A cyst is a cavity formation filled with some kind of fluid. It is often asymptomatic and detected only by vaginal ultrasound. In some cases, it may be accompanied by symptoms, which are always more obvious when complications occur: when the cyst is more than 3 cm in diameter, when it is inflamed, ruptured, torsion of the leg, and others.
Common signs of a cyst:
- nagging pain in the lower abdomen: in the center, right or left;
- discomfort during intimate relationships;
- pressing sensation on the rectum;
- frequent urination and defecation;
- fever, general weakness due to inflammation of the cyst;
- delayed menstrual cycle or strange spotting.
When examined by a gynecologist, a cyst cannot always be detected. If the neoplasm is more than 3 cm in diameter, it can be defined as:
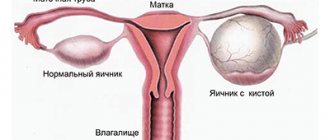
- enlarged ovary on one side, the body of the uterus is identified separately;
- if the appendages are fused to the uterus, the ovary may fit tightly to the body or be located behind. In this case, it seems that the entire body of the uterus is enlarged, as during pregnancy, but at the same time it has a dense consistency;
- The cervix and vaginal mucosa are pale pink in color; when taking smears, they are extremely rarely injured.
The symptoms of conception that have occurred are somewhat similar to those that occur with a cyst:
- delayed menstruation;
- spotting may appear;
- nagging pain in the lower abdomen, a feeling of fullness, pressure on the bladder;
- nausea, vomiting;
- weakness, drowsiness, increased fatigue;
- increase in body temperature (and basal) to 37-37.3 degrees Celsius;
- frequent mood changes.
With a vaginal examination, pregnancy can only be reliably determined from 7-8 weeks. Before this, an ultrasound or hCG test will show more accurately. Signs of early pregnancy:
- slightly enlarged and softened body of the uterus;
- an enlarged ovary with a corpus luteum cyst may be detected on the right or left;
- the cervix and vaginal mucosa are cyanotic, and when taking smears they are easily injured due to changes in hormonal levels.
Reasons why a cyst may be confused with pregnancy:
- similarity of clinical symptoms;
- upon examination, in the case of a short term pregnancy, the uterus is enlarged quite a bit, which may be similar to what it looks like on the eve of menstruation;
- An ovarian cyst can be combined with pregnancy (for example, with a functional one, previously undiagnosed).
The differences between the signs of a cyst and pregnancy on ultrasound are presented in the table:
| Criteria | Ovarian cyst | Pregnancy |
| Uterus dimensions | Normal or may be individually slightly increased | In the early stages it is slightly increased |
| Uterine cavity | The endometrium may be thin or thick | The endometrium is always thick or close to it, the fertilized egg may be invisible for some time if it is still in transit, that is, in the fallopian tubes |
| Appendages | In their area on the right or left, a formation filled with a liquid component is determined | Normally, or in their area, there may be a cyst-like formation - a cyst of the “corpus luteum” or another, previously undiagnosed |
Typically, doubts about whether there is a pregnancy or not arise in the following cases:
- in the early stages (up to 7 weeks), the fertilized egg may not normally be in the uterus;
- with an ectopic pregnancy that does not develop in the early stages, the endometrium does not prepare for pregnancy, and there is no fertilized egg in the uterine cavity.
In an ectopic ovarian pregnancy, the fertilized egg is located in the epididymis itself and grows like a cyst. The embryo is not always clearly visualized. In establishing a diagnosis in this case, a blood test for hCG helps. It is always positive if there is pregnancy.
Tests and examinations to clarify the condition include:
- examination by a gynecologist;
- Ultrasound of the pelvic organs with a vaginal probe;
- blood test for hCG.
If in doubt, repeat tests must be done after 7-10 days . Dynamic observation will give an accurate answer whether the woman has a cyst or is still pregnant.
To find out whether a cyst can be confused with pregnancy, read further in our article.
Categories
AllergistAnesthesiologist-resuscitatorVenereologistGastroenterologistHematologistGeneticGynecologistHomeopathDermatologistPediatric gynecologistPediatric neurologistPediatric urologistPediatric surgeonPediatric endocrinologistNutrologistImmunologistInfectious disease specialistCardiologistCosmetologistSpeech therapistElorologistMammologistMedical lawyerNarcologistNeurologistNeurosurgeon NephrologistNutriciologistOncologistOncourologistOrthopedist-traumatologistOphthalmologistPediatricianPlastic surgeonProctologistPsychiatristPsychologistPulmonologistRheumatologistRadiologistSexologist-AndrologistDentistTherapistTrichologistUrologistPharmacistPhytotherapistPhlebologistSurgeonEndocrinologist
Signs of pregnancy
There are quite a lot of signs indicating the imminent appearance of a new person:
| Sign | Why is this happening |
| Increase in basal temperature | Its growth provides the initial conditions for the development of pregnancy. |
| Delayed menstruation | The uterine endometrium is needed to secure the fetus, form and maintain tissues that enable its development. |
| Nausea, periodically accompanied by vomiting | Changes in the balance of hormones lead to an initial rejection by the body of the embryo, as well as new substances discovered with its appearance. |
| Spotting vaginal discharge | They can be isolated or appear more than once. In the first case, this is explained by the process of embryo implantation, during which the vessels of the mucous membrane are destroyed. Discharge may appear several times with progesterone deficiency, when a certain number of endometrial cells exfoliate and come out. |
| Mood swings, moodiness, sadness or irritability | All these are signs caused by changes in hormonal levels. They can also cause constant fatigue and a desire to sleep. |
| Heaviness and some discomfort in the abdomen, some have pain | These are temporary sensations caused by the presence of a tiny fetus, an enlarged uterus and hormonal changes. |
| Bladder and bowel function differently | A woman is forced to “run small” more often. Changed digestion and a new composition of hormones provoke constipation or diarrhea. |
If we compare the verbal description of the signs of the birth of a new life in the body and the growth of a tumor on the ovary, it seems that we should not be surprised that someone confused a cyst with pregnancy. In addition, expectant mothers, like women with this pathology, may have deteriorated skin, increased blood pressure, and weight gain.
