Follicle size at ovulation
The woman herself will not be able to find out the size of the dominant follicle; even an obstetrician-gynecologist will not do this during an examination. To measure, you will need special equipment. Size plays a big role, because only a developed egg is capable of fertilization. When ovulation occurs, certain symptoms appear. Knowing them, it will be easier for a woman to protect herself from an unwanted pregnancy or, conversely, to choose the best day for conception.
Norm
What is the size of the follicle at ovulation? Immediately at the time the egg is released, the size of the dominant follicle is already 23-24 mm. After its rupture, the egg is alive for 2 days, no more. This is the most favorable period for fertilization.
Can ovulation occur if the size of the bubble formed is smaller than normal? This is unlikely, but if this happens, the underdeveloped egg will not be ready for fertilization.
Deviations
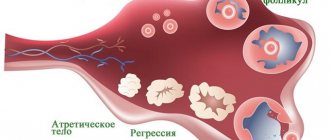
Sometimes deviations occur in the form of atresia and persistence. Atresia is a disorder in which the follicle does not break its integrity during ovulation. On the contrary, it began to shrink again, the unruptured follicle develops into a cyst-like formation.
For atresia:
- there is low progesterone;
- no corpus luteum;
- there is no free fluid behind the uterus.
This pathology is accompanied by the presence of amenorrhea and periodic bleeding, which occurs 3 to 4 times a year, similar to menstruation. Women who have this dysfunction cannot become pregnant.
The disease develops from the very beginning, that is, during puberty or as a result of hormonal failure, in which the level of lutropin and follicle-stimulating hormone decreases and the follicle does not reach the desired size. As a result, there are menstrual irregularities, amenorrhea and polycystic ovaries appear. The worst thing is infertility.
With persistence, rupture of a mature follicle does not occur. It is in the size of 22-24 mm for a week, then menstruation begins. Sometimes they are not there, and the unruptured blister degenerates into a cyst. This happens due to hormonal imbalances. The symptoms of this pathology are as follows:
- progesterone is reduced;
- estrogens are elevated;
- follicle on systematic ultrasound of the same size;
- there is no fluid in the space behind the uterus and corpus luteum;
- delay of menstruation;
- heavy menstruation.
To correct the situation, doctors prescribe hormonal therapy, which normalizes hormone levels. Sometimes laser therapy, ultrasound or electrical stimulation are indicated. Be sure to have good nutrition, healthy sleep, and vitamin supplementation. It is necessary to exclude stress and physical activity.
Why doesn't ripening happen?
The diagnosis of infertility has not been uncommon for a long time. Moreover, the main reason here is often that the follicles simply do not mature. In this case, you need to do a thorough examination, determine the cause of the pathology and begin treatment. A disruption in the maturation process can be caused by:
- Ovarian dysfunction. It is caused by various inflammatory pathologies, trauma, and surgery.
- Various dysfunctions of the endocrine system, in which there is low production of estrogen and progesterone. The second hormone helps the dominant follicle grow and develop, and the first helps suppress small follicular vesicles.
- Brain dysfunction. It can be triggered by injury or inflammatory damage to the membranes of the organ.
- Increased intracranial pressure.
- Benign or malignant tumor in the area of the hypothalamus and pituitary gland.
- Inflammatory or infectious damage to internal organs located in the abdominal cavity.
- Frequent stress, depression.
- Early menopause.
- Following a strict diet or being overweight.
If the functionality of the reproductive system is impaired, a mature follicle does not appear at all, so it is necessary to urgently consult a doctor and undergo treatment.
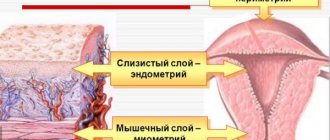
The previously mentioned factors can disrupt the formation process of the presented formation or cause its regression. The follicle fails to grow to the desired size or does not rupture. Ovulation, and therefore pregnancy, does not occur. But even if the egg is ready for fertilization, and the endometrium (endometrium) does not have the required thickness, it simply will not settle in the uterus.
If the follicle matures too early or too late, then this can also be considered a deviation. You also need to pay special attention when a woman’s ultrasound reveals numerous bubbles in the ovarian area. Here the patient is diagnosed with “multifollicular ovaries.” On the monitor, the specialist can see a large number of bubbles. They are located along the periphery of the ovary. These bubbles interfere with the development of the dominant formation, since it cannot mature normally. If the endik is thin, then pregnancy may not occur, despite successful fertilization of the egg.
What is the quantity?
Modern realities are such that women are in no hurry to have children, preferring first to get an education, achieve a certain social position, and earn money. And motherhood is postponed until later. But you can’t fool nature, and after 35 years, the number of germ cells in the ovaries begins to rapidly deplete. After all, whether a woman can become pregnant naturally depends on how many follicles remain in the gonads.
