Menstruation is a natural process in the life of every woman of childbearing age, during which the protective layer of the uterus (endometrium) that has grown over the month is rejected and removed together with the unfertilized egg through bleeding from the vagina. Very often, this physiological process is accompanied by the occurrence of unpleasant symptoms (pain in the lower abdomen, irritability, dizziness, etc.), which is explained by changes in the level of sex hormones in the body and is sometimes considered normal.
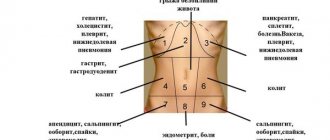
Also, women often complain that their right side hurts during menstruation. This condition may indicate the progression of dangerous diseases of the genitourinary and other systems in the body. It is very important to promptly find out the cause of such an unpleasant symptom in order to prevent irreversible consequences.
Let's understand the term "ovulation"
The duration of the menstrual cycle is determined from the first day of the previous menstruation to the first day of the next. Its duration varies and normally ranges from 21 to 35 days. The ideal menstrual cycle is considered to be a cycle lasting 28 days, which corresponds to a full lunar cycle. The menstrual cycle consists of several phases:
Follicular phase
The follicular phase is caused by the action of estrogens, under the influence of which a dominant follicle is determined in the ovary, in which the future egg matures. This phase lasts an average of 12–18 days, depending on the length of the cycle. With a 28-day period it is 14 days. Towards the end of the follicular phase, the dominant follicle has reached its maximum development, is tense and is preparing to burst.
Ovulatory phase
The shortest phase of the menstrual cycle, its duration is 12 – 36 hours. During this phase, estrogen levels drop, causing the main follicle to burst and release a mature egg, ready for fertilization. What is characteristic is that it is during the ovulatory phase that the level of both estrogen and progesterone is quite low (estrogens are no longer synthesized, since the dominant follicle and egg have already “matured”, and progesterone is not yet produced in sufficient quantities under the influence of luteinizing hormone due to the still unformed corpus luteum in place of the main follicle).
Luteal phase
The synthesis of progesterone increases, under the influence of which proliferative processes occur in the uterine mucosa, preparing it for implantation of a fertilized egg. In the case of unsuccessful fertilization, by the end of the luteal phase, the level of progesterone decreases (the corpus luteum of menstruation dies) and the functional layer of the endometrium is rejected, which is called menstruation.
So, ovulation is nothing more than the process of the release of a mature egg from the dominant follicle at the moment of its rupture. And painful ovulation is called ovulatory syndrome or Mittelschmertz syndrome.
Signs of ovulation
Ovulation (from the Latin word for “egg”) has characteristic signs, and every woman experiencing discomfort or pain associated with it can almost accurately determine its onset:
Pain in the right side or left
Pain occurs on a certain side, depending on which ovary “works” in a given menstrual cycle (most often, right-sided pain is observed, which is associated with better blood supply to the right ovary and its innervation, as well as with the close proximity of the appendix).
As a rule, the pain is minor and may cause only mild discomfort. In some cases, women characterize the pain as cutting, stabbing or cramping. This feeling does not last long, from an hour to a day or two. The intensity of pain depends on:
- character - emotional representatives of the fairer sex feel pain more clearly
- the presence of gynecological diseases contributes to increased pain
- pain sensitivity threshold - the higher it is, the less pain a woman experiences during ovulation.
Thus, ovulation itself is short-lived, and pain in the lower abdomen after ovulation may persist for one to two days. Since only one ovary is involved in ovulation in each menstrual cycle, they function alternately, that is, pain can be on the right in one month and on the left in another.
In rare cases, when both ovaries are involved in the work, 2 eggs mature at the same time, which, if fertilized successfully, leads to multiple pregnancies. In such a situation, a woman feels pain on both sides or a diffuse aching pain in the lower abdomen.
Increased libido
Libido, or sexual desire, increases somewhat during the period of ovulation, which is inherent in nature itself (after all, ovulation is the most favorable moment for conception, and therefore for procreation).
Discharge
On the eve of ovulation, at the moment of its completion, and for another couple of days, the nature of vaginal discharge changes. They become more liquid, stretchy and look similar to egg white. These changes in secretions are necessary to create favorable conditions for the penetration of sperm into the uterine cavity to fertilize a mature egg. The liquid consistency of the discharge in the slightly expanded cervical canal facilitates the passage of the “live animals” into the uterus.
Changes in discharge color
During ovulation and some time after it, the color of the discharge may also change. They take on a pinkish tint or a few drops of blood are found on the underwear (see spotting in the middle of the cycle). This is due to a slight detachment of the endometrium (estrogens are no longer produced, and progesterone has not yet begun to be synthesized).
