Scarlet discharge from the vagina after the birth of the child occurs regardless of whether it was natural or using a cesarean section. The cause of bleeding is normally the restoration of organs, especially where the placenta was directly attached to the wall. As it slowly shrinks to the desired size, the woman's body expels the fluid from the wound.
If scarlet blood comes from the genital tract, most often this is a natural consequence of the birth of a child and it lasts from 14 to 21 days, but it happens that the discharge remains in a different form throughout the entire postnatal period. What is the normal amount of blood? When should you seek medical help if bleeding does not stop within a month after delivery? Let's consider each question in more detail.
"Good" type of bleeding
Dark blood clots that are released after the baby is born may be caused by lochia discharge. This is normal bleeding and is not dangerous to a woman's health.
If the postpartum period is stable and there are no complications, this type of bleeding should completely stop after 14-16 days. Moreover, it should be understood that “good” bleeding after childbirth cannot be abundant. Otherwise, this is a real pathological acute bleeding. In order to reduce the likelihood of severe bleeding after childbirth, immediately after the baby is born, doctors should apply a heating pad with ice to the mother's abdomen. Medicines should also be administered if necessary to stop the bleeding.
Important! All women should continue to bleed for several days or even weeks after giving birth. At the same time, if dark blood is released in small quantities and does not cause pain, then this is considered normal. The opposite picture will occur when a woman has red blood, which is accompanied by a high temperature. This condition is a good reason for an urgent visit to a specialist.
It should also be noted that bleeding occurs during late menstruation, which a woman may accidentally confuse with menstruation.
For those new mothers who do not breastfeed for certain reasons, the normal cycle can return to normal after 20 days.
Bleeding one month after birth
Giving birth to a baby is a complex physiological process for a woman. Bleeding a month after giving birth is not always normal. The threat to life is determined by the amount and nature of the discharge.
general information
When the birth proceeded normally without tears or cracks, then during the first 7-10 days mothers observe heavy bleeding. This physiological process in the body allows you to get rid of the remnants of the placenta, lochia and parts of the placenta.
If more than a month has passed since the birth of the baby, and the discharge has not stopped and has become abundant, pay attention to its nature and quantity. If there is no unpleasant odor and dark blood clots are not observed, then this is normal.
What kind of discharge should there be a month after giving birth:
- lochia is thicker on the first day, and after a week it becomes liquid;
- during the first days the blood has a bright scarlet color;
- on days 10-14 the shade changes to brown, the amount decreases;
- mucous discharge is light pink and odorless;
- after 4 weeks the lochia becomes transparent.
Normally, vaginal bleeding during the postpartum period continues for 6-8 weeks, depending on the health of the mother. The volume of blood lost during this period is about 1.5 liters. The body is completely renewed and cleansed.
Causes of spotting a month after childbirth:
- a caesarean section was performed;
- parts of the placenta remain in the birth canal;
- presence of fibroids;
- blood clotting is impaired;
- there was a rupture of the uterus or birth canal.
When a woman does not breastfeed, menorrhagia develops. This occurs due to hormonal imbalance. With this deviation, menstruation before and after the birth of the baby is accompanied by large loss of blood.
Heavy menstruation is manifested by poor health, decreased blood pressure, and dizziness. The causes are hormonal imbalances, birth injuries, blood clotting disorders and diseases of the genital organs.
If a month has already passed after giving birth, and the bleeding begins to intensify, you need to consult a doctor. Timely diagnosis will allow you to identify the cause and begin treatment on time.
Causes
Bloody discharge 4 weeks after childbirth leads to the death of the woman or removal of the genital organ. Mom, if there are signs such as heavy hemorrhage, dark clots and abdominal pain, needs to call an ambulance.
Causes of bleeding a month after the birth of a child:
- atony or hypotension of the uterus;
- the remainder of the placenta;
- postpartum trauma;
- blood disease;
- inflammatory processes;
- placental polyp;
- hereditary characteristics of the body.