The number of follicles is established even when the girl is in the mother’s womb: in the first trimester of pregnancy, female fetuses already have ovaries with a large supply of primordial follicles, each of which contains primary oocytes. Their number is a record for a woman’s entire life and amounts to up to 2 million.
Once a girl reaches puberty, every month one follicle matures in her ovaries and one egg is released. The phenomenon of double ovulation (when more than one egg matures and is released) is quite rare.
Ovulation calculator
Cycle duration
Duration of menstruation
- Menstruation
- Ovulation
- High probability of conception
Enter the first day of your last menstrual period
Ovulation occurs 14 days before the start of the menstrual cycle (with a 28-day cycle - on the 14th day). Deviation from the average value occurs frequently, so the calculation is approximate.
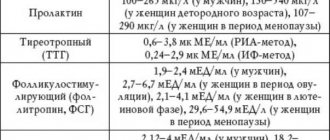
Also, together with the calendar method, you can measure basal temperature, examine cervical mucus, use special tests or mini-microscopes, take tests for FSH, LH, estrogens and progesterone.
You can definitely determine the day of ovulation using folliculometry (ultrasound).
- Losos, Jonathan B.; Raven, Peter H.; Johnson, George B.; Singer, Susan R. Biology. New York: McGraw-Hill. pp. 1207-1209.
- Campbell NA, Reece JB, Urry LA ea Biology. 9th ed. - Benjamin Cummings, 2011. - p. 1263
- Tkachenko B. I., Brin V. B., Zakharov Yu. M., Nedospasov V. O., Pyatin V. F. Human physiology. Compendium / Ed. B. I. Tkachenko. - M.: GEOTAR-Media, 2009. - 496 p.
- https://ru.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ovulation
The process of follicle maturation is called folliculogenesis. It starts after each menstruation. Under the influence of follicle-stimulating hormone, several follicles begin to grow on different ovaries at once. But one remains, and it is called dominant. It is in it that the egg matures, which is destined to be released in this menstrual cycle. The remaining follicles are fading away; their time has not yet come.
If conception occurs, the maturation of new follicles is suspended until the postpartum period. If conception does not occur, the egg dies after ovulation within a day and a half, is excreted along with menstrual bleeding, and the cycle repeats again. In the life of every healthy woman, there are also anovulatory cycles, when the follicle does not mature or the oocyte is not released. It is impossible to conceive a baby during such cycles. Normally, their number is 1-2 per year, but after 36 years the number of anovulatory cycles can reach 5-6 per year, so conceiving a child becomes more difficult with age.
Stages of follicle maturation
The maturation process is controlled by hormones, in particular progesterone and lutein. If the balance of these hormones is disturbed, this leads, first of all, to disruption of the menstrual cycle. In its first phase, with normal hormonal background, the process of follicle maturation begins. Up to ten follicles can develop at the same time, but only the dominant one has a chance to reach the required size. The remaining formations should degrade if the hormonal balance is not disturbed. Otherwise, they continue to develop and inhibit the growth of the dominant follicle.
A normal menstrual cycle is a sign that there are no problems with follicle maturation. Before ovulation, women may feel nagging pain in the lower abdomen, overexcitation or irritability, and mood swings; Vaginal discharge may become more abundant and thick. One of the signs of follicle maturation is also a slight decrease in temperature a day or 12 hours before ovulation. Then the rectal temperature rises by a few tenths of a degree Celsius. You can also track the release of an egg from a follicle using hormonal tests: before ovulation, progesterone levels increase.
Usually the menstrual cycle is accompanied by the maturation of one single follicle, but there are cases when two or more mature simultaneously. This is not a pathology, but the result of the maturation of several follicles is often a multiple pregnancy.
During ovulation
After a mature egg leaves the ovary, a corpus luteum appears in its place, which releases the hormone progesterone into the blood. Thanks to its action, BT rises by 0.5–0.7 degrees. Pregnancy also has such indicators, but the girl knows nothing about it yet. To effectively plan a pregnancy, you need to know the possible days of conception. Typically, the release of the egg occurs on days 14–15 of the cycle.
The monthly cycle is divided into three phases (not counting the days of menstruation):
- follicular;
- ovulatory;
- luteal
In the follicular phase of the cycle, BT will remain at 36.3–36.6 degrees. This is normal and will last for about two weeks. The second phase is ovulatory. At this time, BT will decrease slightly and then increase to 37.0–37.4 C. By the beginning of menstruation, the temperature will drop to its previous level. The day when BT is higher than before is a favorable day for conception.
For accurate data, measure BT regularly, with one thermometer, at the same hours.
How does it change during ovulation?
After the release of the egg, BT reaches its highest level - this is a signal that ovulation has occurred. A sharp jump in BT in one day, by at least 0.3 degrees, is the day of ovulation.
These numbers may not be entirely accurate, as each patient has different characteristics. In 95% of cases, BT when the egg is released is above 37 C.