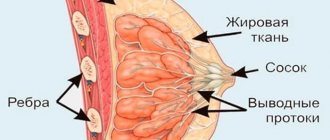
Pain in the mammary glands
Pain or tenderness of the breasts may occur during ovulation (see pain in the mammary glands), which is associated with the initial preparation of the mammary glands for pregnancy and lactation. Such pain (mastodynia) is short-lived and stops by the time the corpus luteum forms.
Survey results
If, as a result of the examination, the gynecologist revealed the presence of an inflammatory disease, then therapeutic measures will be aimed at getting rid of this process. Inflammation of the appendages often affects one side, which is why one side hurts. If there is salpingitis or oophoritis on the right, then pain will bother the patient in the right beech. A manual examination, menstruation, and sexual intercourse will be extremely painful. Adnexitis is also accompanied by severe pain, requiring immediate and adequate treatment.
Therapeutic measures include the use of anti-inflammatory drugs, a complex of vitamins, and if necessary, the doctor will prescribe antibiotics. The treatment is a course, the course is at least 10 days. After the attack is stopped, restorative therapy will be required. It is important to consult a doctor in a timely manner, refusing to self-medicate and take painkillers.
One of the most dangerous diseases is apoplexy. The menstrual cycle is divided into several periods, and during the first, under the influence of estrogen, the follicle matures. At a certain time it ruptures and the egg is released. If such a rupture occurs ahead of schedule, it is accompanied by severe cutting pain. There is no conservative treatment for apoplexy. The patient needs urgent surgical intervention.
No less common is the so-called ectopic or tubal pregnancy. A fertilized egg is not able to penetrate the uterine cavity due to adhesions existing in the fallopian tubes, narrowing their lumen. This becomes the reason that the fertilized egg remains in the lumen of the tube, is implanted, and the embryo begins to develop and, of course, grow, increasing in size.
Despite the presence of a fertilized egg, menstruation may occur regularly for several months, in exact accordance with the menstrual cycle. Menstruation is accompanied by nagging pain in the right side if the fertilized egg is in the right tube.
Causes
There are several causes of pain during ovulation. Before it begins to emerge from the follicle, it must mature and significantly increase in size.
- The large “dimensions” of the follicle stretch the ovarian capsule, which explains the occurrence of pain before ovulation.
- After the dominant follicle has reached the “desired condition,” it bursts and a ready-made egg is released into the abdominal cavity.
- At the moment of rupture of the follicle, in addition to the egg, a certain amount of fluid is poured into the abdominal cavity, which irritates the parietal peritoneum. In addition, the ovarian capsule is damaged, in which small blood vessels burst, resulting in even a small amount of blood entering the abdominal cavity, which also irritates the peritoneum.
- Such nagging pain after ovulation can bother a woman for 12 to 48 hours. But then the blood and follicular fluid in the abdomen are absorbed and the pain syndrome disappears.
- And since at the moment the egg appears in the abdominal cavity, the fallopian tubes begin to peristalt (contract) more strongly in order to have time to capture a viable egg and ensure that it meets the sperm, pain can be maintained by this process.
- An indirect sign of a possible future pregnancy is pain in the middle of the cycle.
But in some cases, the pain syndrome at the time of ovulation is more pronounced, which is due not only to the threshold of pain sensitivity, but also to the presence of certain gynecological diseases, for example:
- adhesive disease of the pelvis, which may be caused by chronic inflammation, a history of surgery or endometriosis
- adhesions do not allow the tubes to contract calmly and tighten the ovary, and in some cases cause compaction of its capsule, all this increases the severity of pain.
Causes of pain in the side before menstruation
Tingling, cutting, aching sensations in the side before the onset of menstruation can be both non-pathological and pathological. In the first case, they are a consequence of physiological processes occurring in the internal genital organs, in the second, they indicate the presence of gynecological and non-gynecological ailments.
Non-pathological factors
At the beginning of the menstrual cycle, a dominant follicle is formed in one of the ovaries - right or left. The egg matures in it. In the middle of the month, 2 weeks before the start of the next menstruation, ovulation occurs. The wall of the dominant follicle bursts, releasing a small amount of blood, and the mature oocyte enters the fallopian tube.
Types of ovulation
There are several types of ovulation:
Premature ovulation is the maturation and release of an egg from the follicle not in the middle of the cycle, but much earlier and can be caused by several factors:
- excessively violent sexual intercourse (see causes of pain during sexual intercourse);
- increased physical activity or heavy lifting;
- stress and strong emotional experiences;
- various diseases, including gynecological ones;
- hormonal disorders and endocrine pathology.
