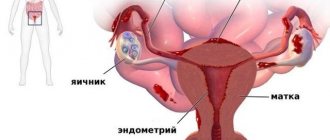
The modern classification of neoplasms in the ovaries is internationally oriented, and therefore each of them is called a tumor.
However, patients are not yet accustomed to such terminology, and specialists sometimes use the terms ovarian cysts (tumor-like formations) and cystomas (true tumors).
Ovarian cysts and tumors are of different nature. Let's take a closer look at their types and features.
At CELT you can get advice from a gynecologist.
- Cost of initial consultation - 2,700
- Cost of consultation with ultrasound - 4,200
Make an appointment
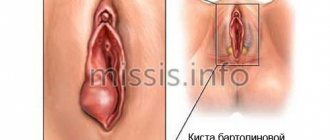
Ovarian cysts
Cysts are tumor-like formations that grow due to the accumulation of contents in them.
The most common causes of cyst formation are chronic inflammatory processes and hormonal changes.
Main types of cysts:
- luteal, or corpus luteum cysts - up to 15% of all cases (according to various sources);
- paraovarian - 10-13% of all cases;
- follicular - more than 80% of all cases.
Corpus luteum cyst
These formations are formed under the influence of luteinizing hormone after ovulation.
The function of the corpus luteum is the production of progesterone, necessary for the development of pregnancy and fetal growth. If during pregnancy the corpus luteum forms a cyst, the neoplasm does not affect pregnancy.
After childbirth or at the beginning of menstruation (sometimes after 2-3 cycles), the corpus luteum cyst, as a rule, resolves without requiring treatment. This cyst never degenerates into a malignant formation.
Treatment is carried out in cases associated with complications - ovarian torsion (emergency surgery), cyst rupture, internal bleeding (with a rupture in the area of the vessel), menstrual irregularities.
Other therapeutic targets for the disease include cysts greater than 4 cm in diameter; symptomatic and recurrent; those in which suppuration has occurred.
Paraovarian cyst
This type of tumor formation is a consequence of abnormal embryonic development. A paraovarian cyst forms between the ovary and the tube, most often between the ages of 20 and 40. It doesn't dissolve.
Small cysts of this type - up to 2.5 cm in diameter - are dynamically observed at intervals of one visit to the gynecologist every six months. Medium (up to 5 cm in diameter) and large (more than 5 cm) are removed surgically (laparoscopically).
Follicular cysts
The reason for their formation is hormonal disorders. Follicular cysts are formed from the largest follicle that has not ruptured to release an egg.
If there are no pronounced pain and other symptoms, if there are no complications (torsion, necrosis, cavitary hemorrhage, relapse), the cyst is dynamically observed. When hormonal levels and other processes normalize, the cyst can resolve on its own. If complications develop, the cyst is promptly removed.
How does the growth of formations on the appendages occur?
Cysts also include functional neoplasms, which sometimes regress on their own. Cystoms never develop back and require surgical treatment. However, over time they may stop growing.
The cyst grows due to the division of its own cells. For this reason, it is classified as a true epithelial tumor. It has a shell that produces a secretion that represents its internal contents. The cyst has a connective tissue membrane that does not increase in size, but only gradually stretches due to the accumulation of fluid inside it.
A cystoma can transform into a malignant neoplasm, so it must be removed. A cyst is a benign tumor, certain types of which can be monitored dynamically due to the possibility of their reverse development.
Any small pathological inclusions of the appendages may not manifest themselves for a very long time and may be discovered during a visit to the gynecologist or an ultrasound scan. Once each of them reaches a certain size, the woman begins to experience pain in the lower abdominal segment, as well as frequent urge to urinate, constipation, etc.
Ovarian cystomas
Ovarian resection
- Cost: 90,000 - 130,000 rubles.
- Duration: 30-60 minutes
- Hospitalization: 2-3 days in hospital
More details
Cystomas, or true tumors, are formations that grow due to cell division and growth. They have different natures and are capable of being reborn.
There are three groups of cysts:
- benign - consist of highly differentiated cells, grow slowly, do not metastasize, account for up to 80% of all cases;
- potentially malignant, or borderline - tumors with a low degree of malignancy, there are mucinous, serous, Brenner tumors;
- malignant - germinate into adjacent tissues, grow rapidly, and metastasize; There are epithelial ones (up to 42% of them are serous carcinomas, up to 15% are mucinous, up to 17% are undifferentiated).
Ovarian tumors are treated with surgical methods, usually laparoscopic.
Conclusions TheDifference.ru
- A cyst is a cavity with liquid contents surrounded by a membrane. A tumor is a pathological growth represented by newly formed tissue.
- The cyst does not grow into other organs and tissues; the tumor can grow and metastasize.