But the similarity of signs is not the only reason why confusion is possible. A diagnosis is not made based solely on interviewing the patient. But if one of the changes in the reproductive system is suspected, an ultrasound is always prescribed. But even after this, in some cases, ambiguity or even substitution of diagnoses remains.
Signs of pregnancy
The first signs of pregnancy may appear at the time of implantation, about a week before the expected start of menstruation. A woman may feel a slight tingling sensation in the uterine area. A rare specific sign of implantation is bleeding. They arise as a result of damage to blood vessels when the embryo implants into the uterus. After this process, the woman’s hormonal background begins to change due to an increase in progesterone levels. This results in the following symptoms:
- nausea and vomiting;
- emotional swings;
- heaviness in the chest;
- stretching in the uterus and ovary from which the egg was released;
- decreased performance;
- development of thrush;
- frequent urge to urinate;
- migraines and dizziness;
- dyspnea.
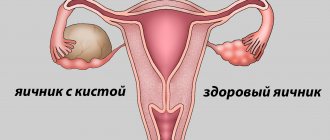
What is an ovarian cyst - the main types
A cyst is usually called a neoplasm, which is a kind of sac filled with liquid. In fact, an ovarian cyst is a benign neoplasm, which for a number of reasons can become pathogenic.
There are two types of such neoplasms: functional and organic. The difference between them lies both in the reasons for which they developed and in the methods of elimination.
Functional cysts are:
- Follicular. It occurs as a result of ovulation failure, when for some reason the follicle does not rupture and the egg does not release from it. In other words, it is formed at the site of the follicle and is filled with a homogeneous liquid. This type of cyst has thin walls and is a single-chamber benign neoplasm. The size can reach 6-8 centimeters. After a while, if her growth stops at 8 centimeters, the reverse process may begin. With this, the cyst resolves on its own. Otherwise, treatment is prescribed, which involves taking hormonal contraceptives, or its removal is recommended. Especially if there is a partial or complete torsion of her leg.
- Luteal or corpus luteum cyst. Forms in the same place as the follicular cyst. However, in contrast, the process of luteal formation begins after the egg has left the follicle after its rupture. A corpus luteum cyst during pregnancy can form due to an exacerbation of certain diseases and abnormalities in a woman’s hormonal background. Quite often its development is monitored, but it is also possible that it will rupture, in which case surgical intervention will be urgently required.
Organic ovarian cysts, unlike functional ones, do not go away on their own.
And there are these types:
- Serous.
- Dermoid.
- Endometrioid.
- Vapor-varial.
- Muciotic.
The first type of cyst is a formation, which is characterized by the presence of fairly dense walls (not elastic) and with clear contours. It is filled with serous fluid with a characteristic yellowish tint.
The second type of formation is formed from a dead embryonic rudiment. Various connective tissues and parts of the embryo are observed in its cavity. For example, bones, teeth.
The third type of endometrioid cyst during pregnancy consists of endometrial cells. The endometrium is the inner layer of the uterus, which for certain reasons has come out of its cavity. With each menstruation of this type of cyst, it increases in size due to an increase in the concentration of menstrual fluid in it.
The fourth type of cyst does not lead to pathological changes in the appendage, despite the fact that it can reach large sizes. It is formed not from the tissues of the ovary, but from its ligamentous apparatus and is a single-chamber formation with thin walls and filled with fluid.
The fifth type of formation quite often consists of several chambers. It is filled with a yellowish liquid and contains connective, gelatinous tissue. At the same time, it can reach a large size.
Top
Can an ultrasound be wrong?
Can an ultrasound be wrong about an ovarian cyst? Yes, a neoplasm can be confused with pregnancy. Often, in the results of studies, a woman is diagnosed with a cyst, but when preparing for treatment it turns out that there is no tumor.
The cyst can be confused if the girl did not follow the preparatory measures before the ultrasound examination, for example, she underwent diagnostics during her period. The tumor may be incorrectly differentiated.
Cystic formation is usually benign in nature. Treatment of the tumor depends on various factors. The most effective way is surgical therapy. Ultrasound is one of the most common and reliable methods for detecting tumors.
Is it possible to confuse a cyst with pregnancy?
