Pregnancy after the ovulation process usually occurs 2-3 weeks after it occurs. Conception is the successful act of fertilization leading to the birth of a new human life. The first signs are sometimes not so noticeable and the woman may not even feel anything. Ovulation occurs almost monthly, a mature egg unites with a sperm, as a result of the fusion, conception occurs, and then pregnancy occurs. The body of the expectant mother immediately begins to rebuild, gradually transforming into the most interesting and diverse stage, which is called nine months of happiness.
FSH and phases of the menstrual cycle
The first phase in the menstrual cycle is the follicular or estrogenic phase. During this period, the production of FSH begins, which helps stimulate the follicle in the ovary. At the same time, luteinizing hormone influences the follicle cells, and estrogen is released (a steroid hormone on which the possibility of conception largely depends). In the middle of the cycle, estrogen levels increase and FSH levels decrease.
Follicle stimulating hormone helps the follicular phase to begin. A week from the beginning of the phase, one follicle matures and continues to grow until the end of the period. The egg matures inside it for another 2 weeks. From the beginning of the phase until ovulation, the FSH level increases rapidly.
During the second phase - ovulation - luteinizing hormone reaches a certain value. The follicle then bursts, releasing the egg. She, in turn, moves to the uterus, and the follicle becomes the corpus luteum and begins to produce the pregnancy hormone (progesterone). The next phase is called the luteal phase, which is characterized by the active production of progesterone.
Progesterone blocks the production of hormones by the pituitary gland. If fertilization does not occur, the corpus luteum shrinks and dies, and progesterone levels return to normal. When progesterone levels drop, the pituitary gland begins to produce hormones again and a new follicle matures. Thus, the menstrual cycle repeats.
At conception, the pituitary gland begins to actively produce human chorionic gonadotropic hormone (hCG), which makes it possible to identify pregnancy using a simple test.
Dashuchok-Shmashuchok
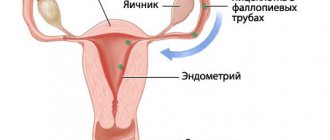
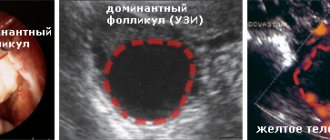
Ovulation is the process of release of a mature egg from the ovary into the abdominal cavity. After this, she lives for 24 hours and is capable of fertilization. Ovulation is preceded by a peak of LH (pituitary hormone), ovulation should occur 24 hours after this peak. For an LH peak to occur, the concentration of the female sex hormone, estradiol, must increase and reach a sufficient level. Estradiol is secreted by the growing follicle in the ovary. In parallel with the increase in estradiol levels, the mucous membrane of the uterus, the endometrium, grows; after ovulation, a corpus luteum forms at the site of the ruptured follicle, which secretes the hormone progesterone, which promotes the maturation of the endometrium and its preparation for implantation of the embryo. Estradiol helps reduce basal temperature, progesterone increases it. The maximum follicle on the eve of ovulation (with a diameter of 20 mm) secretes the maximum amount of estradiol - the peak of estradiol on the eve of the LH peak - the retraction of BT, but it may not be caught with a single measurement per day. Fertilization is possible only during ovulation, so before it the body is rebuilt to increase chances of fertilization: the cervical canal opens (the “pupil” phenomenon upon examination), the secretion of cervical mucus increases to facilitate the advancement of sperm (egg white), its properties change (extensibility increases), and in parallel the properties of other fluids (the test for saliva - obtaining the "fern" symptom - characteristic arrangement of fibers), mood changes, libido increases, blood supply to the genitals and erogenous zones increases. In the second phase, under the influence of progesterone, the hormone that supports pregnancy, subjective sensations characteristic of pregnancy arise: changes in mood, libido, fluid retention, engorgement of the mammary glands, enlarged uterus, increase in BBT, and sometimes general body temperature - if these changes are severe and worry, it's called premenstrual syndrome. To confirm ovulation, the following diagnostic methods are used: basal temperature chart, functional tests (pupil symptom, assessment of the properties of cervical mucus), ultrasound monitoring of the ovaries and endometrium, hormonal monitoring of LH, estradiol and progesterone levels, including rapid tests for ovulation based on determination of the LH peak, endometrial biopsy, determination of “stigma” - the site of release of the egg - by laparoscopy. Carrying