The external female genitalia includes the vulva. It includes anatomical structures that are located from the outside of the pubis in front to the opening of the back behind. They are presented:
- pubis,
- large and small private lips,
- clitoris,
- hymen,
- vestibule of the vagina,
- external opening of the urethra,
- Bartholin ducts (large vestibular),
- skene (small vestibular, paraurethral) glands
- other various glandular and vascular structures.
The pubis is a rounded increase formed by adipose connective tissue, which is located above the pubic symphysis. The amount of fatty tissue in the pubic area increases during puberty and gradually decreases after menopause. The pubic skin becomes covered with curly pubic hair during puberty, which thins out after menopause. The upper border of the hairline in women usually forms a horizontal line, but can vary; hair grows downwards along the outer surface of the labia majora, and forms a triangle with the base at the upper edge of the symphysis - a shield. The pubic skin contains sweat and sebaceous glands.
The labia majora are two rounded folds of skin that extend from the pubis to the perineum on either side of the pudendal slit. Embryologically, the labia majora are homologous to the male scrotum. In front they form the anterior commissure of the labia, in the back - a transverse bridge slightly raised above the surface of the skin - the posterior commissure of the labia. The labia majora are 7-8 cm long, 2-3 cm wide and 1-1.5 cm thick; contain adipose and fibrous tissue, sweat and sebaceous glands.
Venous plexuses in the thickness of the labia majora, when they rupture due to injury, contribute to the development of hematoma. In the upper part of the labia majora, the round ligament of the uterus ends and the obliterated vaginal process of the peritoneum, the nuc canal, is located. Vulvar cysts can form in this canal.
By puberty, the outer surface of the labia majora does not differ from the surrounding skin. During puberty, the labia majora become covered with hair on the outside. In children and women who have not given birth, the labia majora are usually in a closed position and completely cover the pudendal fissure; their inner surface is smooth, thinned and resembles a mucous membrane. After childbirth, the labia majora do not close completely; their inner surface becomes more skin-like (although not covered with hair), which is more noticeable in women who have had many births. After menopause, the labia majora undergo atrophy, and the secretion of the glands decreases.
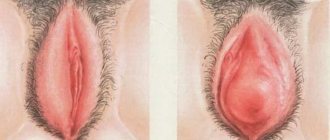
The labia minora are two small, thin, reddish folds of skin that are located medial to the labia majora and obscure the entrance to the vagina and the external opening of the urethra. The labia minora vary greatly in shape and size. In women who have not given birth, they are usually covered by the labia majora, and in those who have had many births, they protrude beyond the labia majora.
The labia minora are covered with stratified squamous epithelium, do not contain hair follicles, but have numerous sebaceous glands and several sweat glands. The sebaceous glands enlarge during puberty and atrophy after menopause. The thickness of the labia minora contains connective tissue with numerous vessels and some muscle fibers, as in typical erectile structures. The presence of numerous nerve endings in the labia minora contributes to their extreme sensitivity. From above, the labia minora converge (the anterior frenulum of the labia) and each of them is divided into two smaller folds, the lateral part of which forms the foreskin of the clitoris, and the medial part forms the frenulum of the clitoris.
In the lower part, the labia minora gradually become thinner and form the posterior frenulum of the labia, which is noticeable in nulliparous women. In women who have given birth, the labia minora below gradually merge with the inner surface of the labia majora.
The clitoris is a small, cylindrical organ, usually no more than 2 cm long, which is located in the upper part of the vestibule of the vagina between the upper ends of the labia minora. The clitoris consists of a head, a body and two legs and is homologous to the male penis. The long, narrow crura of the clitoris arise from the inferior surface of the ischiopubic rami and unite beneath the middle of the pubic arch to form the body of the clitoris. The latter contains two cavernous bodies, in the wall of which smooth muscle fibers pass.
The glans of the clitoris usually does not exceed 0.5 cm in diameter or 1/3 of the length of the clitoris. It is formed by spindle-shaped cells and covered with stratified squamous epithelium, which contains numerous sensory nerve endings. When the clitoris is erected, its vessels are combined with the bulbs of the vestibule - cavernous tissue, which is localized on both sides of the vagina, between the skin and the bulbospongiosus muscle. The clitoris is the main erogenous zone of a woman.
