating or gymnastics, combined with poor diet can also lead to amenorrhea.
Abnormal uterine bleeding
Abnormal uterine bleeding (AUB) occurs with heavy, prolonged and irregular menstruation.
Most cases of AUB are caused by an imbalance between the levels of estrogen and progesterone in the body, which leads to thickening of the endometrium. A thick endometrium can lead to heavy bleeding.
Girls with heavy periods have to change pads or tampons every 1-3 hours, and the menstruation itself can last more than 7 days. This can lead to complexes and reluctance to appear in public places these days due to the lack of ability to control bleeding.
Since many teenagers experience minor hormonal imbalances during puberty, girls often face the problem of heavy periods. But in some cases, heavy menstrual bleeding can be caused by problems such as:
- Fibroids (benign tumors) or polyps in the uterus
- Thyroid diseases
- Poor blood clotting
- Swelling, irritation, or infection in the vagina or cervix
- Dysmenorrhea (painful menstruation)
There are two types of dysmenorrhea that can prevent a girl from going to school, studying, sleeping and leading a normal lifestyle:
- Primary dysmenorrhea is very common during adolescence. This condition may be caused by prostaglandins. Large amounts of prostaglandin can lead to nausea, vomiting, headaches, back pain, diarrhea and severe cramps. Fortunately, these symptoms usually last no more than two days.
- Secondary dysmenorrhea is pain caused by polyps or fibroids in the uterus, endometriosis, pelvic inflammatory disease (PID), or adenomyosis. In this case, you should immediately consult a doctor.
Endometriosis
With endometriosis, the endometrium, which is usually found only in the uterus, begins to grow outside of the uterus - in the ovaries, fallopian tubes, or other parts of the pelvic cavity. It can cause abnormal bleeding, dysmenorrhea, pelvic and lower back pain.
Treatment
The selection of methods to eliminate the disease is carried out taking into account the cause of the disease. Most often, hormonal therapy is performed. But in some cases, surgery may be necessary. If menorrhagia is caused by the use of contraceptives, they are canceled. The selection of other medications is made only after the examination.
Therapeutic
Such treatment begins with taking iron supplements and ascorbic acid . They allow you to avoid the consequences of heavy periods and improve a woman’s well-being. To reduce the amount of menstrual flow, oral contraceptives are prescribed. Their action is based on adjusted proportions of gestagen and estrogens. The course of treatment is 3-6 months. The most common drugs include Yarina, Novinet, Jess, Regulon . They are distinguished by different concentrations of hormones, so the tablets are selected strictly on an individual basis.
One of the methods of treating menorrhagia is the use of an intrauterine system containing levonorgestrel . It has a contraceptive effect and suppresses endometrial growth, which automatically reduces the intensity of menstrual flow. After drug treatment, physiotherapeutic procedures are prescribed. The course includes 10-15 visits to the physiotherapy office.
Surgical
Surgery is necessary to eliminate tumors. Hysteroscopy involves curettage of the uterine cavity. The obtained tissue samples are sent for research. Reducing the thickness of the endometrium allows you to reduce the amount of blood loss several times.
Hysterectomy is performed in extreme cases when other methods are not suitable. The operation involves removing the genital organs or parts thereof. The main indications for such intervention are conditions that threaten the woman’s life. These include:
- adenomyosis and endometriosis;
- cancerous tumors;
- 3 or 4 degree of uterine prolapse;
- organ rupture as a result of bearing a child or labor;
- myomatous nodes;
- multiple polyps.
Heavy bleeding during menstruation - what to do?
For every woman of reproductive age, menstruation is normal. Since each body is individual, in some cases some disruptions may occur that affect the menstrual cycle.
As a result, heavy bleeding may occur during menstruation with unpleasant symptoms.
It is very important to know what to do in such situations, how to distinguish heavy discharge from bleeding, and when you need the help of a specialist.
Heavy bleeding during menstruation - causes
Excessive bleeding can be caused by several factors. Let's look at each of them in detail.