out functional diagnostic tests (cervical mucus distensibility, fern symptom, etc.) is quite labor-intensive and requires the patient to come to the gynecologist for several days in a row during the cycle; The reliability of these tests, according to the literature, does not exceed 50%. The subjective sensation of “egg white” - the release of the mucous plug of the cervical canal - is also unreliable. The existing opinion that the regularity of the menstrual cycle is a guarantee of ovulation, and irregularity indicates the absence of ovulation, is erroneous. Hormonal monitoring is difficult to use with an irregular cycle; it is not known on what day to determine progesterone levels. As the experience of virtual and face-to-face consultations shows, with a blind examination “for hormones” on days 5-7 and 18-22 days of the cycle, the diagnosis of “anovulation” is often made based on low progesterone levels, while with a long cycle ovulation occurs later. The level of progesterone is indicative in the middle of the second phase; it is difficult to guess this time with an irregular cycle, which leads to unnecessary paid tests, unnecessary unfounded diagnoses and unnecessary unjustified treatment of a non-existent pathology. The same difficulty lurks when using home ovulation tests based on determining the LH peak - with an irregular cycle, it is not known when to start testing. In this case, you have to use several packages of tests, which is very expensive. In addition, in chronic stressful conditions, which are not uncommon in modern women who are planning a pregnancy and doubt their ability to become pregnant, the LH level is constantly elevated, and the ovulation test may give a diagnostic line without connection with ovulation. You must also remember about polycystic ovary syndrome and some other pathologies of the endocrine system, in which the LH level is constantly elevated. Another problem associated with hormonal monitoring is that it shows ovulation after the fact - an increase in progesterone levels in the second phase by 10 times compared to phase 1 indicates that the corpus luteum has formed in this cycle, but does not allow use periovulatory period for targeted pregnancy planning. In addition, the analysis for hormones takes several days, outside the performing laboratories - up to 2 weeks, and urgent determination of the hormone is quite expensive and, again, not possible in all institutions. And there is a contingent of women who need ovulation monitoring specifically to plan the rhythm of their sexual life (for example, during rare meetings with their husbands due to long business trips or when performing artificial insemination). Basal temperature is measured in the rectum in the morning, without getting out of bed, at the same time (6-8 hours), every day with a mercury thermometer in the anus at a depth of 5-6 cm. If something changes in the regime: on Sunday measured not at 8, but at 12 o’clock, or the general body temperature rose, or there were night rises, or sexual intercourse the day before, bowel dysfunction, taking medications - everything that could lead to an increase in rectal temperature is indicated in a separate column. A physician should evaluate rectal temperature data. A lot matters: the temperature values themselves, and the presence of two phases: at the beginning of the cycle the temperature is lower, at the end it is higher, and the difference between the average value of the first and second phases, and the duration of the second phase, and the minimum value before the rise. It is incorrect to measure rectal temperature in the mouth and in [email protected] #$%&, even if phase fluctuations are also observed - we are not interested in body temperature, but in the blood temperature in the ovarian vein, which depends on the level of ovarian hormones. Measuring basal temperature is convenient due to its cost-effectiveness, the fact that it does not require the woman to come to a medical facility, as well as the constant, and not fragmentary - on some days of the cycle, like hormonal monitoring - receipt of information. Unfortunately, in addition to ovarian function, the BT level is influenced by many extraneous parameters: general body temperature, sleep patterns, time of measurement, type of thermometer, medication intake, bowel function, alcohol intake, sex life, etc. Without taking these factors into account, it is impossible to correctly interpret BT data . But, as observation has shown, in approximately 5% of patients, even if all the rules for measuring BT are fully observed and all “special circumstances” are recorded, BT is unreliable: its data (monophasic curve, lack of proper rise in BT) contradict the data of ultrasound monitoring, measurement of progesterone levels and successful pregnancy. Ultrasound