- A cyst is always a benign formation; a tumor can be malignant.
- The cyst can twist and rupture, most often it is small. The tumor can grow to enormous sizes.
- A cyst is dangerous for the body due to its complications, a tumor is dangerous due to its growth into other organs and destruction of surrounding tissues.
Ovarian cysts and tumors - diagnosis
MRI of the pelvic organs
- Cost: 7,000 rub.
More details
If you suspect a cyst:
- examination by a gynecologist (bimanual examination, speculum examination);
- Ultrasound of the pelvic organs;
- blood tests for tumor markers;
- other laboratory tests, determination of hormonal status.
If a tumor is suspected:
- examination by an oncologist (bimanual examination, examination in mirrors);
- Ultrasound of the pelvic organs;
- MRI - magnetic resonance imaging (allows you to examine tissue layer by layer and make a diagnosis with high accuracy);
- according to indications: examination of the intestines (colonoscopy), mammary glands (mammography), endometrium (hysteroscopy);
- blood tests for tumor markers;
- diagnostic laparoscopy.
The scope of the examination and the method of surgical intervention are determined by the specialist individually in each specific case. The prognosis for treatment is favorable.
If you suspect an ovarian tumor, you can contact gynecologists at the CELT multidisciplinary clinic, undergo the necessary examination and receive adequate treatment. The main thing is to see a doctor on time!
Main Difference
The difference between a cyst and any cystoma is that it very rarely becomes the cause of an oncological process. Cystoma, having gone through several stages of its development, can transform into cancer. That is why such a tumor is subject to mandatory surgical removal.
Cysts have a thin shell that is easily damaged, as well as an almost ideal spherical shape and usually small in size (except for teratomas). They do not have an internal epithelial lining. They do not affect nearby tissues, because they grow due to an increase in the amount of internal contents.
The inside of the ovarian cyst is lined with epithelium. Having become a malignant tumor, it often grows into neighboring tissues and organs. Over time, it most often acquires impressive dimensions.
The cyst can transform into a cystoma. If this happens, the woman is recommended to undergo surgery to excise the tumor. In most cases, a true epithelial tumor is formed from a simple cyst of any ovary. Sometimes it is multi-chamber.
Our services
The administration of CELT JSC regularly updates the price list posted on the clinic’s website. However, in order to avoid possible misunderstandings, we ask you to clarify the cost of services by phone: +7
| Service name | Price in rubles |
| Transvaginal ultrasound of the uterus and appendages | 2 800 |
| MR tomography of the pelvis | 7 000 |
| Endoscopic ovarian resection | 95 000 — 125 000 |
All services
Make an appointment through the application or by calling +7 +7 We work every day:
- Monday—Friday: 8.00—20.00
- Saturday: 8.00–18.00
- Sunday is a day off
The nearest metro and MCC stations to the clinic:
- Highway of Enthusiasts or Perovo
- Partisan
- Enthusiast Highway
Driving directions
Types of cysts
In medical practice, false and true cysts are distinguished. Depending on the origin - congenital and acquired, according to the mechanism of formation - traumatic, retention, dysontogenetic, parasitic and tumor.
- Retention cysts are located in the glandular-secretory organs. They can form due to partial or complete cessation of the outflow of secretions from the gland. This occurs due to blockage of the duct by microscopic debris (stones, pollen, etc.), tumors or scars. Stagnation of secretion occurs in the duct or glandular lobule. As a result, they are stretched. A cavity is formed with various contents. The wall of such a cyst consists of the epithelium of the gland or its duct.
- Trichodermal cyst, or atheroma, is diagnosed in 5-10% of the population.
- A ramolitic cyst develops when tissue becomes necrotic as a result of hemorrhage, inflammation, or infarction. The dead tissue then softens or dissolves. The wall is formed from the cells of the organ in which it is localized, and can later be replaced by connective tissue cells. Often this type of neoplasm is located in the brain or spinal cord and in tumors.
- Parasitic. This is the vesicular larval stage of tapeworms.
- Traumatic. Formed due to the displacement of epithelial cells. They are located on the fingers, palms, iris and pancreas.
- Dysontogenetic cyst. Often occurs in displaced cells during embryo formation. These include cysts from gill slits, remnants of the vitelline tract, and others.
- Tumor. It develops in situations where a growing tumor forms various cavities. Often found in glandular organs.
Pathological cystic cavity
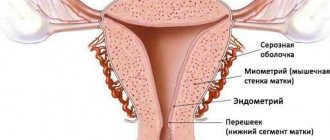
Ovarian cyst
This species is very common. The reasons for its occurrence have been little studied. The prerequisites may be hormonal imbalances.
- Mucinous ovarian cyst is a benign neoplasm and occurs in women of any age.