Atony and hypotension of the uterus represent a deviation, resulting in an empty space between the vessels through which blood leaks. This condition is dangerous to health, since blood loss is up to two liters.
When to see a doctor if spotting starts a month after giving birth:
- bloody discharge lasts more than 42 days;
- the shade changed to dark;
- the appearance of pus, black spots and an unpleasant odor.
Heavy bleeding is caused by inflammatory processes due to parts of the placenta remaining in the uterus. Postpartum sutures and hematomas lead to blood loss. This is due to suppuration of the suture or late detection of internal ruptures.
The pathology is diagnosed by a gynecologist during an examination. To do this, a woman will need to undergo blood and urine tests, as well as undergo an ultrasound of the genital organs. Frequent and heavy bleeding indicates the presence of pathology.
Complications
During the postpartum period, a woman should carefully monitor her well-being. If any deviations from the norm appear, or if bleeding occurs a month after childbirth, you need to pay attention to the quality of vaginal discharge.
When to see a doctor for complications:
- the blood acquired a bright scarlet hue and became liquid;
- the amount of discharge has increased, a postpartum pad lasts no more than one hour;
- nagging severe pain in the abdomen and uterine area;
- increased body temperature;
- the appearance of blood clots with an unpleasant odor.
Any inflammatory processes in the uterus require diagnosis and treatment. If a woman in labor does not pay attention in time to increased bleeding one and a half months after birth, the consequences can be negative.
Complications:
- endometriosis;
- lack of muscle contractions;
- blockage of the uterus;
- inflammatory infections.
Endometriosis develops both in the genitals and in the abdominal region. It is believed to be caused by blood entering the fallopian tubes. The disease manifests itself both after menstruation and in the postpartum period.
The absence of muscle contractions of the uterus will not allow the organ to return to its original form. Signs of atony are blood clots and a decrease in the patient’s blood pressure. The pathology very often leads to death due to large blood loss and hemorrhagic shock.
Inspection
A full diagnosis is carried out for women who have a predisposition to bleeding. Pathologies are associated with genetic and chronic diseases. Doctors pay attention to the size of the uterus, placenta previa, and blood clotting.
How is an examination carried out for late discharge with blood after childbirth:
- checking the fundus of the uterus;
- examination of the genitals;
- measuring blood pressure, pulse and body temperature;
- general diagnostics;
- Prescribing tests and ultrasound.
When a woman has strong, bright red discharge a month after giving birth, the examination begins with checking the fundus of the uterus and bladder. Then the quality and quantity of lochia are assessed. To do this, weigh the pad 15 minutes after filling.
Bleeding is often caused by trauma, due to which the uterus does not contract and does not return to its previous shape. If the organ has been checked and no abnormalities are found, pay attention to pain and the vagina.
It is important to monitor the general condition of the patient. Blood pressure, pulse and body temperature are measured. Normally, the skin should be light in color, lips pink, mucous membranes without dryness.
With internal bleeding, the pain will be severe, radiating to the pelvic area. The vagina swells and the skin tone changes to dark blue.
Next, black discharge appears a month after the birth of the child, which indicates the presence of a laceration inside or outside.
Treatment
Uterine bleeding is treated in stages, depending on the condition of the woman in labor. First, a diagnosis and examination is carried out to determine the cause of the pathology. Throughout the entire period, the nurse monitors the woman’s blood pressure and pulse.
The functioning of the uterus is restored with the help of medications. For each patient, the drug and dosage are selected individually based on the characteristics of the body. To relieve cramps and stop bleeding, cold is applied to the lower abdomen.
Drugs to stop bleeding one month after childbirth:
- Oxytocin – used to contract muscles. It is used in the form of droppers both during childbirth and after the birth of the child;
- Methylergometrine is prescribed intramuscularly only during the postpartum period. Accelerates contraction of the uterine muscles.
The doctor examines the uterus and inserts a tampon with a substance inside that helps the organ contract. If remains of the placenta are found inside the cavity and in the birth canal, the organ is cleaned under general anesthesia.