For several months a year, every woman does not have favorable days for conception due to an unripe egg. This phenomenon is called anovulation. This is absolutely normal, and BT will not increase significantly in such months. But if you have not observed ovulation at your basal temperature for several months, contact your gynecologist.
How to determine ovulation by basal temperature
BT should remain at least 37.1 degrees. During the maturation of the egg, BT will begin to rise slightly, but in some cases, on the contrary, it drops by one or two tenths of a degree. This is not scary, this is a feature of the patient’s body. BT will remain at 37.0-37.4 degrees for 24-48 hours. These indicators also depend on the girl’s physiology.
In very rare cases, BT does not rise above 36.9 C. But this does not mean that the egg has not been released. This “behavior” of BT indicates that the girl’s normal body temperature is slightly lower than 36.6.
Follicle size before ovulation
To conceive, they must develop normally so that a full-fledged egg is released from them. Let's consider what the dominant undergoes during the month.
Norm
What size should a follicle be before ovulation? When they reach seven days of age, their size is between 3-7 mm. On an ultrasound examination, the specialist will see several structural elements that have different stages of development. There shouldn't be more than a dozen of them. From the eighth to the tenth day, the dominant follicle is already visible, which grows to 14 mm. Everyone else becomes smaller and disappears. In 24 hours it increases by 3 mm.
1-2 days before the release of the egg, a vesicle is approximately 18-22 mm in size. It all depends on the menstrual cycle, on days 12-16 the ovulatory phase begins and it bursts.
Deviations
What follicle size before ovulation is abnormal? If before this, and on any day of the cycle, they are all approximately the same size and there is no dominant one, this is a bad signal. This can be seen on ultrasound diagnostics. If one follicle does not mature, then the egg will not be released, as it will not be able to conceive.
Sometimes there are two or three dominant follicles. Afterwards there may be two (three eggs) and the outcome is positive, that is, twins or triplets. Otherwise, the follicles freeze and do not develop further - this is called persistence. There is no ovulation.
Another deviation is the complete absence of follicles. In this case, the reproductive system is completely disrupted and infertility occurs.
Such deviations arise as a result of:
- improper functioning of the ovaries;
- failure, dysfunction of the endocrine system;
- the presence of pituitary or hypothalamic formations;
- frequent inflammatory processes in the reproductive organs;
- regular nervous breakdowns, stress or depression;
- climate change (moving to another country);
- early menopause.
To avoid serious complications, you should not neglect preventive examinations by a gynecologist. If you experience the slightest discomfort or abnormality in the pelvic organs, seek medical help immediately. The gynecologist will clearly tell you at your appointment what size the follicle should be during ovulation.
Sometimes the doctor makes a diagnosis of polycystic disease in question. Why? Everything is very simple. Not in all cases, the presence of multiple follicles indicates pathology. This may be temporary and will go away after ovulation. This sometimes occurs after birth control pills, malfunction of the thyroid or adrenal glands, or an excess of prolactin. To find out the cause and establish an accurate diagnosis, you should do an ultrasound examination on certain days of the cycle, which will help you see the dynamics. In addition, hormone tests are taken, the doctor examines the patient in a gynecological chair, and only after all this can we say something more confidently.
Empty follicle syndrome
Currently, two types of this syndrome are described: true and false. What differentiates them is their hCG level. We can say that thanks to IVF technology, scientists have examined under a microscope the phenomenon when the follicle is “empty”.
According to statistics, in women under 40 years of age, this syndrome occurs in 5 - 8% of cases. The older a woman gets, the higher the number of empty follicles. And this is no longer a pathology, but a norm. Unfortunately, it is impossible to accurately and immediately diagnose this syndrome. To do this, you will need to completely eliminate damage to the ovaries (structural abnormalities), lack of ovarian response to stimulation, premature ovulation, hormonal imbalance, defects (pathologies) in follicle development, premature aging of the ovaries. That is why there is no such diagnosis as “empty follicle”.
But scientists have found the reasons that accompany the development of the syndrome. Namely: Turner syndrome, incorrect time of administration of the hCG hormone, incorrect dose of hCG, incorrectly selected IVF protocol, incorrect technique for collecting and washing the material. As a rule, a competent reproductive specialist will carefully collect anamnesis before making this diagnosis.
Main reasons for absence
When there are no follicles in the ovaries, we can talk about hormonal imbalance. Other factors that provoke the lack of follicle development include:
- natural early menopause,
- improper functioning of organs,
- surgical early menopause,
- decreased estrogen production,
- pituitary gland disorders
- the presence of an inflammatory process.
Ovarian and uterine cycle
The ovaries and uterus respond differently to hormone fluctuations. Each organ undergoes its own changes, the purpose of which is to prepare for pregnancy. Therefore, in gynecology there is a division into the ovarian and uterine cycles. The countdown for each of them begins from the first day of menstruation.