The vestibule of the vagina is an almond-shaped space between the clitoris above and the posterior frenulum of the labia minora below, laterally limited by the labia minora. The vestibule of the vagina is a structure similar to the embryonic urogenital sinus. In the vestibule of the vagina, 6 openings open: the urethra, the vagina, the Bartholin ducts (large vestibular) and, often, the Skene (small vestibular, paraurethral) glands. The posterior part of the vaginal vestibule between the vaginal opening and the posterior frenulum of the labia forms the navicular fossa, or fossa vestibule, usually noticeable in women who have not given birth.
Bartholin's glands, or large vestibule glands , are paired small complex structures with a diameter of 0.5 to 1 cm, which are located at the bottom of the vestibule on both sides of the entrance to the vagina and are analogues of Cooper's glands in men. They are located under the muscles surrounding the entrance to the vagina and are sometimes partially covered by the bulbs of the vestibule.
The ducts of the Bartholin glands are 1.5-2 cm long and open into the vestibule of the vagina outside the lateral edge of the vaginal opening, between the maiden membrane and the labia minora. During sexual arousal, Bartholin's glands secrete a mucous secretion. Closure of the gland duct in case of infection (by gonococci or other bacteria) can lead to the development of a Bartholin gland abscess.
The external opening of the urethra is located in the middle of the vestibule of the vagina, 2 cm below the clitoris on a slightly raised surface (papillary elevation), usually looks like an inverted letter B and can stretch up to 4-5 mm in diameter. The length of the urethra in women is 3.5-5 cm. The lower 2/3 of the urethra is located directly above the anterior wall of the vagina and is covered with transitional epithelium, the distal 1/3 is covered with stratified squamous epithelium. Under the external opening of the urethra there are openings of the small vestibular (skenovian, paraurethral) glands, which are analogues of the male prostate gland. Sometimes their ducts (about 0.5 mm in diameter) open in the posterior wall of the urethra, inside its opening.
Functions of the labia majora and minora
The function of the labia majora is to protect the vestibule organs from mechanical stress and prevent infection of the genitourinary system. The labia minora are the second layer of protection against infection of the vagina and urethra, and are also largely involved in moisturizing the mucous membrane. In addition, the labia minora take an active part in sexual intercourse. During sex, additional stimulation of the penis occurs with the help of the labia minora. But organs are also involved in a woman's orgasm. Despite the fact that one of the main erogenous zones of the female body is the clitoris, the labia minora are amplifiers of pleasant sensations during sexual intercourse. Because the labia are attached to the clitoris, their movement during sex provides additional stimulation, which helps achieve orgasm.
Patient complaints
Many women are simply embarrassed by such a special appearance of their genitals, experiencing all sorts of psychological discomfort due to this circumstance. As a result, they most often partially or completely refuse sex, feel constrained during intimate caresses, are embarrassed to undress in front of a man and believe that such a look will compromise them in some way. This condition can be aggravated by a nervous breakdown, a prolonged search for a partner, along with loneliness and extremely low self-esteem. In addition to a negative psychological state, the presence of the third and fourth degrees may lead to a decrease in active lifestyle, along with the abandonment of certain types of sports and limitation of movements:
- It is difficult for such women to sit in one position for a long time, causing pain and discomfort.
- Ladies are starting to refuse to go to swimming pools, saunas and even public beaches.
- Some sports are prohibited and considered unacceptable for this condition.
- Any hygiene procedures turn out to be more difficult.
- Pain may occur during intimacy with a partner.
- While riding a bicycle, pain may occur with deterioration of well-being due to hypertrophy of the labia minora. Photos of women with this problem are presented.
- The presence of underwear and tight-fitting clothing causes significant inconvenience.
- Constant friction can cause various chronic inflammatory processes in the labia minora area.
