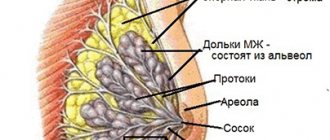
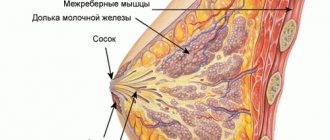
It is not uncommon for mammography to detect a lot of calcifications when examining a woman’s breast. Most women, hearing that there are calcifications in the mammary gland, are very worried, since a formation in the breast indicates health difficulties. In order to eliminate the processes of calcium accumulation, you first need to find out what it is and see the root cause of breast pathology.
What are microcalcifications in the mammary gland?
Microcalcifications are small deposits of calcium salts. They can accumulate not only in the mammary gland, but also in any other internal organ. The discovery of such a problem is a reason to send the woman for a more detailed examination (you may even need a biopsy of the gland tissue).
It is impossible to detect them on your own, since calcifications are microscopic in size, so if there is any suspicion of such a phenomenon, the patient will be sent for a mammogram.
Doctors consider microcalcifications as a symptom that can indicate various pathologies and even the development of an oncological tumor.
The diagnosis will depend on several calcium salt factors:
- localization;
- size;
- form;
- accuracy;
- quantity.
It is important for the doctor to know all these parameters in order to clarify additional research methods.
It is important to understand! If large deposits of calcium salts are found, this is not a symptom of a precancerous condition. This phenomenon only indicates increased cell activity.
Breast massage at home
One of the effective ways to prevent and treat microcalcifications in the breast is daily breast massage.
The procedure can be carried out at home, since the technique for performing it is quite simple, namely:
- place your free hand on the surface of the sore chest;
- fix the palm and fingers so that they cover the entire area of the gland;
- make 30 smooth and leisurely movements clockwise so that every centimeter of tissue is warmed up;
- perform similar movements in the opposite direction.
It is recommended to do at least 5 sets of 30 repetitions in each direction daily. The main purpose of therapeutic massage is to improve local blood circulation, activate the protective function of immune system cells, and maintain the tone of glandular tissues.
It is important to remember that the breast should not be squeezed too much and put compressive pressure on microcalcifications, as there is a high risk of developing an inflammatory process.
Microcalcifications that appear in the mammary gland are foreign neoplasms with which a woman can live her whole life and not experience any discomfort until the calcium deposits are detected by mammography.
At the same time, under the influence of unfavorable environmental factors, poor nutrition, and a weakened immune system, microcalcifications can become a catalyst for the oncological process with the formation of a cancerous tumor. With timely initiation of drug treatment, the prognosis for getting rid of microcalcifications and complete recovery is positive.
Author of the article: Stella Mille (stellamille)
Article design: Oleg Lozinsky
It is worth considering that cancer in the early stages of development is treatable, so the sooner treatment for breast cancer begins, the greater the chance of recovery. In this case, it all depends on the patient and her mood.
In other cases, the prognosis is favorable. The reasons that led to calcifications are corrected by diet, massage and hormones.
If a woman’s mammography reveals calcifications, then do not despair. First find out the reason, perhaps all the fears are false.
What are the types of deposits?
There is a rather complex classification of microcalcifications. According to the form of formation, there are: large, dotted, cotton wool-shaped, broken, croup-shaped, worm-shaped. By type: diffuse, regional, grouped, linear, segmental.
Let us examine in more detail the types of deposits, which are distinguished by their location in the mammary gland.
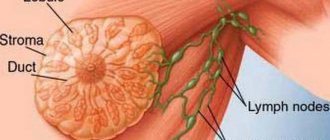
Ductal calcifications
From the name it becomes clear that calcium salts begin to accumulate in the ducts of the gland. If the main cause of the accumulation of microcalcifications is diseases such as mastitis or ductal ectasia, then the shape of the accumulation is vermiform with an interrupting structure. In the case when the formations have the form of small blurry segments or dots, this indicates a high probability of a malignant tumor.
Lobular calcifications
In most cases, they talk about a benign process. They arise as a consequence of atrophy of glandular tissue. This species has a characteristic appearance - round-shaped formations that are located in one or several lobes of the gland. When examined by a doctor, a painful lump will be detected during palpation, and an x-ray will show shapeless spots resembling crescents. In this case, we can confidently talk about fibrocystic mastopathy. To rule out cancer, the doctor must order a biopsy.
Stromal microcalcifications
This is the safest type of microcalcifications in the mammary gland from the point of view of oncological pathologies. They are easy to diagnose. They are large in size, varied in shape with a porous structure. The main cause of accumulation of stromal calcium salts is the death of adipose tissue or fibrous formations.