Indeed, one can doubt the diagnosis. Especially if it is a short term pregnancy. Everything is determined by the individual characteristics of a woman’s anatomy, as well as the list of gynecological diseases that she has suffered. This is due to the following:
- similarity of clinical symptoms;
- upon examination, in the case of a short term pregnancy, the uterus is enlarged quite a bit, which may be similar to what it looks like on the eve of menstruation;
- An ovarian cyst can be combined with pregnancy; it can be either a functional cyst (corpus luteum) or a previously existing one, but not diagnosed.
Reasons for the unreliability of ultrasound
Cases of erroneous diagnosis by ultrasound are not so frequent, but are still known in medical practice. There may be several reasons for this:
- Equipment malfunction is a common case in which both the ultrasonic sensor and the screen may be faulty. In both cases, the picture of the pelvic organs will be blurry.
- Insufficient qualifications or inattention of the ultrasound specialist.
- The presence of an inflammatory process in the ovaries or uterus. With inflammation, these organs will be enlarged, so several diseases can be confused.
- Some types of cysts, such as dermoid cysts, are not always visible on ultrasound. But if they are present, the uterus will be enlarged and the endometrial layer will be thickened. In this case, it is very easy to mistake the cyst for pregnancy.
- The opposite situation, when pregnancy is mistaken for a cyst, is a low level of the hCG hormone. This happens when the pregnancy is early, the egg has just been fertilized, and the ovary from which it came is enlarged. In this case, the fetus is not yet visible, and the enlarged ovary is mistaken for a cyst.
- The uterus may be swollen in almost all cases of cysts. If during pregnancy the process of enlargement of the uterus is a physiological norm, preparation for bearing and giving birth to a child, then with a cyst it will be a pathology.
If doctors still confuse the diagnoses or the patient herself has any doubts about the reliability of the tests, she should undergo a re-examination in a week or two, on a different day of the cycle.
If the cyst is still confirmed, this is not a reason to despair. In most cases, such neoplasms are treated without surgery, with hormonal therapy, or even go away on their own after several cycles. After complete recovery, there is a high probability of pregnancy.
Watch the shocking story of how doctors confused an ovarian cyst with twins:
Regular visits to the gynecologist are one of the essential conditions for maintaining women’s health. But sometimes, when there are alarming changes in well-being, even a visit to the doctor does not bring clarity. Sometimes women have to wonder: can a cyst be confused with pregnancy? After all, during reproductive age, both are likely. And although it would seem that confusion is impossible, there are cases when the disease was mistaken for pregnancy, and vice versa.
Read in this article
Diagnosis – disease or child?
It seems that modern medicine has reached such a level of development that the question of whether an ovarian cyst can be confused with pregnancy seems completely absurd. However, not everything is so simple.
Doctors confirm that in very early stages, ultrasound shows an ambiguous diagnosis. The embryo is still too small, so an ovarian cyst and pregnancy show the same picture. A thickening of the lining of the uterus or an increase in its size can signal both the body’s preparation for pregnancy and a hormonal imbalance due to a cyst. Even a qualified gynecologist cannot make an unambiguous diagnosis based solely on ultrasound results when the concepts of ovarian cyst and pregnancy are intertwined.
To understand why ovarian cysts and pregnancy confuse qualified specialists, let’s compare the symptoms of both.
Characteristic signs of pregnancy:
- delay of menstruation;
- “smear” from the vagina;
- blood pressure problems;
- change in skin condition;
- mood swings;
- frequent urge to go to the toilet;
- nausea, sometimes vomiting.
Symptoms that are diagnosed with an ovarian cyst:
- in most cases, menstruation is delayed from 5 to 40 days;
- nausea and weakness;
- frequent trips to relieve yourself;
- intestinal disorders;
- pressure surges;
- weight gain;
- sebaceous skin.
Can an ovarian cyst be confused with pregnancy? As can be seen from the clinical picture, an ovarian cyst and pregnancy manifest themselves in many ways, so ultrasound and examination do not give a definite answer. You should be alerted to unpleasant sensations such as heaviness, aching pain or a feeling of fullness in the ovarian area. Pain is different from discomfort during menstruation. Discomfort is concentrated in a specific area - the right or left ovary.
Ovarian cyst or pregnancy - how to distinguish? The answer will be a blood test for hCG (human chorionic gonadotropin). This hormone is actively produced after the embryo is fixed in the uterus.
Normal pelvic ultrasound findings
During reproductive age:
- Dimensions of the ovaries: length 3-4 cm, width 2.5-3 cm, height 1.5-2 cm;
- In the ovarian parenchyma, multiple follicles ranging in size from 0.3 to 0.6 cm are visible;
- In the right or left ovary, at the time of ovulation, a dominant follicle measuring from 1.5 to 3 cm is determined;
- After ovulation, a corpus luteum measuring up to 2 cm is detected in the ovarian tissues. A small amount of free fluid is detected in the pelvic cavity.
During menopause:
- The ovaries are reduced in size;
- Follicles are not detected;
- The corpus luteum is not detected in the second phase of the cycle.