Uterine fibroids
This is a benign neoplasm that forms in the muscular layers of the organ. In the first stages of tumor development, any clinical manifestations may be absent. It is important to pay attention to any changes in your body and undergo annual preventive examinations with a gynecologist in order to identify the pathology in time and undergo treatment.
Among the complications of this disease are:
- problems conceiving a child;
- ectopic pregnancy;
- malfunctions of the organs of the reproductive system;
- twisting of the tumor stalk.
Adenomyosis
This is a pathological proliferation of endometrial tissue. In this case, drug treatment is not always effective and surgical intervention may be required. Complications of the disease include anemia and disturbances in the functions of the reproductive organs.
Endometrial polyposis
In some cases, doctors diagnose the presence of small benign formations that form from endometrial tissue. If treatment is not carried out, a number of serious consequences may develop:
- infertility;
- constant pain and discomfort;
- malignancy of neoplasms.
Cancer
This cause of bleeding during menstruation is the most dangerous. That is why you should not let such a symptom take its course. It is also very important to undergo a systematic examination by a specialist.
Pregnancy
Bleeding may occur during pregnancy, in the first trimester. At this time, the fertilized egg attaches to the walls of the uterus; this process may be accompanied by bloody discharge, since the body sometimes rejects the foreign body.
Other causes of heavy bleeding during menstruation
Other reasons include:
- attachment of the fertilized egg outside the walls of the uterus;
- spontaneous termination of pregnancy;
- emotional stress;
- hormonal imbalances;
- the presence of pathological bending of the cervix;
- artificial termination of pregnancy;
- presence of an intrauterine device;
- acute deficiency of B vitamins;
- Chronic diseases of the reproductive system.
Heavy periods or bleeding - how to determine?
Traditionally, menstruation begins between the ages of 12 and 15 years. The duration of monthly bleeding is on average up to 50-55 years. Next, the woman begins the period of menopause. The average duration of the menstrual cycle is 21-35 days. The first day of spotting is called the “first day of the cycle.”
Usually menstruation lasts no more than 7 days. During this period, the body is cleansed of epithelial cells and unfertilized eggs. On average, a woman loses about 70 ml of blood. In the first few days, the discharge may be heavy, this is normal.
Determining on your own whether it is normal or pathological is not always easy. The number of gaskets used can be a guide. There should be no more than 2-3 of them during the day.
You can distinguish normal from pathology by the following symptoms:
- sharply increased volume of blood released;
- the duration of critical days is more than a week, while the discharge does not reduce the severity;
- menstruation occurs more often than once a month;
- small traces of blood appear during menopause;
- discharge mixed with blood is present after sexual intercourse.
If you have at least one of these symptoms, you need to visit a qualified specialist.
First aid for heavy bleeding during menstruation - what to do?
First aid for heavy bleeding during menstruation at home is to take a Dicinone tablet. This drug can be purchased at any pharmacy chain without a doctor's prescription. It must be remembered that the medication is taken only in case of intense bleeding. Next, you should consult a doctor who will determine the cause of the problem and prescribe a competent treatment regimen.
To reduce the severity of discharge, you need to follow certain rules:
- drink as much clean water, teas, herbal infusions as possible;
- avoid excessive physical activity;
- do not take a steam bath;
- do not drink coffee and alcoholic beverages;
- take vitamin C and B.
You can also use a cold compress. Fill a heating pad with water at room temperature and apply to your lower abdomen. The duration of such a procedure should not exceed 15-20 minutes.
Also, to improve your condition, you can use:
- Decoction of stinging nettle. Drop 1 tbsp. plants in a glass of boiling water. Let it sit for half an hour. Then strain and drink throughout the day.
- Barberry decoction. Pour a glass of boiling water over a tablespoon of the plant and place on low heat. After half an hour, turn off the heat. When the broth has cooled, take a tablespoon three times a day. This remedy helps the walls of the uterus contract faster and promotes vasoconstriction.
- Lemon. This product is suitable for those women who do not suffer from diseases of the digestive system. To stop bleeding, you need to eat lemon and sugar in one go.
- Parsley decoction. Pour two tablespoons of parsley into a glass of boiling water. Let it sit until it cools completely. Then drink on an empty stomach before each main meal.