- An endometrioid cyst is a formation that develops on the ovary and consists of menstrual blood.
- A wandering cyst appears and disappears under the influence of various factors. It is dangerous because of sudden rupture.
A cyst differs from a cystoma in its slow development. The size reaches 15 cm. They can be distinguished by ultrasound results. Cystoma of the right or left ovaries has unclear boundaries. Cystomas can develop into a malignant tumor.
Classified depending on occurrence and localization:
- Follicular. Develop due to ovulation disorders and follicle enlargement. They occur asymptomatically and have a size of up to 6 cm. They are often detected due to cycle disorders. In the follicular form, the cyst may rupture. In this case, pain appears in the lower abdomen.
- Dermoid (pararectal). The contents of such a cyst are often represented by appendages rather than fluids. The cavity may contain bone tissue, teeth, and fat cells.
- Vapor-varial. Localized in the area of the fallopian tubes. The size can reach up to 20 cm.
- Corpus luteum cyst. Localized in the non-regressed corpus luteum. Due to circulatory disorders, hemorrhagic fluid accumulates in the center and the tumor grows.
- Endometrioid. It develops from endometrial tissue and is localized inside the ovary. The size can reach up to 15 cm.
The most terrible complication is considered to be rupture of the corpus luteum. Cystic formation can develop during pregnancy. In this case, the neoplasm is monitored throughout the entire pregnancy. During pregnancy, a placental cyst may develop in response to inflammation.
During reproductive age, an anechoic ovarian cyst may develop.
To distinguish a cystic formation from cancer, a determination is made for tumor markers, including CA 125. The norm for women is 0-15 IU/ml, for a cyst – 0-30. If the indicator is increased to 100, this means the possible development of oncology. They also analyze hormones, blood serum levels, blood biochemistry, and test for infection.
If a benign tumor has become malignant, urgent surgical intervention is required.
The main method for removing cystic formations is laparoscopy. It is considered minimally invasive. After laparoscopy there is a short rehabilitation period.
If the cyst bursts, it is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- pain in the lower abdomen;
- nausea;
- vomit;
- increased body temperature;
- abdominal swelling.
The body can cope with some types on its own, while others need to be treated with hormonal and anti-inflammatory therapy.
Cyst of the cervix and breast
This species is not dangerous because it does not develop into a malignant form. But it requires urgent treatment, due to the risk of increasing in size. An enlarged tumor can cause cervical deformation or other diseases.
Inflammation and suppuration can also negatively affect the general condition of the body. Medicine uses different approaches in the treatment of pathology. Including radio waves and laser destruction. In both cases, a non-contact action is carried out on the tumor. This significantly shortens the rehabilitation and recovery period.
The pathology develops asymptomatically. It is discovered during a medical examination or when it is physically palpated. There are unilateral and bilateral forms, as well as single and multiple.
Diagnosis is carried out using ultrasound or mammography. The attending physician preliminarily performs palpation. Development occurs without pain, so it is almost impossible to independently detect pathology. For prevention, it is recommended to conduct self-examinations at home and, at the slightest suspicion, seek medical help.
When prescribing therapy, the patient’s age, cyst size and current condition are taken into account. For small sizes, absorbable and anti-inflammatory therapy is used. Hormone therapy is also prescribed.
If the neoplasm is large and easily palpable, a chest puncture is prescribed. In this case, the contents of the tumor cavity are pumped out and medications are administered. After this manipulation, the cyst resolves and the patient recovers completely.
If there is a suspicion that the cyst has turned into a tumor, the attending physician may prescribe surgery. The cyst is removed and drug therapy is prescribed. If the patient wants to restore the aesthetic appearance of her breasts, she can use the services of a plastic surgeon.
The diet is part of complex therapy. Nutrition should be balanced.
Male testicular cyst
Testicular cyst
In men, the cyst is localized in the groin and is detected during an external examination. Externally similar to other neoplasms. Therefore, to clarify the diagnosis, ultrasound and general tests are performed. In men, elevated levels of hCG in the blood can be a sign of a testicular tumor. Diseases of other organs can increase hCG levels.
The causes of pathology in the groin area are poorly understood. Trauma and inflammation may be prerequisites.
In children, the pathology often resolves without treatment. If therapy is not possible without surgery, then laparoscopy is used. The consequences may vary, but complications are rare. If the outcome is positive, reproductive ability and male health are completely restored.
Kidney cyst
Kidney cyst is a common pathology. Diagnostics became possible with the introduction of ultrasound into medical practice. If the cystic formation is up to 60 mm in size, then it does not disrupt the function of the organ and does not manifest itself in any way.
If there are no complaints and normal test results, doctors do not perform surgery, but prescribe periodic examinations. If this pathology is detected, a puncture can be performed.