The etiology of late ovulation includes various hormonal problems, including menstrual irregularities.
In connection with the described types of ovulation, pain, accordingly, does not occur, as is customary, in the middle of the cycle, but much earlier or, on the contrary, later, which can become a cause for concern for a woman (see also symptoms of premenstrual syndrome). Therefore, an indirect sign of a possible future pregnancy is pain in the middle of the cycle.
Anovulation
Speaking about ovulation, one cannot help but touch upon the problem of its absence or anovulation. Normally, anovulation is observed in pregnant women and premenopausal and menopausal women. And, of course, ovulation cannot occur while taking hormonal birth control pills.
If a woman of reproductive age does not ovulate for several cycles in a row (2 or more), she should start sounding the alarm, because no ovulation - no egg - no possibility of getting pregnant.
As a rule, the cause of anovulation is hormonal imbalances in the body, which, with appropriate treatment, are stopped and the woman has a chance to become a mother. To clarify the date of ovulation, you can use ovulation tests or undergo an ultrasound, where the doctor will accurately see the mature follicle and the release of the egg from it (of course, ultrasound is performed several times during the period of expected ovulation).
How to make it easier
No matter how sure a woman is that the pain that appears in the right or left lower abdomen is associated with ovulation, she should not self-medicate, but rather consult a doctor. After all, any pathology, not only gynecological, can cause pain, which accidentally coincides with the middle of the cycle.
During the examination, the specialist will rule out other causes of pain and recommend the optimal treatment (see also how to reduce pain during menstruation).
- If ovulatory syndrome bothers a woman every menstrual cycle, she is advised to relax as much as possible on the days of ovulation, eliminate stressful situations and adhere to a certain diet.
- In therapeutic nutrition, they limit dishes and products that increase the load on the gastrointestinal tract, increase intestinal motility, which aggravates pain, cause flatulence and excite the central nervous system. These are primarily spicy and fatty foods, legumes and white cabbage, chocolate, coffee and strong tea.
- Warm baths with aromatic oils or medicinal herbs help relieve pain. heat descends to the lower abdomen, which reduces contraction of the uterus and tubes and relieves pain, but only if acute infectious and surgical diseases are excluded.
- Of the painkillers of choice, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are the method of choice, which block the synthesis of prostaglandins, relieve pain and inflammation (ibuprofen, indomethacin, naproxen, ketoprofen).
- Taking antispasmodics (no-shpa, spazgan, spasmalgon) is also effective.
With constant ovulatory syndrome, the gynecologist may recommend taking oral contraceptives (pros and cons of taking them), which, by blocking ovulation, prevent the occurrence of pain. But, if a woman wants to get pregnant, their use is excluded, and it is also not permissible to use a heating pad on the lower abdomen and take any medications on the days of ovulation, as this may affect the quality of the egg.
Severe pain
In some cases, very intense pain may appear in the middle of the cycle. Severe pain in the ovary or in the right/left side of the groin may be a sign of an emergency:
Each of the listed conditions requires emergency medical care, and in most cases even surgical intervention, so delay only aggravates the situation and, in the literal sense, as Peter I said, is like death. You should not wait out very severe pain, trying to relieve it yourself; you must immediately call an ambulance.
When to sound the alarm
You should consult a doctor as soon as possible if you experience severe pain in the lower abdomen and/or the following signs:
- the pain continues for more than two days (“it hurts for a week during ovulation” - a clear sign of the disease);
- the temperature has risen and lasts for more than an hour;
- nausea/vomiting occurred;
- bloody discharge from the genital tract appeared, regardless of its intensity;
- when taking drugs that stimulate ovulation;
- a history of acute gynecological diseases, surgeries, endometriosis;
- sudden fainting;
- progressive deterioration of the condition.
Menstruation is a natural process in the life of every woman of childbearing age, during which the protective layer of the uterus (endometrium) that has grown over the month is rejected and removed together with the unfertilized egg through bleeding from the vagina. Very often, this physiological process is accompanied by the occurrence of unpleasant symptoms (pain in the lower abdomen, irritability, dizziness, etc.), which is explained by changes in the level of sex hormones in the body and is sometimes considered normal.
Also, women often complain that their right side hurts during menstruation. This condition may indicate the progression of dangerous diseases of the genitourinary and other systems in the body. It is very important to promptly find out the cause of such an unpleasant symptom in order to prevent irreversible consequences.
Why does my lower abdomen hurt after menstruation?
