- Pregnancy from A to Z
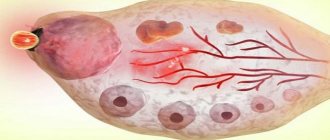
The corpus luteum is a temporary gland in a woman’s ovary, formed at the site of the follicle from which a mature egg was released. And they called it that because it is filled with a yellow liquid containing hormones. Without the corpus luteum, pregnancy and normal childbearing are impossible.
Quick navigation through the article:
- What are the disorders in the development of the corpus luteum?
- Hypofunction of the corpus luteum during pregnancy
- Absence of the corpus luteum during pregnancy
- Treatment for functional deficiency or absence of the corpus luteum
- Corpus luteum cyst during pregnancy
How does the corpus luteum appear?
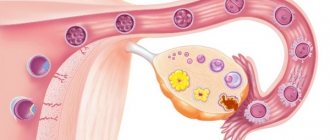
Regularly, every month, an egg matures in one of the ovaries of a woman of childbearing age. It develops in the follicle during the first half of the menstrual cycle. After maturation, the follicle bursts and the egg is released into the abdominal cavity. This process is called ovulation.
While the egg moves through the fallopian tube, a corpus luteum forms at the site of the ruptured follicle, producing estrogen and progesterone. The latter is especially important - after all, it is he who prepares the woman’s body for conception and pregnancy.
In the second half of the menstrual cycle, the corpus luteum actively produces progesterone, which promotes pregnancy. If fertilization does not occur, the corpus luteum atrophies, progesterone levels drop sharply and menstruation begins. And in the ovary the process of maturation of the next follicle is initiated.
What it is?
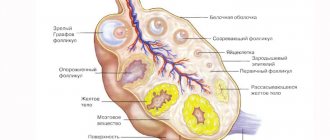
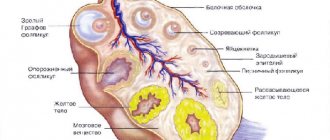
Each monthly cycle, follicles mature in a woman’s ovaries, most of which die by the time of ovulation. One of them remains - the “strongest” one, which continues to develop, increasing in size. It is called the dominant follicle. It is in it that the egg matures, which, after meeting the sperm, will be fertilized.
As soon as the dominant has reached the desired size, it ruptures and the egg is released into the lumen of the fallopian tubes.
Blood begins to accumulate at the site of the former dominant follicle. Special cells resembling grains appear in it, which actively produce lutein. It is this temporary neoplasm that is called the corpus luteum, since it has a characteristic yellow color.
Functions of the corpus luteum
Under the influence of progesterone (also called the pregnancy hormone), the endometrium of the uterus grows and swells, preparing for the implantation of a fertilized egg - a zygote. The fallopian tubes slowly contract, advancing the zygote, and the cervix dilates to allow the large female reproductive cell to pass through.
But progesterone, on the contrary, relaxes the muscles of the uterus, preventing it from contracting. Under the influence of hormones from the corpus luteum, the glands of the uterus secrete first a mucous secretion, which increases the passage of sperm, and later another, which promotes the penetration of the zygote into the wall of the uterus. The uterus itself is preparing for active expansion.
Progesterone suppresses the maturation of subsequent follicles and prepares the woman’s nervous system for bearing a child. Alveoli, the glands that produce milk, begin to develop in a woman’s breasts.
The functioning of the corpus luteum itself is controlled by hCG (human chorionic gonadotropin), produced by the membrane of the embryo. Thus, if fertilization does not occur, the corpus luteum does not receive the “order” to grow further and degrades.
If conception has occurred, the corpus luteum will develop and produce hormones until the placenta is fully formed, approximately until –16 weeks of pregnancy. Then the baby's place will take over the production of progesterone and estrogen, and the corpus luteum will be reduced. However, for some women, it persists until childbirth.
During an ectopic pregnancy, the corpus luteum grows slowly. This is due to the fact that an embryo attached in the wrong place (tubal wall, ovary, abdominal cavity...) does not have the opportunity to develop normally. The chorion (membrane) grows incorrectly, so hCG is released in insufficient quantities.
Gnomik.ru recommends Rmh24.ru Repair of refrigerators at home in Moscow and the region. We repair refrigerators of all brands. Free visit of a specialist and diagnostics!
Use promo code: Gnomic.ru
and get a guaranteed 10% discount
We work in Moscow and the region.
