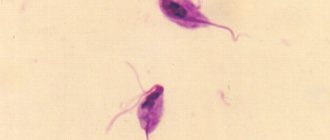
Symptoms of sexually transmitted diseases in women occur differently than in men. The reason for this lies in the physiological characteristics of the body. Women need to pay attention to vaginal secretions, which may indicate an infection. As for gonorrhea in women, the main symptom of the disease manifests itself in the form of pathological discharge, photos and characteristics of which you can find below in this article.
Prevalence of gonorrhea
WHO estimates that more than two million new cases of gonorrhea occur each year in the United States.
More than a quarter of them are among teenagers aged 10 to 19 years.
In Russia, the incidence of gonorrhea is also at a fairly high level.
In the Russian Federation it was registered:
- In 2002 - 134,950 cases of the disease
- In 2003 – 117,572 cases of the disease
- In 2004 - 112,980 cases of the disease
At the same time, many patients attempted treatment at home or in private commercial clinics, and therefore were not taken into account within the framework of the data.
Late seeking of medical support leads to widespread spread of the disease and the development of severe complications of the disease affecting reproductive health.
Complications
Pelvic organ damage
When infection penetrates the fallopian tubes and ovaries, chronic adnexitis develops. The disease is accompanied by the development of a large number of scars, which leads to the development of ectopic pregnancy, obstruction of the fallopian tubes and infertility.
With gonorrhea, purulent discharge often affects the skin. Purulent inflammation of the Bartholin glands and bladder develops. When infection penetrates the tissue, parametritis develops.
Lesions of other organs
When the infection spreads through the blood, joints, eyes, and meninges can be affected. But these complications are extremely rare.
Where does gonorrhea come from?
The causative agent of gonorrhea is a strict parasite of humans.
Once in the external environment, the gonococcus will die at temperatures above 56°C or less than 18°C, drying, exposure to direct sunlight and antiseptics.
The survival rate of the microorganism in the environment varies from 30 minutes to 4-5 hours.
The source of gonococcal infection can be a patient or a gonococcal carrier.
The main route of transmission of infection is sexual, however, household transmission is also possible - through infected surrounding objects.
The incubation period for infection with gonococci can last up to 1 month.
The first discharge from the patient's urethra during gonorrhea appears, as a rule, already on the 3-4th day.
What STIs and STDs have discharge similar to gonorrhea?
Patients complain of the presence of discharge in most sexually transmitted diseases:
- chlamydia;
- trichomonas infection;
- candidiasis (thrush);
- ureaplasmosis;
- mycoplasmosis.
Discharge in women can provoke the development of bacterial vaginosis (violation of the ratio of normal and opportunistic vaginal microflora).
One of the significant reasons for this symptomatology in representatives of both sexes is nonspecific bacterial microflora (staphylococci, E. coli, etc.).
How does gonorrhea occur in men?
The classic form of infection in male patients is gonorrheal urethritis.
Anterior urethritis, acute
Discharge from gonorrhea in men will be purulent, yellowish-green in color, and profuse.
They are characterized by free flow from the urethra, leaving stains on clothes.
In this case, urination is painful for the patient (dysuria).
When conducting a test with two glasses, we find cloudy urine in the first container, and almost transparent urine in the second container.
When examining the penis, you can see hyperemia and swelling of the external opening of the urethra.
On palpation, the urethra is compacted, the touch is accompanied by pain.
Total urethritis, acute
This is a process that has spread to the back of the urethra.
In men, urination becomes more frequent, there is an imperative urge to urinate, and sharp pain occurs at the end of urination (because the internal urethral sphincter spasms).
When conducting a two-glass test, cloudy contents are observed in both glasses, since the purulent discharge is constant.
The patient may also complain of frequent and painful erections, frequent emissions, which are also painful, and bloody discharge in the semen (hemospermia).
The general well-being of the patient does not suffer.
Urethritis, subacute
Discharge from the urethra is white, purulent and mucopurulent.
There is little discharge compared to previous forms of the disease.