- Other herbs. You can also drink teas based on medicinal plants - cinquefoil, mint, raspberry, strawberry leaves, knotweed, valerian root.
Experts say that you cannot treat diseases of the reproductive system on your own. The mentioned remedies can be taken as first aid and only for one day. If heavy bleeding during menstruation does not decrease, you should visit a doctor.
Errors during menstruation
There are certain mistakes women make that can contribute to disruptions in the menstrual cycle.
On critical days you cannot:
- Exercise. Even minor physical activity can negatively affect increased blood flow in the pelvic organs. The consequence is bleeding. Intense exercise in the first two days of menstruation is especially dangerous.
- Complete bed rest. You shouldn’t go from one extreme to another by spending these few days in bed. A state of absolute rest can cause blood stagnation and increased pain.
- Taking a bath and other ways to overheat the body. With strong vasodilatation and increased blood circulation, bleeding may occur.
- Maintaining an active sex life. According to most experts, it is better to refuse intimacy these days.
- Wrong diet, strict diet. An unbalanced diet causes vitamin deficiency, and this negatively affects the condition of all internal organs, the level of hemoglobin decreases, and there is a risk of bleeding.
- Alcoholic drinks. Doctors say it is better to refrain from drinking alcohol during this period.
- Use tampons exclusively for hygienic purposes. Failure to maintain personal hygiene when changing tampons or pads.
Medicines for heavy bleeding during menstruation
It is important to remember that any medications should be prescribed only by a doctor. The following tools are usually used:
- dicinone;
- calcium gluconate;
- ascorutin.
Such drugs are used for mild symptoms. In case of severe bleeding during menstruation, medications are administered by injection:
- vikasol;
- dicinone;
- tranexam.
Typically, with serious bleeding, the patient must be hospitalized and treated in a hospital. Oral contraceptives, hemostatic drugs, and Oxytocin are also prescribed for rapid contraction of the uterine walls. It is imperative to prescribe medications containing iron, with which you can restore hemoglobin and prevent the development of serious anemia.
Ways to treat heavy period bleeding
The treatment prescribed in each individual case is different, it is determined by the characteristics of the body, the main factor in the development of pathology:
- To stop bleeding, special medications are prescribed.
- The use of hormonal drugs is indicated.
- Women who have given birth may be prescribed surgical cleaning.
- Taking immunostimulants and vitamin preparations.
- Sedative drugs.
- Drugs to restore hormonal balance.
- Drugs to stop bleeding.
Implantation bleeding
When the fertilized egg attaches to the walls of the uterus, slight bloody discharge may be present. This is due to the fact that when a fertilized egg implants into the uterus, it leaves behind microdamages.
The duration of such discharge is no more than two hours. They should not be intense or accompanied by suspicious symptoms: weakness, fever, dizziness, fainting. Their color normally varies from pink to brown. Painful sensations may also occur. You should not do anything on your own; it is better to consult a gynecologist.
Bleeding from the genital tract in the postpartum period
Postpartum discharge is a natural phenomenon; the body cleanses itself. Their duration should not exceed 8 weeks. Otherwise, you need to contact specialists.
A gynecologist may suspect the development of pathological processes if the following symptoms are present:
- pronounced unpleasant odor of discharge;
- excessive bleeding, changing the pad every hour;
- At the same time, you feel severe weakness, dizziness, and your blood pressure drops sharply;
- There are no clots, the discharge is watery.
In what cases should you immediately call an ambulance?
You should contact your doctor if you change pads too often, if there is heavy discharge with clots, if heavy bleeding lasts a week, and if the following symptoms appear:
- intense pain in the lower abdomen;
- weakness and lethargy due to loss of large amounts of blood;
- nausea or vomiting.
Such symptoms require immediate contact with a gynecologist.
Source: https://GetFirstHelp.ru/krovotechenie/silnoe-krovotechenie-pri-mesyachnyh
Menorrhagia in adolescents
The development of pathology in girls aged 12 to 16 years is due to hormonal imbalance . This phenomenon is typical during puberty. The pathology is aggravated by blood clotting disorders, changes in the structure or volume of the thyroid gland, and genital infections.