Hormonal imbalance
The genital organs, like other body systems, depend on hormonal levels. Hormones in large quantities increase the cycle, making the pain stronger and longer. Symptoms due to hormonal imbalance remain even after menstruation.
Pain that ends after a period of one or two days indicates hormonal surges. If the pain lasts longer or has nonspecific symptoms: fever or discharge, then you should consult a specialist.
Adnexit
Adnexitis is inflammation of the ovaries and fallopian tubes (appendages). Inflammation can be unilateral or bilateral, as well as acute and chronic.
The disease occurs when intimate hygiene is not observed. Harmful bacteria enter sterile organs and cause inflammation. These can be: bacteroides, staphylococci. In addition, you can get such inflammation through sexual contact. Hidden infections from chlamydia, ureplasma, trichomonas aggravate the situation.
Symptoms of adnexitis include:
- Severe pain in the lower abdomen. It is aching and long-lasting. The pain radiates to the lower back or anus.
- Elevated temperature up to 38 degrees.
- Depressed and depressed state, weakness.
- Nausea.
- Problems with urination.
- Bloating.
- White discharge.
- Infertility.
If acute adnexitis is not cured in time, it can develop into chronic adnexitis. Chronic inflammation is the cause of infertility and ectopic pregnancies.
Cervicitis
Cervicitis refers to inflammatory processes. It affects the cervix. The causes of the disease are different. These include:
- venereal diseases;
- genital herpes;
- vaginal infection;
- candidiasis;
- human papillomavirus;
- injuries during childbirth;
- improper intimate hygiene or lack thereof;
- allergy.
Without an examination by a gynecologist and tests, it is impossible to accurately determine inflammation of this kind. The first alarming symptom should be pain after menstruation and heavy vaginal discharge.
Symptoms of inflammation:
- burning and redness, accompanied by itching, of the genitals;
- painful urination;
- discharge characterized by abundance and unpleasant odor;
- bleeding that has started again;
- pain during and after sexual intercourse;
- pain in the abdomen or lower back during intercourse, bleeding or some blood after it;
- nausea, dizziness;
- elevated temperature;
- swelling of the cervical canal.
The causative agents are: herpes virus, trichomoniasis, HPV, gonorrhea, chlamydia. Untreated inflammation leads to cysts, infiltrates, and infertility.
Vulvitis
Inflammation of the mucous membranes of the external genitalia is called vulvitis. Self-diagnosis and treatment lead to serious complications.
Causative agents of inflammation: Escherichia coli, fungi, staphylococci, streptococci. Infections such as gonorrhea, trichomoniasis, and mycobacterium tuberculosis maintain and aggravate inflammation.
Physiological pain
If during the procedure a woman feels nagging pain in the abdominal area, which does not in any way impair the quality of her life, then this phenomenon is considered normal.
During menstruation, the endometrial layer, which has grown over the course of a month to fully secure the egg, begins to be rejected and removed along with the unfertilized egg from the body through bleeding from the vagina. During this process, small capillaries and nerve endings in the uterine body are damaged, which provokes pain. Also, in order to quickly remove the egg and the protective layer from the body, the muscles of the uterus begin to contract, which also contributes to the appearance of pain.
If pain appears in the right side, this may indicate the presence of dangerous pathologies, usually of the genitourinary system. You should immediately contact a gynecologist who will help determine the true cause of the pain.
Why does my right side hurt?
Appendicitis
This is the name for inflammation of the appendix, a small extension of the large intestine. The first sign of appendicitis is a dull pain near the navel or in the upper abdomen, which descends along its right lateral surface and becomes sharp.
The pain may be accompanied by loss of appetite and an increase in body temperature to 37–39 °C, nausea and vomiting, and bloating.
What to do
This requires emergency medical care and surgery. Therefore, immediately go to the hospital to see a surgeon or call an ambulance.
Your appendix will most likely be cut out laparoscopically - through small incisions on the abdominal wall.
Anna Yurkevich
Gastroenterologist. Author of a blog about proper nutrition and digestive health.
Scientists do not have convincing evidence of the negative impact of appendectomy (removal of the appendix) on human health. It is much worse not to have surgery, because the appendix may burst. Then peritonitis will begin - inflammation of the tissue that covers most of the abdominal organs.
Gallstones
When there are gallstones, we may feel sudden and rapidly increasing pain in the upper right side of the abdomen, under the breasts, in the back between the shoulder blades, and even in the right shoulder. Nausea or vomiting may also begin.
The duration of pain varies from a couple of minutes to several hours.