There are two phases for the ovarian cycle:
- follicular – the dominant follicle grows and the egg matures;
- luteal phase - a temporary hormonal organ is formed in place of the follicle - the corpus luteum.
Follicle growth is triggered by an increase in the concentration of FSH in the blood. Under the influence of this hormone, the follicle increases in size, and the granulosa cells surrounding the oocyte begin to produce large amounts of estrogens. At the same time, the level of receptors for FSH and LH increases in the follicle.
By the end of the first phase, the concentration of estrogen in the blood increases significantly, which stimulates the peak release of LH. 12 hours after this, ovulation occurs - the follicle bursts and the egg is released into the abdominal cavity.
LH continues to affect the remnants of the follicle, and the corpus luteum forms in its place. Its function changes. Instead of estrogen, it synthesizes progesterone, the main pregnancy hormone. It triggers changes in the uterus and body that are necessary for pregnancy to occur.
The second phase of the cycle continues until the beginning of the next menstruation, the corpus luteum gradually dies. But if fertilization has occurred, then the activity of progesterone is supported by human chorionic gonadotropin, synthesized by the embryo from the first days of its existence.
In the first phase, the egg matures
The uterine cycle is a reflection of ovarian function. But it has more phases, this is due to the peculiarities of cyclic changes:
- desquamation phase - corresponds to the beginning of menstruation, due to regression of the corpus luteum, a spasm of the vessels that feed the endometrium occurs, it is separated out with a small amount of blood;
- regeneration phase - starts almost simultaneously with the previous one, under the influence of a gradual increase in estrogen, the mucous membrane begins to recover, it ends on the 4th day of menstruation;
- proliferative phase - the thickness of the functional layer of the endometrium increases under the influence of estrogens secreted by the ovaries;
- secretory phase - it is influenced by progesterone produced by the corpus luteum, the number of glands in the endometrium increases, glycogen accumulates.
On days 6–7 after ovulation, the most favorable conditions for embryo implantation are created. If this does not happen, after 3 days the trophic processes in the mucous membrane are disrupted and it prepares for the next menstruation.
What it is?
The growth rate of vesicular formations located on the surface of the female reproductive glands is a very important process that affects a woman’s fertility and her ability to bear children. Any disruption of this process threatens infertility. Follicles begin to mature in a healthy woman at the beginning of a new menstrual cycle. There are several of them. Under the influence of hormonal accompaniment of this process, one follicle (rarely two) remains dominant, inside which a germ cell develops - an oocyte, which is also called an egg. When the vesicle reaches the desired size, under the influence of luteinizing hormone it ruptures - ovulation. In this case, the egg leaves the follicle and enters the fallopian tube, where it will meet with male reproductive cells.
The follicle itself is a formation that resembles a sac for the egg maturing inside. It has shells, inside it there is a nutrient fluid in which the maturation of the oocyte occurs.
Follicles are formed in a girl even when she herself is in the mother’s womb. Already in the sixth week of pregnancy they are formed from the embryonic sex petals. Immature oocytes appear in them a little later, they are not active, and until the onset of puberty they “sleep”. The ovarian reserve of a newborn girl is several million oocytes; by the beginning of puberty, no more than 30% of it remains, and by the age of 30, no more than 10%. Some cells die from the action of unfavorable factors - diseases, ecology. The rest must ensure the fertility of girls and women throughout their lives.
Ovulation calculator
Cycle duration
Duration of menstruation
- Menstruation
- Ovulation
- High probability of conception
Enter the first day of your last menstrual period
Ovulation occurs 14 days before the start of the menstrual cycle (with a 28-day cycle - on the 14th day). Deviation from the average value occurs frequently, so the calculation is approximate.
Also, together with the calendar method, you can measure basal temperature, examine cervical mucus, use special tests or mini-microscopes, take tests for FSH, LH, estrogens and progesterone.
You can definitely determine the day of ovulation using folliculometry (ultrasound).
- Losos, Jonathan B.; Raven, Peter H.; Johnson, George B.; Singer, Susan R. Biology. New York: McGraw-Hill. pp. 1207-1209.
- Campbell NA, Reece JB, Urry LA ea Biology. 9th ed. - Benjamin Cummings, 2011. - p. 1263
- Tkachenko B. I., Brin V. B., Zakharov Yu. M., Nedospasov V. O., Pyatin V. F. Human physiology. Compendium / Ed. B. I. Tkachenko. - M.: GEOTAR-Media, 2009. - 496 p.
- https://ru.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ovulation
After the follicle ruptures during ovulation, a corpus luteum forms in its place, which takes on temporary responsibilities for producing progesterone. If pregnancy has occurred, then other endocrine active structures will take care of this, if not, then the corpus luteum dies, progesterone drops, and menstruation begins.