monitoring consists of determining the state of the endometrium, the growth of the dominant follicle and determining the corpus luteum in the place of the former dominant follicle simultaneously with changes in the characteristics of the endometrium. With a competent approach (the first ultrasound is as close as possible to the day of expected ovulation, with a known cycle length - 16-18 days before menstruation, with an unknown one - starting from the 10th day of the cycle), it is sufficient to conduct ultrasound twice per cycle, in extreme cases - three times, since based on the size of the dominant follicle determined in the first study, it is possible to calculate the approximate time of ovulation (taking into account the average follicle growth rate of 2 mm/day, the diameter of the preovulatory follicle = 20-24 mm). It is very easy to confirm that ovulation has occurred by measuring the level of progesterone in the blooming phase of the corpus luteum, knowing exactly the day of ovulation, i.e. One hormonal analysis per cycle is sufficient, which saves the patient’s costs. Using ultrasound monitoring, it is possible to determine signs of inferiority of the corpus luteum (discrepancy between the thickness and maturity (echogenicity) of the endometrium and the presence of the corpus luteum and the thickness of the endometrium before ovulation). Thin (less than 0.9 cm) endometrium in the second phase in the presence of the corpus luteum may be a sign of chronic endometritis, insufficiency of the corpus luteum or the absence of a second peak of estradiol, impaired reception of the endometrium to steroid hormones, impaired blood supply, immunogenetic features of the endometrium (synthesis of growth factors and etc.). The diagnosis can be clarified by the level of progesterone and estradiol in the middle of the luteal phase of the cycle and endometrial biopsy data. Ultrasound monitoring turned out to be more informative, reliable and economical than all other methods of determining ovulation; if the data from ultrasound monitoring and other methods did not coincide, the planning outcome corresponded precisely to the ultrasound data (non-occurrence of pregnancy in the absence of ovulation on ultrasound, despite the rise in temperature in the second phase (the temperature may rise due to a drop in estrogen levels after regression of the non-ovulated follicle); non-occurrence of pregnancy with insufficient thickness of the endometrium in the second phase, despite the rise in BT and normal levels of progesterone (insufficient reception of the endometrium to progesterone, estrogens, insufficient estrogen levels, chronic endometritis, impaired blood supply to the endometrium); the onset of ovulation despite an insufficient difference (or absence of a difference) in temperature on the graph BT; absence of ovulation despite positive results of the ovulation test; onset and maintenance of pregnancy, despite the “low” temperature in the second phase - 36.8C and even (in an isolated case) - 36.6C!.) It is also necessary to mention the psychological aspect of ultrasound ( provided that the patient is explained what the resulting picture means). With all other diagnostic methods, if they have not shown ovulation, the patient remains in the dark - there is never ovulation at all, and she is infertile, or there is no ovulation in this cycle and there will not be and there is nothing to hope for, or there is no ovulation yet, but tomorrow she may be. With ultrasound monitoring, you can predict the expected date of ovulation, and not just conclude that it is not happening today. Of course, the most informative methods for verifying ovulation are invasive: endometrial biopsy and determination of “stigma” on the ovary during laparoscopy, but they are not applicable when planning pregnancy in this cycle and also determine ovulation after the fact. Of all the existing methods, the balance of safety, price and reliability is most optimal for ultrasound monitoring of the follicle and endometrium with a vaginal sensor on a high-quality device performed by a qualified ultrasound diagnostic specialist and with interpretation by a qualified gynecologist. An important condition for correct interpretation is the personal presence of the attending physician during the ultrasound and his own assessment of the resulting picture, based on personal comparative experience. Advanced training in the interpretation of ultrasound data by gynecologists involved in planning and managing pregnancy is absolutely necessary.
Follicle-stimulating hormone test
Venous blood is taken for testing. Before the procedure, you should refrain from eating and smoking for 3 hours. You should not worry or overuse physical activity for 24 hours. Stop taking steroids and thyroid hormones within two days.