The photo shows a normal echographic picture during ultrasound of the ovaries:
What is a cyst, its symptoms
An ovarian cyst is a benign formation, usually of a hormonal nature. Some types of cysts, for example, functional ones, form before ovulation and resolve on their own with the onset of menstruation. Some neoplasms do not go away on their own and require treatment, mainly hormonal, and in some cases surgical.
Whatever type of cyst is diagnosed, with this neoplasm the woman experiences the following symptoms:
- Pain in the lower abdomen on the side where the tumor is localized. For example, if pain on the right indicates a cyst on the right ovary. There may be a feeling of bloating, like after a fatty or heavy meal.
- Pain or discomfort during sexual intercourse. There may be a decrease or increase in sexual desire (libido).
- If the ovarian cyst reaches a large size, it begins to put pressure on neighboring organs, so you may feel the need to urinate more often (if there is pressure on the bladder), disruptions in the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract in the form of constipation or diarrhea. Sometimes nausea or even vomiting occurs (a rare symptom).
- In some cases, there is weakness, drowsiness, and general malaise.
The main sign of the presence of a cyst is menstrual disorder. Since cysts are hormonal in nature, ovulation may not occur at all or may occur with a delay. The work of the ovaries is disrupted (since instead of the corpus luteum, a cyst is localized on the ovary) and as a result, instead of the usual menstruation, the woman observes spotting.
There are other specific signs of a neoplasm that indicate the hormonal nature of the disease:
- the presence of acne, especially in the chin area;
- weight gain;
- increased oily skin and greasy hair.
Comparison of symptoms
It would seem how one can confuse an ovarian cyst with pregnancy if the neoplasm is localized on the ovary, and the fetus develops in the uterus. However, pregnancy has a number of symptoms similar to a cyst, but there are also differences.
| Diagnosis Symptom | Pregnancy | Cyst |
| Disorders of the menstrual cycle, delayed menstruation | The first and most important sign to suspect pregnancy is a delay in menstruation | There may be a delay or change in the nature of menstruation, for example, very scanty discharge. |
| Nausea, vomiting | Yes, often. This is due to changes in hormonal levels and blood composition | Maybe, but rarely |
| Gastrointestinal disorders (constipation, diarrhea) | Eat. This is again due to a hormonal surge | Eat. Associated with the pressure of the cyst on the intestines |
| Presence of vaginal discharge, its nature | May be present throughout pregnancy. Sometimes they have a natural course in the form of detachment of a certain amount of the endometrium, sometimes they talk about the threat of termination of pregnancy (if they are mixed with blood) | Eat. Can appear at any time of the cycle, have a different color and consistency |
| Basal temperature* | Increasing. This is a natural physiological process that creates favorable conditions for the development of the fetus. Is not a pathology | Absent. May increase slightly with the onset of ovulation |
| Presence of pain in the abdomen | Yes, but in the early stages this symptom is not always present. Pain may be felt in the uterus | There is, on one side, in the area of the ovary where the cyst is located |
| Frequent urge to urinate | Present due to changes in hormone ratios, as well as changes in the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract | Present due to pressure of the cyst on the bladder |
| Manifestations of libido, presence of pain during sexual intercourse | Libido manifests itself differently for everyone, some increase, some decrease. There should be no pain during sexual intercourse during normal pregnancy. | Libido may also increase or decrease, pain is present during sex |
| Manifestations from the central nervous system | Drowsiness, fatigue, sudden mood swings, excessive irritability, moodiness may appear | Possible feeling of weakness, malaise, fatigue |
| External manifestations: weight, quality of skin, hair | Subject to change. As a rule, the quality of skin and hair improves, weight increases | They can change, but unlike pregnancy, for the worse: hair falls out, becomes dull and brittle, and acne appears. Weight may change or remain the same |
| Pain and engorgement of the mammary glands | Present. Breasts increase in size during pregnancy and their sensitivity also increases. | As a rule, there are none, since ovulation does not occur |
*Basal temperature can be measured in the mouth, rectum or vagina. To more accurately determine pregnancy, it is better to use the latter method.
Options for ultrasound examination and features of its implementation
In gynecological practice, three types of ultrasound of the pelvic organs are used:
- Transvaginal ultrasound involves examining the reproductive organs through the vagina. The method is considered the most informative, since the distance to the internal organs is reduced. Allows you to identify small cysts. Not used in virgins;
- Transabdominal ultrasound is performed through the anterior abdominal wall. The distance to the pelvic organs is quite large, so the method is not very informative for small cysts;
- Transrectal ultrasound. The sensor is inserted into the rectum. In terms of information content, it is comparable to a transvaginal examination. It is used in virgins in cases where the transabdominal method did not produce results.
Scheme of transvaginal ultrasound.
The ultrasound procedure lasts from 5 to 15 minutes. This is enough for the doctor to detect an ovarian cyst or other pathology. All information about the examination is provided on the form. The ultrasound results are interpreted by a gynecologist.
Ultrasound examination in women of reproductive age is carried out on the 5-7th day of the menstrual cycle. If your periods are short, you can do an ultrasound earlier; if your periods are long, the examination will be postponed to a later date. During menstruation, ultrasound is performed only for emergency reasons. Before the onset of puberty and during menopause, an ultrasound examination can be done on any convenient day.