If fat necrosis or true fibroadenoma is observed, then the calcifications have a round shape with uneven edges (in the picture they look a little like popcorn). Microcalcifications in this case resemble pieces of stones, and if they are identified, a biopsy will be required for a more accurate diagnosis.
Microcalcifications under X-rays
Look at the picture below. It looks like a scattering of stars, a cluster of Perseids under the sight of an electronic telescope, and even small asteroids.
These are precisely calcifications or areas of calcification in glandular tissues. In exceptional cases they are quite large, but more often they are tiny formations that are impossible to palpate.
Calcifications are painless formations that do not betray their presence in the breast, formations that arose against the background or as a consequence of other pathologies of the mammary gland, that’s what it is. And this is not an independent disease!
They can be very small (microbrasion, microcalcifications) and quite large (macrobrasion). These formations are usually detected by chance during routine mammography and during examination for any diseases of the bust.
The main reasons for the accumulation of calcium salts
In most cases, the detection of microcalcifications in the mammary gland does not pose any danger to the patient’s life. However, there is still a small chance that this is a symptom of a cancerous tumor.
In addition to the development of a malignant neoplasm, the following processes in the body can provoke the accumulation of calcium salts:
- menopause;
- cystic formations;
- overdose of vitamin D3 and calcium supplements;
- milk stagnation during breastfeeding;
- violation of metabolic processes;
- necrosis of adipose tissue;
- benign tumors;
- age-related changes.
Some symptoms may initially indicate the complexity of the process. But in order to find out the exact cause, you need to undergo a series of examinations.
Causes of breast tissue calcification
These formations can be benign or malignant in origin. Among the benign ones, calcifications are distinguished:
- dishormonal;
- inflammatory;
- exchange (metabolic) origin.
Such formations may appear as a consequence of involution of the mammary glands during menopause or in the early postmenopausal period (diagram No. 1).
Diagram No. 1
More often, calcification of the glandular tissues of the bust is caused by a combination of several local causes:
- increased calcium levels in your body fluids;
- inflammatory processes;
- neoplasia or tissue necrosis;
- traumatic changes.
- is pathological in nature;
- performs a protective function - protects healthy tissues from damage due to decay or damage to surrounding tissues.
Sometimes we ourselves are to blame for the calcification of breast tissue, for example, by allowing lactostasis and not solving the problem quickly.
You know that 100 ml of mammary gland secretion contains about 32 mg of Ca. In its normal state, the acidity of human milk is within 3-6 Turner degrees, and its pH is determined in the range from 6.8 to 7.4.
When milk stagnates directly in the milk ducts, the secretion begins to ferment (lactic acid fermentation) and local acidosis occurs (the word acidus is of Latin origin and means “sour”). This means that pH, acidity increases, and calcium salts precipitate!
In women suffering from mastopathy, mastitis or other problems with the soft tissues of the bust, metabolic processes in these tissues are disrupted, the environment “acidifies” and the same effect is obtained - calcium salts precipitate!
Sometimes people suffer from high calcium levels in the blood (hypercalcemia). Pathology occurs:
- with excessive intake of vitamin preparations (vit. A or D), calcium supplements and some other medications;
- for malignant neoplasms;
- for endocrine diseases.
If there is a lot of calcium in the blood, its salts begin to settle in the tissues, including the mammary gland.
During involutive processes of the mammary glands, if the process occurs with fibrocystic changes, “pockets” with liquid (hollow formations) are formed in the bust tissues, which sometimes “petrify from the inside.” In the cyst, calcium salts are released from its liquid secretion and settle on the walls of the “pockets”.
What to do if calcifications are detected in the mammary gland
Calcium salt deposition is being diagnosed more and more often. Of course, you will be tormented by a feeling of fear, but you should calm down and tune in to a positive mood, because in 80% of all cases, a diagnosis such as “Calcifications in the mammary gland” is a symptom of non-life-threatening diseases.
If such a pathology is detected, a woman is recommended to undergo prescribed examinations, including mammography, because there is still 20% left, which doctors allocate to the development of malignant processes.
It is important for a woman to register with a mammologist and not ignore his recommendations. You should not engage in self-treatment until the root cause is identified. As soon as a diagnosis is made, the doctor will prescribe effective therapy, which can be supplemented with traditional methods.