Call
Call a specialist
Localization
The corpus luteum cannot be located either in the uterus, as some women think, or in the fallopian tubes, or anywhere else outside the ovaries. It always strictly develops exclusively on the ovary from which ovulation occurred. A woman has two ovaries. Follicles grow on both at the very beginning of a new cycle, but there is usually one dominant one, the rest undergo reverse development. The dominant follicle is located either on the right or left ovary. The corpus luteum also occupies the place that previously belonged to the follicle vesicle.
Sometimes a woman develops two corpora lutea at once. What this means is not difficult to understand - there was double ovulation, two dominant follicles burst at once, so there is a high chance that a woman can become pregnant with twins or even triplets. The phenomenon of double ovulation itself is not very common; the body saves its follicular reserve, since it is not replenished or renewed in a woman, and the number of eggs is given to her once for her entire life.
What are the disorders in the development of the corpus luteum?
The main deviations in the normal formation of the corpus luteum are:
- functional failure; - cyst.
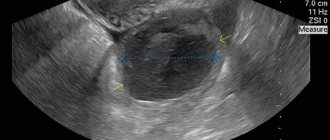
Both diagnoses are made after comprehensive examinations, which include ultrasound, blood tests for progesterone and hCG levels, gynecological examination, and study of the basal temperature chart. A woman is not at risk of harm from ultrasound during pregnancy; at the moment, ultrasound is the most informative and absolutely safe method of studying the condition of the fetus. It can be performed as many times as needed and at any stage of pregnancy.
Corpus luteum cyst is considered a harmless disease and rarely requires treatment. But it is better to detect the insufficiency or absence of the corpus luteum as early as possible, since this pathology threatens the termination of pregnancy in the early stages or the further development of placental insufficiency.
VT during pregnancy
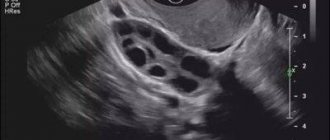
In the early stages of pregnancy (12-13 weeks), women are recommended to undergo ultrasound diagnostics. In some cases (if the doctor suspects possible violations) an ultrasound is sent even earlier. This study is painless and does not pose a threat to the health of the expectant mother and her unborn baby.
Ultrasound allows you to see at the earliest stages the correct development of the fertilized egg, the condition of the ovaries and the uterine cavity.
The size of the corpus luteum is one of the main criteria for determining the correct development of pregnancy. We have already said that this small temporary gland plays a major role in the production of progesterone, without which the natural development of the fetus is impossible.
The less iron, the less quantity it can produce the desired hormone. The less progesterone in a pregnant woman’s body, the less chance of maintaining the pregnancy.
If the diameter of the corpus luteum is less than 10 mm, then doctors diagnose its insufficiency. If it is excessively large (more than 30 mm), this is a signal of the presence of a cyst.
Both the first and second deviations from normal values are undesirable during pregnancy. However, cystic changes, as a rule, do not threaten the development of the fetus. Indeed, in this case, the temporary gland produces the required amount of progesterone, therefore, the fetus can develop normally. And after a few months, the cyst resolves on its own, without the influence of medications. The only recommendation for such a diagnosis is regular monitoring by a gynecologist.
If the corpus luteum is not visualized or its size is too small, it is necessary to urgently begin drug therapy, since in this case there is a high probability of termination of pregnancy.
Hypofunction of the corpus luteum during pregnancy
Lack of corpus luteum function during pregnancy is a very serious disorder. It leads to the inability to get pregnant, to spontaneous abortions, to a threat to the life of the fetus if the placenta has formed abnormally.
An incomplete cycle of the corpus luteum phase is one of the causes of infertility. If the corpus luteum develops in less than ten days and dies, then the amount of progesterone it produces is simply not enough to prepare the mother’s body for pregnancy. The zygote may not have time to penetrate the uterine wall during this time. Or the uterus will reject it as a foreign organism if the hormonal background is not formed correctly.
Insufficiency of the corpus luteum during pregnancy is a reason for emergency medical intervention. Functional deficiency of the corpus luteum means that it produces fewer hormones, primarily progesterone, than are necessary for the normal development of pregnancy. Progesterone deficiency can significantly affect the formation of the placenta and the nutrition of the fetus. But most often, low levels of pregnancy hormones lead to miscarriage in the first or second trimester.