Tests and examinations to clarify the condition
In order to accurately establish a diagnosis, it is necessary to combine examination methods. So, to determine pregnancy you need:
- conduct an examination by a gynecologist;
- perform an ultrasound examination of the pelvic organs with a vaginal sensor;
- take a blood test for hCG.
If in doubt, you need to undergo repeated tests after 7-10 days. Dynamic observation will dispel all doubts about whether the woman has a cyst or is still pregnant.
How is diagnosis carried out?
Regular visits to the doctor allow you to constantly monitor the well-being of a pregnant girl. Throughout the entire 9 months, the doctor must observe the pregnant woman and conduct laboratory and instrumental studies. In the first trimester, with a significant size of the tumor, the doctor may notice an asymmetry of the abdomen and identify a round formation in the area of the projection of the uterine appendage.
Using ultrasound, the diameter, location, and echogenicity of the tumor are determined. Already at this stage, preliminary conclusions can be drawn about this pathology. To clarify the diagnosis, additional instrumental diagnostic methods are also carried out.
To exclude malignancy of the process, a laparoscopic biopsy is prescribed. The obtained biological material is examined histologically. The pregnant woman’s blood is also checked for changes in the concentration of hormones and the presence of tumor markers.
Main signs of a cyst
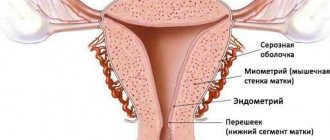
A cyst is a cavity formation filled with some kind of fluid. It can be of different sizes, functional or permanent. Ovarian cysts are often asymptomatic and are detected only during vaginal and ultrasound examinations. In some cases, it may be accompanied by symptoms, which are always more obvious when complications occur: when the cyst is more than 3 cm in diameter, when it is inflamed, ruptured, torsion of the leg, and others.
Among the most common signs of a cyst are the following:
- nagging pain in the lower abdomen: in the center, right or left;
- discomfort during intimate relationships;
- pressing sensation on the rectum;
- increased urination and bowel movements if the cyst compresses the bladder or rectum;
- fever, general weakness due to inflammation of the cyst;
- delayed menstrual cycle or strange spotting.
When examined by a gynecologist, a cyst cannot always be detected; it all depends on its size and location. If the neoplasm is more than 3 cm in diameter, it can be defined as:
- enlarged ovary on one side, the body of the uterus is identified separately;
- if the appendages are fused to the uterus, for example, due to an inflammatory process, the ovary may fit tightly to the body or be located behind. In this case, it seems that the entire body of the uterus is enlarged, as during pregnancy, but at the same time it has a dense consistency;
- The cervix and vaginal mucosa are pale pink in color and are extremely rarely injured when taking smears.
We recommend reading about the features of menstruation with an ovarian cyst. From the article you will learn about the types of ovarian cysts and their effect on menstruation, possible complications if left untreated.
And here is more information about the causes, symptoms and treatment of paraovarian ovarian cysts.
Ways to distinguish an ovarian cyst from pregnancy
When carrying out diagnostic procedures, there are cases when pregnancy is confused with a cyst. Most often this happens when the equipment is faulty or the specialist is insufficiently qualified. But sometimes even a doctor with many years of experience has doubts. This is due to the similarity of the symptoms of a cyst with pregnancy.
There are procedures to distinguish a cyst from pregnancy. These include the following:
- Donating blood for hCG or using a pregnancy test. A positive result can be either in the case of a cyst or pregnancy. Taking the analysis over time helps to get a more accurate answer. With cysts, hCG does not increase.
- Ultrasonography. The procedure allows you to determine the nature of the origin of the neoplasm in the uterus by external signs. The uterus will be enlarged in any case. The endometrium is larger during pregnancy than during cysts. The shape of the tumor in the uterine area may vary. Diagnosing an ovarian cyst is much easier because it is located on one of the appendages.
Why can it be confused?
Both pregnancy and cysts are accompanied by significant hormonal changes. Therefore, their symptoms are similar to each other. Doctors recommend not drawing conclusions based on external signs. The reason for the change in the woman’s well-being is determined after a detailed examination.
Dyspnea
During pregnancy, shortness of breath occurs as a result of lack of oxygen. It ensures the proper functioning of the child's organs. The intensity of shortness of breath increases as the baby grows. This is due to pressure on the diaphragm. With cysts, shortness of breath occurs in advanced cases when the tumor becomes too large.
Chest pain
Painful sensations in the mammary glands occur under the influence of hormonal changes. During pregnancy, the cause of pain is a sharp increase in progesterone. It retains fluid in the body, which leads to breast swelling. With cystic neoplasms, there is no pronounced enlargement of the mammary glands, but pain is present. This is due to the fact that cystic formations have the ability to secrete progesterone.
Fatigue
Decreased performance is a normal reaction of the body to a surge of hormones. It is also typical for the premenstrual period. During pregnancy, this symptom manifests itself much more strongly. It is accompanied by drowsiness and bad mood. Unmotivated bouts of activity may also occur. With cysts, fatigue occurs infrequently.