What to do
If these symptoms appear, you should either immediately go to a therapist or call an ambulance. Stones can cause inflammation of the gallbladder - cholecystitis, blockage of the pancreatic duct and, as a result, pancreatitis.
Frequent attacks of colic are an indication for removal of the gallbladder. This operation is called cholecystectomy. It is usually performed through small incisions in the abdominal wall.
Anna Yurkevich
At an early stage, when the stones are still small, you may be prescribed medications to dissolve them.
Stones in the kidneys
They cause sudden, excruciating pain in the lower and side of the abdomen, but more often in the back. It waxes and wanes.
What to do
A nephrologist will help you deal with the problem, so go to him right away. He will prescribe medicine for small stones.
Severe pain and large kidney stones may require hospitalization and surgery.
Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS)
Gases collecting in the intestines stretch its walls and cause pain in different parts of the abdomen, including the right side.
Usually there is nothing serious about this. But this is a chronic disease, which means it will either disappear or appear again.
What to do
To relieve symptoms, you need to take prebiotics, possibly laxatives or antibiotics. They should be prescribed by a gastroenterologist.
Inflammatory bowel diseases
The most common are Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis.
If your intestines are inflamed, you will experience pain, cramping, and swelling in your abdominal area. Other symptoms include bloody diarrhea, weight loss and weakness.
The causes of inflammation are not exactly known, but experts suggest that it is genetics and problems with the immune system.
What to do
Visit a gastroenterologist. For diagnosis, he will refer you for a stool test or colonoscopy. And as a treatment, he will prescribe something from this list: aminosalicylates or mesalazines, antibiotics, immunosuppressants, biological products.
Constipation
If you can't go to the toilet, you feel discomfort and heaviness in your stomach, this is constipation.
What to do
A laxative will help here. If you have persistent constipation, consult your physician or gastroenterologist.
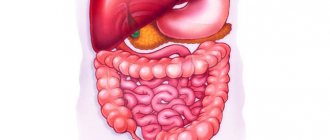
Duodenal ulcer
An ulcer is a deep defect in the mucous membrane. In most cases, it occurs when the bacterium Helicobacter pylori enters the duodenum. In addition to pain in the right side, bloating, a feeling of heaviness, heartburn, belching, and nausea may appear.
What to do
First diagnose the ulcer. Contact a gastroenterologist as soon as possible to perform an esophagogastroduodenoscopy - an examination of the intestinal walls. This is popularly called “swallowing the probe.”
Most often, treatment involves only medications; surgery is rarely required.
Period
A nagging pain can be felt in the lower right side before and during menstruation. This is usually not dangerous, but very unpleasant.
What to do
Be patient or take a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug. If the pain is very severe, you need to be examined by a gynecologist. He will prescribe you hormonal oral contraceptives or strong painkillers.
Ovarian cyst
A twisting or rupturing cyst causes pain in the pelvic area, ranging from dull and mild to sharp and sudden. Specific symptoms are pain during sex, irregular and heavy periods, frequent urination.
Causes of pain
To the existing question of many about why the right side hurts during and before menstruation, doctors have a scientific answer. This often happens due to the progression of dangerous inflammatory gynecological diseases in the body. It is in this area of the abdomen that the reproductive organs are located. And the appearance of unpleasant sensations precisely on critical days is explained by the fact that changes in the level of sex hormones reduce pain and provoke minor inflammatory processes, in which the symptoms of the existing disease become more pronounced.
Treatment
It is practically impossible to cope with abdominal pain during menstruation on your own, since such a phenomenon often indicates the progression of dangerous diseases.
The doctor, based on the diagnostic results obtained and the individual characteristics of the body, prescribes the most appropriate treatment method.
If foci of inflammation are found in the body, anti-inflammatory drugs are prescribed. For diseases associated with hormonal imbalance, hormonal drugs are prescribed. If the pain was caused by the intrauterine device, it is removed. If tumors are present, surgery is required. The attending physician will advise you in more detail about each method of treating the present disease.
What to do if you have pain in your right side
As you can see, side pain can be a symptom of a variety of health problems. Therefore, you should not ignore it - be sure to see a doctor. “The severity of the disease that caused the situation cannot always be determined by the nature of the pain syndrome. This applies, first of all, to older people and patients suffering from diabetes - serious diseases of the abdominal cavity can be erased (the pain syndrome may not be expressed at all or disappear completely), says Bulat Yunusov. — Thus, if abdominal pain does not go away within several hours and is accompanied by an increase in body temperature, nausea, vomiting, loss of appetite, stool disorders (constipation or diarrhea), discomfort when urinating, a decrease in blood pressure, then the only correct solution is an in-person consultation doctor."