Viability of the gland
In the absence of conception, the lifespan of VT is no more than 10 days. After their expiration, the iron degenerates into scar tissue and stops producing progesterone, being rejected during menstruation along with the endometrial cells of the uterus. Before rejection, such a formation in the ovary is called the white body - it forms a scar after itself. Under the influence of regressed glands, the tissue of the appendage becomes scarred.
With successful fertilization of the egg and fixation of the fertilized egg in the walls of the uterus, the corpus luteum continues to function. Its viability period increases to three months - until the resulting placenta begins to fully produce progesterone. After this, the gland dies off as unnecessary.
Treatment for functional deficiency or absence of the corpus luteum
Treatment of the disease is carried out with hormonal drugs, usually containing progesterone. There are a lot of such drugs, but only a professional doctor can determine which one is right for you after conducting various tests and examinations.
With hormonal therapy, not only the dosage matters, but also the timing of taking the medication. If corpus luteum deficiency is the cause of infertility, then the doctor will prescribe hormonal medications after ovulation. The time of ovulation needs to be known exactly, because progesterone suppresses it.
If you have already had miscarriages and there is a suspicion of hypofunction of the corpus luteum, then at the first signs of pregnancy you should consult a doctor. Once the diagnosis is confirmed, hormonal adjustments will be required to maintain the pregnancy. It will take a long time to be treated until the placenta is completely formed. Naturally, treatment should be accompanied by constant monitoring of hormone levels in the blood.
About ultrasound
Before you understand the features in diagnosing the corpus luteum on ultrasound, you should understand the operation of the device. As mentioned earlier, diagnostics using ultrasound was introduced into medicine relatively recently. This technique is based on ultrasonic waves; bats use them in nature.
During the examination, the device, through a transducer (a sensor that is in contact with the surface of the skin and which the doctor constantly moves in order to study the organ under study in different projections), emits ultrasonic waves of a given frequency, which in turn are reflected from the organs and return back, being registered through the sensor and are visualized on the device monitor.
These waves do not harm the human body in any way, which allows them to be used in gynecology many times. You can also see small elements on an ultrasound, for example, the corpus luteum.
Corpus luteum cyst during pregnancy
Sometimes the corpus luteum develops incorrectly. The walls of the follicle from which the mature egg has emerged begin to thicken and stretch, and the internal cavity is filled with serous fluid. A tumor-like formation is formed - a corpus luteum cyst. However, there is no need to panic - a corpus luteum cyst never degenerates into a malignant formation.
Causes of corpus luteum cysts can be:
- disturbances in the functioning of the lymphatic and circulatory systems of the ovaries;
- infectious diseases of the genital organs;
- taking hormonal medications;
- harmful working conditions, bad habits;
- stress;
- extreme diets.
In most cases, the cyst does not interfere with the development of pregnancy and does not require medical intervention, since it is a modified corpus luteum and secretes sex hormones in sufficient quantities. Usually after two to three months it begins to resolve on its own and disappears completely.
The size of the cyst usually does not exceed 6–9 cm; it rarely causes concern to a pregnant woman. But the doctor will still monitor her, and the woman will recommend moderate physical activity and careful sex so as not to cause rupture of the cyst or twisting of its leg.
Diagnosis of a corpus luteum cyst is carried out using ultrasound, gynecological examination, hormonal analysis, and laparoscopy. A woman may feel nagging pain in the lower abdomen or side. If the pain is always localized in one side, then this may be a symptom of an ovarian cyst. Another sign is menstrual irregularities and bleeding outside of menstrual periods.
A corpus luteum cyst can be eliminated on its own, so usually it is not touched, but only observed. If there is no hope for spontaneous atrophy, then the cyst is removed using laparoscopy.
Cyst rupture is the most serious complication of this disease. It is accompanied by acute pain, bleeding and requires surgical intervention. A ruptured, untreated cyst can lead to the development of an acute infection of the internal organs.
Twisting of the cyst pedicle also requires surgical treatment, since compression of the tissues leads to their necrosis.
Thus, the main danger associated with the corpus luteum during pregnancy is its lack of functionality. But you shouldn’t be upset - the level of development of modern medicine allows us to help women bear a healthy child even with insufficiency of the corpus luteum. It’s just that in this case, in order to maintain the pregnancy, you may need to take hormonal medications. And only a doctor can choose their dosage - trust him.