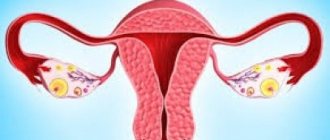
The ovaries are an important organ of the female reproductive system. They produce hormones, including estrogens and progesterone, which affect a woman's menstrual cycle and well-being.
They are also responsible for the formation of the egg, without which pregnancy is impossible. Pain in the ovaries can be physiological, that is, natural, and pathological.
If pain occurs, you need to eliminate all suspicions by visiting your gynecologist.
Many women associate nagging pain in the lower abdomen with the ovaries. But it is very difficult to determine this without examining a doctor.
Similar sensations occur with pathologies of the fallopian tubes, uterus, bladder and intestines. Therefore, for chronic pain, you need to seek help from a doctor and not self-medicate.
How to determine what pain is in the ovary
Feeling pain in the lower abdomen, a woman often doubts whether it is the ovaries or some other organ that hurts (for example, appendicitis). How to understand that the ovary hurts? Unfortunately, it is quite difficult to independently determine the cause of discomfort. Many diseases of the pelvic organs are localized in the lower abdomen and can radiate to the lower back, leg or hip. Therefore, it is strictly forbidden to take any medications without consulting a doctor. Where do the ovaries hurt? If the gynecologist confirmed that the discomfort is actually caused by the appendages, then most often the pain appears in the lower abdomen and is aching, pulling or stabbing in nature. Sometimes it radiates to the leg, lower back or entire back. It often happens that only the right ovary hurts. This is due to the fact that it was in the right appendage that ovulation occurred, a cyst appeared, or some other disease arose.
Why do the ovaries hurt and what to do about it?
The ovaries are paired glands located on either side of the uterus. They produce female sex hormones, on which the monthly cycle and the development of secondary sexual characteristics depend. And also - eggs, the “harvesting” of the future baby (if, of course, the egg is fertilized).
Considering the rather significant load, the ovaries can sometimes ache, this is a natural process. However, in some cases, nagging pain in the right or left lower abdomen is a symptom of serious illnesses. And it is important not to lose sight of this difference.
Why do the ovaries hurt?
Lifehacker has collected six main reasons.
Ovulation
Some women experience pain in the ovaries as they release a mature egg into the fallopian tube (a process called ovulation). Typically, this occurs around the middle of the monthly cycle.
The pain can vary. For some it lasts literally a few minutes. For some it lasts for hours.
Doctors have not yet figured out the causes of painful ovulation (aka mittelschmerz, from the German mittelschmerz - “middle pain”). It is assumed that the unpleasant sensations arise due to the sensitivity of a particular woman to the rupture of the follicle - the sac where the egg is contained and which she ruptures in order to break free.
Another theory suggests that Mittelschmertz occurs due to a sharp increase in the size of the egg in the ovary just before ovulation.
What to do
In general, nothing. Mittelschmerz goes away on its own and rarely lasts longer than a day. The sensations are most often tolerable, and to relieve the discomfort, it is enough to take an over-the-counter pain reliever - for example, ibuprofen.
You can try to get rid of Mittelschmertz altogether. To do this, contact your gynecologist and tell us about the problem. The doctor will prescribe you a suitable contraceptive that will simply prevent the egg from maturing and causing you pain.
Ovarian cyst
Sometimes it happens that the egg is not released from the ovaries during ovulation, but remains inside its own membrane - the follicle. Such an unbursted follicle is called a cyst.
Cysts usually have no symptoms and dissolve on their own over time.
But if the cyst is large, it can cause a dull, aching pain in the area of the affected ovary. Or even worse - at some point it will burst. The rupture is accompanied by sudden acute pain and bleeding into the abdominal cavity, which can lead to extremely unpleasant consequences, including peritonitis and death.
Neoplasms in the ovaries
Not only large cysts, but also tumors can cause pain. We are not necessarily talking about cancer: neoplasms in the ovaries can also be benign. You can assume that some foreign object has appeared in the ovaries based on the following symptoms:
- a bursting sensation often appears in the lower abdomen;
- you have an increased urge to urinate;
- diarrhea or constipation occurs regularly and seemingly without reason;
- you have lost your appetite or feel full after eating just a couple of bites;
- you are losing weight, although you have not changed your diet or physical activity.
Endometriosis
We talk about endometriosis when the tissue lining the walls of the uterus (endometrium), for some reason, begins to spread beyond the uterus. Sometimes it affects the ovaries.
The problem is that the endometrium is a hormone-sensitive tissue.
When the period comes, it is rejected. And at the same time it causes inflammation and swelling of the organ on which it has grown. In our case - the ovaries.
You can assume ovarian endometriosis if, in addition to aching pain in the ovarian area, you observe the following signs:
- prolonged and painful periods;
- pain during intercourse and defecation.
Inflammation of the ovaries
Perhaps they have become infected. Most often this happens with sexually transmitted diseases. But the causes of inflammation can be other - for example, autoimmune diseases, endocrine disruptions or hypothermia.
Sometimes inflammation of the ovaries is practically asymptomatic - except for nagging pain. But, as a rule, other signs are still present:
- pain during sex;
- vaginal discharge, often with an unpleasant odor;
- fever;
- weakness;
- painful urination.
Referred pain
The question is: are you sure that it is the ovaries that hurt? There are many other organs located next to them. Perhaps the pain comes from them? Here are a few common conditions whose symptoms can be confused with ovarian pain:
- constipation;
- current pregnancy;
- urinary tract infections;
- stones in the kidneys;
- developing appendicitis.
When you need to urgently seek help
Call an ambulance or contact a gynecologist as soon as possible if there is pain in the ovary area (no matter the right, left or both at once):
- sudden and strong;
- accompanied by nausea or vomiting;
- seems to you to be directly related to an increase in temperature to 38 °C or more.
All three symptoms are a clear indication for immediate examination and, possibly, surgery. You need to act especially quickly if weakness, dizziness and sticky cold sweat appear along with these signs.
But even if there are no health and life-threatening signs, you still need to listen to yourself. At a minimum, this can save you from possible problems in the future.
Source: https://Lifehacker.ru/bolyat-yaichniki/
Causes of pain in the ovaries associated with the phases of the menstrual cycle
Throughout the entire menstrual cycle, a woman’s reproductive organs and hormone levels change. Likewise, the ovaries are constantly undergoing changes.
During ovulation
Some women do not feel signs of ovulation. Others, on the contrary, say that the pain in the ovarian region during this period acquires a stabbing, pulling character. Brief discomfort does not pose a threat to the body and does not require any treatment. This is due to the rupture of the follicle, which releases a mature egg for conception. Also, during ovulation, the ovary may prick due to exacerbation of inflammatory processes in the pelvic organs (adnexitis, oophoritis). At the same time, after training, stress, or lifting weights, unusual discharge is observed. To reduce pain and relieve discomfort in the lower abdomen, a woman is recommended to take analgesics (Spazmalgon, No-Shpa). If after taking a painkiller the ovaries still hurt, then the reason is not ovulation. The patient needs to consult a doctor, be examined, and begin appropriate treatment.