Prevention
To prevent the development of dangerous diseases and the appearance of unpleasant symptoms, experts recommend adhering to the following rules:
- Visit a gynecologist at least 2 times a year;
- Play sports;
- Give preference to healthy foods;
- Give up bad habits;
- Use condoms;
- Avoid promiscuity;
- At the first unpleasant signs, go to the hospital.
The premenstrual period often causes girls to feel worse, discomfort and pain. For most women, pain is observed in the lower abdomen, lumbar spine and chest, but there are cases when the right side hurts before menstruation. Whether this symptom is pathological or normal will be discussed further.
During menstruation, sometimes there is pain in the side
What are the physiological causes of pain?
Normally, during the premenstrual period, minor pain may be felt, which disappears on the second day of regulation.
If your right side hurts before your period, there may be physiological causes:
- disruption of the circulatory system, leading to blood stagnation in the uterus;
- bend of the uterus;
- hormonal disbalance;
- primary dysmenorrhea;
- failure of ovarian function;
- injuries to the back or internal genital organs.
It is impossible to independently identify the exact reason why your side hurts during menstruation, since the provoking factor is associated with the functioning of the internal organs.
If discomfort bothers you every menstrual cycle, it is advisable to visit a gynecologist to determine the cause and possible identification of pathologies for timely treatment.
If you experience frequent pain, you should see a doctor
What pathologies may be
Pain in the hypochondrium on the right side can be caused by pathological reasons, which include the development of diseases in different areas of the body:
- appendicitis;
- cholecystitis;
- inflammation of the genital organs;
- adnexitis;
- polycystic disease;
- apoplexy;
- endometriosis;
- myoma.
It is not uncommon for the right side to hurt during menstruation due to the installed intrauterine device used for contraception. The spiral itself does not cause such a symptom, but in case of injury during sex or improper installation, displacement can occur, which provokes a pathological symptom.
Could there be pregnancy?
After fertilization of the female egg occurs, the follicle moves through the fallopian tubes to attach to the wall of the uterus. During this period, most women feel not just discomfort, but also painful sensations that may occur in the side area. However, if pregnancy occurs without pathologies, then normally, menstruation does not occur, and 3 to 5 days after conception the pain disappears.
In case of fertilization, if the side hurts a week before menstruation, the woman may have an ectopic pregnancy. A feature of this condition is severe pain in the lower abdomen and lower back, which radiates to the right or left side.
In the absence of menstruation and the presence of pathological symptoms, you should not delay a visit to specialists. An ectopic pregnancy poses a risk to a woman's health and life.
Is the symptom a result of previous operations?
Surgical intervention of the gynecological type leads to injury to the functionality of the reproductive organs, the circulatory system and the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract. The causes of pain in the side before menstruation may be a consequence of a previous operation.
In addition to surgical interventions aimed at eliminating pathologies in a woman’s genital area, the cause may be an abortion.
Any form of abortion, in the absence of complications, should not cause pain in the left side during menstruation (as well as on the right). But with complications, for example, infection or perforation, the pain is intense in the lower abdomen, spreading to the lateral and lumbar areas.
The cause may be abortion or other gynecological procedures
Another reason is considered to be diagnostic curettage performed with violation of the procedure technique and damage to the muscle tissue of the uterine cavity.
Pain during PMS: localization and causes
According to various sources, from 75 to 90% of women[1] experience premenstrual syndrome. It is expressed to varying degrees in everyone: some feel only a slight discomfort, which they are accustomed to not paying attention to, while others suffer from severe pain. This condition requires mandatory diagnosis to determine the causes and subsequent treatment. But more often, PMS occurs in a mild or moderate form: the pain is moderate in nature, but in combination with psycho-emotional disorders it disrupts the usual course of life.
At the same time, in different women, pain due to PMS has different localization, character, and accompanying manifestations. In this regard, it is customary to distinguish between several forms of premenstrual syndrome.
- Cephalgic. Headache comes to the fore, constant or in the form of attacks, sometimes quite intense. Nausea and vomiting often occur, sensitivity to odors increases, pain in the heart area, irritability and a decreased emotional background are noted. PMS headaches can be similar to migraines.
- Edema. It is characterized by a slow removal of fluid from the body, manifested primarily by swelling and soreness of the mammary glands. The face, legs (especially legs), and hands also swell. The woman notes bloating, the scales show an increase of 1–2 kg. There may be complaints of increased sweating, itching, general weakness and malaise.