An analysis for gonadotropic hormones is prescribed for the following deviations:
- infertility;
- congenital chromosomal abnormalities;
- disruptions in the menstrual cycle;
- suspected pathology of the pituitary gland;
- sexual dysfunction;
- abnormal growth and development of children;
- taking hormonal drugs.
The study helps confirm the fact:
- infertility;
- a certain phase of the menstrual cycle;
- sperm deficiency and problems with their production;
- accelerated and delayed sexual development;
- primary or secondary sexual dysfunction.
Also, analysis of gonadotropic tests allows you to monitor the effectiveness of hormone therapy. To confirm male and female infertility, follicle-stimulating hormone and LH tests are performed. The results help create a treatment plan.
Why does ovulation occur early?
All processes in the female body are very closely related to the menstrual cycle. In each phase, certain hormones (estrogen, progesterone, luteinizing hormone, follicle-stimulating hormone) exhibit the greatest activity, which cannot pass without leaving a trace. And it is quite logical that almost any changes, fluctuations and shocks can affect the duration of the menstrual cycle and the time of ovulation.
Colds, stress, overwork, changes in climatic and weather conditions, changes in diet and sleep can “move” ovulation closer to the beginning or end of the cycle. The cause of early ovulation can also be alcohol abuse, taking certain medications, and brain disorders.
Sometimes early ovulation can be evidence of certain diseases and pathologies in your body: inflammatory processes in the genital organs, dysfunction of the adrenal cortex and others.
In general, there is nothing wrong with the fact that ovulation occurs earlier than usual. However, in some cases, such haste may have specific consequences.
FSH norm
In the analysis table, I indicate the level of FSH and LH in international units per liter. The test is carried out 3-5 days after the start of the menstrual cycle. For women, the norm will differ depending on the period of the cycle:
- Follicular – 2.8-11.3 mU/l.
- Ovulation – 5.8-21 honey/l.
- Luteal – 1.2-9 honey/l.
If FSH is insufficient, a woman is diagnosed with infertility, lack of ovulation, reduction in menstrual flow, atrophy of the genital organs and mammary glands. The cause may be polycystic ovary syndrome and pathologies of the hypothalamus. Weight plays an important role in this matter.
With a high concentration of FSH, women experience bleeding in the uterus in the absence of menstruation. The causes may be pituitary tumors, insufficient ovarian function, or cysts. Also, the level of the hormone increases with alcoholism and radiation. During menopause, an increase is considered normal.
In men, FSH levels are relatively constant. The norm is determined within the range of 1.37-13.58 mU/l. A low test result may indicate testicular atrophy, impotence and low sperm concentration in the ejaculate. The most common cause of decreased FSH levels in men is insufficient functionality of the pituitary gland.
Elevated levels of FSH are detected with dysfunction of the gonads and kidneys, and pituitary tumors. The ratio of sex hormones also affects the indicators. The cause of the increase may be radiation, alcoholism and medication.
In both sexes, with a low result, a weakening of sexual desire and secondary sexual characteristics are observed.
What is early ovulation?
For some reason, many girls think that ovulation always occurs in the middle of the cycle. But in reality this is an ideal case. It is believed that on average ovulation occurs 14 (12-15) days before the start of the next menstruation, which is the middle in a 28-day cycle. However, even such girls with an “ideal” cycle are not recommended to use the calendar method of contraception, since ovulation is an unstable phenomenon. In each cycle it can happen earlier or later than usual, happen twice or not happen at all. And if you don’t measure your basal temperature, you may not even know anything.
Within normal limits, any woman can experience several anovulatory cycles per year, and ovulation can shift in either direction.
If the release of a mature egg from the follicle took place earlier than it always happens for you, then such ovulation is early. Ovulation on the 9th or 11th day of the cycle is not always premature, so this interpretation of the term is not entirely correct.
A woman who conducts at least some monitoring of her can judge that ovulation has occurred prematurely. If you usually (for several cycles in a row) ovulate on days 11-15 from the start of menstruation, then ovulation that occurs on day 8 in this cycle will be premature. However, it is not at all excluded that in some cases such early ovulation is the norm.
More on the topic
When does ovulation occur?