Polycystic disease is removed through surgery. This is a phenomenon when an organ is affected by a large number of small cystic formations. In other cases, when pathology is diagnosed, there is no need for urgent surgical intervention.
Cyst in human kidney
Tooth cyst
Location: gums, in the area of the tooth root. The cause may be injury or infection. First, periodontitis develops, which provokes tissue proliferation and the appearance of granuloma. Then the granuloma degenerates into a cyst and is filled with liquid contents.
The formation of cystic formations can be asymptomatic. Then the cyst grows and the roots of the teeth are damaged. As a result, other symptoms may appear. High body temperature, weakness, headaches or swelling on the cheek are symptoms of inflammation and the growth of cystic formations.
There are no specific signs. Pathology is often discovered by the dentist when taking x-rays of adjacent teeth. In this case, the therapeutic method is effective. It is lengthy and expensive, but 70% of patients get rid of the pathology.
The method is based on the treatment of a damaged tooth, drilling, cleaning the root canal and joining with a cystic formation. Drilling is carried out so that the liquid contents flow out. In this case, antimicrobial agents and disinfectant solutions are introduced, and then the cavity is filled with a substance that promotes the development of bone tissue.
After these procedures, the tooth is temporarily filled. After six months, an x-ray is taken. If the cystic formation has not developed again, the tooth is finally processed. Also in this case, laser removal can be performed.
Depophoresis is a modern method of treating cystic formation. The essence of the method is to introduce a suspension into the canal, which destroys microbes and damaged tissue. Manipulations are carried out under the influence of a weak electric current. The method is high-quality and fast, but not all medical institutions have the equipment necessary to carry out depophoresis.
Cystic tooth disease
Surgery is performed using two methods. Hemisection involves removing the root and part of the tooth. The appearance is subsequently restored using a crown. Cystectomy is a procedure in which a cystic formation is removed without affecting a healthy tooth. The operation is complex, and not all dentists agree to perform it on molars.
Bone cyst
Cystic formations can develop not only on internal organs, but also on bones and muscles. There are several types:
- Aneurysmal bone cyst is a benign tumor-like pathology, often found in children and adolescents. In 80% of cases, the disease is detected in people under 20 years of age.
- Ganglionic (ganglionic, ganglionic) cyst is a cystic formation in the form of a sac of fluid that forms on a joint or tendon. The description of the ganglion first appears in the writings of Hippocrates as “a node containing mucus.”
- At the site of old injuries, a parameniscal (parameniscal) cyst may develop.
A cyst on the leg can be localized in different areas. In the 19th century, a cyst was first discovered, which was localized in the knee joint. It is named after the doctor who discovered it.
Cystic formation in the bone
Baker's cyst of the knee joint
A knee joint cyst is an elastic benign tumor located in the popliteal fossa. Develops due to inflammation of the mucous intertendinous bursae. A meniscal cyst can also form, both lateral and medial. As the cystic formation increases, liquid contents from the joint cavity enter the popliteal region. Because of this, disturbances in the functioning of the joint occur and movements become difficult.
If pathology is quickly discovered, a puncture is performed. The liquid contents are pumped out and anti-inflammatory treatment is carried out. In this case, it is possible to do without surgical intervention, using only medications.
Patients have high hopes for traditional medicine. The use of such methods is acceptable as additional measures. In this case, it is necessary to consult with your doctor.
Often this type of cystic formation occurs in athletes or people who have constant stress on the kneecap. The cause may be injury, cartilage damage, or a large amount of physical activity.
You should not delay treatment, as cystic formations are dangerous due to their consequences. Complications may include varicose veins, blood flow disorders or thrombosis.
Thyroid cyst
It is a nodular formation, inside of which there is a liquid with a spherical capsule. The node can be single or multiple, in a toxic or calm state. Just like in other organs, it develops asymptomatically and does not cause discomfort or pain. When the formation grows to a large size, the patient begins to feel it. This may cause hoarseness, pain when swallowing, soreness or suffocation.
Dangerous consequences of cystic formation can be inflammatory processes of neighboring tissues and purulent formations. The most critical complication is the transition of the node to a malignant tumor. To avoid consequences, it is necessary to start treatment on time.
Stages of development:
- Stage 1. Minor changes occur in the tissues.
- Stage 2. The changes become more pronounced and palpable.
- Stage 3. Areas of skin degeneration appear.
You can detect a cystic formation and clarify its size and structure using an ultrasound machine. Based on the results of the studies, the attending physician will prescribe treatment. To clarify the diagnosis, laryngoscopy, bronchoscopy or CT can be performed.
To eliminate small cysts, conservative treatment methods are used. In this case, the following groups of drugs are used:
- Antibiotics.
- Anti-inflammatory.
- Iodine-containing drugs.