During your period
It is considered normal if pain in the ovaries appears a few days before the start of menstruation and becomes stronger during it. On the first day, women feel mild nausea and dizziness. The nature of the pain is twisting, stabbing, aching. There are cases when, towards the end of menstruation, a woman begins to vomit. This is a rather rare symptom of menstruation, therefore, if such a “side effect” has not been observed before, you should undergo a gynecological examination and ultrasound diagnostics.
Lifting weights, overwork, disturbances in the psycho-emotional state, and constant stressful situations lead to an increase in pain and a worsening of a woman’s general well-being. What can be done in this situation and how to reduce the pain? No treatment is required for painful periods. A woman just needs to take a painkiller (for example, Tamipul) or apply a warm heating pad to her lower abdomen. Herbal infusions and decoctions are good for relieving pain in the ovaries during menstruation. If it is summer at this time, you can collect fresh leaves of the hogweed, red brush, chamomile flowers, or simply purchase ready-made herbal infusions at the pharmacy.
During menopause
Menopause is accompanied by a series of hormonal changes in the body due to the lack of bleeding. She appears individually. Menopause occurs at the age of 45-50 years. The onset of menopause can provoke pain in the ovaries, but such pain does not last long. During this period, a woman is more susceptible to infections and viruses. If the discomfort in the lower abdomen does not go away for a long time, painkillers do not help, and the pain only grows and intensifies, you need to urgently contact a gynecologist.
The following are the causes of pain in the ovaries after menopause:
Pain in the ovaries is accompanied by changes in vaginal tissue, frequent urination, sweating, impaired bowel movements, and increased body temperature. Therapy depends on the nature of the complaints and the identified cause of discomfort.
Left ovary hurts: causes and treatment methods
The ovaries are the paired female genital organs, which are responsible for the proper production of hormones and the maturation of the egg.
Their sizes, reactions and secret activities at different times are not the same. Quite often, women turn to a gynecologist complaining of pain in the ovarian area. The appearance of pain in the lower abdomen is the main symptom of a disease of the appendages. Most often, pain occurs on the left side, which can radiate to the hip or lower back. In this article we will tell you why the left ovary hurts and in what cases it is necessary to contact a gynecologist.
Causes of pain on the left
If a woman has pain in the ovary on the left, this may indicate not only ovulation or the imminent onset of menstruation, but also the development of diseases of the reproductive organs.
The following are the causes of pain:
- inflammation;
- rupture of the appendage (apoplexy);
- cyst;
- torsion;
- ectopic pregnancy;
- recent pelvic surgery.
Let's look at each cause of pain in more detail.
Inflammatory diseases
If the left ovary is pulled and there is sharp pain in the spine or lower abdomen, this indicates inflammation (oophoritis). The disease first develops in one appendage, and then affects the other. As a result, the patient has pain in the right and left ovaries at the same time.
The appearance of oophoritis is facilitated by infection in the pelvic organs. Most often, infection is caused by mycoplasma, ureaplasma and other microorganisms. Inflammation quickly manifests itself in a woman’s body, resulting in pain in the left ovary.
This may be tingling in the lower back, pulling or aching pain in the groin area.
Some of the main causes of inflammation are hypothermia, a weakened immune system, and overwork of the body. A woman becomes irritable, has poor sleep, headaches and decreased performance. Soon pain appears in the lower abdomen. Incorrect treatment or its absence leads to the inability to bear a child or become pregnant.
If you experience acute pain in the left ovary or intense tingling in the lower back, you should immediately consult a doctor!
Apoplexy
Ovarian rupture
Apoplexy is a violation of the integrity of the ovary, which is accompanied by increased heart rate, fever, vomiting, weakness and excessive sweating. If the rupture occurred on the left, then, accordingly, the left appendage tingles. The pain is acute, it is impossible to endure it. Sometimes a woman may lose consciousness.
Important! If a woman experiences sharp, acute pain in the ovarian area that cannot be relieved with painkillers, you should immediately call an ambulance! Otherwise, not only internal bleeding may occur, but also death.
Cyst
A cyst is a neoplasm on the ovary, the symptoms of which can easily be confused with other diseases of the pelvic organs. It can occur on both the left and right ovary. If several cysts appear on both appendages, the patient is diagnosed with polycystic disease.
Cystic formation threatens apoplexy, torsion of the leg, and infertility. Increasing in size, the cyst begins to put pressure on nearby pelvic organs.
Such pressure leads to poor blood circulation, disruption of the normal functioning of other organs, inflammation and death of appendage tissue.
During this period, the girl experiences a dull pain, which is localized on the side where the tumor appeared. For example, a cyst on the left ovary will manifest as discomfort in the left side of the abdomen.
Torsion
Ovarian torsion is a revolution of the ligaments of the appendage, in which there is compression of the vessels and disruption of the nutrition of the ovary. Accompanied by nausea, vomiting, spasmodic and stabbing sensations in the lower abdomen on one side (in this case, the left). Sometimes the left ovary tingles.
Most often, ovarian torsion occurs during sports, heavy work, or other physical activity. As a result, mobility of the appendages occurs, which soon begin to ache. This disease often occurs in active girls during childhood.
Types of incorrect embryo attachment
Ectopic pregnancy
If the fertilized egg attaches incorrectly, for example, to the left ovary, an ectopic pregnancy develops. In this case, the woman experiences a pulling or cramping pain on the left side of the abdomen, which radiates to the lower back or rectum.
An ectopic pregnancy should be terminated as early as possible in order not only to prevent the development of complications, but also to preserve reproductive function.
If the left ovary hurts and at the same time there are other signs of a pathological pregnancy (bloody discharge, weakness, etc.), you need to contact a gynecologist and have an ultrasound of the pelvic organs.
Pain after surgery
Absolutely any surgical intervention is considered a major injury and shock to the body. That is why pain after surgical procedures is acceptable and does not pose a threat to the body. But if the ovaries do not stop pulsating, aching, or dragging for several weeks, and the pain intensifies, the woman needs to consult a specialist.
One of the common operations of the appendages is follicular puncture, the postoperative period of which is also accompanied by painful sensations.
A woman may also experience discharge with an unpleasant (sour) odor, severe bloating and aching pain in the left ovary.
Such signs are associated with injury to the tissues and vessels of the appendage, although the injection itself is practically painless.
During the puncture, a small bleeding wound or hematoma is formed, which aches for some time. The pain lasts no more than five days. If the pain does not subside, is accompanied by fever, unusual discharge appears, bloating or loss of consciousness, you should consult a doctor.
Pain during intercourse
Active sex using a variety of positions is sometimes accompanied by discomfort in the lower abdomen. In this case, pulsation, aching, and pricking may occur in both the left and right ovaries. Unfortunately, this manifestation does not bode well.
The main causes of pain during sex in the left ovary can be:
- inflammation and infections of the genital organs;
- cyst;
- penetration too deep;
- muscle tension;
- cervicitis;
- vaginal dryness;
- adhesive processes.
In any case, if painful sensations are observed with every sexual intercourse, you should consult a gynecologist.
Painful sensations in the left ovary in early pregnancy may indicate the presence of a corpus luteum cyst.
Pain during pregnancy
Among many women, there is an opinion that pain in the ovaries is the main sign that a girl is pregnant. But statistics show that this pain syndrome is absolutely not associated with the appendages. This is due to the fact that during the period of bearing a baby, the uterus stretches, the ovaries rise above the place where they were previously located.
