Pipelle endometrial biopsy is the removal of a small fragment of the mucous membrane from the uterine cavity for subsequent analysis. The manipulation is carried out using a special catheter, a small flexible plastic tube with a diameter of about 3 mm. Compared to traditional aspiration biopsy, which is performed using a special syringe or vacuum instrument, the pipell procedure is more gentle, does not require anesthesia and takes 7-10 minutes.
Indications for use
Indications for the study are:
- bleeding during menopause;
- lack of menstruation (amenorrhea);
- scanty periods (dysmenorrhea);
- long, heavy periods;
- acyclic uterine bleeding;
- infertility;
- recurrent miscarriage;
- endometrial polyps;
- myoma;
- endometrial hyperplasia;
- endometrial tumors to determine their malignancy;
- suspected endometriosis;
- suspicion of an inflammatory disease of the uterine mucosa (endometritis);
- assessment of the effectiveness of hormonal treatment.
Pipelle biopsy is often recommended before IVF to increase the likelihood of embryo implantation.
Histological examination of pipell biopsy of the endometrium
Histological examination of pipell biopsy of the endometrium
- histological examination of the internal mucous membrane of the uterus, which was obtained using the “Pipel biopsy” method and the prescription of effective treatment. Pipelle biopsy is a technique for vacuum aspiration of the endometrium for further diagnostic research. To perform aspiration biopsy, the Pipel instrument is used. This is a flexible plastic cylinder with a diameter of 3 mm, which is inserted into the uterine cavity.
Pipelle endometrial biopsy is a new method of endometrial biopsy that avoids many of the problems that can occur with traditional biopsy. This biopsy method has advantages over the conventional procedure in cases where the patient is at risk of spreading endometriosis, cancer cells, and certain general diseases (diabetes, etc.).
The procedure is painless and is performed under local anesthesia. Moreover, a pipel biopsy is included in the list of mandatory studies performed before conception and during the examination for miscarriage.
The advantages of Pipelle endometrial biopsy: a low-traumatic procedure, minimal intervention in the uterine cavity, no risk of spreading infection or cancer cells, painlessness, the ability to be performed on an outpatient basis, a low percentage of complications and high information content of the material obtained.
The purpose of histological examination is to detect pathological deviations from the normal structure of tissues, identify malignant cells or their precursors, and the extent of the pathological process.
Indications:
- Bleeding in women during menopause.
- Bleeding when taking hormonal drugs.
- Suspicion of endometrial cancer.
- Suspicion of endometriosis.
- Suspicion of endometrial hyperplasia.
- Identifying the causes of menstrual irregularities.
- Endometrial polyps.
- Suspicion of uterine fibroids.
- Diagnosis of inflammation of the uterine mucosa.
- Suspicion of oncological processes in the uterine cavity.
- Assessment of the condition of the internal mucous membrane of the uterus in case of infertility.
- Assessment of the condition of the endometrium after hormone therapy.
- Taking a sample of endometrial tissue for bacteriological examination.
Preparation
Conditions for preparation are determined by the attending physician.
Before performing a pipell biopsy of the endometrium, it is necessary to conduct some studies:
- blood test for HIV, hepatitis, RW;
- general blood analysis;
- vaginal smear for microflora and cytology;
- ultrasound diagnostics to identify the localization of the pathological focus.
Preparation for the procedure
During the last menstrual cycle before the biopsy, it is necessary to protect against pregnancy, as it is a contraindication to the study.
Since the research method is a surgical intervention, the following tests will be required:
- general blood and urine tests;
- blood biochemistry;
- blood for HIV, syphilis, hepatitis B and C;
- vaginal smear for microflora to identify a possible inflammatory process;
- smear for oncocytology;
- hCG test to exclude pregnancy;
- coagulogram to detect bleeding disorders.
On the eve of the procedure, it is necessary to maintain sexual rest, do not use suppositories, tampons, or douche. The doctor may recommend taking No-Shpa 40 minutes before the examination to relieve possible spasm of the uterine pharynx. The dosage of the medicine is selected individually. Immediately before the procedure, you must empty your bladder.