If the bleeding cannot be stopped, the problem is solved surgically:
- uterus removal;
- stitching lacerations and injuries inside the organ;
- squeezing damaged vessels.
Surgery is used only as a last resort when medications have not eliminated the problem. All surgical procedures are performed under general anesthesia. In case of severe blood loss, a blood transfusion is prescribed.
“Bad” type of discharge
Dangerous is the bleeding that occurs a month after childbirth , as well as cases when a woman goes to the toilet with blood . In addition, bleeding is regarded as pathological in the following cases:
- When after childbirth there is bleeding for three or more days and at the same time it has a bright red color (lochia cannot have such a shade, which indicates uterine bleeding).
- If the blood began to flow a month after a strong emotional experience, intimate relationship or sports stress on the body.
- With increasing blood loss, when a woman needs to change hygiene products literally hourly.
- The blood acquires a putrid odor and a strange consistency.
- The appearance of secondary impurities in the blood, which can be signs of an acute purulent focus in the reproductive organs.
- Bleeding, which is accompanied by disturbances in blood pressure, pallor of the woman and other signs of a pathological focus.
Important! Until the cause of bleeding is determined, the gynecologist after childbirth does not advise women to breastfeed, because if the source of the blood is an infection, then it can harm the baby.
What should cause concern
If, instead of decreasing, the volume of discharge suddenly increases sharply, the woman should consult a doctor, since in this case it may be a symptom of uterine bleeding. If for several hours in a row a standard pad becomes saturated with blood within 40–60 minutes, we are talking about internal bleeding.
Read also:
Delicate problem after childbirth with urinary incontinence
If the discharge acquires an unpleasant putrefactive odor or a yellowish-green tint, then most likely an inflammatory process develops in the internal genital organs. It may be caused by kinking of the uterine tubes and, as a result, the accumulation of lochia there.
An inflammatory process in the uterus can lead to the development of endometritis. It may be accompanied by severe pain in the lower abdomen, fever and purulent discharge. Once the diagnosis is confirmed, the doctor will definitely prescribe a course of antibacterial drugs and uterine curettage.
In addition to the factors listed above, reasons for urgently seeking medical attention are also:
- the appearance of clots and mucus;
- pain in the lower abdomen;
- increased body temperature, weakness, deterioration of health;
- The duration of discharge is more than 6–7 days.
In order for the uterus to recover quickly after the birth of the baby, doctors advise sleeping on your stomach more often, or at least resting in this position. Also, you should not walk with a full bladder; it is better to go to the toilet at the first urge.
In most cases, discharge that continues in women for a month after childbirth is a natural phenomenon and does not require any measures or treatment. However, it is during this period that problems that arose during childbirth, for example, erosive processes in the cervix or remnants of the placenta in the uterus, can make themselves felt. Therefore, the woman in labor should carefully monitor the intensity and nature of the discharge in order to notice alarming symptoms in time.
Features of bleeding
How many days a woman will bleed or bleed after giving birth is determined by the following factors:
- The presence or absence of problems with blood clotting.
- Method of childbirth. Thus, during the natural birth of a baby, the woman’s uterine cavity is more traumatized, and during a caesarean section, the muscles of the anterior abdominal cavity are affected.
- Success of childbirth, fetal weight and the presence of postpartum injuries.
- The general health of the mother in labor and the presence of severe chronic diseases.
- The state of the woman's immune system.
- Practice breastfeeding (if a woman frequently puts her baby to her breast, the uterine cavity clears faster and the volume of lochia decreases).
- Correct adherence to postpartum measures (application of a cold compress, administration of a number of medications, cleanliness during childbirth, etc.).
- Physiological characteristics of a woman and her tendency to recover.
- The presence of postpartum complications, such as infections or inflammatory processes in the reproductive organs.
- The state of a woman’s hormonal levels, as well as the presence of a number of endocrine disorders.