Pain during pregnancy is caused by stretching of the ligaments that support the appendages and uterus. Ovarian tension occurs in women. The expectant mother can cope with such discomfort on her own through proper nutrition, frequent rest and light exercise.
If the pain bothered you even before pregnancy and continues further, then you should visit a doctor. It is necessary to find out the causes of pain in the left ovary as early as possible, since it can not only be enlarged, but also pose a threat to the child.
You should also remember the preparation for conception and preventive methods of diseases even before pregnancy, since the appendages can get sick already during pregnancy and have completely different consequences, including miscarriage and placental abruption.
Causes of pain not associated with serious illnesses
The main reason why the ovary may hurt is considered to be hormonal changes in the female body that occur during menstruation and ovulation. Ovulation is accompanied by the rupture of the dominant follicle and the release of the egg.
As a result, irritant effects occur on the nerve endings, which can lead to variable pain on both sides at once. However, if a mature egg has come out of a follicle located on the left ovary, then, accordingly, there will be discomfort on the left.
There have been cases when women felt ovulatory pain even at 8 DPO (day after ovulation)
Many people are interested in why pain occurs in the appendage area during menstrual periods. This is due to a decrease in estrogen levels or endometriosis. It is endometriosis that manifests itself most during menstruation. A woman experiences not only pain in the appendages, but also constant nausea, weakness, loss of strength, and difficulty urinating and defecating.
Primary diagnosis and pain relief
As mentioned earlier, if a girl feels discomfort in the left ovary, then there are various reasons for this. Some do not pose a threat to health and disappear on their own in the near future. Others appear periodically and with varying intensity.
It is these symptoms that should alert you, as they can lead not only to a deterioration in your general health, but also to infertility. What to do in this situation? The first thing you need to do is contact a specialist and undergo a gynecological examination.
Using palpation, the gynecologist will palpate the ovaries, determine their size and localization of pain. This pressure on different areas of the lower abdomen makes it possible to find out the main cause of discomfort in the left ovary and will direct you to an ultrasound to confirm or refute the diagnosis.
To determine the cause for sure, a specialist may also prescribe tests.
You can relieve painful symptoms yourself. However, this should only be done after consulting a doctor. To do this, you must adhere to the following recommendations:
- pause training and avoid other intense physical activities;
- eat well and add as many vitamins as possible to your diet;
- do not drink or smoke;
- avoid conflict situations and stress;
- take painkillers.
Thus, the appearance of even minor pain in the left ovary requires a mandatory examination and compliance with all the instructions of a specialist.
Source: https://oyaichnikah.ru/zabolevaniya/vospalenie/bolit-levyj.html
Causes of pain that require treatment
As mentioned earlier, if pain in the ovaries lasts more than two to three days, and discharge of an uncharacteristic color and odor appears, this indicates a disease of the pelvic organs. Most often it is inflammation, cystic neoplasm, cancer, miscarriage or ectopic pregnancy. Let's look at each reason in more detail.
Inflammation of the ovaries
Inflammation may be accompanied by severe pain in the lower abdomen and fever. It can be unilateral (affects one appendage) or bilateral (occurs on two ovaries at once). In acute inflammation, the following symptoms appear:
- sudden severe pain in the ovarian area;
- fever;
- chills;
- purulent vaginal discharge;
- abdominal cramps;
- constipation;
- nausea.
Due to lack of treatment and resulting scarring, symptoms may persist for years, even after healing. If there is a sharp stabbing in the lower abdomen, then the ovary is inflamed. The occurrence of infection of the appendage is influenced by:
- frequent change of sexual partners;
- vaginal contraceptives (spiral);
- smoking;
- regular vaginal douching;
- curettage, abortion.
Treatment of pelvic inflammatory diseases occurs with the help of oral antibiotics and vaginal suppositories. Therapy depends on the nature and severity of the pathology. If the ovaries are very painful, the symptoms are pronounced, up to loss of consciousness, hospitalization and intravenous antibiotics are required.
Burning sensation when urinating and constipation
A burning sensation in the appendages when emptying the bladder can be caused by cystitis, recent surgery, or genital tract infections. In these cases, it may be accompanied by sharp, aching pain. With cystitis, there is a constant urge to urinate.
With prolonged constipation, the intestines compress the pelvic organs. A burning sensation may occur in the appendages. This discomfort is especially likely to occur during ovulation and in the presence of a cyst. The symptom goes away after the bowel movement is restored.
Inflammatory processes
Both appendages are susceptible to inflammation, but most often only one of them is affected. With this ovarian pathology, other signs of the disease are present:
- increase in body temperature,
- fever,
- pathological vaginal discharge,
- aching pain in the lower abdomen,
- nausea, vomiting.
Treatment must be started immediately. Otherwise, there is a high probability of the inflammatory process spreading to nearby organs.
Oncology
Ovarian cancer begins with the formation of a neoplasm. As it grows, symptoms of the disease appear - burning of the appendages, aching pain in the lower abdomen. Patients complain of general malaise and decreased immunity. The prognosis for recovery depends on the type of tumor and the stage at which the disease was detected.
Women over 45 years of age with a history of miscarriages, abortions, and long-term inflammatory diseases of the genital organs are most susceptible to the oncological process in the appendages.
Pain in the lumbar region and lower abdomen
In 90% of cases, girls and young women complain of simultaneous pain in the ovarian region and at the lumbar level. Banal prolonged hypothermia is the first reason for the occurrence of such unpleasant sensations. If hypothermia is excluded, then this indicates the presence of one or more pathologies of the genitourinary system, for the diagnosis of which the nature of the pain, frequency of occurrence, and also its duration are of great importance.
Relieving pain with folk remedies
What to do at home when your ovaries hurt? After visiting a specialist and with his permission, you can resort to treating the problem with the following folk remedies:
- To treat problems with the ovaries, courses of healing mud baths with clay or sea salt are prescribed.
- Also, to relieve pain in the female genital area, it is recommended to eat juniper berries three times a day or drink a decoction based on them. To prepare the drink, pour boiling water over 100 grams of berries. Let the product sit for two hours. Take this remedy 4 times a day at the dosage prescribed by your doctor.
- Pour boiling water over 15 grams of viburnum berries and let stand for a quarter of an hour. The resulting viburnum tea should be drunk in small sips at a time.
- To gradually reduce pain in the ovaries, you can drink 30 grams of aloe juice twice a day before meals.
- Mix 100 grams of dried cucumber with 75 grams of knotweed and 100 grams of sweet clover. Pour 30 grams of the resulting herbal mixture into 500 ml of boiling water. Let it sit in a thermos overnight. Drink the strained tincture four times a day, 100 ml before eating.
- Mix licorice root with string, horsetail, rose hips, immortelle, elecampane and alder in equal proportions. Pour 30 grams of the resulting herbal mass into 500 ml of boiling water and let stand in a warm place for 12 hours. The finished infusion should be drunk 1/4 cup three times a day before meals for two to three months.
- It is recommended to drink chamomile infusions, teas or take baths based on it.
It is also important to change your diet. Avoid fried and salty foods. Eat more vegetables, fruits, dairy and fermented milk products. The best option for pain in the genitals is to drink yogurt and pumpkin juice.