How to prepare for the procedure
Before taking biological material, the patient needs to perform the following studies:
- general blood analysis;
- smear for oncocytology;
- smear on vaginal flora;
- blood test for HIV, syphilis (RW), hepatitis B and C;
- It is advisable to have an ultrasound of the pelvic organs.
Preparing for a pipell endometrial biopsy is not difficult.
Do not take blood thinning medications for about 5 days. On the eve of the study, refrain from sexual contact. Do not douche. Perform a cleansing enema before the procedure.
How the research is carried out
The doctor appoints a day for the procedure according to the indications. For example, to assess the condition of the endometrium and identify insufficiency of the second phase of the cycle, a biopsy is performed on days 21-23 from the start of the last menstruation, and to exclude chronic endometritis, it is necessary to carry out the procedure on days 9-13 of the cycle - during this period there are normally no inflammatory cells in the endometrium.
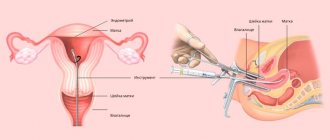
The procedure is performed on an outpatient basis and almost always without anesthesia. At the first stage, a gynecological examination is performed on a chair and the vagina and cervix are sanitized with special medications, while the latter is fixed with bullet forceps.
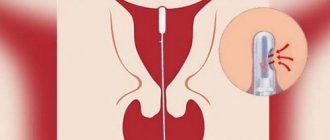
The biopsy technique involves inserting a sterile disposable pipell instrument, which is a flexible plastic tube with a piston, like a syringe, into the uterine cavity through the vagina and cervix. When pulling the piston, negative pressure is created, as a result of which the catheter is suctioned to the wall of the uterus and endometrial particles are aspirated through the side hole in the tube. Tissue is collected from three different areas of the mucosa. The resulting material is placed in a formaldehyde solution and sent for histological examination.
What is pipell endometrial biopsy?
Aspiration pipel biopsy of the endometrium is performed using a pipel-type probe. It is a hollow flexible silicone tube with a diameter of about 3 mm, at the end of which there is a hole. A piston is inserted on the opposite side.
To collect tissue, the doctor carefully inserts the probe into the uterine cavity and pulls back the piston. This creates negative pressure. The endometrium is stretched and enters the cavity of the tube, the contents of which are then sent to the laboratory.
A flexible, soft and thin tube provides the most delicate effect on the tissues of the genital organs, so aspiration performed using the “Pipel” is a painless and minimally invasive manipulation.
The procedure is prescribed:
- For bloody discharge during the intermenstrual period (acyclic bleeding).
- For bleeding in menopausal women.
- For pain during sexual intercourse.
- If ultrasound reveals endometrial pathology.
- For the diagnosis of infertility and miscarriage.
- To monitor the condition of the endometrium during hormonal therapy.
Pipel endometrial biopsy before IVF or when planning pregnancy is also included in the list of mandatory studies.
Advantages of the method
Pipelle endometrial biopsy is a minimally invasive and virtually painless procedure, in contrast to diagnostic cleaning, which is essentially a surgical intervention. Curettage is performed exclusively in a hospital using general anesthesia. After it, the woman needs to stay in the clinic for several hours, and if complications arise, for a day.
Pipelle aspiration biopsy of the endometrium is performed on an outpatient basis. The insertion of the probe does not require dilation of the cervical canal, is less traumatic and involves the use of local anesthesia. Due to the minimal invasiveness of the intervention, the risk of complications is minimized. The procedure, as a rule, does not affect the woman’s well-being, which allows the patient to leave the clinic immediately after the procedure.
In terms of its diagnostic value, the Pipelle biopsy technique is not inferior to curettage.
Pipel endometrial biopsy: interpretation of results
Histological examination of the endometrium is completed on average within a week.
Results of pipell biopsy of the endometrium during histological examination:
- The analysis may not reveal deviations from the age norm and cycle phase. This is a negative result, which means the woman is healthy.
- The study can diagnose pathological growth (hyperplasia) of the endometrium and determine its type.
Hyperplasia is a benign pathology caused by an excess of female sex hormones. Most cases (about 75%) occur during the premenomaus period.