Sometimes during ovulation the follicle does not rupture, and ovulation naturally does not occur. Such a follicle turns into a cyst. Single cysts are often physiological in nature, they are not dangerous for a woman and are beneficial in matters of pregnancy planning. But if too many of them are produced, the ovaries become polycystic, which is a common cause of infertility in women.
What processes occur in the female body
The follicular phase lasts half of the cycle. During this period, the hypothalamus begins to produce gonadotropin-releasing hormone. It is a luteinizing and follicle-stimulating substance that affects the production of the corresponding hormones. The follicular phase ends with the onset of ovulation.
In the first phase of the cycle, with the onset of menstruation, red blood cells and platelets decrease, and hemoglobin decreases. This period is accompanied by physiological blood loss. Chronic diseases and increased physical activity during this period can aggravate the condition.
At the beginning of the first phase, it is important to ensure a sufficient supply of foods rich in iron and B vitamins, as well as to maintain a drinking regime.
After the end of menstruation, the process of restoration of the endometrium begins, the glands that produce mucus increase, and spiral arteries grow. The vaginal secretion becomes more watery to facilitate the passage of sperm.
How follicles grow
Follitropins are substances under the influence of which follicles begin to form in the ovaries. One of them subsequently becomes dominant. This follicle participates more intensively than others in the production of estradiol. The follicles grow until the adenohypophysis rapidly synthesizes luteinizing hormone. This substance is necessary for the normal functioning of the female reproductive system, is involved in the production of estrogen, and is the initiator of ovulation.
This is how follicles grow in the ovary
Maturing follicles synthesize hormones that stimulate restoration processes in the uterus. After 2 weeks, when the follicular phase is completed, the follicle releases the egg and the body prepares for conception. The site of the ruptured follicle is replaced by the corpus luteum, which begins to actively produce progesterone.
Features of the maturation process
It is quite complex and multi-stage. The process of maturation in the ovary begins in the first phase of the menstrual cycle. This is facilitated by the hormones lutein and progesterone. Their insufficient quantity can upset the balance of the functionality of the reproductive system.
Every month, several (up to 10) follicles develop in the female body. However, only one of them reaches the required size. He is considered dominant. The remaining bubbles begin to regress. If there is a failure in the hormonal system, then these small formations do not die off and prevent the dominant follicle from growing to the required size.
If you have a normal and regular menstrual cycle, you can determine the period of maturation yourself: according to your own feelings, by measuring basal temperature. In patients who have undergone ovarian stimulation, this process is monitored using an ultrasound procedure performed on different days.
The following symptoms indicate that the follicle has matured and the woman will soon begin ovulation:
- nagging pain localized in the lower abdomen;
- an increase in the amount of white mucous discharge from the vagina (some patients confuse it with thrush);
- a decrease in rectal temperature, which occurs 12-24 hours before the day of ovulation, and then an increase by 0.2-0.5 degrees;
- increased levels of progesterone in the blood (this can be determined using special tests);
- mood change: the woman becomes more sensitive and irritable.
During one menstrual cycle, one follicle usually matures in a woman’s body. However, in some cases there may be several of them. There is no pathology in this; the patient simply has an increased chance of fertilizing the egg or having a multiple pregnancy.
Follicle formation
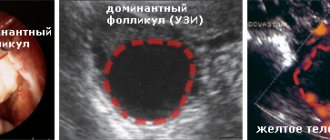
Actually, the follicle is several layers of connective and epithelial tissue surrounding the growing egg. By the time of release, it must reach certain parameters, which is why the size of the follicle before ovulation is so important.
In the first half of the menstrual cycle, out of the many follicles contained in the ovary, one, the dominant one, begins to enlarge and mature faster than others.
This phenomenon occurs in each ovary alternately, i.e. rest and restoration of follicular growth of one appendage takes 2 monthly cycles. In rare cases, when two dominant follicles mature in one ovary, or both ovaries are active, ovulation is possible with the release of two eggs and then there is a chance to become a mother of twins.
In order to track the progress of the development of folliculogenesis, ultrasound diagnostics are performed in the first phase of the menstrual cycle, when the size of the dominant follicle begins to be determined, and directly during the ovulatory period, when it ruptures. This procedure allows you to identify pathological changes and correct them during the following cycles.
Follicle maturation by cycle day
Follicles in the ovary. Maturation of the dominant
The follicle matures gradually. On an ultrasound it can be seen like this:
- on the 7th day, small 5-6 mm vesicles containing fluid are visible in the ovarian area,
- from day 8, intensive growth of education begins,
- on the 11th day, the size of the dominant follicle is 1-1.2 cm in diameter, while the rest begin to regress and decrease,
- from the 11th to the 14th day of the menstrual cycle, the size of the formation is already approaching 1.8 cm,
- on the 15th day, the follicle becomes very large (2 cm) and bursts, an egg ready for fertilization comes out of it, that is, ovulation occurs,
If the follicular formation is larger than 2.5 cm, then we can already talk about the presence of a cyst. In this case, it is necessary to carry out treatment.