Preventive actions
The mammary gland is predisposed to frequent formation of diseases. Therefore, it is important to regularly carry out preventive measures to identify and clarify the nature of calcification (and at the same time other difficulties):
- annual mammography of the breast provides a chance to reveal pathology
- biochemical study demonstrates the number of calcium salts
- analysis of hormonal levels through blood serum testing reveals problems
- biopsy is prescribed if necessary
It is better to prevent every dystrophic disease than to cure it. Therefore, any woman is obliged to monitor her own condition, undergo a breast examination every year, analyze biochemistry and not ignore various symptoms in her body. Since breast calcifications do not cause pain, you need to worry about your health and undergo examinations. It is important to eliminate breast calcifications and the onset of a dangerous disease in a timely manner.
The main role is given to preventing calcification of calcification. However, we must not forget that in established situations, calcium deposits can indicate cancer and cells are not capable of regeneration. Breast calcifications are often associated with oncological processes. Therefore, careful examination and constant monitoring of the dynamics of the formation of salt deposits can help to identify a malignant breast tumor in time.
It is better to ask questions to the doctor, even if he is a man. Be sure to get an annual mammogram and follow your doctor's instructions. Breast calcification in women does not cause any pain at all, but you need to understand the danger if the calcite does not resolve. It is worth remembering the importance of a doctor’s opinion and every patient should undergo a breast examination. A woman must maintain her health. Important factors affecting cancer prevention are a healthy diet and the use of lymphatic massage.
Diagnostic methods
This phenomenon will be identified by a specialist in the diagnosis and treatment of the mammary gland - a mammologist. To identify calcifications, palpation will not be enough, even if the formations are large. The X-ray method can help with this.
In addition to x-rays, a number of additional studies will be required:
- mammography;
- MRI of the chest;
- Ultrasound of the affected breast;
- biopsy of damaged tissue (performed by an oncologist if cancer is suspected).
Important! Every woman who cares about her health should undergo a mammogram 1-2 times a year. This will help to promptly identify salt deposits and determine the root cause.
In addition, the doctor will prescribe a hormonal test and a biochemical blood test.
Classification of calcifications
Not all bust calcifications belong to the “micro” group. There are also relatively large calcifications. During the diagnostic process, the doctor determines:
- type of calcifications;
- their dimensions;
- distribution by gland;
- shape;
- origin.
Most often, doctors encounter multiple microcalcifications in the breast tissue. Less often they have to diagnose relatively large single calcifications.
The shape and size of education for doctors serve as a diagnostic criterion for their origin. The shape and size are also affected by the localization of calcium salt deposits.
- Form dense groups or clusters of small calcifications, barely reaching 10 mm in diameter.
- Form diffuse groups scattered throughout the glandular tissue.
Based on the volume of damage, it is customary to distinguish:
- cluster calcifications are polymorphic formations grouped in small “scatterings”;
- segmental calcifications are localized in a single lobe of the gland;
- regional - deposits of calcium salts scattered throughout the milky lobe;
- covering the right or left mammary gland (a symmetrical lesion is not typical for this pathology, although both breasts can be involved in the process).
Traditional Treatments
The resulting microcalcifications in the mammary gland will never disappear. The woman will have to register with a mammologist and follow all his recommendations. In order to eliminate the root cause that contributed to the accumulation of calcium salts, a number of therapeutic measures will be required.
Drug treatment
In order to eliminate the cause and stop the process of salt deposition, the woman will be prescribed medications individually after diagnosis. It can be:
- Hormonal therapy. This method is most often prescribed to women during menopause, as hormonal drugs correct the imbalance. In other cases, drugs are selected individually.
- Vitamins and minerals. Preparations must contain a minimum amount of calcium and vitamin D
- Hepatoprotectors. The prescribed medications will protect the liver and improve its functioning. They are also involved in the water-salt balance of the body.
You should not self-medicate, because not knowing the cause of the pathology can only worsen the condition.
Surgery
The operation is prescribed quite rarely, since when microcalcifications are detected, the method is not effective due to the fact that it affects healthy tissue. Surgical intervention is recommended if large calcifications or a malignant tumor are detected. In this case, sectoral resection is recommended.
Indications for the procedure:
- early stage of cancer;
- nodular mastopathy;
- fibroadenoma;
- suspicion of cancer (carried out as a primary diagnosis).
To perform the operation, the size of the tumor should not exceed 3 cm. After the intervention, radiation therapy will be prescribed.
The procedure is safe, performed under general anesthesia and ultimately does not affect external changes in the breast.
The woman will be given antibiotics intravenously for a week. For the first three days, the operated breast will hurt, so you will need to take prescribed painkillers. On the seventh day the stitches will be removed.