The combination of these medications gives good results. After puncture, the cystic formation can quickly gain fluid and restore in size. In such situations, surgery is necessary.
The thyroid gland is involved in regulating the functions of the entire body, so surgical interventions are performed only when absolutely necessary. Often a complication can be dysfunction of the vocal cords. Therefore, doctors, if possible, avoid surgery and prescribe medication therapy.
Preventive measures include consuming iodine and vitamins in sufficient quantities. If cystic formations are detected, it is necessary to regularly undergo physiotherapy and be observed by an endocrinologist.
Liver cyst
This type of neoplasm is common and, depending on the cause, there are two types:
- Parasitic.
- Non-parasitic.
The main cause of cystic formations in the liver is considered to be helminths. The tapeworm larva has the shape of a capsule and can remain in this state for a long time. The capsule cavity is filled with liquid contents and contributes to the development of infections.
Non-parasitic cystic formations are divided into congenital and acquired. Congenital or true may be the following:
- Single.
- Polycystic diseases.
- Congenital liver fibrosis.
Cystic human liver
They are often diagnosed and are a consequence of congenital pathologies. False (acquired) develops due to previous operations or injuries. The initial manifestations of pathologies are similar.
As in other cases, a cystic formation begins to manifest itself after a significant increase in size. The first stages are asymptomatic. A patient rarely learns about his diagnosis without an examination of the damaged organ.
As the pathology progresses, other symptoms appear, such as nausea, weakness, poor appetite, and pain in the right side. The metabolic function of the liver may also be impaired.
The most dangerous complications are suppuration, bleeding, rupture of cystic formations and the spread of parasites. When the pathology is diagnosed, large tumors are removed. Small cysts that do not interfere with the functioning of the organ are observed by a specialist.
A radical method of treatment is the removal of a cystic formation from the affected area of the liver, enucleation of the cyst, and excision of the wall of the tumor. Palliative methods can also be implemented.
Cyst in the head
Cystic formations can be localized in the face or ear. In the ear, they are often located in the lobe due to the large number of sebaceous glands.
The tricholemmal type of skin tumors is located on the scalp. A subcutaneous, or migratory, granuloma may develop on the face. Do not do anything yourself!
A cyst of the pineal gland (epiphysis) can provoke the development of epilepsy.
The causes of development are hemorrhages, trauma, congenital pathologies or inflammation.
Depending on the location of the cyst, there are two types:
- Intracerebral. It is located in the brain.
- Arachnoid. Located between the meninges. It is more often diagnosed in men than in women.
Cystic formations are classified depending on the tissue in which the pathology was formed:
- Arachnoid.
- Dermoid.
- Colloidal.
- Epidermoid.
- Pineal.
All cystic formations, excluding arachnoid ones, are classified as intracerebral. They form asymptomatically. For these pathologies, surgical operations are performed. An arachnoid cyst can be observed by specialists for a long time without surgical intervention. This pathology is less common in children than in adults.
When a cystic formation grows, it begins to put pressure on nearby tissues and disrupts the outflow of cerebral fluid. A neoplasm can develop in the chiasmal-sellar region. The optic nerves are there. Diagnosis of small tumors is possible using MRI or CT.
As the cyst grows, dizziness, pain, hearing impairment, tinnitus, hallucinations, impaired coordination, nausea, and vomiting appear.
Symptoms may progress. If they appear, you should consult your doctor. When selecting a treatment regimen, the location, size and shape of the cystic formation are taken into account.
The affected areas and the state of the brain are examined using Doppler ultrasound. If there are no signs of growth, drug treatment is carried out. They use drugs that restore blood circulation and promote the resorption of adhesions.
If the pathology is diagnosed early, the prognosis is favorable.
Bladder cyst
Pathology can form on the surface of the bladder or inside the organ. In the bladder, neoplasms develop in the mucous membrane. The disease is asymptomatic, but pain may occur when urinating. The problem is identified during a pelvic examination.
Cyst in the abdominal cavity
In the abdominal cavity, cystic formations often form in the gallbladder, intestines and spleen. A characteristic symptom is an increase in the size of the abdomen.
A gallbladder cyst is a secondary pathological process in which mucus accumulates inside the organ.
With a common bile duct cyst, the bile duct is stretched.
Cyst in newborns and children
- An adrenal cyst is a benign tumor. An adrenal cyst is a rare pathology that often forms during embryonic development. The disease manifests itself in adulthood. The consequences for the child will be favorable if treatment is not delayed.
- Presacral is localized in the pararectal tissue and is often congenital. The exact cause of tumor formation is unknown.
- Bronchogenic (bronchopulmonary, bronchial cysts), or mediastinal cyst is a congenital neoplasm that is localized in the mediastinal space.