Many women worry whether their menstrual cycle will be disrupted after hysteroscopy. This procedure is performed to examine the inner surface of the uterus. Most often, it is necessary to make a diagnosis of endometriosis. It should be done on days 6-10 of the menstrual cycle, while follicle maturation is on the 7th day. That is, hysteroscopy does not have a significant negative effect on a woman’s reproductive function.
How to determine the period of ovulation
The ovulation period is the only day in the cycle when conception is possible. That is why they are trying to calculate this date for a faster onset of pregnancy, or vice versa, in order to “protect” against it (calendar method of birth control). The presence of ovulation indicates the proper functioning of the reproductive system and its health. Now it has become clearer what the ovulation period is. But how to calculate it?
Determination methods
1. Calendar method
It is successfully used by women who scrupulously keep their menstrual calendar, that is, they mark the beginning of menstruation every month; in this situation, it is important to know exactly when your period began, and not its duration. This way you can determine the length of the menstrual cycle
It is necessary to take at least 3-4 cycles and calculate the average duration. Suppose we have calculated it, but how can we determine the ovulation period if the cycle is, for example, 28 days? As a rule, the most likely day for conception occurs exactly in the middle of the cycle. That is, in this case, most likely, this is the 14th day (± 2). However, not every month a woman’s egg matures; there are also “sterile” months. Moreover, the older the woman, the more such months there are, and the probability of pregnancy, accordingly, is less.
2. Method of measuring basal temperature.
It has been practiced for several decades. When women did not yet have the opportunity to donate blood for hormones as freely and cheaply as they do now, there was no ultrasound and other things necessary for a correct diagnosis, doctors prescribed their patients (mainly those who suffered from infertility) to measure the basal temperature in the rectum and build graphs. Based on these graphs, the doctor made conclusions regarding the reason for the lack of pregnancy - insufficiency of the first or second phase of the cycle, or perhaps lack of ovulation. How can its presence or absence be determined?
The method cannot be called very simple. It is necessary to measure the temperature in the rectum throughout the entire menstrual cycle using a regular thermometer.
It is very important to do this every day, immediately after waking up and getting out of bed, at the same time. It is very important to reduce the likelihood of influence on the temperature scale by factors not related to our experiments
For example, incorrect values can be obtained in the case of a general increase in the body as a result of illness, due to sex shortly before measurements, etc. Now about the most important thing. In the first half of the cycle, the temperature does not exceed 37 degrees, or rather, it is below this mark. A few hours before the release of the egg, you can observe a slight drop in temperature, and immediately after ovulation occurs, a jump up by 0.4-0.6 degrees - the temperature exceeds 37 degrees. Here's how to calculate your ovulation period.
3. Ultrasound examination.
Sometimes the day of ovulation needs to be known exactly, for example, when pregnancy does not occur for a long time, or for IVF (to collect eggs). That's when the ultrasound method is used. You will have to go through the procedure several times. The doctor will monitor the development of the dominant follicle (if it forms, of course). After ovulation, the follicle disappears (the membrane ruptures), and a small amount of fluid is found in the retrouterine space - this is a reliable sign that the egg has already been released to meet the sperm. Sex during ovulation for a healthy couple often ends in pregnancy.
4. Tests.
There are tests not only for pregnancy, but also for ovulation. And the latter are very quickly catching up in popularity with the former. Their price is quite affordable, and the procedure is very simple, the same as in the case of diagnosing pregnancy. 2 stripes indicate the period of ovulation. But in this case, the tests only react to luteinizing hormone, which is released during this period of the menstrual cycle. Its content remains elevated for 1-2 days, and only during this time is conception possible.
5. Own feelings.
There are women, although there are not many of them, who determine the period favorable for pregnancy by analyzing their own feelings. For example, pain during ovulation is not a rare symptom. They are not strong, but noticeable. Most often, the ovary where the egg was “born” hurts within a few hours after ovulation, but there are no signs of inflammation or any disease.
Another sign is discharge during ovulation. They are transparent, stretchy, but odorless and without impurities of pus. An attentive woman will definitely notice them.
And finally, the third sign is an increase in libido. Thus, nature itself takes care of the continuation of the human race.
Diagnosis and treatment
Ovulation is closely related to menstrual cycles. Even small delays can signal problems, meaning that the follicle does not mature in the time allotted for this by nature. The absence of pregnancy during normal sexual activity without contraception for a year indicates that the probability of infertility on the part of the woman in this case is high. But both partners need to undergo the examination, so the male factor may also be the cause.
There are many methods for diagnosing infertility. The examination strategy is chosen by the attending physician. He can prescribe hormonal tests, ultrasound, and various studies, the results of which may indirectly indicate the reasons for the malfunction of the female reproductive system.