Nausea
Toxicosis is one of the main signs of pregnancy. Its appearance is caused by hormonal changes. At first, the body mistakes the fertilized egg for a foreign object. For this reason, protective forces begin to activate. This leads to an increase in body temperature and the appearance of symptoms of intoxication, which include nausea. With cystic formations, nausea is considered an alarming signal. It occurs when there is a high risk of cyst rupture.
Frequent urination
Frequent urination is the result of pressure on the bladder. In the early stages of pregnancy, frequent trips to the toilet provoke increased blood circulation in the pelvic area. The urge to urinate may occur every hour. With cysts, urination becomes more frequent in advanced cases.
Spasms
At the beginning of pregnancy, many women are unaware of their situation due to the painful sensations characteristic of menstruation. The spasms are caused by the attachment of the embryo to the uterus. In case of pathological formations, pain indicates the need to see a doctor. Delay threatens cyst rupture.
Backache
During pregnancy, pulling sensations in the abdomen are accompanied by lower back pain. This is explained by the anatomical features of the body. Minor pain is not a pathology. With cystic formations, they indicate pressure on the intestines and adjacent organs.
Dizziness
Hormonal changes are often accompanied by dizziness and headaches. The reason is changes in blood pressure. In this case, pregnant women just need to eat something sweet. For cysts, taking medications will help correct the condition.
Indications for ultrasound
Ultrasound examination is prescribed for the following complaints:
- Menstrual irregularities: delayed menstruation, shortening or lengthening of menstruation, change in the volume of monthly discharge;
- Acyclic bleeding from the genital tract or full bleeding;
- Pain in the lower abdomen, presumably associated with pathology of the reproductive organs;
- Detection of a round formation in the projection of the appendages during bimanual examination.
An ultrasound is also performed when an ovarian cyst has already been identified to monitor its growth. A control ultrasound examination is mandatory after surgical treatment (after 1, 3 and 6 months).
Ultrasound helps to determine the presence of a cyst, its size and suggest what type of formation it belongs to.
This is what an ovarian cyst looks like on an MRI scan.
There are no contraindications for performing ultrasound. The method is considered safe and can be performed on women of any age, including during pregnancy and lactation.
Cyst and pregnancy - main symptoms, causes, treatment
A cyst is often discovered during the next ultrasound examination or palpation performed by a gynecologist during an examination. This is due to the fact that it can develop asymptomatically until it reaches a significant size.
The main symptoms of the presence of a cystic formation on the appendages will be the following:
- Drawing, aching pain in the lower abdomen, which, if worsened, can become shooting and radiating to the ribs.
- Increased body temperature, nausea and vomiting.
- Hands hurt during pregnancy, all joints hurt due to general weakness.
- Uterine bleeding, which can be sudden, scanty and spotting.
- Enlargement of the abdomen in one of the parts where the cystic formation is located.
- Frequent urination, loose stools and pain when going to the toilet.
Cystic formation often occurs even before pregnancy. But you should know that cyst and pregnancy are concepts that are most often interconnected and caused by the following factors:
- Heredity. If a woman's mother develops a cyst during pregnancy, she is also at risk of developing it.
- Frequent stress. An unstable psycho-emotional state affects the reduction of the body's protective functions.
- Reduced immunity and exacerbation of diseases of the pelvic organs.
- Injuries. These should also include previous surgical interventions.
- Hormonal imbalance, which is not surprising in early pregnancy.
- Sexual abstinence and sexually transmitted diseases.
Treatment for ovarian cysts during pregnancy should be selected based on the indicators obtained in the course of research. Often it is simply observed, painful symptoms are relieved with the help of a number of medications.
However, there are times when classical treatment is not suitable. In particular, this occurs when the cyst ruptures and torsions. In this case, the pregnant woman may undergo surgery. For example, laparoscopy. Basically, even with conventional surgery, when a woman needs to undergo general anesthesia, it is possible to maintain a pregnancy and bear a healthy child.
Top
Similarities
There are striking similarities between the signs of ovarian cysts and pregnancy. Below are 12 signs that will show how easy it is to confuse a cyst with a fetus.
Dyspnea
Pregnant women require more oxygen, the fetus needs it for the normal functioning of all organs and systems. As the fetus grows, additional pressure is placed on the mother's diaphragm and lungs, making breathing difficult.
However, pregnancy is not the only condition that can cause shortness of breath. This is a common symptom of ovarian cysts. Shortness of breath becomes more of a concern when the cysts increase in size.
Chest pain
Soreness of the mammary glands occurs due to changes at the hormonal level, it becomes more tender and sensitive, and increases in size. A hollow tumor can also trigger the appearance of this symptom.
This is due to the fact that the uterus and ovaries are interconnected with the breasts. If a disturbance or malfunction occurs in the reproductive system (in this case, a hollow tumor interferes with the functioning of the part of the female genital organs where the egg is formed), this affects the mammary gland.
Fatigue
The progression of the pathological formation leads to constant fatigue. This symptom and cysts are associated with the fact that they can affect the production of hormones in the body.
During pregnancy, fatigue occurs only in the first trimester. The woman feels overwhelmed and wants to sleep constantly. Later the symptom goes away.