Slightly more in the morning, as accumulation occurs during the night during sleep.
All other symptoms are mild: swelling, pain, manifestations of posterior urethritis bother the patient much less than in acute forms of urethritis.
Urethritis, torpid
Discharge from the genital tract is mucopurulent, has a whitish tint, and is found in scanty quantities only in the morning after sleep.
There may be virtually no pain; in this case, the disease often goes unnoticed.
Signs of inflammation when examining the penis are barely noticeable.
The torpid form of gonorrheal urethritis occurs monotonously and often develops into the chronic form of gonorrhea.
Chronic urethritis
Manifestations of the disease are subtle.
About 60% of patients have no complaints at all.
There may even be no morning discharge at all, or there may be a symptom of a “morning drop” - a very small amount of discharge is detected only in the morning urine.
The patient's complaints appear after complications of the infection develop.
Inflammatory changes in any organs of the genitourinary system can complicate the course of the disease in males.
Often the prostate gland is affected.
Discharge with gonorrheal prostatitis has no special features.
How does gonorrhea occur in women?
Discharge from gonorrhea in women is extremely weak.
Typically, female gonorrhea is characterized as “silent gonorrhea.”
This happens in 75-91% of cases.
Since the female urethra and reproductive tract are quite short relative to the male urethra, infection affects several sections at once.
We can highlight:
- Gonorrhea of the lower genital organs: the lower part includes all structures up to the cervix, including the cervix itself
- Gonorrhea of the upper genital organs (endometritis, metroendometritis - concern the uterus, adnexitis - ovaries, pelvioperitonitis - inflammatory process in the pelvis)
How to diagnose gonorrheal infection by discharge?
Let us immediately note that gonorrhea should be treated immediately after the first pale yellow or slightly green discharge.
With pus
Greens
There is no need to hope that such secretion will go away on its own. Naturally, this color of discharge may not be a direct sign of a pathogenic gonococcus, but there is still an inflammatory process, so treatment is extremely necessary.
You also need to remember that with this disease, the vaginal secretion has a rather pungent and unpleasant odor. But it is the smell of rot, which can resemble rotten fish, that most often appears only when the venereal disease has acquired a chronic form.
As for menstruation, the infection also negatively affects the menstrual cycle. Menstruation becomes longer, and in its composition a woman may find purulent streaks and fluid of unknown origin.
Itching and burning in the genital area is also possible, but such signs do not always appear.
Possible symptoms in women with gonorrhea
Gonorrhea in women can manifest itself as complaints of pain at the beginning of urination, increased frequency of urination and pain at the end.
Upon examination, the urethral sponges look inflamed and swollen.
When pressing on the urethra, purulent discharge may appear - it contains gonococci.
And it would be right to explore it.
If a woman suffers from a chronic form of gonorrhea, she usually has no complaints, there is no discharge, and the walls of the urethra become thicker due to constant inflammation.
In both men and women, serious inflammatory complications are accompanied by a rise in body temperature to 38-39°C.
The abdominal wall becomes tense and painful, and changes in blood tests occur.
Such situations require mandatory medical attention and hospitalization.
Special forms of gonorrhea (extragenital)
Let's consider forms of gonorrhea that do not affect the urethra and genital apparatus.
Gonorrheal proctitis
It develops, as a rule, in women, secondarily: when pus leaks from the genital tract or during rectal sexual contact.
Discharge from the anus with proctitis of gonorrheal etiology is also purulent and can be detected in the stool.
Upon examination, fissures in the anus, severe redness and swelling of the anal area are revealed.
In the chronic form of gonorrhea, genital warts can grow rapidly.
Oropharyngeal form of gonorrhea
There is no discharge from the mouth with oropharyngeal gonorrhea.
As a rule, the patient's complaints are limited only to pain and sore throat.
Sometimes the tonsils and lymph nodes become inflamed.
However, in 70-80% of cases it is asymptomatic.