Most often, the delay or absence of follicle maturation is explained by hormonal disorders. Insufficient levels of female hormones lead to the fact that communication between the follicles and the body practically disappears. It’s as if they don’t receive a command to act. That is why this problem can be solved, in particular, by introducing the missing hormones.
But pregnancy can occur when follicle maturation is stimulated. Doctors monitor expectant mothers who have undergone hormonal therapy throughout the entire period of pregnancy, as well as postpartum.
Watch a video about follicle maturation and ovulation
Married couples who turn to specialists in time due to the impossibility of conceiving a child with regular sexual activity for one year are sent for examination. Doctors prescribe standard tests to detect the true cause of infertility. One of the mandatory studies is folliculometry. During this procedure, it is possible to observe folliaculogenesis and track the moment of ovulation, if it occurs. If ovulation occurs, folliculometry allows you to identify the menstrual cycle and determine the most favorable days for conception.
Observation of folliculogenesis as part of the diagnosis of infertility makes it possible to track the behavior of the dominant follicle and give a general assessment of a woman’s reproductive abilities.
In the absence of ovulation, determined during folliculometry, a number of tests are prescribed, including hormonal tests. Don't despair if you don't ovulate. Hormonal therapy very often helps the follicle mature and the release of an egg ready for fertilization. But the reasons may not only be a lack of hormones. A number of different diseases, many of which are not gynecological, can inhibit the maturation of follicles. Even a common cold very often leads to disruption of the normal menstrual cycle. The attending physician takes into account all factors related to folliculogenesis.
The psychological state, in particular nervousness and fear of not getting pregnant, almost always negatively affects the maturation of follicles. The vast majority of women who seek help from the Reproductive Medicine Clinic come with their own fears. And there is nothing reprehensible in this, because for a woman there is nothing more important than being fulfilled as a mother. Inability to bear children is a severe psychological problem for them.
The doctor’s task, already at the examination stage, is to remove as much as possible the fear of not being pregnant in women. This is helped by the friendly atmosphere in the clinic, as well as communication with grateful clients who, thanks to the qualified doctors of the clinic, have succeeded.
It should be noted that modern reproductology has advanced tremendously over the past decade. Today, if a doctor believes that there is a chance for motherhood, then this means a really high probability of success.
A large number of tests that are prescribed to diagnose infertility are by no means a medical whim, but professional actions. To detect the true causes of follicle immaturity, the entire prescribed range of examination is necessary. This will give a complete picture of the state of a woman’s reproductive functions and will help determine the possibility of a particular treatment.
One of the most common types of follicle examination is ultrasound. Ultrasound sensors are able to detect the dominant follicle. If it is constantly recorded (regardless of the phase of the menstrual cycle), then a diagnosis of persistence is made. This disease is curable in most cases. But at the same time, there is a considerable probability of the Graafian vesicle turning into a cystic formation.
Since the behavior of follicles is shaped by hormones, it is endocrine disorders in a woman’s body that most often cause the absence of ovulation. The second most common cause is a cyst, into which the follicle has transformed, from which the egg has not been released. If the diameter of the vesicle exceeds 25 mm, then the doctor has every reason to suspect a cystic formation. If the diameter is less than that indicated above, then we are talking about persistence or so-called luteinization. Such cysts with a diameter of up to 50 mm resolve without any treatment in one to four months. Smaller cysts require hormone therapy or surgery.
Follicle development disorders
Malfunctions in the functioning of the ovaries and the development of follicles are one of the main causes of infertility. To diagnose disorders, folliculometry is done, which is performed via ultrasound. This method allows you to track all stages of folliculogenesis - the step-by-step process of growth and development of the follicle up to ovulation - and find out which of them fails. Ultrasound of the ovaries with folliculometry can reveal disorders associated with an excess or lack of follicles, their abnormal growth and development.
Many follicles
If there are many bubbles maturing in the ovaries (8 or more), they speak of multiple follicles. Their increased number is not a pathology if ovulation occurs, the cycle is regular, and hormonal levels are not disturbed. In this case we are talking about multifollicular ovaries, which are a variant of the norm. If the cycle is irregular, then multifollicular ovaries are considered a pathology.
If there are more than 30 follicles and there is a disturbance in reproductive function, this deviation is called polycystic ovary syndrome. With it, ovulation does not occur, the follicles do not burst, releasing eggs, but fill with fluid, forming cysts. The causes of polycystic ovary syndrome are not fully understood, but there is an assumption that the syndrome is provoked by an excess of androgens due to an increase in the level of insulin in the blood.
The disease can be caused by heredity, stress, sudden fluctuations in body weight or metabolic disorders. Women who suffer from it often experience symptoms such as acne, excess weight, hypertension and menstrual irregularities. Many people experience excess body hair growth in the abdominal area and face.