Recipe with viburnum juice and honey
If pain in the ovaries is caused by the formation of a cyst, the doctor may advise making a remedy at home from fresh viburnum juice and natural flower honey. The drink is prepared from the specified components mixed in equal proportions. Treatment regimen for pain in the ovaries:
- It is recommended to drink 1/4 tsp for seven days. before breakfast.
- The next week you can take 0.5 tsp. healing medicine in the morning on an empty stomach.
- Over the next seven days, it is recommended to use 1 tsp of the product. twice a day.
- In the fourth week, you need to drink the medicine at a time in the amount of 15 grams twice a day.
After drinking viburnum juice with honey for a month, it is recommended to take a break for seven days. Then the treatment is resumed, but gradually a single dosage of 2 tbsp. l. must be reduced to 1/4 tsp. In other words, therapy is carried out in the opposite order.
Read more in the article “TOP 10 folk remedies for ovarian cysts”
Recipe with white acacia
To treat pain in the ovarian area caused by adnexitis, you can use white acacia. The plant is used for internal use and douching.
To make an infusion, take 5 grams of dried white acacia flowers and pour 250 ml of boiling water. Cover tightly with a lid and let the product sit for 20 minutes. The resulting drink is drunk 4 times a day. Taking the product is not difficult, as it has sourness and a pleasant aroma. For better taste you can add a little honey.
To syringe 30 grams of dried white acacia flowers, pour 1 liter of boiling water. Simmer over low heat for five minutes and wait until the product becomes warm. The decoction is used for douching twice a day for two to three weeks. Douching with white acacia is recommended to be combined with the use of infusion.
More recipes for relieving discomfort in the ovarian area with adnexitis HERE.
Recipe with burdock
Burdock is used in the form of gruel and juice to treat pain caused by inflammation of the ovaries.
Turn the burdock leaves into a pulp and place them on the bottom shelf of the refrigerator in a jar. The mixture can be stored for no more than three days. Therefore, for a month, once every three days, you should prepare a new remedy from burdock.
During the first two days, take 1 tsp. twice a day. The next three days you should take 1 tsp. three times a day. Then for the next three days you need to consume 15 grams of gruel three times a day. Repeat the described treatment regimen four times. Take a month off and take the course again.
Squeeze the juice from the burdock leaves and let it sit for five days. After a while, the resulting product should be drunk three times a day, 12 tbsp. l. before the meal. The course of treatment can take up to 24 months.
How to quickly relieve pain due to inflammation of the ovaries at home, read the article “Treatment of inflammation with folk remedies”
Steam baths
Mix chamomile with yarrow, rue and wormwood in a 1:1 ratio. Pour 30 grams of herbal mixture into 1 liter of boiling water and simmer for 5 minutes over low heat. Pour the finished product into a bowl. Stand over it, legs apart and covered with a blanket. It is important to carry out steam baths carefully so as not to harm the vaginal mucosa. Therefore, if the steam is too hot, it needs to be cooled slightly.
After the procedure, it is recommended to immediately go to bed in a warm bed. A full course of steam baths consists of five procedures. You should not take steam baths during menstruation. It is best to resort to such procedures after consulting a doctor in order to avoid unpleasant consequences.
Ovarian cyst, adnexitis, inflammation of the appendages
Is it necessary to do something if there is prolonged discomfort in the lumbar region, but the ovaries do not hurt much and nothing else bothers you? With such seemingly minor complaints, it is still worth visiting a gynecologist - these may be the initial symptoms of the early stage of adnexitis (inflammation of the ovaries) or the development of cystic formations on the ovaries.
- Pain in the lumbosacral region is a sure sign of inflammation of the appendages (oophoritis). In this case, pain in the right ovary is observed much more often than pain in the left ovary.
- The left ovary hurts, it pulls the lower abdomen only on the right side, it hurts your back? In this case, you need to do an ultrasound, make sure there is no cystic formation and begin treatment of right-sided adnexitis or ophitis.
- Does your right ovary hurt? In this case, you need to be more alert and monitor changes in your well-being. Despite the fact that the right-sided localization of cystic blisters is observed almost 2 times more often, acute appendicitis also falls under the same painful symptoms, the treatment of which is not provided and surgical intervention is required.
Possible causes of pain in the ovary
In the ovaries, eggs mature and can be fertilized after leaving the follicular membrane. If these paired organs are healthy and functioning normally, this process is regularly repeated every month. At the same time, the ovaries produce sex hormones that affect the reproductive and general health of a woman. Any pathology that occurs in these organs (an inflammatory process or the appearance of neoplasms) leads to disruption of their functioning, which is manifested by changes in hormonal levels, cycle disruption, and often infertility.
The right ovary usually hurts more often. This is explained by the fact that processes associated with the maturation of follicles and ovulation occur in it more actively than in the left one. The reason for this phenomenon is the difference in their blood supply and nutrition with useful elements. Due to its activity, the right ovary is more vulnerable to possible damage and infection. In addition, on the right side, directly next to it, is the appendix. When it becomes inflamed, bacteria easily enter the ovary.
Pulling, aching, shooting, constant or paroxysmal pain may appear. Unpleasant sensations are not always associated with diseases. Sometimes their appearance is explained by the peculiarities of natural physiological processes in the body.
Physiological reasons
Overwork, stress. A weak aching pain in the ovary occurs if a woman is worried, physically tired, or hypothermic. As a rule, such pain quickly disappears after the source of stress is eliminated.
Cystitis
Acute and chronic cystitis is another reason for pain in the lower abdomen and back. In addition to severe paroxysmal pain, the following symptoms are indicative of the disease:
- increase or decrease in temperature;
- nausea (up to vomiting);
- frequent and false urge to urinate, which may be painful at the end of the act.
During periods of exacerbation, there may be blood in the urine and slight spotting. Cystitis cannot be ignored. The chronic form can lead to interstitial cystitis, which requires lifelong treatment.
Why does it hurt where the ovaries
Purely female diseases, characterized by pain in the ovaries, often occur in women of all ages. Physiological, mild pain does not cause much concern.
Others may be the result of serious pathologies of the reproductive or organs located in the pelvis.
Therefore, every woman needs to know where the ovaries are located, when and why they can hurt, and what to do if certain symptoms occur.
Answers to basic questions
The main questions that worry women and to which you need to know the answers so as not to miss a serious illness or complication.
When to call a doctor
You should call an ambulance in case of sharp, sudden, throbbing pain, accompanied by nausea, vomiting, fever, and general weakness. With these symptoms, the patient requires mandatory hospitalization.
If there is throbbing pain on the side of the left or right ovary, this may indicate torsion of the cyst stalk.
An increase in temperature, spotting, pulsation in the lower abdomen after hysteroscopy or ablation (curettage) of the uterine mucosa requires immediate medical intervention.
There is throbbing pain, nausea, vomiting, abdominal tension, bleeding - the main symptoms of a ruptured tube during an ectopic pregnancy, spontaneous miscarriage (abortion), ruptured appendix - you urgently need to call an ambulance.
Important: Such conditions, which doctors call “acute abdomen,” are dangerous to health and life. Therefore, you should not hesitate to see a doctor.
Pulsation radiating into the leg is a consequence of diseases such as complications of a hernia, femoral or inguinal, purulent inflammation of the appendages, acute appendicitis. The best decision is to call an ambulance for immediate hospitalization.
Which doctor should I contact for pain in the ovary?