- Psychovegetative. The picture is dominated by emotional disturbances of various types. We'll talk about it a little lower.
The above division is arbitrary: all these forms are rarely found in isolated form; usually the manifestations are mixed. Most often, PMS causes pain in the head, lower abdomen, lower back, and the mammary glands swell and become sensitive.
This is interesting . It has been noticed that the manifestations of PMS increase with age. If young girls relatively rarely experience severe discomfort before menstruation, then women after 30–35 years of age present such complaints much more often.
It is known that PMS pain is associated with hormonal changes. In the second phase of the cycle, progesterone levels decrease, and estrogen production, on the contrary, increases. This, in particular, may be the answer to the question of why headaches and swelling occur during PMS. Breast engorgement is caused by excess prolactin, produced by the pituitary gland during the luteal phase.
Why does premenstrual syndrome occur with different intensity? It can be assumed that the reason is the individual reaction of the female body to hormonal changes. In addition, there are factors that undoubtedly contribute to the painful manifestations of PMS. This:
- heredity;
- age over 30 years;
- hormonal imbalance caused by various reasons;
- gynecological diseases;
- frequent childbirth and abortion;
- disturbances in the functioning of the endocrine glands (in particular, thyroid disease);
- diseases of the nervous system;
- frequent or prolonged stress;
- overweight;
- bad habits;
- sedentary lifestyle;
- poor nutrition;
- lack of certain vitamins and minerals (for example, magnesium, zinc, vitamin B6).
PMS usually occurs 7-10 days before the onset of menstruation, and with the onset of discharge, all discomfort goes away. But for many girls and women, pain in the first days of menstruation is also typical. They are most often localized in the lower abdomen and lumbar region.
What to do if you have pain
It is not recommended to fight pain in the side on your own during the premenstrual period or during menstruation. The reason can be quite serious and lead to complications that will affect the life of the patient.
To alleviate the condition, you can take a painkiller or antispasmodic before visiting a doctor. Before taking the drug, you must read the instructions to make sure there are no complications.
It is advisable to consult a gynecologist when a symptom appears, and not delay until the end of the menstrual cycle. In some cases, diagnostics at the time of menstruation will facilitate the examination and provide more accurate data on the clinical picture.
What diagnostics
A medical examination begins with a detailed questioning of the patient about all the features of symptoms. After the doctor’s conversation with the woman, a gynecological examination is performed to assess the presence of possible gynecological pathologies.
Ultrasound examination is often performed
Diagnostic measures must be carried out:
- taking a smear;
- donating blood to check hormone levels;
- Ultrasound of the genital organs.
If a specialist in this field does not identify complications, the patient may be sent to another doctor. Further examination depends on the suspected diagnosis.
How to treat unilateral pain
Carrying out any measures to independently combat pain in the sides during menstruation involves a high risk of developing more severe complications.
Treatment for pain in the side should be prescribed only after all the necessary diagnostic methods have been carried out and an accurate diagnosis has been established.
Important! For pain in the left or right side, do not use traditional medicine. Do not heat the painful area, use compresses or herbal decoctions. Also, do not take uncontrolled amounts of painkillers or medications that have a targeted effect (for example, anti-inflammatory drugs).
All treatment features are determined by the doctor and depend solely on the diagnosis.
Watch the video to learn about the causes of pain in the right side:
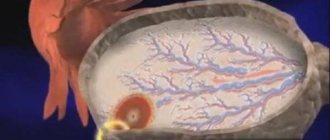
Pain in the ovaries after menstruation
The ovaries form an integral part of the female reproductive system. A woman’s ability to become pregnant, the development of the fetus and the general state of women’s health depend on them. Any pathological changes, pain syndromes and discomfort can be caused by organic changes in the body.
Organ structure
The organ is made up of connective fibers tightly intertwined with arteries, capillaries and vessels. On average, the volume of one ovary is 8 cm3, but during the menstrual cycle this size may change.
The ovaries are located on the sides of the pelvis. They connect to the fallopian tubes. The feeling of pain in the ovaries after menstruation makes itself felt because the ligaments with these tubes are penetrated by nerve fibers.
These organs can undergo changes throughout life, in particular, there are two types of development of changes:
- Irreversible – release of the follicle and maturation of the egg;
- Regular – changes within one menstrual cycle.
Pain after menstruation
Before menstruation begins, a woman's hormonal background undergoes several changes. The corpus luteum actively produces estrogen, the body prepares for future fertilization. When fertilization does not occur, menstruation begins. And after they are over, the hormonal levels return to normal.