Diet food
The patient’s diet will be tailored to her symptoms and the cause of her illness. The main rules will be to avoid salt, fried and fatty foods, as well as alcoholic beverages. It is recommended to eat more fruits and fresh vegetables.
It is also important to remove the following foods from your diet:
- dairy products;
- porridge (oatmeal and wheat);
- legumes;
- sweets (halva, cakes, biscuits);
- poppy seeds, sunflower seeds and sesame seeds;
- trembling;
- cheese (hard and processed).
These products contribute to the further accumulation of calcium salts, which is why they should not be in the diet.
Symptoms of pathology
Microcalcifications in the mammary gland are tiny neoplasms. In most cases, their formation goes unnoticed. Only after the mineral deposits become dense and overly saturate the glandular tissue does the woman begin to experience some signs of illness.
They are as follows:
- discomfort in the area of one or two breasts at once, reminiscent of a slight aching pain;
- if calcium salts have accumulated in one area closer to the subcutaneous layer, then spherical compactions may be felt, which become painful when pressed with your fingers;
- an atypical liquid of a completely transparent color or with an admixture of ichor is periodically released from the nipples, which indicates a sluggish inflammatory process;
- an increase in temperature to 37 degrees Celsius or higher if a woman has not sought help from her doctor for too long despite feeling pain and discharge from the chest.
This symptomatology can also occur with other diseases of the mammary glands. Therefore, it is so important to contact a doctor for examination and undergo a mammography procedure. Only this diagnostic method will confirm or refute the presence of microcalcifications in the breast tissue.
A mammologist or gynecologist should examine breast tissue.
After an initial examination of the breast, the specialist prescribes the woman to undergo the following types of diagnostics:
- donating blood from a finger for clinical analysis;
- taking venous blood to perform a biochemical study for the balance of sex hormones, the presence of cancer cells, and pathogens of infectious diseases;
- X-ray of the chest (if there are calcium deposits, the image will show characteristic dots accumulated in a certain part of the tissue, depending on the type of stones);
- Ultrasound diagnosis of the breast, inside of which discomfort is felt;
- surgical selection of a fragment of glandular tissue to conduct a biopsy and refute oncology;
- Mammography, which is the main research method for suspected microcalcifications in the breast.
Based on the diagnostic results, the attending physician forms a therapeutic course aimed at removing foreign tumors. In parallel with the treatment process, actions are taken to eliminate the causative factors that cause the deposition of salts in the chest.
The basic principle of dietary nutrition for microcalcifications in the mammary gland is to limit the following foods that contain calcium salts or that promote its absorption.
They are as follows:
- all types of dairy products;
- sunflower seeds, poppy seeds, peanuts, sesame seeds, almonds;
- ocean fish, especially sardines;
- confectionery;
- garlic, parsley;
- chicken eggs, regardless of the method of their preparation;
- beans, peas, beans, soybeans;
- oat and wheat porridge.
To eliminate microcalcifications in the mammary gland, you need to follow a special diet.
In addition, a woman must avoid eating fatty, fried, and smoked foods. Most of the dishes in the diet should be steamed, stewed in the oven or boiled in water in the traditional way. Alcohol, tobacco and drugs are strictly prohibited.
Breast cancer is a terrible diagnosis that is increasingly heard from doctors. Therefore, women who are worried about their health undergo periodic examinations.
The most informative method, which shows all formations, even the smallest ones, is mammography. And very often during the examination, single calcifications are detected in the mammary gland.
What are these formations and are they harbingers of cancer?
From the name it is clear that we are talking about formations of calcium, namely, calcifications are called clots of calcium salts that form at the site of damaged breast tissue. Calcium is part of all organs of the human body, but when metabolic processes are disrupted, it tends to accumulate in the form of grains.
It is immediately worth noting that a single calcification of the mammary glands is a possible cause of cancer in only one out of five cases. Calcifications can be seen during mammography, and the same examination provides their full characteristics.
They are classified according to several criteria. Depending on location:
- Ductal. The key location is the milk ducts, which can be observed along the ducts or inside. They are usually small in size and arise as a result of stagnation of secretions or the development of malignant cells.
- Lobular. The most common type of formation, in 95% of cases it is benign. They are located in the glandular part of the mammary glands and arise against the background of cysts and other formations.
- Stromal. Breasts that are distant from the tissues are formed on blood vessels and the skin around the glands. They are larger in size than others, more than 1 mm.