Types of female labia
The shape and size of the labia minora are individual for each woman. On average, their thickness is half a centimeter and their length is 2-4 cm . There are several classifications of the labia minora. By lenght:
- Short (there is a shortening of the distance from the clitoris to the posterior commissure, which is why the organs do not perform their protective function, since they do not close);
- Long (closing, forming additional folds).
According to edge modifications:
- Smooth (very rare);
- Serrated (like cockscombs, observed most often and in many cases are asymmetrical).
By thickness:
- Thin (occurs in adolescents and is characterized by a lack of volume);
- Thick (have significant volume, characterized by decreased turgor).
It should be noted that all of the above variants of the labia minora are normal variants and do not require any correction.
Postoperative complications
In some situations, women who decide to have surgery may develop certain complications. Among the most common problems are the following:
- The appearance of persistent postoperative scars.
- The occurrence of bleeding, hematomas.
- Loss of sensitivity of the labia minora.
- Development of hypercorrection.
- The appearance of infectious and inflammatory processes.
According to statistics, eighty-nine percent of women who treated hypertrophy of the labia minora through surgical techniques are satisfied with the results of the operation. In addition, seven percent decide to undergo re-intervention due to low satisfaction with the obtained functional or aesthetic results.
Thus, hypertrophy of the labia minora is a noticeable lengthening or enlargement of a given part of the body, or a set of defective deviations, sometimes in combination with their asymmetrical shape. The classic version is when the tissues in this part of the female body do not protrude out, but, on the contrary, are completely hidden through the labia majora. Such a condition is not considered a disease and can only be eliminated surgically based on the consent of the patient herself and only at her personal request.
Organ deformities and their causes
Sometimes it happens that the labia minora do not correspond to any of the normal options. In such cases, we talk about deformations, of which the most common are:
- Hypertrophy (the usual protrusion of skin folds beyond the genital opening is not called hypertrophy, this term implies a total increase in length, thickness and volume, which results in very large labia, causing significant discomfort during sexual intercourse and in everyday life);
- Elongation (the essence of this deformation is to increase the length of the skin fold with its maximum stretching; depending on the stage, it can vary from 2 to more than 6 cm);
- Protrusion (this term refers to the protrusion of the labia minora beyond the labia majora, and this phenomenon is not always a deviation from the norm, only in the most advanced cases);
- Asymmetry (various length and volume of the labia).
Also among the changes in the labia minora one can distinguish their depigmentation or, conversely, hyperpigmentation. More often the second is determined. It is not known exactly what the size and shape of the labia depends on, but there are several reasons:
- Hereditary factor (most often the shape of the labia is embedded in the genes of the female body);
- Hormonal imbalance (increased production of male sex hormones);
- Prematurity and birth trauma (can lead to underdevelopment of any organs and genitals, including);
- Involutionary processes in the body (aging leads to a decrease in turgor and skin elasticity);
- Traumatization;
- Masturbation (it is not completely known whether protrusion of the labia actually occurs during masturbation, but, as practice shows, this is possible);
- Childbirth;
- Various infections and chronic diseases of the genitourinary system;
- Congenital anomalies.
Causes
There are quite a lot of reasons for such a condition to arise. Conventionally, they can be divided into three main groups.
- Congenital or genetic nature of occurrence. Hypertrophy is observed in premature babies or among low birth weight newborns; it can be transmitted along the genetic line. At the initial stage, this deviation may not affect the girl’s condition in any way, and at the same time it does not cause discomfort. But when puberty begins or the first sexual contacts occur, the tissue can increase in size even more, stretching and changing. What other causes of labia minora hypertrophy could there be?
- The influence of diseases, inflammatory processes and individual characteristics. A provocation for an increase in this area can be a history of chronic and acute vulvitis along with lymphodermatitis. Sometimes the change is the predominance of male hormones in the female body with increased sensitivity to estrogen. Lengthening can also be observed among women who have suddenly lost weight.
- Mechanical or traumatic influence. Enlargement of the labia can occur when they are stretched due to age upon reaching fifty to sixty years of age. Sometimes signs of hypertrophy are observed after childbirth, especially if there are two or more children. Installed piercings along with sex can also lead to stretching, changes in size and asymmetry.