Causes
The main causes of bleeding in this condition are:
- Rapid childbirth, which became the culprit of severe damage to the woman’s birth canal. In this condition, a woman in labor may experience severe ruptures of organs. At the same time, copious bleeding can be observed for several days after rapid labor.
- Pathologies of the attachment of the placenta to the uterus, which subsequently provoke severe bleeding.
- Poor blood clotting in a woman in labor can provoke excessive bleeding. In such a condition, doctors should urgently administer hemostatic drugs to the woman. Otherwise, death from blood loss cannot be ruled out (which is why it is dangerous to give birth outside a hospital setting without medical supervision).
- Presence of changes in the uterus.
- Poor contractility of the uterus, which can be caused by very strong stretching of its walls.
- Rupture of the uterus, which was provoked by difficult childbirth (usually occurs with a large fetus).
- Accumulation in the uterus of amniotic mucous tissue that has not yet come out.
- The appearance of blood that cannot completely leave the organ due to reflexive contraction of the uterus. This condition is often observed during cesarean section.
- The presence of a focus of acute inflammation, which led to a slowdown in the recovery process.
Diagnostics
At the first suspicious discharge of blood, a woman should contact her observing gynecologist. After the initial examination and history taking, the doctor may also prescribe the patient an ultrasound examination and blood tests.
If blood appears, the woman must be urgently hospitalized and given medicinal treatment.
The doctor must also determine the type of bleeding: primary (occurs immediately after childbirth and in the first three days after it) and secondary (develops after several weeks).
Treatment
Immediately after the baby is born, doctors take a number of steps to prevent postpartum hemorrhage. Therefore, the woman needs to stay in the delivery room for two hours after giving birth. This is necessary to take emergency measures in case of bleeding.
During this period, the condition of the woman in labor is monitored by staff who monitor pulse, blood pressure and the amount of blood released.
For women who are giving birth for the first time or have had a difficult labor, the doctor examines the vagina and uterus to look for damage. If necessary, the affected areas of the ruptures are stitched and treated with antiseptics.
The permissible amount of blood loss during childbirth should not exceed 500 mg. Otherwise, the woman's blood loss will be regarded as bleeding.
If bleeding occurs, the following treatment measures are taken:
- Administration of drugs to stop bleeding. They are selected by a doctor in each individual case.
- Applying cold to the lower abdomen.
- Carrying out external massage of the uterine area. To do this, the doctor places his hand on the fundus of the uterus and gently squeezes it until the organ contracts. For women, such an event is unpleasant, but it can be endured without anesthesia. A hand can also be inserted into the organ to examine its walls. After this, the hand is clenched into a fist.
- Inserting a tampon into the vagina. The tampon itself must be soaked in a special agent that will cause uterine contractions.
- If there is severe bleeding, the patient needs an urgent blood transfusion.
If bleeding is advanced, a woman may need surgery. The following operations can be used to stop bleeding:
- Complete removal of the uterus.
- Squeezing of affected vessels in the reproductive system.
- Stitching of uterine injuries.
Important! If bleeding is severe, it is impossible to stop it at home. Moreover, if a woman tries to cure herself using traditional methods, she will only waste precious time. The wisest thing to do in such a condition is to call an ambulance.
Diagnosis of the mother’s condition during uterine bleeding
If bleeding occurs, it is necessary to guess its cause as accurately as possible. Only in this case can the most correct therapeutic and diagnostic measures be taken.
With early postpartum hemorrhage, there is no time for any additional manipulations. Therefore, everything is immediately done to stop it. In this case, only the amount of blood that the woman has lost is assessed. This is of fundamental importance for the course of treatment measures.
Regarding late postpartum hemorrhage, it is necessary to clarify the reason why it occurred. The following methods are used:
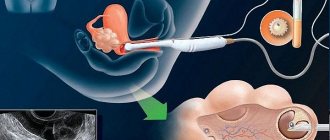
- Ultrasound examination of the pelvic organs. Using it, you can identify signs of inflammation and suspect a placental polyp. It is also important to exclude a new pregnancy, first menstruation and other pathologies.
