Our expert:
Tatyana Nikolaevna MOKRINSKAYA
Doctor's Instagram:
https://instagram.com/doctor_tani?igshid=1dxfkx7d5dzl9,
obstetrician-gynecologist, gynecologist-endocrinologist, leading specialist of the Laguna-Med clinic, doctor of the highest category. Work experience - 37 years.
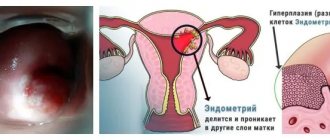
Endometrial hyperplasia... Usually this unpleasant diagnosis frightens women, as it is associated with a precancerous condition, and these fears are not always unfounded. However, in most cases, the disease does not pose a threat to the health and especially the life of a woman, if, of course, treatment is started on time. What is the endometrium and why its growth is dangerous, we will talk in this article.
Analysis for histology of the cervix
Histological examination is the most informative way to determine diseases of the female reproductive system. The procedure can be prescribed to patients of any age. Unlike cytology, this is not a preventive, but a planned study.
Histological analysis helps to find and eliminate the causes, if indicated:
- infertility, non-developing pregnancy, miscarriages;
- unstable uterine cycle (menstrual, secretory phases), absence of menstruation, bleeding outside the menstrual cycle - a bad symptom;
- pain in the abdomen, uncharacteristic vaginal discharge, discomfort during sexual intercourse;
- suspicion of the presence of cancer when abnormal cells are detected during a screening cytological study;
- establish the state of the endometrium at the beginning of the cycle and at its end.
Important! Analysis of the histology of the cervix is contraindicated if the patient has low blood clotting, pregnancy, menstruation, or an inflammatory process has been detected in the organs of the reproductive system.
This method, due to sufficient trauma, is used only in cases where other types of diagnostics do not provide all the necessary information to establish a diagnosis or the results of other studies have a number of contradictions.
Histology analysis is prescribed if there are signs:
- leukoplakia (whitish plaques in areas of keratinization in women of reproductive age);
- endometrial hyperplasia (abnormalities in the growth of tissues or organs during cell division in the body);
- a large number of malignant cells were detected in the cytological smear;
- unevenness of the cervical canal (transition of the cervix to the uterus).
Preparation and execution
During the day before the scheduled test, it is not recommended to:
- use vaginal suppositories;
- use any gynecological medications (except those prescribed by a doctor);
- douche;
- have sexual intercourse.
Obtaining the endometrium of the uterus for analysis can be done in several main ways.
- Excisional biopsy. It is produced by excision of a small amount of the necessary material during surgery.
- Pipelle biopsy. It is based on the introduction of a nominal device into the uterus, which is a thin plastic tube with a hole that captures tissue. The manipulation is painless, easy to perform and quite popular in gynecological practice.
- Needle biopsy. In this case, special long needles are used to allow the collection of the endometrium and the liquid contents of neoplasms in the uterus, if any. Most often, the method is used when malignant tumors are suspected.
- Forceps biopsy. One of the most common gynecological methods for collecting material for research. It is performed by biting off the required amount of tissue in the uterine cavity with medical forceps. The disadvantage of the method is the selective targeting of material collection: biopsy forceps touch the tissue locally and pathological formations (polyps) that are too small in size may not be in the area of the forceps. The doctor has to perform several such pinchings.
- Aspiration biopsy. The technique is based on suction with a special electrical device of a solution previously introduced into the uterus, which contains pathological cells. The method allows you to obtain a wash from the entire surface of the endometrium, which is important in the diagnosis of endometritis.
- Curettage or scraping of the inner walls of the uterus. It is carried out to collect endometrium from the inner uterine surface, the cervix.
- Sometimes the study is carried out by excision of tissue from already removed organs, for example, after a hysterectomy.
The accuracy of determining the disease depends on the volume of the material studied. The effectiveness of the indicators is also influenced by the chosen method of collecting the endometrium of the uterus for histological examination.
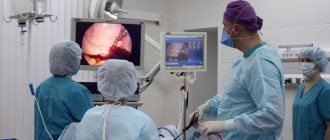
How is a histology analysis done and methods of tissue sampling?
Unlike a conventional smear, histology examines the structure of the tissue as a whole and is able to assess the localization of atypical blood vessels and the boundaries of the area of the pathological process. For the study, a cervical biopsy (tissue sampling) is performed, the optimal method of which is determined by the doctor.
Among the methods of tissue collection are:
- biopsy (incisional, excisional);
- scraping of the cervix;
- puncture – puncture with a needle under the cervix;
- fingerprint smear (taking a tissue sample from the endocervix - the mucous membrane of the cervix).
Before the procedure, it is recommended to prepare: take a blood test for the presence of sexually transmitted diseases, a smear for cytology, examine the cleanliness of the vagina, refuse sexual intercourse and suspend local treatment for two days. So it is better to avoid douching and chemical products for intimate hygiene. This precaution reduces the likelihood of erroneous results. The duration of the procedure, when a smear is taken for cytology, is 15 minutes along with the examination.