Correction and reduction of the labia minora
For women who have certain complexes or are not sure whether men like large labia, there is such plastic surgery as labiaplasty. This operation is performed to restore the correct shape of the skin folds in case of any deformation. There are no direct indications for surgery. The operation is performed only at the request of the woman. However, like any therapy, this correction has its contraindications:
- Age up to 18 years (it is not advisable to make changes, since the lips are not yet fully developed);
- Any infectious, bacterial, fungal diseases in the genital area;
- Tumor processes;
- Mental disorders.
To undergo labiaplasty, you should first visit a gynecologist. After consulting with a doctor, you will need to undergo some standard tests, and only then go for surgery. Labia reduction is best done a couple of weeks after the end of menstruation.
This operation is called a one-day operation, since its duration does not exceed one hour, and after the procedure the girl can immediately go home. Anesthesia is most often local, but depending on individual cases, it can also be general. Any discomfort, pain or swelling will disappear within a week. But the resumption of sexual activity should be postponed for a couple of weeks. During rehabilitation, which lasts several weeks, in addition to abstaining from sex, you should avoid open water, elevated temperatures and excessive physical exertion. To prevent infection, antibiotics are prescribed for the first 5 days after surgery. Complications:
- Prolonged pain syndrome;
- Sensitivity disorders in the labia minora;
- Impaired regeneration in a surgical wound;
- Lack of closure of the genital slit, which leads to vaginal gaping;
- Violation of the protective and moisturizing functions of the labia minora;
- Ruptures of the vulva during childbirth.
These complications are quite rare, but you should still keep them in mind before deciding to undergo labiaplasty. It should be understood that any surgical intervention on the body can lead to unexpected consequences. And if there is no vital need for it, then it is better not to risk it. We also must not forget that most types of labia minora are normal variants and do not need correction. The operation is advisable only in cases where enlarged or, conversely, small labia bring significant discomfort to everyday life.
Correction as part of treatment
Correction of the labia minora is aimed at reducing their size, and, in addition, at giving an aesthetic appearance. For this purpose, several options can be used at once, which depends on the degree of enlarged tissue, the wishes and characteristics of the patient. The procedure is often performed under local anesthesia, but sometimes in individual situations general anesthesia is also possible. In modern practice, several methods of performing labiaplasty are used. Many specialists favor a V-shaped wedge-shaped removal, performed by excision of protruding tissue. This method allows for modification and reduction to the desired size.
Photos of hypertrophy of the labia minora before and after surgery are of great interest to patients.
The W-shaped removal procedure involves resection of the labia minora and giving it a beautiful and rounded shape from an aesthetic point of view. This method may be complicated by loss of pigmentation in the corrected areas. Carrying out bilateral de-epithelialization is also in high demand among most specialists. The effectiveness of the technique lies in the fully guaranteed preservation of vascular nutrition in the tissue and sensitivity.
Following the operation, there is no need for the patient to stay in the hospital. In the next 24 hours, an unpleasant sensation is observed in the bikini area along with swelling and burning. After one week, the symptoms disappear and tissue sensitivity returns. For one month you must refrain from visiting the sauna, and, in addition, from sexual intercourse and taking a hot bath. Complete restoration of the labia usually occurs after three months.
What hinders this?
You can simply ignore this; by the way, no part of the body is absolutely identical. It should also be noted that there are a sufficient number of men who like long or thickened labia, including saggy labia. To verify this, you can type this phrase in any Internet search engine.
However, aesthetically this does not suit everyone, and moreover, it often leads to certain inconveniences. There are even specific complaints in the presence of drooping labia. First of all, this is rubbing, pain during movement, sex, playing sports, and the inability to wear tight-fitting underwear or a swimsuit.
Correction without surgery
You can start with fillers, the most famous of them is an operation called “labiaplasty”. There will most likely be little benefit; they can be effective only if the labia are not enlarged or elongated, that is, when there is a simple age-related decrease in tissue tone.
In addition, you need to remember that the procedure will need to be repeated every three months, and this involves the introduction of hyaluronic acid using a syringe, which is quite painful, because the genital area is very sensitive.