It is during these days that symptoms of chronic diseases and pathological changes may appear. These include:
- Displacement of the reproductive organs - it can be a consequence of active drug therapy for infertility, hormonal contraception, or is a congenital anatomical feature. When using hormonal drugs, the reproductive organs increase slightly in size and can put pressure on neighboring organs and mucous membranes penetrated by nerves.
- Instability of psychological state. Since the menstrual cycle does not pass without changes in hormonal levels, a woman may experience despondency, insomnia, anxiety, and fear. Depressive conditions can cause a decrease in the activity of hormonal organs. In this case, the ovaries can suddenly become ill and calm down just as quickly if the root cause is eliminated.
- Endometriosis. This disease is characterized by excessive separation of the uterine endometrium and its growth. At the same time, the endometrium can end up in both the fallopian tubes and the ovaries. This can cause pressure on the nerve networks from the inside.
- Ectopic pregnancy. Despite the fact that menstruation has finally begun, the development of the fertilized egg in the fallopian tube often makes itself felt much later.
- Peritonitis. Inflammatory foci in the abdominal area are manifested by the fact that after menstruation the entire area of the lower abdomen hurts. Peritonitis occurs against the background of diseases that worsen during menstruation - cysts, neoplasms, hemorrhages into the ovarian cavity.
Pain on the left
Common reasons why pain may occur in both ovaries after the end of menstruation have been listed. Some patients complain that the ovary on the left and only one hurts.
Even when the disorders listed above affect both ovaries, some of them may be localized and affect the left one. This area of the peritoneum contains the intestines and urinary system. Therefore, pain in the left ovary can become a symptom:
- Oophoritis is an inflammation that most often affects the left ovary; the pain is paroxysmal;
- Cysts are accumulations of fluid in a small oval that puts pressure on the ovary;
- Apoplexy - effusion of blood into the ovarian cavity.
In this case, the symptoms and pain are more pronounced than with a similar diagnosis for the right organ, since the intestine is located nearby. The pain will be more pronounced when the intestines are swollen and feces pass through it.
Pain on the right
If the right ovary hurts after menstruation, the reasons may be hidden in the same diseases as for the left one. But there are several conditions that are more typical for the right ovary and pain in it:
- Apoplexy is damage to blood vessels in the right ovary due to infection, inflammation, or heavy physical activity. Most often it occurs in the right ovary due to the fact that it is fed by a large artery.
- Appendicitis - developing inflammation of the appendix can also cause pain in the area of the right ovary.
Also, pain for both ovaries can also occur due to an increase in the size of the uterus, which puts external pressure on the organs and displaces them somewhat. This condition is accompanied by acute pain and requires medical attention.
Cyst and neoplasms
Any of the ovaries can be subject to cyst formation. Most often, the cyst affects the left side, but doctors find it difficult to answer what these statistics are related to.
The formation of a cyst occurs due to the inability of the egg to be released and the thickening of the ovarian membrane. The organ can hurt both before and after menstruation. Additionally, the cyst is accompanied by symptoms such as increased urination, nausea, menstrual irregularities, and slight bleeding in the middle of the cycle.
A discovered cyst requires constant gynecological monitoring, treatment, and sometimes immediate removal is required if it increases in size and interferes with the functioning of other organs.
Apoplexy
A fairly serious disorder, which may be accompanied by pain after menstruation, is bleeding. It occurs due to vascular damage, excessive physical activity, as a complication of inflammatory processes in the pelvic organs.
Most often observed in the right ovary. Symptoms of apoplexy are sharp pain in the ovary throughout the menstrual cycle, which can radiate to the lower back, groin, and rectum. Pale skin, dizziness, vomiting and nausea, chills and increased body temperature may also indicate organ apoplexy.
If pain develops, body temperature increases, and the condition becomes worse, immediate help is required to prevent the development of intra-abdominal bleeding.
Treatment measures
Self-treatment of pain syndrome is possible only when it is caused by anatomical features, or the pain is provoked by a cyst and special medications are prescribed by the gynecologist. In all other cases, it is recommended to contact a specialist and eliminate the root cause.
In addition, regularity, smooth movement, and lack of physical activity are recommended. Painkillers may be taken. It is advisable to avoid sexual contact, stress, lack of sleep, and eat well before consulting a doctor.
Pain and disrupted menstruation that last the entire month, regardless of the day of the cycle, require diagnosis of the pelvic organs, ultrasound, additional blood and urine tests, as they can be caused by gastrointestinal diseases, only radiating pain to the pelvic area.
Source: https://GormonOff.com/zabolevanija/reproductive/bol-v-yaichnikax-posle-mesyachnyx