- Hysteroscopy, which is performed if a placental polyp or pathology of the uterine cavity is suspected.
- Usual RDV if no other examination is possible.
- Study of blood clotting abilities - coagulogram.
All obtained material is sent for histological examination. Based on his conclusion, we can talk about the true cause of the bleeding.
Why is blood released: normal
According to gynecologists and obstetricians, after the birth of a child, small amounts of blood can be released for up to four weeks in a row. If the woman’s condition is satisfactory, she does not suffer from pain, high temperature and other dangerous signs, then this process is regarded as a physiological norm.
Gradually, the uterus will clear itself of postpartum injuries and restore its mucous layer.
Important! After a caesarean section, the woman’s recovery process takes longer, since the muscles and walls of the uterus are injured by surgery. In this condition, the healing period of the organ will be longer.
Preventive measures
In order to reduce the risk of pathological bleeding after the birth of a baby, it is important for young mothers to adhere to the following doctor’s recommendations:
- Avoid sexual intercourse with a man for several weeks to allow the uterus to fully recover and heal birth wounds.
- Regularly take clinical blood tests to monitor white blood cells in the blood, as well as hemoglobin and platelets. If any malfunctions are detected, take normalizing medications prescribed by your doctor.
- Before the birth of a child, it is very important to take blood tests for clotting. This way, the woman herself and the doctors will specifically understand what they need to be prepared for.
- It is strictly prohibited to smoke or drink alcohol during the postpartum period, especially if the woman is breastfeeding.
- Carefully observe personal hygiene of the genitals. In this case, you need to regularly change sanitary pads and wash with simple baby soap.
- For two months after the birth of the child, any physical activity, especially heavy lifting, is strictly contraindicated. During such a period, a woman needs to take maximum care of herself, especially if she had a caesarean section (stress can not only cause bleeding, but also contribute to the divergence of the stitches).
- To improve lactation, it is useful to enrich the diet with fermented milk products.
- Carefully monitor your diet. In this state, it is very useful for a woman to eat cereals, soups and vegetable dishes. At the same time, food should be cooked mainly by steaming, baking or boiling. You need to forget about fatty, smoked, salted and fried foods for a long time.
- On the first day after giving birth, be sure to apply a cold ice compress to your stomach.
- To cleanse the uterine cavity as quickly as possible, a woman is recommended to lie on her stomach.
- When you first feel the urge to urinate, you should immediately visit the toilet so that a full bladder does not lead to unnecessary contractions of the uterus.
- Spend more time outdoors. At the same time, it is very useful to practice long walks with the baby, as these actions will be useful for mother and child.
- In order to reduce the likelihood of postpartum complications, every week a woman must undergo a follow-up examination with a gynecologist. Only a specialist will be able to identify problems with the uterus in a timely manner and prescribe the necessary treatment.
It should be understood that it is important not only how long the bleeding occurs, but what nature it has, and what additional symptoms are observed in the woman. At the same time, heavy discharge of blood can be extremely dangerous to health, so you should not delay in contacting a doctor when it appears.
5 / 5 ( 1 vote)
Return of critical days
Among women who decide to breastfeed, about 80% can expect to start menstruating within 10 to 11 months. Breastfeeding delays menstruation and ovulation by approximately 20 weeks or more. However, it is not uncommon for menstrual periods to be much longer than 20 weeks. Each woman and her hormone levels are unique, so it is difficult to say exactly when your period will return. For some women it returns the following month after birth, while for others it returns only after breastfeeding has ended.
Read also: After childbirth, teeth hurt, darken, crumble and break - What to do?
In the first months after the birth of the baby, menstruation will occur very irregularly and last shorter or longer than the normal menstrual period. Some women find that their first periods are so heavy that they use both pads and tampons due to the intensity of the flow.
Menstruation is an inconvenience for a new mother, but as long as the amount of fluid produced is normal, there is no cause for concern. In case of excessive volume, you should consult a doctor.