If you experience mild pain that does not require urgent medical intervention, you need to make an appointment with your local gynecologist and undergo an examination. If there is an assumption that the symptoms are caused by other concomitant pathologies, the doctor will prescribe consultations with the appropriate specialists.
What tests can doctors prescribe for pain in the ovary?
The list of studies depends on the presumptive diagnosis, the possibilities of outpatient or inpatient treatment.
- general or detailed blood and urine tests;
- Ultrasound of the pelvic organs;
- intravaginal gynecological examination.
If infectious inflammation of the reproductive organs is suspected, vaginal smears or bacterial culture of microflora, sexually transmitted infections (mycoplasma, chlamydia, ureaplasma, gardnerella, gonococcus, candida) are prescribed.
If syphilis or HIV is suspected, an appropriate venous blood test is prescribed.
To identify endocrine disorders of the reproductive glands, blood tests are prescribed for the following hormones:
- LH – luteinizing;
- FSH – follicle stimulating;
- testosterone, estrogen, prolactin, progesterone;
- TSH – thyroid stimulating;
- SHBG – sex hormone binding globulin;
- DEA-S04 – dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate.
If a thyroid disease is suspected, additional tests for hormone levels are prescribed:
- T4-thyroxine;
- T3 – triiodothyronine;
- AT-TPO and AT-TG – antibodies to thyroid peroxidase and thyroglobulin.
If viral pathologies are suspected, blood tests are prescribed to possibly detect cytomegalovirus, papilloma viruses, herpes, and Epstein-Barr.
To clarify the diagnosis and simultaneous treatment, puncture and laparoscopy may be prescribed.
Can the ovaries hurt?
Of course they can. But it is impossible to independently determine whether the glands or other pelvic organs are suffering. Only a doctor can make an accurate diagnosis and prescribe treatment. If pain occurs, it is not recommended to take analgesics on your own, so as not to blur the clinical picture of a possible disease.
When the ovaries hurt
Pain syndrome in the lower abdomen, on the right or left, can manifest itself in various diseases of both the pelvic organs and the abdominal organs. Therefore, in such cases, differential diagnosis is necessary to exclude concomitant pathologies.
Why does the ovary hurt?
Tingling in the ovary is not always a sign of pathology. Symptoms such as aching, stabbing pain, aggravated by walking, can be observed after ovulation, when the contents of the follicle enter the abdominal cavity.
Tingling in the area of the right ovary occurs during pregnancy, as the growing fetus puts pressure on the glands and fallopian tubes.
In any case, only a specialist can make an accurate diagnosis.
How to understand that it is the ovary that hurts
It is impossible to answer unequivocally the question of why women’s ovaries hurt without a full examination. If the ovary is pulled for a long time, after menstruation, you definitely need to consult a gynecologist.
Why does my right ovary hurt?
The right ovary hurts and pricks when the egg matures in it. This is the so-called ovulatory syndrome, which does not require emergency treatment. The right ovary can be pulled before, sometimes during menstruation, during rough sex.
The pain may be due to a developing cyst, benign or malignant tumor.
Infections, hormonal disorders, endometriosis, apoplexy, ectopic pregnancy, torsion of the pedicle of the cyst, appendix provoke pain on the right side.
Why does my left ovary hurt?
Accordingly, similar causes of pain in the right ovary may appear in the left. But the left ovary hurts and stings less often than the right. The reason is that on the right side there are more arteries supplying the female organ. The gallbladder and appendix are located on the same side. Pain on the left side can be caused by the sigmoid colon, which is stretched due to untimely bowel movements.
Why do ovaries hurt in women?
Ovarian pain can be a natural physiological reaction of the body that occurs before and after menstruation, or it can be caused by pathological processes.
Another reason is the abolition of long-term use of oral contraceptives. After stopping the medications, the functioning of the glands is restored, which is accompanied by aching symptoms, tingling, and nagging pain.
Discomfort also occurs after surgery, which goes away after complete healing of the operated organ.
What to do if your ovaries hurt
Whatever pain you experience, you should definitely consult a gynecologist.
After the examination, the doctor will determine the causes, establish a diagnosis, give recommendations for therapeutic exercises, and prescribe medication or surgical treatment.
Please note: Many gynecological pathologies do not always have a clearly defined clinical picture. And it very often happens that when visiting a doctor, the gynecologist notes with regret that the disease is advanced. This is especially tragic for ovarian cancer pathologies.
Where do the ovaries hurt?
Paired organs are located in the lower abdomen, in the iliac region. Accordingly, pain occurs there.
Adnexit
Pain, constant, aching, with inflammation of the ovaries most often occurs on the right side, does not depend on the female cycle. Differentiation from appendicitis is necessary, especially if fever, nausea, and vomiting occur.
A sharp pain radiating to the hypochondrium and shoulder occurs when the fallopian tube ruptures. Accompanied by bleeding, weakness, dizziness, loss of consciousness. History: delayed menstruation, weakly positive pregnancy test. Help must be urgent. Apoplexy
If ovulation is too rapid, damage to the ovary occurs, followed by bleeding. The main symptoms are severe pain, weakness, cold sweat, and poor health. Surgical treatment may be necessary.
The first stages are asymptomatic or with subtle manifestations. Sometimes a woman consults a doctor when the cancer has already reached the third or fourth stage. Therefore, if pain occurs, it is better to receive qualified advice and the necessary treatment than to later suffer from complications or end your life with premature death.
Primary diagnosis and pain relief
Pain that occurs once, or its mild manifestations, often does not require medical intervention, as it is caused by natural physiological processes in the ovaries.
Recurrent pain syndromes require a thorough examination of the patient:
- external and intravaginal gynecological examination;
- Ultrasound of the reproductive organs, bladder, intestines;
- clinical and biochemical tests of blood and urine;
- diagnostic laparoscopy or puncture of the abdominal cavity followed by histological examination.
Source: https://mypochki.ru/pochemu-bolit-gde-jaichniki/
Ovulatory syndrome
Dull and aching pain in the ovaries, sometimes with slight spotting, and back pain can occur in the middle of the menstrual cycle. At the moment of ovulation, when the ovarian follicle bursts and the mature egg is released, a slight hemorrhage occurs. The cause of pain is blood entering the peritoneum. The duration of such pain is short - from 15 minutes to several hours. The pain occurs alternately and only on one side:
- pain in the right ovary indicates that during this monthly cycle, it was he who did the work of “growing” the egg;
- pain in the left ovary - signals its monthly activity.
You should not be surprised if there is a malfunction in the order of the ovaries. Pain in the right ovary can be observed several times in a row - according to nature’s orders, it is almost 2 times more active than the left one.
The cramping, spasmodic pain that occurs on the eve of menstruation is caused by the production of specific hormones - prostaglandins - during this period. For half of women, such moderate discomfort does not cause any particular problems. Treatment consists of taking painkillers and antispasmodic drugs, reducing physical activity, maintaining peace and avoiding conflict situations.
Possible causes of pain in the left ovary area
Pain in the left ovary is a sign of both physiological changes in the body and a signal of the development of pathologies. In order to detect the presence of the disease, it is necessary to conduct a diagnosis. Deviations in the functioning of the left appendage are often accompanied by menstrual irregularities.