Ophthalmogonorrhea (gonorrheal conjunctivitis)
Discharge from the eyes with gonorrheal conjunctivitis is manifested by severe suppuration.
The eyelids swell and the patient develops photophobia.
The conjunctiva is red, rough, and bleeds easily.
The most severe complications of ophthalmogonorrhea are damage to the cornea, the formation of ulcers and possible perforation.
Gonorrhea: questions for a venereologist
Let's look at the most frequently asked questions by patients about gonococcal infection and answer them in detail.
What is the discharge from gonorrhea?
The consistency of the discharge immediately after its appearance is heterogeneous.
They look like whitish flakes when urinating, but as the inflammatory reaction progresses they become more formed: homogeneous and thick, purulent and fetid.
What does gonorrhea discharge smell like?
Patients note the fetid, putrid, unpleasant nature of the discharge.
What does gonorrhea discharge look like?
Basically, the color of discharge from gonorrhea varies from yellow to greenish, the bulk of it is white or beige.
Does discharge appear soon after gonorrhea infection?
Already on days 3-4, specific discharge can be detected.
In different people, formalized gonorrheal discharge may appear within 2 to 7 days.
In females, discharge usually occurs a little later.
When does gonorrhea discharge disappear during treatment?
It is wrong to rely on the disappearance of discharge during a gonorrheal infection.
There is no need to stop the course of drug therapy based on the fact that the discharge from the urethra has disappeared.
Without therapy at all, their number would also decrease spontaneously, up to complete disappearance.
In different patients, after starting therapy, the discharge may disappear at different speeds - the next day or after a week, this should not be your point of reference.
Is it possible to do instillations with gonorrhea discharge?
Instillations (Latin instillatio - dropwise infusion) is the drip administration of medicinal solutions into the urinary tract and bladder.
For gonorrhea, instillation as a method is not used, since it can become a factor in the upward spread of the infectious process.
In addition, the mucous membranes of the urinary tract become especially vulnerable when affected by gonorrhea.
During instillations, additional injuries and complications in the form of bleeding are possible.
How to suspect gonorrhea based on discharge?
To suspect gonorrhea, note that you have recently had unprotected sex.
The discharge has a thick consistency and a foul odor, yellow-green or beige in color.
Appeared 2-7 days after intercourse with a suspected carrier of the infection, you have other signs of gonorrhea.
If there are no other signs, you also need a thorough examination at the CVD.
When does discharge disappear during therapy?
Gonorrhea has different types. In the initial form and localization in the urethra, one injection or a one-day course of medication is enough and after 2-4 days the discharge disappears.
In other cases, the disease spreads to the internal genital organs of a man: the scrotum, testicles. This provokes the occurrence of gonorrheal prostatitis.
In women, localization is most often on the genitals. The infection affects the cervix, ovaries, fallopian tubes, and peritoneum. In these cases, longer treatment is required over several days, and if the patient’s condition is severe, therapy is carried out in a hospital under the supervision of specialists. The discharge continues for a longer period. Their disappearance depends on how long the treatment takes.
In severe cases, treatment may occur in a hospital
In some cases, there is no discharge at all or it is very scanty. Many people, relying on this sign, stop taking antibiotics, which leads to negative consequences.
Differential diagnosis of gonorrhea
The discharge may look similar to gonorrhea if a person has the following infections:
- trichomonas;
- ureaplasma;
- candida;
- chlamydial
All of them are mainly transmitted through sexual contact.
What tests are taken for discharge from gonococcal infection?
For acute gonorrheal urethritis, a microscopic examination of a smear may be sufficient.
The secretions are applied to a special glass, stained, and the contents of the urethra are examined under a microscope.
In addition to the microscopic method, polymerase chain reaction (PCR) methods, which examine the genetic material of the bacterial cell, and cultures are often used.
The latter method is not very convenient in terms of time: it will take several days for gonococcus colonies to germinate.
However, it is the bacteriological method that will make it possible to immediately determine the sensitivity of the pathogen to antibacterial drugs and specifically and effectively prescribe antibacterial therapy.