Nausea
Nausea is one of the earliest signs of pregnancy. This is precisely why most women recognize through symptoms that a long-awaited event has occurred—conception. Changes in the balance of hormones lead to an initial rejection by the body of the embryo, as well as new substances discovered with its appearance. Therefore, during pregnancy, nausea occurs, periodically accompanied by vomiting.
Nausea with ovarian cysts is also associated with hormones. As the pathological condition progresses, an imbalance of hormones occurs in the body, which leads to the appearance of this symptom.
Frequent urination
Pregnancy is accompanied by a lot of unpleasant sensations, including problems with urination. As the child grows, the pressure on the bladder increases; the fetus needs more space, so it puts pressure on the bladder, leaving only a small place for urine to accumulate. The reason for frequent urination during pregnancy can also be muscle relaxation, activation of metabolic processes (the kidneys begin to work faster), and fluid retention in the mother's body.
In the later stages of pregnancy, the baby's kidneys begin to work. Due to this factor, the frequency of fluid excretion in the mother may increase.
For patients with ovarian cysts, the need for frequent urination most often has nothing to do with the kidneys. Large lesions press against the bladder, reducing its ability to retain fluid.
Spasms
Pain and cramping in the abdomen may indicate a cyst and pregnancy, or a complication. Only an additional examination will confirm what the pain means.
Backache
Back pain may indicate early pregnancy. It is a sign that a woman's body is weakening, the baby inside is growing and putting pressure on the back.
But it can also be a symptom of a serious pathological condition in the reproductive system. He says that the cysts are increasing in size.
Dizziness
Pregnant women are prone to experience dizziness or fainting as a result of low blood pressure or low sugar levels. By drinking enough water and eating well, you can avoid these signs.
But with a cyst, such methods of overcoming dizziness will not help. Here it is necessary to take special medications, because the symptom is associated with an increase or decrease in blood pressure, which cannot be prevented by eating well. The reasons in this case are different, so the treatment will also be different.
Gentle abortion options
The medicinal method is considered milder. Such early termination of pregnancy does not entail multiple complications and health problems. But even in this case there are some contraindications. It is necessary to use medications that provoke abortion only in doses prescribed by a doctor and only after an examination by him.
At 6 to 12 weeks, you can resort to vacuum abortion. It is prescribed exclusively by a doctor and also requires a preliminary examination. Most often, local anesthesia is used during a vacuum abortion. Upon completion of the operation, complications do not arise and the function of the woman’s genital organs is not impaired.
Preparing for diagnostics
Before going for an ultrasound, you need to get a referral from your doctor for diagnostics. The form must indicate a preliminary diagnosis. This way, the doctor in the ultrasound room will be able to quickly navigate the situation and will specifically look for a specific pathology.
You need to take with you to the study:
- Documents: direction, passport, policy;
- A clean sheet or diaper;
- A towel (needed after the procedure to remove the gel from the skin);
- Shoe covers or replacement shoes.
Preparation for the procedure differs depending on its type. Before a transabdominal ultrasound, it is necessary to fill the bladder. This is necessary in order to displace the intestine from the imaging area to obtain a clear image. Otherwise, the intestinal loops will block the pelvic organs, and it will not be possible to see the cyst. To fill the bladder, you need to drink 1-1.5 liters of still water 1-2 hours before the procedure and not urinate until the study is completed.
Conducting transabdominal ultrasound.
No preliminary preparation is required before transvaginal ultrasound. On the contrary, you need to empty your bladder immediately before the procedure so that nothing interferes with examining the pelvic organs.
Before performing a transrectal ultrasound, it is important to have a bowel movement either naturally or with an enema. Enema can be done the evening before the procedure
Examinations and tests
A diagnosis cannot be made based on the patient’s external manifestations and sensations alone. It is necessary to conduct a comprehensive examination, which includes several stages:
- Pregnancy test. If you suspect pregnancy, the first thing you can do on your own is to do a rapid test for the presence of the hCG hormone.
In some cases, the test may give a false positive result:
- when taking certain hormonal drugs that stimulate ovulation (if a woman is undergoing treatment for infertility);
- if the test is performed after a miscarriage, abortion, surgical removal of an ectopic pregnancy, then the hCG hormone can remain in the blood for another couple of months.
A false negative result occurs when conception occurred shortly before the start of menstruation, if the period is already more than 12 weeks, with an ectopic pregnancy and the threat of miscarriage. Errors may also occur due to excessive intake of fluids or diuretics. The test results may be incorrect if the test is expired, of poor quality, or damaged in any way.
Usually the results do not depend on the time of day, but many experts advise doing it in the morning for more accurate results.
- A blood test for hormones in general and the presence of hCG in particular will help to create a more accurate picture - with a cyst, hCG is not produced, but there may be a change in the ratio of other hormones.
- An examination by a gynecologist may show an increase in the size of the uterus if pregnancy has occurred, or an enlargement of the ovary if a cyst has formed on it. The ovary can also be enlarged due to an inflammatory process - oophoritis, so the doctor takes smears to determine the presence of pathogenic microflora.
- An ultrasound examination (ultrasound) is mandatory, which helps to more accurately determine whether the patient has a cyst or pregnancy.