Causes of pain
Without instrumental and laboratory tests, it is difficult to identify the cause of organ pain. There are two types of pain in the left ovary - physiological and pathological. The first ones can be distinguished independently; to do this, just listen carefully to your own body.
Physiological
The symptom occurs on certain days of the cycle. It is not very intense and causes virtually no discomfort to the woman. Possible causes of pain in the left ovary:
Cycle dayCauses
| 1-3 | The course of menstruation. Due to temporarily increased blood circulation during menstruation, there is pain in the left ovary. The symptom is especially acute in the presence of functional cysts. |
| 8-13 | Stage of follicle maturation. Their increase may be accompanied by slight nagging pain in the woman’s left ovary. |
| 14-15 | Ovulation. When the Graafian vesicle ruptures and the egg is released, there is sometimes a short-term acute pain of low intensity in the left lower abdomen. The duration of the symptom is from several hours to 1-2 days. |
| 26-28 | Preparing for the start of menstruation. |
The ovary on the left most often hurts during ovulation; discomfort is least often noted in the second half of the cycle.
A physiological symptom may be completely absent. Its presence is determined by the individual characteristics of the body. Often women who feel such pain in the left ovary experience severe discomfort in the lower abdomen during menstruation.
Pregnancy
Pain of natural origin includes pain during pregnancy. Successful conception may be manifested by unpleasant sensations in the left lower abdomen. The sign appears from the first days of a missed period. Its absence cannot exclude pregnancy, since its occurrence is individual.
The symptom is caused by the growth of the corpus luteum, which produces progesterone. This is explained by the body’s increased need for this hormone during gestation. Pain in the left ovary is often accompanied by nausea, dizziness, weakness and drowsiness. All these signs are a consequence of increased progesterone levels.
Pathological
Pain associated with the course of diseases of the left ovary appears regardless of the day of the menstrual cycle. They can have a pulling, stabbing, cutting or aching character and are more intense than physiological pain syndrome.
Types of pathologies that cause discomfort in the left appendage:
Disease Description and symptoms
| Inflammatory processes in the uterus and appendages | Nagging pain in the lower abdomen, painful menstruation. Possible disruption of the monthly cycle. With an acute type of organ inflammation, body temperature rises. |
| Infectious lesions of the genital tract | Pain syndrome occurs only when the infection is widespread. Accompanied by pathological vaginal discharge with an unpleasant odor, itching and burning of the external genitalia. |
| Hormonal disbalance | Pain in the left ovary due to hormonal imbalance often indicates its multifollicularity or the occurrence of functional cysts. At the same time, there are frequent delays in menstruation, probably their complete absence. Menstruation is characterized by high profuseness and pain. |
| Tumors | In the first stages of development of any tumor, there are no symptoms. Pain occurs only when the tumor reaches a size of more than 4-5 cm. Large tumors are manifested by asymmetry of the abdomen, with pain radiating to the left ovary and lower back. During the course of the malignant process, the menstrual cycle is disrupted, health deteriorates, weakness appears, and performance decreases. |
| Endometriosis | Initially it affects the uterus, then through the fallopian tubes the ovaries. It is determined by nagging pain in the lower abdomen, intermenstrual uterine bleeding, and interruption of menstruation. |
| Rupture of the appendage or its cyst | It manifests itself as acute severe pain in the left ovary; over time, its focus becomes impossible to determine due to the spread of pain throughout the entire abdomen. Distinctive signs of apoplexy are cold sweat, drop in blood pressure, increased heart rate, loss of consciousness or faintness. |
| Ovarian torsion or cysts | The symptoms are similar to a rupture, but are much less intense. Prolonged presence of an organ in a state of torsion can lead to its necrosis. |
| Adhesive process | It occurs as a result of a long course of inflammatory processes, endometriosis, as a postoperative complication. If the left ovary is affected by adhesions, there may be pain in the lower abdomen and disruption of the menstrual cycle. |
| Ectopic pregnancy | Until 6-8 weeks it manifests itself only as a delay in menstruation. Subsequently, the fertilized egg causes severe sharp pain in the area of the left ovary or fallopian tube. Surgery is required to eliminate it, otherwise the fallopian tube may rupture. |
Source: https://TvoiYaichniki.ru/vospalenie/boli-sleva
Endometriosis, fibroma
If a woman has severe pain in her ovaries during menstruation, her back is strained, and she experiences heavy bleeding, then these are clear signs of fibroids, fibromyomas, or endometriosis.
In fact, during menstruation it is not the ovaries that hurt, but the contracting uterus. Such contractions are needed to free its cavity from “unnecessary” endometrium. Therefore, severe pain indicates diseases of the uterus, not the ovaries.
To avoid persistent infertility, these pathologies require urgent treatment.
If your left side hurts, what should be the algorithm of action?
Pain in the left side when walking is a very common occurrence. More often they are harmless, but it is worth examining their possible causes in order to avoid complications.
Causes of pain in the left side
Pain in the left side can be functional or occur due to inflammation. To make a diagnosis, you need to have an idea of what organs may be involved in this process.
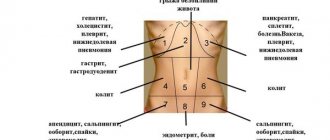
Subcostal area
Here are the left lobe of the liver, pancreas, stomach, spleen, part of the colon, small intestine, lower part of the lungs, diaphragm, heart.
Unpleasant sensations in this area can be caused by diseases of the heart, lungs (pneumonia and pleurisy), stomach, spleen, pancreas, duodenum, intercostal neuralgia, diaphragmatic hernia.
The digestive organs suffer not only from bacteria , but also from unhealthy diet, stress, and bad habits.
A rupture or bruise of the spleen is especially dangerous. The pain is sharp, characterized by the appearance of a bruise around the navel, a hematoma in the left side of the abdomen, colic can radiate to the back. In this case, it is necessary to call an ambulance.
Inflammation of the lungs can also be accompanied by dull pain in the left hypochondrium , aggravated by coughing. With pleurisy, they intensify not only during coughing, but also when changing body position and even when breathing.
Intercostal neuralgia is characterized by sharp pain in the side, which manifests itself even with the slightest movement or inhalation. Acute colic is observed with osteochondrosis and neuralgia, myalgia and injuries.
Stitching pain (usually in the muscles) can occur if the load is distributed incorrectly or if there is no preliminary warm-up before training.
Left side
Here are the intestines, kidneys, ureter, spleen, pancreas, stomach, genitals (uterus and ovaries in women, prostate and testes, testes in men). Most of the discomfort in this area is associated with the intestines.
Possible causes of pain in the left side:
- Colitis is accompanied by pain from flatulence, it is acute, cramping, and often occurs after eating. They may also be accompanied by false urges to empty the bowels, diarrhea, sometimes with mucus and blood.
- Nonspecific ulcerative colitis - pain is accompanied by general intoxication.
- Intestinal obstruction – pain does not depend on food intake and can occur at any time of the day. Their character is sharp and combative. If help is not provided, they may subside in 2-3 days. But this is not a recovery, but a complication. The clinical picture is complemented by constipation, bloating and asymmetry of the abdomen, nausea and repeated vomiting.
- Colon cancer - in advanced cases.