Histology allows us to identify 4 types of hyperplasia:
- Simple diffuse or glandular.
- Complex (adenomatosis).
- Local, which means the presence of single polyps.
- Atypical, which is characterized by the presence of atypical cells.
Reference! Cells with a disrupted structure that do not correspond to their normal (typical) characteristics are called atypical. Atypia may be characterized by loss of polarity of arrangement and disruption of the structure of the nuclei.
Detection of cellular atypia is important for the prevention of endometrial cancer, since some of their types are capable of malignancy and are considered a precancerous condition.
- Endometrial cancer is diagnosed when malignant cells are detected.
- Histological examination may reveal insufficient thickness of the mucous membrane - atrophy or hypoplasia.
- Based on the results of the analysis, a diagnosis of endometritis can be made - an inflammatory process of the tissue lining the uterine cavity.
- The discrepancy between the thickness of the endometrium and the phase of the cycle during which the material was collected indicates hormonal disorders in the patient.
After the procedure
After the biopsy, there may be bloody discharge, which should not contain clots, pus or an unpleasant odor. If these phenomena still appear, you should immediately consult a doctor. Normally, minor bleeding stops quickly, as it is a reaction to mechanical stress. Contractions of the uterus are also possible, but they disappear during the day or after taking antispasmodics.
During the recovery period, which lasts 2 weeks, you cannot:
- engage in sexual activity until the bleeding stops;
- take a bath, you should limit yourself to a shower;
- lift weights;
- visit the bathhouse and sauna;
- perform douching;
- use tampons.
pregnancy after endometrial biopsy
Girls, hello everyone. I'm back with my thoughts again. But suddenly you had something similar. What we have. 33 years old, no pregnancies, abortions, no terrible gynecological diagnoses. The cycle is stable 28-30 days, months. They go well and are not painful. All my life my endometrium was 7-8 mm in the second phase of the cycle, none of the doctors ever told me that this was bad and needed to be treated. My husband and I have been planning a child for almost a year, there is no pregnancy yet, my husband has oligospermia of 10 ml. in 1 ml. My husband is being treated by Mskhalaya, I underwent examinations at the Eco Clinic and am being observed by Re. Well, considering my age, my husband’s diagnosis and the result of a year of attempts, I was mentally ready to go for IVF, so we went straight to the Eco clinic. What they did to me: 1. Hysteroscopy to remove an endometrial polyp in 2015, according to histology everything is ok, chronic. no endometritis. Afterwards I took only antibiotics, no other treatment was prescribed. 2. This year Pipel biopsy at 20 dc, the endometrium corresponds to the early stage of the secretion phase. HE no. Ryo said it’s not critical, but it can be improved, like the endometrium is a little late to mature. I asked to do Paypel with IHC, Ryo told me I didn’t need it. 3. Doppler of the uterus. The blood flow is excellent. 4. Hormones are all normal, except for a slightly elevated DHEA-S. But Ryo doesn’t focus on this. 4. Actovegin, Curantil, Divigel, vitamins were prescribed 2 cycles ago. Against the backdrop of all this (I sin on Divigel), the fall grew. cyst (maybe a coincidence, but before there were no cysts or were not found, as they say). The endometrium has grown to 8.5 mm, which means there is a response to medications. It's 1 month now. Ryo appointed Yarina. If the cyst goes away, he prescribes magnetic therapy and Actovegin, Curantil WITHOUT Divigel. BUT Re never identified the reason for the thin endometrium, I asked her, she tried to explain something to me about receptors and that’s it. The blood flow is good, cholecystectomy was not performed in the anamese, there were no cleanings other than hystera, hormones seem to be normal. And then what? Does it even make sense in my case to go to physio, maybe it’s just my endometrium, my peculiarity. As I understand it, physiotherapy gives an effect for 2-3 months, plus you cannot plan physiotherapy during a cycle. That is, we will not be able to plan now that my husband is drinking clostobegyt to improve his SG, and after it is discontinued, his SG will return to normal. That is, the treatment of my husband and I turns out to be quite inconsistent. As a result, we have 1-2 cycles with good endometrium for our tests. And then IVF, to which, logically, I will have to undergo physiotherapy again? In general, is it possible that there is no specific reason for thin endometrium or is it a feature of my body and does not need to be treated? Or did they just not examine me further and send me straight to physio?