Causes of errors during ultrasound
Ultrasound examination is considered informative for the differential diagnosis of pregnancy and ovarian cyst. However, based on its results, it is also not always possible to say with complete confidence what the woman’s complaints and the doctor’s doubts are. The main parameters are presented in comparison in the table:
| Criteria | Ovarian cyst | Pregnancy |
| Uterus dimensions | Normal or may be individually slightly increased | In the early stages it is slightly increased |
| Uterine cavity | The endometrium may be thin or thick | The endometrium is always thick or close to it, the fertilized egg may not be visible for some time if it is still moving in the fallopian tubes |
| Appendages | In their area on the right or left, a formation filled with a liquid component is determined | Normally, or in their area, there may be a cyst-like formation - a cyst of the “corpus luteum” or another, previously undiagnosed |
Typically, doubts about whether there is a pregnancy or not arise in the following cases:
- in the early stages (up to 7 weeks), at which time the fertilized egg may not normally be in the uterus;
- with an ectopic pregnancy that does not develop in the early stages. At the same time, the endometrium does not look like it is preparing for pregnancy; there is no fertilized egg in the uterine cavity.
Expert opinion
Daria Shirochina (obstetrician-gynecologist)
In an ectopic ovarian pregnancy, the fertilized egg is located in the epididymis itself and grows like a cyst. The embryo is not always clearly visualized. In establishing a diagnosis in this case, a blood test for hCG helps. The result will always be positive if there is pregnancy.
Why can it be confused?
Whether it is possible to confuse an ovarian cyst with pregnancy, despite the use of ultrasound, is not an idle question, because such cases are known. There are subjective and objective reasons for the phenomenon:
- In both conditions, the uterus is enlarged and the endometrium is thickened. This is natural for pregnancy, because the organ is preparing to bear the fetus. Hormones create the conditions for a long gestation process. The cyst itself changes the composition of substances or occurs against the background of a disorder in this area. Therefore, on ultrasound it is visible as swollen, spherical, in size corresponding to several weeks of pregnancy.
- If the level of hCG in the mother’s blood is at the lower limit of acceptable values, then the fertilized egg is not visualized. Even an ultrasound with a vaginal probe does not help. But an enlarged ovary, from which a female reproductive cell has emerged, soon fertilized, can be mistaken for a cyst.
- New growths are also not always clearly visible. This happens especially often with dermoid type cysts. And a thickened endometrium and a swollen uterus falsely indicate pregnancy.
- Insufficient specialist qualifications and low-quality equipment. Recently, both are becoming more common. Therefore, there is no doubt whether an ovarian cyst can be confused with pregnancy.
- One of the reasons for the appearance of a neoplasm is inflammation. It also causes an increase in BT. And if a woman is watching her, she will detect the sign, but will interpret it incorrectly, mistaking the cyst for a dream come true to soon become a mother.
The increase in the number of gynecological diseases that prevent pregnancy, their “rejuvenation”, and the forced postponement of motherhood due to the need to pursue a career have become commonplace. And this leaves no doubt whether the cyst can be confused with a future addition to the family. Pathology is becoming more common. But it also happens the other way around: the “cyst” turns out to be pregnancy
Therefore, it is important not to fall into despair, but to undergo a more thorough and comprehensive examination
Why is there confusion?
By comparing the descriptions of an ovarian cyst and the birth of a new life, we can come to the conclusion that it is quite possible to confuse the symptoms due to their similarity. In order to be sure whether you have a cyst or pregnancy, you need to consult a gynecologist. The formation is formed on the surface of the genital organ, and the development of the child occurs in the uterus, so making an accurate diagnosis for the doctor will not be a problem. The diagnosis is never made solely on the data of a patient interview. One of the most popular diagnostic methods is ultrasound examination.
Important! But in some cases, even during an ultrasound examination, the gynecologist has doubts. The cyst may look like a ball-like formation, similar in size to the picture at the fourth to seventh week of pregnancy.
Dermoid formations are particularly difficult to diagnose. With such a cyst, the endometrium thickens and the uterus swells. Thus, an insufficiently qualified doctor may come to a false conclusion during diagnosis. To prevent this from happening, it is very important to contact a trusted and qualified specialist who will make an accurate diagnosis.
We recommend you learn: Histology of ovarian cysts and why ovarian cysts appear after childbirth
Technique for performing gynecological examination
The procedure is carried out in a specially equipped room. During a transvaginal ultrasound, you need to undress to the waist and lie on your back with your knees slightly bent. A special sensor, packaged in a condom, is lubricated with gel and then inserted into the vagina. The procedure is unpleasant, but painless. During the examination, the woman may feel slight pressure from the inside and feel the urge to empty the bladder.
To perform a transabdominal ultrasound, it is enough to expose the lower abdomen. The doctor moves the sensor, lubricated with gel, over the area being studied - below the navel, on the left and right in the iliac region. The pressure of the sensor increases the urge to urinate, but you will have to endure it. Immediately after completing the procedure, you should urinate.
Transrectal ultrasound is performed through the rectum. A sensor lubricated with gel is inserted into the anus. During the procedure, the patient lies on her side with her legs bent. When the sensor is inserted, a feeling of heaviness, bloating and discomfort is felt.
Options for ultrasound images for vaginal and abdominal examination.