- Diseases of the genitourinary system - inflammation of the uterus and appendages, sexually transmitted diseases, intestinal infections, atypical appendicitis, cystitis, urethritis, endometriosis, ovarian cysts, tumors, ectopic pregnancy and menstrual irregularities. These pains can radiate to the lower back, anus and groin. Emergencies include torsion of an ovarian cyst and ectopic pregnancy. These pathologies require immediate hospitalization.
Localization and nature of pain
Pain is divided according to the mechanism of its occurrence, as well as according to its characteristics. They can feel like cutting, stabbing, dull and sharp, drilling, bursting, shooting, aching and encircling.
Classification of pain by source of origin:
- Visceral - appears due to inflammatory processes, injuries and bleeding from internal organs. It is associated with peristalsis of the intestines and stomach, and occurs during spasms or strains of the muscles of these organs.
- Neurological – occurs when the nerve trunks become inflamed.
- Somatic – constant and clearly localized. The pain is sharp, cutting, appears due to irritation of the peritoneum, for example, with peritonitis.
- Reflected - spreads from distant organs along nerve fibers due to the irradiation of unpleasant sensations. It does not arise in the organs of the left side, but comes here. For example, with left-sided lower lobe pneumonia, pleurisy, heart attack, liver disease.
Classification by pain intensity:
- Acute – intense, cannot be relieved with analgesics.
- Chronic – periodically occurring low-intensity unpleasant sensations that are relieved by analgesics.
Back pain occurs with pleurisy and inflammation of the lung. Lower back pain may indicate kidney pathology.
Pain after eating is usually associated with digestion. They are characterized as heaviness, discomfort and tingling, and may be accompanied by fever, chills, nausea and gas formation. This may also indicate the development of disorders in the pancreas . More often than not, all this is associated with poor nutrition.
When there is aching and pulling on the left side below the ribs in front, this is a symptom of sluggish duodenitis (inflammation of the duodenum).
If it stings on the side under the left rib during training or strength training, then this indicates insufficient warm-up. The body simply did not have time to prepare for the increase in blood circulation. They pass quickly and have no consequences.
When the aorta ruptures, the pain is sudden, severe in the abdomen or from the back. Immediately after this, collapse occurs - a sharp drop in pressure. A person can die in a matter of minutes from bleeding. You need to call an ambulance without wasting a second.
Stones and sand in the urinary tract cause sharp pain because the tissue and capsule of the organ are stretched, pressure increases and pain occurs, mainly under the ribs in the back.
The left side hurts in a woman and a man: what are the differences?
In men, this may be a consequence of inflammation in the genitourinary system. As a rule, this is accompanied by an increase in temperature.
Sharp pain may indicate:
- prostatitis;
- vesiculitis
- inflammation in the bladder, urethra;
- stones in the prostate gland;
- malignant tumors;
- inguinal hernia;
- gonorrhea, chlamydia, trichomoniasis.
In women with endometriosis or an ovarian cyst, there is nagging pain (both on the left and on the right). Similar to menstrual ones, but appear at any time. And the periods themselves lengthen and become more painful.
Nagging pain in the lower abdomen in women indicates problems with the left ovary . They get worse when walking. Although this may be due to inflammation of the fallopian tubes and uterine mucosa, and oncology.
In women, pain in the left side of the lower abdomen may occur during pregnancy due to intestinal displacement by the growing uterus. There is no danger if it does not become acute and is not accompanied by spotting and bloody discharge.
Even if the pain under the ribs, on the left, below, in the navel area or in the center quickly subsides, but is accompanied by vomiting, burning, fever, an ambulance should definitely be called. Any intake of food, water, or pills is not advisable. All this can blur the picture, complicating the diagnosis.
If a rare pain syndrome occurs, you can take painkillers. However, this method is optimal only if the pain is not accompanied by acute symptoms, such as fever, chills and nausea.
Important! Seeing a doctor is mandatory if the pain recurs and all the remedies used are useless.
Prevention
As for prevention, the basis is a proper balanced diet. It is advisable to minimize hot and spicy foods. Legumes can irritate the mucous membranes and cause flatulence.
It is important to give up bad habits such as smoking and alcohol , get proper rest and get a good night's sleep. Any training should be carried out only 1.5-2 hours after eating.
To avoid gynecological problems, women need to treat existing inflammation of the genital organs and undergo regular examinations by a gynecologist.
Doctors' advice
Doctors strongly recommend:
- Do not engage in self-diagnosis and treatment.
- In case of acute pain, do not endure it, but call an ambulance. This is the case when it is better to be safe.
- If the pain is not intense, dull, then it is better to consult a doctor at the clinic. You need to describe all your sensations without any embarrassment.
There is no need to assume that the pain in the left side will go away on its own; it is better to consult a doctor and identify the true cause. Taking painkillers gives only a temporary effect, but does not eliminate the disease itself. If pain occurs suddenly and lasts more than half an hour, it is better to play it safe and call an ambulance.
Source: https://mybegom.com/hotba/iz-za-chego-bolit-levyj-bok-pri-hodbe.html
Pregnancy
During pregnancy, complaints of pain in the lower abdomen and lumbar region are due to an increase in the load on the spinal column. But in the early stages of pregnancy, when the weight of the fetus and the weight of the woman herself have not yet increased significantly, such complaints may signal a threat of miscarriage.
If the pulling sensation does not cause pain, but is quite uncomfortable and occurs after the 20th week, false Braxton-Hicks contractions can be suspected. The reason for this phenomenon is considered to be increased excitability of the uterus, which does not require special treatment and goes away after taking warm water procedures and walking at a calm pace.
Ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome
The reason for the occurrence of acute lumbar pain and tension in the ovarian area may be the procedure of drug stimulation of ovulation. Symptoms may occur immediately or within 7 days after the hCG injection and do not always indicate a positive result.
As a result of an incorrectly selected dose of stimulant drugs, and most often due to an overdose of stimulant tablets by women and improper dilution of hCG powder, hyperstimulation syndrome develops.
In mild form, it causes discomfort in the lower abdomen and lumbosacral region, the ovaries increase in size and are tense, and the abdomen is often bloated. In more severe cases, fluid accumulates in the peritoneum, the ovaries clearly hurt, metabolism is disrupted, and the woman often gains weight.
Treatment consists of stopping any stimulant medications.
Chronic pelvic pain
Painful symptoms in the lower abdomen and below the level of the kidneys that persist for more than 6 months are called chronic pelvic pain. In 75% of cases it is caused by advanced gynecological diseases. The remaining 25% are classified as diseases that affect both women and men equally:
- development of adhesions in the pelvic area;
- diseases of the rectum and bladder pathologies;
- intervertebral hernia or vertebral lesions (arthritis, arthrosis);
- stroke;
- osteoporosis;
- in men – prostatitis.
What to do if you have pain
Once again you can safely repeat yourself - just consult a doctor, namely a gynecologist. This is the only reliable option that is highly likely to quickly return you to Noma. You also need to know about preventive measures, which we’ll talk about a little below. When you contact a doctor, he will examine you using ultrasound and x-rays, get acquainted with the test results, prescribe effective therapy, and then you will need to follow all his recommendations to the smallest detail. Treatment often includes the use of painkillers, antibiotics and antispasmodics. After surgery, treatment will be more intensive, gentle and extensive. You need to rest more, be less nervous and do all the prescribed procedures. Also avoid strenuous physical activity, eat well and give up bad habits.