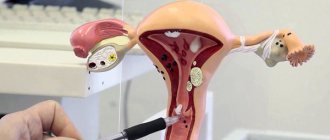
Ovarian cystoma (left and right): what is it and how does it differ from a cyst?
Last update: 10/08/2019
Many women who have encountered problems when visiting a gynecologist are concerned with the question - what is an ovarian cystoma, how to prevent it and why does it appear?
What is a disease
Ovarian cysts and cystomas are neoplasms in the epithelial tissues of the organs of the reproductive system that are benign in nature.
The difference between a cystoma and a cyst is rapid progression. The cyst develops slowly, gradually increasing in size. They sometimes reach up to 15 centimeters in diameter.
Such a neoplasm is often diagnosed and can develop from existing cysts.
A cystoma is a capsule containing exudate. Attachment to the ovarian tissue occurs due to the stalk.
The age category in which cystomas most often appear is from 30 to 60 years. Among all patients, most of the representatives of the fair half of the population are in the premenopausal period.
Etiologically, primary formation is divided - it arises from the structures of the organ, and secondary - it arises as a result of metastasis.
Why does it appear
There are no specific reasons that would provoke the appearance of a cystoma. But there are a number of factors predisposing to the onset of the disease, among which are:
Dysfunctions in the functioning of the ovaries, disruptions in the menstrual cycle, prolonged absence of menstruation, severe bleeding and other disorders.
- Genetic predisposition.
- Inflammatory processes in the organs of the reproductive system of chronic etiology - colpitis, endometriosis.
- Infectious processes of viral genesis.
- Early onset of menstruation.
- Late menopause.
- A large number of artificial abortions.
- Attachment of the fertilized egg outside the uterus.
- Surgical treatment of the ovaries.
One of the provoking factors is poor nutrition - the presence in the menu of foods with a large number of lipid structures, nicotine and alcohol addiction.
Classification of diseases
The following categories of neoplasms are distinguished:
- Consisting of epithelial structures.
- Consisting of connecting structures.
- Hormonally active.
- Teratomas.
Based on the type of development, tumors are divided into:
- Benign - some develop slowly; as they increase in size, neighboring organs and tissues experience stress and pressure.
- Proliferating are those that are on the border between benign and malignant.
- Malignant - rapidly progress, penetrating into neighboring structures, giving multiple metastases.
All cystomas are divided into good and malignant. The former can become malignant, being previously in the borderline stage.
In the absence of treatment and conditions favorable for the tumor, it quickly progresses, metastasizing.
All types of such formations rupture very rarely, under certain circumstances, for example, during intense physical strain or as a consequence of an abdominal injury.
A cyst, like a cyst, can appear on one ovary or on both; their type and structure may differ.
How is a cystoma different from a cyst?
During an ultrasound examination, the cyst is visualized in the form of a rounded growth with thin walls. The edges of the cyst are smooth and clear, the contents are homogeneous.
The cystoma of the right or left ovary has unclear edges, its structure is heterogeneous, there are additional tissue inclusions inside the formation. There are no other clinical manifestations that would allow differentiating these types of formations.
Additional histological examination of the tissues of the formation after its resection can help in making a diagnosis.
Ovarian cystoma Ovarian cyst
The difference is also that the shell of the cystoma consists of epithelial layers; these structures tend to produce their own secretion (contained inside the formation), as well as a constant increase in the size of the growth.
This pathology never resolves on its own (but a cyst can). Its growth may slow down, but it will not disappear, so it must be treated using radical methods. The cyst has shells consisting of connective tissue.
This type of formation does not grow, it can only stretch under the influence of accumulated contents.
Clinical manifestations of pathology
If the growth is small, there are no clinical manifestations against its background. Typically, this pathology is discovered by chance, during a gynecological examination or ultrasound examination.
When the volume of the neoplasm becomes larger, manifestations arise, the intensity of which increases as the cystoma grows:
- Aching pain of a pulling nature, it can radiate to the groin or lower back, becomes more intense after exercise, intimacy, bowel movements;
- Feeling of heaviness, fullness;
- Dysfunctions in the digestive system, accompanied by prolonged difficulties with bowel movements or intestinal disorders;
- Frequent urge to empty the bladder, this symptom appears due to the pressure of the tumor on the organs of the urinary system;
- Fluid in the abdominal cavity, accompanied by an increase in the size of the abdominal cavity;
- External violation of the symmetry of the abdominal cavity;
- Swelling of the lower extremities.
- Sometimes dysfunctions appear in the menstrual cycle.
If the tumor stalk is twisted, the symptoms worsen sharply - intense pain syndrome appears, hyperthermia, disturbances in heart tone, nausea, the muscular apparatus of the abdominal cavity is always in strong tone.