Few follicles
A small number of follicles in the ovaries may indicate a decrease in ovarian reserve. The fewer there are, the lower the chances of conceiving a child. The presence of 7–15 bubbles means that pregnancy can occur. A number of 4 to 6 means it will be difficult to get pregnant. The probability of conception with single follicles is extremely low; if they are absent, there is no hope at all.
The causes of this pathology may be:
- chronic inflammatory diseases of the pelvic organs;
- alcoholism, drug addiction;
- unfavorable environmental conditions;
- hormonal imbalances;
- psycho-emotional stress;
- autoimmune diseases.
Other pathologies
Normally, under the influence of hormones, the dominant follicle, having reached its maximum size, bursts, releasing the egg. Due to a lack of luteinizing hormone, ovulation does not occur and the tertiary follicle continues to exist throughout the cycle. This pathology is called persistence of the follicle, and the pathology has no pronounced symptoms. The reasons may be:
- physical and emotional overload, stress;
- taking medications that affect the pituitary gland;
- diseases of the pituitary gland and hypothalamus;
- hormonal changes.
Follicular regression is a disorder in which the dominant follicle grows, but then stops developing and shrinks. Ovulation does not occur. If the disorder occurs, menstruation may be absent for a long time. Instead, scanty bleeding is observed a couple of times a year. They last longer than normal menstruation.
If the follicle does not burst and the egg remains inside, as a result of its further growth, a benign formation may develop - a follicular cyst. Usually it does not manifest itself in any way, but sometimes due to decreased functioning of the ovaries, menstruation delays occur. Usually it resolves after 3-4 months. The cause of the phenomenon may be a disorder of the hormonal function of the ovaries caused by infections, inflammatory processes or abortions.
If the egg does not leave the follicle in due time, another anomaly may develop - luteinization of the follicle. Despite the fact that ovulation does not occur, the processes accompanying it continue. A corpus luteum forms inside the vesicle, producing progesterone. The reasons for the violation are:
- stress;
- excess of androgens;
- inflammation;
- infection;
- adhesive process.
Decoding the results
You need to understand that a doctor must interpret the results of folliculometry; independent attempts to establish certain diagnoses for yourself can lead to mistakes.
Determining the period of ovulation
During pre-ovulation studies, the size of the ovaries as a whole and the size of the antral and dominant follicles are assessed. This will help you understand when to expect ovulation. In this case, it should be understood that the norms are quite average, and in each specific case the size of the main follicle may differ.
- The period from days 1 to 4 of the cycle - menstrual flow occurs, but several antral follicles ranging in size from 3 to 5 mm can be visualized in the ovaries. If there are from 5 to 9, there is nothing to worry about, there is a follicular reserve and ovulation in this cycle is very likely.
- Measurements on days 5-6 of the cycle usually show several antral follicles with a diameter of 5-7 mm.
- On the 7th day, the dominant follicle stands out, its size is already larger than the others, it reaches 9-10 mm.
- On the 8th day of the cycle, the number of antral follicles begins to decrease, they undergo reverse development, and only the dominant one grows, it already reaches 12 mm.
- From the 9-10th day of the cycle, it is possible to visually determine the cavity with the egg in the follicle, the size of which is from 13 to 16 mm.
- On the 11th day of the cycle, the follicle grows to 18 mm, and by the 12th day its size can be recorded to 20 mm.
- On the 13th day of the cycle, it is possible to visually determine the location of the stigma - it is at this point that the follicle will rupture when it reaches its maximum size. In the meantime, its diameter is about 22 mm.
- Day of ovulation – the size of the dominant vesicle reaches 24 mm.
Determining the fact of accomplished ovulation
A completely healthy woman of childbearing age may have anovulatory cycles, when no egg is released. This cycle is indicated by the absence of a dominant follicle before the day of ovulation or its slow growth, as well as the absence of the corpus luteum after the date of ovulation.
Ultrasound signs of completed ovulation are:
- disappearance of the dominant follicle after its maximum growth has been recorded;
- 3-4 days after expected ovulation, a corpus luteum is detected in the ovulated ovary, the size of which normally ranges from 10 to 30 mm;
- within 1-2 days after ovulation, free fluid is detected in the woman’s abdominal cavity.
Additionally, to assess the condition of the corpus luteum, the thickness of the endometrium is measured. The inner layer of the uterus, due to the effects of progesterone produced by the temporary gland, should increase. A mutual decrease in the endometrium and the size of the corpus luteum indicates progesterone deficiency and insufficiency of the luteal phase of the cycle, which can cause miscarriage or infertility.
It should be noted that ovulation can occur simultaneously from two ovaries, and in this case it is called double, then two corpus luteum are detected at once, and if fertilization occurs, the woman has a chance of becoming the mother of charming twins. But folliculometry cannot establish the fact of pregnancy, and the detection of the corpus luteum itself does not indicate whether the woman became pregnant this time or not. This is a sign of ovulation and nothing more. If there was no ovulation, the cycle was anovulatory, then the corpus luteum is not visualized in the ovary.