Important! For preventive purposes, the appearance of pain in the left lower abdomen should be visited by your local gynecologist twice a year.
If your doctor has prescribed antibiotics for pain in your left ovary, then you strictly need to take them at a certain time. It is advisable to use some drugs clearly after 12 hours. Others may be prescribed three times a day. The main thing here is to maintain a strict period of time. As for painkillers, they can be used both to prevent pain and strictly when it occurs. In any case, an individual approach and the same method of selecting therapy are needed, based on the cause of the disease and the intensity of its manifestation.
We also recommend viewing: Using suppositories for ovarian inflammation: benefits, main types
Throbbing pain
Pains of a pulsating nature require special attention, especially if they last more than half an hour.
If there is pulsation on the left, the left ovary hurts, the temperature rises and general weakness occurs, then you should immediately consult a doctor or call an ambulance. If you contact your doctor with questions about why your left ovary hurts and what to do, you will probably hear in response - immediate hospitalization, you have torsion of a cystic ovarian pedicle!
The peculiarity of the location of the right ovary can cause pulsation in the lower abdomen on the right after curettage of the uterus or hysteroscopy. If pulsation occurs for no apparent reason, the pain increases, bleeding appears, the temperature rises, then the advice is the same - call an ambulance immediately! Not only can the cystic pedicle twist on the right side. Ectopic pregnancy (torsion, rupture of the tube), spontaneous abortion or ruptured appendicitis are the reasons that cause pulsation and pain in the right ovary.
Right ovary hurts and white discharge
Hello! Girls, such problems, I apologize in advance for such details, but yesterday I went to the toilet (in a big way), sharp pains began in the ovaries, as if during menstruation, but much stronger, I could not move, lay in one position and only 5 am I fell asleep. Today my right ovary hurts and there is white discharge. A week ago I had protected sexual intercourse. Could this be pregnancy or do I have a cold?
Woman.ru experts
Find out the opinion of an expert on your topic
Semikolennykh Nadezhda Vladimirovna
Psychologist. Specialist from the site b17.ru
Veronica Viktorovna Dobroselskaya
Psychologist, Weight correction. Specialist from the site b17.ru
Wrzecinska Eva
Psychologist. Specialist from the site b17.ru
Antakova Lyubov Nikolaevna
Psychologist, Consultant. Specialist from the site b17.ru
Tiselskaya Ekaterina Vladimirovna
Psychologist. Specialist from the site b17.ru
Korotina Svetlana Yurievna
Psychotherapist. Specialist from the site b17.ru
Nekrasova Natalia
Psychologist. Specialist from the site b17.ru
Anastasia Sergeevna Shikhaleeva
Psychologist. Specialist from the site b17.ru
Volkov Roman Leonidovich
Psychologist, Psychoanalytic therapist. Specialist from the site b17.ru
Sokol Larisa Ivanovna
Psychologist, Gestalt therapist. Specialist from the site b17.ru
Ovulation, right? During menstruation, the ovaries don’t hurt that much, if anything. Not during pregnancy either.
Looks like thrush
Looks like thrush
There is no pain with thrush. Thrush causes itching.
not only itching! but most likely it’s dysbacteriosis. Now I have the same nonsense, my eggs and discharge hurt. we had sex two months ago. In March, I was checked by a doctor with the same symptoms - they found only gardnerella.
Hello, I was also diagnosed with gardnerella and ureaplasma. Pain, burning, itching, white cheesy discharge. Tell me how you were treated for gardnerella?
Hello. I have this problem, the pain in my right ovary has been going on for almost a week now, and it intensifies when I walk, when I sit down, or when I move in some other way. All this is accompanied by white thick discharge with an odor. What could it be?
Hello. I have this problem, the pain in my right ovary has been going on for almost a week now, and it intensifies when I walk, when I sit down, or when I move in some other way. All this is accompanied by white thick discharge with an odor. What could it be?
Hello, I have the same symptoms, please tell me, did you find out what it was?
They also told me that there is a cyst on my right ovary.
Hello. I have this problem, the pain in my right ovary has been going on for almost a week now, and it intensifies when I walk, when I sit down, or when I move in some other way. All this is accompanied by white thick discharge with an odor. What could it be?
Complaint
Moderator, please note that the text contains:
The complaint has been sent to the moderator
The page will close automatically after 5 seconds
Forum: health
New for today
Popular today
The user of the Woman.ru website understands and accepts that he bears full responsibility for all materials partially or fully published by him using the Woman.ru service. The user of the Woman.ru website guarantees that the placement of materials submitted by him does not violate the rights of third parties (including, but not limited to copyright) does not damage their honor and dignity.
The user of the Woman.ru site, by sending materials, is thereby interested in their publication on the site and expresses his consent to their further use by the editors of the Woman.ru site.
Use and reprinting of printed materials from the woman.ru website is possible only with an active link to the resource. The use of photographic materials is permitted only with the written consent of the site administration.
Posting intellectual property objects (photos, videos, literary works, trademarks, etc.) on the woman.ru website is permitted only to persons who have all the necessary rights for such posting.
Copyright (c) 2016-2019 Hirst Shkulev Publishing LLC
Online publication “WOMAN.RU” (Zhenshchina.RU)
Certificate of registration of mass media EL No. FS77-65950, issued by the Federal Service for Supervision of Communications, Information Technologies and Mass Communications (Roskomnadzor) on June 10, 2016. 16+
Founder: Limited Liability Company "Hirst Shkulev Publishing"
What causes pain in the right ovary?
Pain in the right ovary does not appear just like that, of course, it can be associated with a mild and temporary illness that will go away on its own over time, in some cases it is a sign of a serious illness and the pain cannot be tolerated. You can, of course, take painkillers such as Ketonov, Nosh-pa, Analgin. But remember, pills do not cure, they only help to get rid of pain for a while. And in order to completely get rid of it, you need to know the cause of its occurrence.
The female reproductive system is very sensitive, it is influenced by various factors - viral diseases, hypothermia, fungal diseases, etc. Because of them, various diseases can develop.
Pain in the right ovary is a serious problem that leads to serious consequences, one of them is infertility.
If pain occurs in the right ovary, you need to pay attention to the person’s lifestyle and age.
Pain in the right ovary can occur in girls, women, and teenage girls who have not yet reached puberty. Most often, girls become hypothermic and inflammation occurs in the ovary.
1. Oophoritis provokes severe pain in the right ovary; this is inflammation that occurs due to infection, stress, colds, exercise, and decreased immunity.
2. Adnexitis is an inflammation of the right ovary, which occurs due to candidiasis, chlamydia, ureaplasmosis, mycoplasmosis. The pain occurs not only in the first lower part of the abdomen, but radiates to the lower back. If left untreated, this disease will lead to infertility. You should immediately contact a specialist who will thoroughly examine you, check the tests and prescribe timely treatment.
3. Pain in the right ovary occurs due to polycystic ovary syndrome, this can only be shown by computer diagnostics, the ovaries are filled with balls (cysts). This disease is
Source
Why does the lower abdomen feel tight after ovulation?
Ovulation is rarely accompanied by obvious signs, which makes it difficult to detect. But if the lower abdomen feels tight after ovulation, this is a completely common characteristic. However, there are also situations when you should visit a doctor with such a symptom. Let's look at it in detail.