How to recognize
A doctor can diagnose a cystoma after a preliminary gynecological examination, ultrasound examination of the abdominal organs and reproductive system.
Sometimes additional computed tomography and magnetic resonance diagnostics may be required.
During the examination, the doctor performs palpation to determine the growth. If the size of the tumor is too large, it may extend beyond the pelvic organs, located in the abdominal cavity. The structure of the tumor is determined by its size.
During the examination, it must be differentiated from the following pathologies:
- Cyst;
- Uterine fibroids;
- Adnexitis;
- Attachment of the fertilized egg outside the uterine cavity;
- Neoplasms in the organs of the digestive system, in the organs of the urinary system.
Often, an additional examination method is esophagogastroduodenoscopy, radiography, and ultrasound examination of the digestive system.
To determine the nature of the tumor, it is necessary to collect blood fluid for tumor markers.
If there is a suspicion that the cystoma is malignant, the doctor considers the advisability of performing laparoscopy, during which an ovarian biopsy is taken.
How to get rid of pathology
If a cystoma of the left or right ovary is diagnosed, surgery becomes the only option for the patient.
It is impossible to cure such a disease using traditional treatment options, regardless of its size, type and structure.
Surgical treatment must be carried out necessarily, since there is a high risk of transformation of a benign cystoma into a malignant one.
Additional negative complications may include:
- Dysfunctions in surrounding organs and systems;
- There is a risk of twisting the stem of the growth, the results of which can be very dangerous.
Based on the type, size and structure of the cystoma, taking into account the age category of the patient, the type of surgical treatment is decided.
- If there is no oncology, tumor resection is performed, while preserving the ovary.
- For other types of the disease, it is necessary to remove the ovary, uterus, and tubes.
- If twisting of the stem of the growth occurs or its apoplexy occurs, surgical treatment is emergency.
- If the cystoma has undergone the process of malignancy, after surgical treatment additional therapy with radiation and hormones will be needed. If diagnosis and therapy are timely, the prognosis is generally favorable; in many cases, doctors are able to preserve the reproductive function of the female reproductive system.
Preventive actions
To prevent the appearance of a cystoma, it is recommended to regularly undergo preventive examinations by a gynecologist, undergo ultrasound examinations of the pelvic organs, undergo timely therapy for inflammatory processes, and eliminate menstrual dysfunction.
Another important condition for prevention is correctly selected contraceptives, elimination of smoking, alcoholic beverages, fatty foods, and saturating the body with a sufficient amount of vitamins and minerals.
Source: https://HealthLadies.ru/kista/kistoma-yaichnikov.html
Cyst and cystoma: what is the difference, the difference, is it cancer or not?
A woman’s health is often exposed to negative factors - stress, addictions, hypothermia or hormonal imbalances. As a result, after a gynecological examination and ultrasound, a diagnosis of cyst or cystoma is determined. Let’s take a closer look at what it is, what the symptoms are, whether it’s life-threatening and how these two diseases differ.
A neoplasm of any shape, size, with or without pain symptoms, must be thoroughly examined and be under constant monitoring and observation.
In 30% of cases, women with a regular menstrual cycle and 50% with an irregular menstrual cycle are diagnosed with an ovarian cyst. Often the disease is asymptomatic and is discovered after a random routine examination.
A cyst is a small hollow tumor formation filled with fluid. Formed from an ovarian follicle. As a rule, the formations are harmless and do not require any drug treatment or surgical intervention. They are called temporary or functional.
Cysts of this type arise as a result of an imbalance in the ovulation process. The follicle grows, and the corpus luteum fills with secretions. Most often, after a couple of menstrual cycles, the problem goes away on its own. But sometimes complications are possible - torsion and rupture, accompanied by pain, bleeding and loss of consciousness.
If the cyst does not disappear within three months, it is called abnormal. It occurs due to hormonal disorders and requires mandatory therapy or removal.
Ovarian cysts are diagnosed mainly in women of reproductive age; after menopause, the probability of the disease occurring is 6%.
During pathological processes, a tumor can reach more than ten centimeters in diameter, begins to put pressure and affect other organs. These cysts are removed surgically.
About cystoma and symptoms of the disease
A true ovarian tumor is called a cystoma. It is detected in women from 30 to 60 years old, and a significant part are patients during menopause.
The neoplasm is also a cavity with fluid. A distinction is made between a benign cyst, which, in the presence of a malignancy process, degenerates into a malignant one (cancer). The tumor can reach 15 cm or more.
Signs of the disease:
- painful, heavy or irregular menstruation;
- an increase in the size of the abdomen as during pregnancy - the cystoma grows significantly in volume, putting pressure on neighboring organs. Associated symptoms are swelling and varicose veins of the lower extremities, problems with bowel movements and urination;
- pain in the lower abdomen of a pulling nature and intensifying with any load.