Decoding the results
The results of an endometrial biopsy will be ready in 7-14 days, it all depends on the clinic where the research is carried out and the overall workload of the laboratory. The conclusion, which is issued after a histological examination of the biopsy, consists of 4 parts.
Information content of the sample:
- an uninformative, inadequate sample is determined by the fact that the obtained material does not contain a sufficient number of endometrial cells; blood cells, squamous stratified epithelium of the vagina, columnar epithelium of the cervical canal may be present;
- An informative, adequate sample is characterized by the fact that a sufficient number of mucosal cells are present in the biopsy specimen.
Macroscopic description of the biopsy:
- weight of submitted samples;
- size of fragments (large, small);
- color (from gray to bright red);
- consistency (loose, dense);
- blood clots, blood clots;
- slime.
Microscopic description of the biopsy:
- type of epithelium (cylindrical, cubic, flat, indifferent), its size, number of layers;
- stroma (its presence, density, homogeneity);
- size and shape of stromal cells;
- fibroplasticity of the stroma, that is, the number of connective fibers;
- decidu-like stroma, that is, accumulation of fluid and nutrients;
- uterine glands, their shape, description of the epithelium lining them;
- the shape and size of the lumen of the glands, the presence of secretions inside the glands, branching;
- lymphoid accumulations as signs of inflammation;
- chorion cells, the presence of edema or dystrophic changes in them, indicating that the woman had a frozen pregnancy or an incomplete spontaneous abortion.
Making a diagnosis after receiving the results
Diagnosis:
- It is indicated which phase of the cycle the endometrium corresponds to.
- The presence of hyperplasia (proliferation) of the endometrium.
- The presence of polyps and a description of the tissue from which they consist.
- The presence of endometrial atrophy (thinning of the uterine mucosa).
- Hypoplastic mixed endometrium (borderline condition, not a disease).
- Chorionic villi, which are particles of the fetal membrane, indicate an interrupted pregnancy.
- Degeneration of the epithelium or vessels of the chorionic villi (indicates that the fetus initially did not receive nutrients, which could cause its death).
- The presence of atypia, that is, cells with signs that are not characteristic of a given tissue (indicates a precancerous condition of the endometrium).
- The presence of malignant (cancerous) cells (indicates endometrial cancer).
Often the conclusion contains only one phrase: “Normal endometrium in the proliferation/secretion/menstruation phase.” It means that the endometrium is normal, no signs of disease or changes in cell structure have been detected, there are no polyps or hyperplasia. It is important that the condition of the endometrium corresponds to the phase of a woman’s menstrual cycle and the period of her life.
The results of the study reveal:
- discrepancy between the thickness of the mucous layer and the norm;
- the presence of endometritis;
- malignant neoplasms;
- atypical hyperplasia;
- precancerous condition;
- the presence of fibroids and polyps;
- presence of endometriosis.
After receiving the conclusion, you can contact your doctor to prescribe a therapy regimen or other treatment methods.
Endometrial biopsy: what is it?
An endometrial biopsy is an intravital sampling of tissue from the lining of the uterus (endometrium) for subsequent histological and histochemical analysis. This procedure refers to minor surgical interventions in gynecology and is most often performed as an independent study. But in some cases it is included in the protocol of a “major” operation and is performed intraoperatively on an emergency basis.
A biopsy most often serves purely diagnostic purposes. But in some cases, it is a therapeutic and diagnostic manipulation that allows you to obtain the information the doctor needs and at the same time improve the woman’s condition. The preparation process, the extent of the intervention, and whether the woman will be in pain or not also depend on the type of biopsy used.
Possible complications
As after any surgical intervention, complications are possible after a pipel biopsy:
- prolonged bleeding;
- accession or activation of latent infection;
- long-term painful sensations;
- damage to the uterine wall.