According to the form, the following types are considered:
- large (more than 1 mm, have a clear shape);
- point (single formations, located far from each other);
- croup-shaped (do not have a clear shape);
- vermiform (has an elongated shape);
- cotton wool-shaped (large, but no clear shape);
- broken lines (have the shape of regular figures).
Breasts hurt a lot before menstruation - what to do? Read more
Informational video that will help you understand why breast cancer occurs and what the underlying causes may be.
The process of early diagnosis and treatment is complicated by the fact that calcifications do not signal themselves with any symptoms. The general condition of the breast is normal; the lump cannot be felt during palpation.
Disturbances in the metabolic process, deposits of calcium salts can be seen during mammography. In addition, certain indicators of a biochemical blood test and hormone analysis also indicate possible problems.
There are no obvious symptoms that a woman could notice, the breasts look normal, no pain occurs. Signs can only appear when the deposits reach large sizes, more than 1 cm in diameter, and become noticeable upon palpation. But such cases are rare; usually calcifications in the mammary glands are not large.
There is a fairly wide range of reasons due to which calcifications can occur. Experts prioritize various formations, lumps, cysts, and adenomas. The most dangerous of them is breast cancer. In 20% of cases, it becomes the key factor in metabolic disorders and the formation of calcifications in the glands.
In addition, there are other reasons that can cause this process; doctors name the following factors:
- stagnation during lactation (this happens when too much milk is produced or when a woman stops the feeding process, but the milk still remains);
- the period of menopause, this is the most critical time for the condition of the breast; against the background of hormonal changes, various formations may appear;
- excess vitamin D3 in the body, this occurs as a result of metabolic disorders;
- metabolic disorders, this condition occurs as a result of disturbances in the functioning of the endocrine, digestive, and nervous systems;
- increased calcium levels due to metabolic disorders;
- age-related changes.
These factors are a catalyst for the formation of calcifications; under their influence, an inflammatory process develops in the breast cells, against which deposits appear.
It is impossible to predict this process; it has an individual nature.
Even specialists are not always able to determine the exact cause of the development of the process; more detailed information can only be obtained after an examination.
Interesting fact: There is no specific age category that falls into the risk group. Formations can occur in teenage girls, women during lactation and older people. However, according to statistics, more than 40% of patients are women over 40 years of age.
An informational video that will help you understand what mammography is, who needs it, and what symptoms require this diagnostic test.
Treatment with folk remedies
As you know, our descendants used to cure all diseases exclusively with the gifts of nature. Treatment of calcinosis with folk remedies will be aimed at increasing the consumption of magnesium-containing foods, which will help absorb calcium in the body. If the amount of calcium and magnesium in the body is within normal limits, salt deposits will dissolve and be removed from the body. In addition, calcium will begin to be well absorbed in the bones.
How to treat calcinosis with herbal remedies
Among the medicinal herbs, there are those that normalize the water-salt balance, relieve pain and help dissolve and remove excess calcium from the body.
Let's look at effective recipes:
- In a coffee grinder or blender you need to grind rose hips and juniper, as well as valerian roots. Mix everything. Take ¼ tsp. herbal mixture and pour 400 ml of boiling water. Let it brew for 30 minutes. This is a basic infusion that should be consumed every day, adding it to purified water (1 tsp of infusion is mixed in 500 ml of water). Take 100 ml before meals three times a day. On the second day, take 1 tablespoon per 500 ml of water. infusion, and on the third 2 tbsp.
- Grind dill, elderflower flowers, coriander seeds, mint leaves and dandelion roots in equal proportions. Pour 500 ml of boiling water over 1 tbsp. medicinal mixture. Let it brew for 30 minutes. Take 150 ml three times a day.
- Grind chamomile flowers, calamus root, valerian root, and juniper fruits in equal proportions. Take 1 tsp. mixture and boil in 1 liter of water for 15 minutes. Strain the broth and let it brew. Take 1 tbsp. before every meal.
Important! If discomfort appears, your heart rate increases, or your blood pressure deviates from normal, you should stop taking it and give your body a rest for 5 days. Perhaps these symptoms indicated an overdose. After 3-5 days, you can continue treatment, but reduce the dose.
Signs
But none. Unless education takes up the lion's share of your gland. Calcifications are usually found by chance by radiologists during routine mammography. The clinical picture coincides with the clinic of the main disease:
- discomfort and pain with mastopathy;
- discharge from the nipple due to mastopathy and intraductal papilloma or cancer;
- changes in breast shape, skin color and texture due to cancer.
It is extremely difficult to palpate calcification. And this is possible if it is very large.