Gynecologists call the following root causes of the appearance of a true ovarian tumor:
- menopause ;
- diagnosis of papillomavirus and genital herpes;
- lack of sexual activity, pregnancy and childbirth;
- abortions;
- chronic miscarriage ;
- irregular menstrual cycle;
- a history of inflammatory or infectious diseases of the genitourinary system;
- bad habits – smoking and frequent drinking of alcohol;
- high fat diet
When a cyst is diagnosed, it must be removed in order to avoid malignancy and the beginning of the process of metastasis to other organs. Timely treatment of the tumor gives a chance to preserve the ability to bear children and there is no danger to life.
What is the difference between tumors
These are purely female diseases that arise in the ovaries. A cyst is considered a benign formation, while a cystoma is potentially malignant due to its properties of malignancy and metastasis.
A cyst is a small formation that often disappears on its own within several cycles. A true tumor is not characterized by reverse development; it continues to constantly increase, grows to gigantic parameters and must be removed.
Complications in the presence of cysts are rupture and twisting; such phenomena are extremely rare in cysts.
On ultrasound, the cyst looks like a cavity with thin walls, clear boundaries, filled with secretion. The cystoma has uneven contours, the thickness of the walls varies, and sometimes contains tissue inclusions inside.
A cyst grows due to an increase in fluid volume, and a cystoma grows due to cell division.
These two neoplasms may be asymptomatic. It is important for every woman at any age to undergo regular examinations in the obstetric chair and ultrasound, listen to her body and not be careless about pain and other alarming symptoms.
Quite often, patients turn to the gynecologist too late, when the cyst has ruptured or the cyst has grown to a gigantic size with processes of metastasis to other tissues. Having detected a tumor in time and carried out the necessary therapy, a woman preserves her reproductive organs and continues to live a full life.
Source: https://onkologia.ru/dobrokachestvennyie-opuholi/zhenskaya-reproduktivnaya-sistema/kista-i-kistoma/
Reasons for appearance
Common causes of cysts are surgical interventions affecting the pelvic organs and abortions. Natural childbirth, abstinence from sexual intercourse, or, conversely, promiscuity can also provoke the development of the disease.
Factors provoking the development of the disease:
- Hormonal disorders. An imbalance in the hormonal background does not allow the egg to mature normally. Disturbances in the balance of hormones can be observed during menopause, with endocrine diseases, stressful conditions and strict diets.
- Early appearance of menstruation. We are talking about the beginning of the cycle at 10 years.
Inflammatory pathologies affecting the reproductive system (endometritis, adnexitis, etc.).- Sexually transmitted diseases.
- Heavy heredity. According to statistics, if there have been cases of the disease in the family, then the likelihood of developing cystadenoma is higher.
Key differences between a cyst and an adenoma
Comparison table
| Feature for comparison | Adenoma | Cyst |
| Where is it formed? |
| In any organ, right up to the brain. |
| Causes |
|
|
| Could it be congenital? | No | Yes |
| Appearance |
|
|
| Why are they dangerous? |
|
|
We see that it is impossible to say whether a cyst is the same thing as an adenoma or not. Let's take a closer look at their differences using the example of the behavior of both neoplasms in one organ - the liver. How do they differ at the level of symptoms, diagnosis and treatment?
Liver cyst
It is detected in the same way as an adenoma. With growth up to 7-8 cm or damage to 20% of the organ, it causes the same symptoms. In terms of gender distribution, the cyst differs from liver adenoma - women are affected 2 times less often than men.
Are divided into:
- true congenital, which can be simple and multilocular;
- false acquired, formed as a result of inflammation, operations, injuries, damage by parasitic worms, such as echinococcus.
The reasons for the appearance of congenital cysts are unknown, but there is an assumption that, as with adenomas, hormonal drugs have an effect: in this case, those that the girl’s mother took before her birth.
There are differences in the treatment of liver cysts from adenomas. If the size of the congenital form is less than 4 cm, observation is carried out, but no intervention is required. For removal with growth up to 7-8 cm, not only laparoscopy and resection are used, but also less traumatic methods: emptying the contents through a needle, diverting the cyst duct into the duodenum or stomach.
Benign neoplasms
How does a cyst differ from a benign tumor? Any tumor is a consequence of a disruption in the process of cell growth and division. Benign tumors grow rather slowly and are usually diagnosed when visiting a doctor with other problems.
Typically, such formations do not metastasize and do not spread to neighboring tissues. Patients rarely report deterioration in health. If formations appear in the brain, then intracranial pressure may increase, which causes constant pain.
Risk factors include:
- poor environmental conditions in a certain region;
- work in hazardous production;
- smoking and abuse of alcohol and drugs;
- poor nutrition;
- ultraviolet radiation.