Tissue collection for cytological examination takes longer and is performed as follows:
- The patient sits on a gynecological chair, the doctor examines the cervical canal using a colposcope to identify the area of pathology;
- Using various techniques (scalpel biopsy, laser, electric knife), material from the affected tissues is obtained. The prepared drug is sent to the laboratory for research;
- The damaged area of the cervix is treated with a hemostatic drug, and if bleeding is present, it is sutured.
After the procedure, a piece of tissue is placed in formalin or ethanol, the doctor makes a thin section and stains it using hematoxylin and eosin. In some cases, the histological specimen may be placed in paraffin. Under the influence of the dye, the composition of the tissue changes color: proteins become red, and nucleic acids acquire a blue tint. The histologist places the section under glass and uses an electron microscope to examine the prepared sample in order to identify pathology and deviations from the norm. Healthy cervical epithelium is brown in color with the same cell size; deviations from the norm indicate the presence of a disease.
How the material is studied
There are two main methods for histological examination of the endometrium: standard and accelerated.
Accelerated
It is prescribed mainly in emergency cases, when the result of the study must be obtained within an hour. For example, this is necessary during an operation directly on the operating table, when the surgeon urgently needs to make a decision about removing or preserving an organ.
A sample of the endometrium taken from a woman is frozen, cut into thin layers, and in this form is carefully studied using special laboratory equipment. Typically, samples are examined using electron, light, fluorescence, or scanning microscopes. And the use of a phase-contrast apparatus allows you to obtain a more accurate result and notice those inclusions that cannot be detected using standard microscopy.
Standard
Tissue samples studied using the standard method are filled with formalin, osmic acid or ethanol, cut into thin fragments and stained. The staining process occurs with the help of eosin or hematoxylin, which make it possible to discern the presence of pathologies in the endometrial tissues of the uterus. For example, a substance such as hematoxylin colors acids blue and proteins red.
If there is no need to study samples for some time, they are stored in a formaldehyde solution in cut form. This method helps preserve the structure of materials indefinitely and delay the time of analysis.
Deciphering the histology of the cervix
A histologist (pathomorphologist) examines samples for about 7 days - a complete analysis. For emergency situations, there is express diagnostics - a quick but less accurate method that allows you to get results within 24 hours after the procedure.
Important! In a private clinic, a transcript form is given to the patient in writing, which indicates personal data, date of collection and material, solution, type of diagnosis. All tissues and possible neoplasms are listed at the end of the document. All terms are in Latin.
The laboratory doctor only issues a conclusion. The document, regardless of the result obtained, does not contain any recommendations. Your doctor will help you decipher all the information on the form during your appointment. He compares the results of histological examination, analyzes the clinical picture with the medical history and other diagnostic methods. Based on all available information, the doctor makes a diagnosis and prescribes treatment, the duration of which depends on the severity of the identified pathology.
What does the analysis of cervical histology show?
Histological examination reliably establishes or refutes the presence of any pathologies, malignant formations, and determines the degree of differentiation (predisposition of elements).
The results of the study are divided into groups:
- normal (all cervical tissues are absolutely healthy);
- atrophic and inflammatory processes were identified due to age, hormonal changes, and the presence of a pathogen;
- mild dysplasia (low grade), koilocytosis;
- moderate and severe dysplasia (high degree of epithelial change);
- invasive cervical cancer (hidden or mild symptoms).
Analysis of the histology of the cervix shows the degree of cell atypia: the nature of the cell changes is of a background superficial nature or changes in the epithelial tissue occupy half (more than half) of the cell layers.
Classification, histology for cervical oncology
The CIN and WHO classification systems help the physician to correctly evaluate the histology results.
The abbreviation CIN stands for cervical intraepithelial neoplasia. This is a malignant lesion. The main cause of cervical dysplasia is considered to be HPV (human papillomavirus) strains 16 and 18 (oncogenic types). There are three stages of the disease. The first two stages of CIN 1 and CIN 2, if detected in time, respond well to radiation and combination therapy and are successfully operated on. CIN 3 is considered difficult to treat. Over three stages, squamous epithelial cells change, approaching cervical cancer.
In 2013, the definition of CIN was changed to SIL. It is essentially a precancerous condition and is defined as a squamous intraepithelial lesion. There are two stages: mild and severe, although doctors still use the previous classification.
Methods of modern diagnostics and therapy help prevent the degeneration of dysplasia into cancer. Cure with surgery is 95%. If you skip the three stages of cervical damage, over time, atypical epithelial cells will replace healthy ones, which will cause oncology.
Depending on the histological type, the following types of cervical cancer are distinguished:
- squamous cell (keratinizing, poorly differentiated, non-keratinizing) in the exocervix;
- adenocarcinoma (glandular cancer).
Histological examination, as the most informative method, determines the structural features of tissues, identifies benign and malignant formations, which allows treatment to begin at an early stage of the disease and guarantee success.
Video: histology. How is the research conducted?
Histology. How is the research conducted?
Conclusion
The developed system of diagnostic measures for patients with reproductive failures caused by impaired endometrial receptivity provides for the assessment of ultrasound, Doppler and morphofunctional characteristics and endometrial microbiota, the use of diagnostic hysteroscopy and determination of endometrial receptivity according to the developed prognosis model, which allows diagnosing receptive disorders with 92.5% accuracy endometrium and detail their cause.
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
*e-mail; https://orcid.org/0000-0002-4090-0578