The following symptoms indicate their development and the need to see a doctor:
- heavy bleeding (more than 3 pads in 2 hours);
- severe pain in the lower abdomen and lower back that does not subside after taking painkillers;
- bleeding for more than 5 days;
- discharge with an unpleasant odor;
- temperature rise above 37.5ºС.
The most dangerous complication of a biopsy is endometritis. It is characterized by abdominal pain and the appearance of foul-smelling uterine discharge with signs of suppuration. Its development is associated with hypothermia or non-compliance with the regimen after the procedure and the doctor’s recommendations.
When is a pipell endometrial biopsy performed?
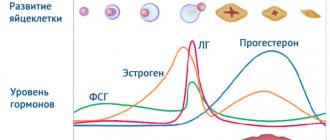
Since the endometrium is a hormone-dependent tissue, when taking a biopsy it is important to choose the right day of the monthly cycle. It depends on the purpose of the diagnosis.
On what day of the cycle is a Pipe biopsy performed?
To confirm the diagnosis of chronic endometritis, mucous tissue is collected in the first phase of the cycle. If the corpus luteum is insufficient, the analysis is performed in the second phase.
In case of luteal phase deficiency, a sample is taken on the first day of menstruation or the day before it begins.
For polymenorrhea (heavy periods) - on days 5-10 of the cycle. In case of acyclic bleeding, a biopsy should be performed in the first 2 days after the onset of menstruation or bleeding.
To track the dynamics of hormonal therapy, tissue is taken in the second phase of the cycle. If a malignant neoplasm is suspected, a pipel biopsy can be performed on any day of the cycle.
Pipel endometrial biopsy
To accurately evaluate the endometrium, it is necessary to take a sample of the uterine endometrium for further testing in the laboratory. This procedure is necessary in order to assess the presence of pathologies of the uterine mucosa. This procedure is used in the comprehensive diagnosis of female infertility.
A gentle method of obtaining material for research is pipell biopsy of the endometrium.
Pipelle biopsy of the endometrium is a modern method for diagnosing pathological conditions of the endometrium. During the procedure, a thin plastic tube (Pipel) is inserted into the uterus, and a small part of the mucous membrane is removed from it. The material is sent to the laboratory for histological, cytological or immunohistochemical studies.
Based on their results, the doctor can clearly say whether the patient has endometrial pathologies such as:
- Polyps, fibroids
- Endometritis
- Endometrial hyperplasia
- Endometrial hypoplasia
- Oncological diseases and others.
Pipel biopsy helps to identify the cause of menstrual irregularities, heavy menstrual bleeding, bleeding from the uterus, and also monitor the condition of the endometrium after hormone therapy.
Thanks to this procedure, the doctor can choose the right tactics for treating female infertility or reduce the risks of implantation failure in an IVF protocol.
Pipelle biopsy, unlike conventional biopsy, does not require dilation of the neck, since the instrument (Pipel) is quite thin - 3 mm. Pipelle biopsy is performed on days 7-11 of menstruation. cycle. If an immunohistochemical study is planned, then the procedure should be carried out on the 19-21st day of menstruation. cycle. The results of the study are usually ready 7-10 days after the pipel biopsy.
Advantages of pipell endometrial biopsy:
- It is carried out quickly (no more than 5 minutes)
- Pipelle biopsy is practically painless and does not require anesthesia
- Performed on an outpatient basis
- Only disposable sterile instruments are used, infection is excluded
- Better cost than conventional biopsy
- Reduces the risk of inflammation
The procedure itself is simple and gentle for women.
Indications:
- carrying out diagnostics before planning IVF
- infertility of unknown origin
- suspicion of polyps, uterine fibroids
- failures in IVF programs
- recurrent miscarriage
- menstrual irregularities
- heavy menstrual bleeding (including bleeding during menopause)
- changes in the endometrium identified by ultrasound examination
- monitoring the condition of the endometrium after hormone therapy
Contraindications:
- common infectious diseases
- suspicion of pregnancy
- inflammatory processes of the cervix or vagina
- pathology of the hemostatic system
You can undergo the pipel biopsy procedure in Nizhny Novgorod at the full cycle infertility treatment clinic “Dad, Mom and Baby”.
Our specialists will carry out this procedure as quickly and safely as possible!