In some cases, heavy menstruation develops against the background of polycystic ovary . Cysts form on the appendages, which cause a delay in menstruation. Meanwhile, the endometrium is actively growing. At a certain point, it is rejected, which causes prolonged and heavy bleeding. To treat the disease, you need to contact a gynecologist-endocrinologist.
As part of the general examination, the level of hemoglobin . If necessary, prescribe iron-containing medications. To normalize the cycle, hormonal drugs are prescribed. When selecting them, the weight, age and hormonal status of the patient are taken into account. In adolescence, low-dose drugs with an estrogen content of no more than 35 mcg are indicated.
Common menstrual problems
Premenstrual syndrome (PMS)
Before menstruation begins, women often experience symptoms such as mild bloating or breast tenderness. In addition, PMS is accompanied by a number of emotional symptoms that begin in the second half of the menstrual cycle and end after the period begins.
PMS includes a variety of physical and emotional symptoms, such as:
- Acne
- Bloating
- Chest pain
- Headache
- Constipation
- Diarrhea
- Increased feeling of hunger
- Depression
- Irritability
- Anxiety
PMS worsens 4 days before the start of menstruation and disappears 2 to 3 days after it begins.
Although the exact cause of PMS is unknown, it appears to be due to changes in hormone levels in the body. In the second half of the menstrual cycle, the amount of progesterone in the body increases. Then, about 7 days before your period begins, both progesterone and estrogen levels begin to drop.
Some girls are more sensitive to hormonal changes than others. Talk to your daughter's doctor if the symptoms she is experiencing are interfering with her normal activities.
Spasms
Girls often experience lower abdominal cramps during the first few days of their period. They are caused by the chemical prostaglandin. These involuntary contractions can range from slight to sudden and intense.
Ibuprofen, which is recommended to be taken for the first 2-3 days, will help get rid of cramps. If the spasms progress to severe seizures that keep her from going to school or going out with friends, see a doctor.
Irregular cycle
In adolescents, the cycle becomes regular up to 2 - 3 years after the first menstruation. During this time, the body adjusts to the influx of hormones that characterize puberty. A typical adult woman's cycle is 28 days, although some may have 24 or 38 days.
Changing hormone levels affect the length of menstruation. In one month it may last only a few days, and in the next it can last a whole week. In addition, one month menstruation may be completely absent, and the intensity of bleeding may also change.
If after 3 years the cycle has not stabilized, consult a doctor to find out the reason. It is worth consulting a doctor if the cycle is less than 24 days or more than 38 days, as well as if there is no menstruation for 3 months.
Late menarche
Girls reach puberty at different times. For some, menarche (the medical term for the first menstrual bleeding) occurs at age 9 or 10. For others, at a later age. So just because your daughter is a late bloomer doesn't mean anything is wrong.
Genetics plays an important role in the beginning of the menstrual cycle. Very often, girls' first periods begin at the same age at which their mother or grandmother began. Additionally, some ethnic groups go through puberty earlier than others. For example, African American girls experience puberty earlier than Caucasian girls.
It is worth worrying if menstruation has not appeared by age 15 or 3 years after the onset of puberty, which begins with breast development.
Prevention of menorrhagia
Heavy periods have a significant impact on a woman's quality of life. They reduce performance and worsen overall well-being. Prevention of pathology helps to avoid unnecessary health problems. It is recommended to adhere to the following principles:
- Regular visits to a specialist help identify gynecological ailments in the early stages of their occurrence.
- Maintaining hygiene will reduce the likelihood of developing infectious diseases.
- Control over sports activity will help prevent menorrhagia caused by physical fatigue.
- Proper nutrition and giving up bad habits have a beneficial effect on the functioning of the circulatory system.
- Wearing warm clothes in cool weather and protection from drafts will protect against inflammatory processes in the pelvis.
- To prevent menstrual irregularities, it is recommended to avoid sudden climate changes and stressful situations .
- Keeping a monthly calendar helps in early diagnosis of abnormalities.