Can ovulation occur during pregnancy?
What is ovulation and how long does it last?
Ovulation and pregnancy
How long does ovulation last?
Ratio of FSH and LH
The ratio of FSH and LH determines a person’s fertility, that is, the ability to reproduce. The fertility rate is determined by dividing LH by FSH.
At different periods of life, changes in the levels of FSH and LH occur. Before puberty, the hormone ratio is the same. A year after the start of menstruation, it increases to 1.5:1. Two years after the onset and until menopause, the ratio remains at 1.5:2.
With polycystic disease and ovarian depletion, as well as pituitary tumors, the hormones correlate by 2.5.
Signs of ovulation
Each person’s body is individual, and among women there is a noticeable difference in the subjective signs and timing of the onset of ovulation. Even for the same woman, these periods can vary from month to month. Some people have irregular cycles throughout their lives, others may be longer (35-45 days) or shorter than average (less than 28 days). But in most cases, ovulation occurs regularly.
During ovulation, the mucous membrane of the uterine body becomes loose, the glands produce a secretion that promotes the attachment of the fertilized egg and the further development of the fetus. Changes also occur in the mammary glands: they are preparing for potential breastfeeding (if pregnancy does occur).
If pregnancy does not occur, the unfertilized egg dies, the endometrial layer is shed, and the next menstruation begins.
Subjective signs of ovulation include pain and a feeling of heaviness in the lower abdomen. Objective signs are an increase in the amount of mucous discharge from the vagina, a decrease in rectal temperature on the day of ovulation with its increase the next day, as well as an increase in the level of progesterone in the blood plasma.
Ovulation disorders can be caused by various types of inflammation of the female genital organs, dysfunction of the thyroid gland and adrenal cortex, complications after colds, as well as stressful situations.
Failure of the usual cycle, when the duration of menstruation is 1-2 days, uterine bleeding can indicate anovulation (lack of ovulation during childbearing age), which is always the cause of a woman’s infertility. In order to restore ovulation, you need to contact a gynecologist and determine the causes of anovulation.
FSH test results
There is a huge list of factors that influence the synthesis of sex hormones. Increased and decreased results help determine the root cause. Only an experienced endocrinologist or gynecologist can analyze the results and compare them with the overall picture of health.
It is not recommended to try to independently decipher the results of the analysis for luteinizing and follicle-stimulating hormone, because it is very easy to make a mistake in this matter. And the results themselves may be erroneous, because accurate calculations require modern equipment and experience.
A high FSH reading may indicate the following abnormalities:
- Diseases of the pituitary gland, including tumors.
- Hereditary and genetic pathologies.
- Underdevelopment of the follicle.
- Ovarian wasting syndrome (cessation of hormone production in women of childbearing age).
- Cysts in the uterus.
- Testicular tumors (in men).
- Kidney failure.
- Tumors associated with hormone secretion.
Factors that increase FSH levels include smoking and exposure to radiation. Some medications can also increase FSH levels (naloxone, phenytoin, tamoxifen).
A decrease in FSH hormone levels may indicate:
- Hypogonadism (reduced production of hormones from the pituitary gland and hypothalamus).
- Pituitary apoplexy (Sheehan syndrome).
- Excess prolactin (the hormone reduces the level of sex hormones).
- Chronic intoxication.
The analysis will show low levels of FSH in obesity, fasting, and after surgery. Drugs that reduce the amount of FSH include carbamazepine, bromocriptine, growth hormone, and valproic acid.
Why is early ovulation dangerous?
Mainly, early ovulation poses a danger for girls who use the calendar method of contraception. Despite doctors' convictions that it is unreliable, many of us continue to rely on fate. In this case, early ovulation can play a cruel joke on you: an unwanted and “unlikely” pregnancy will turn out to be more than real.
Women planning a pregnancy can also “miss the mark.” Early ovulation may cause a woman's inability to conceive a baby. This is observed mainly in women with very short or irregular menstrual cycles. Such situations require qualified treatment with hormone therapy. Hormone-containing drugs are injected into the woman's navel or thigh area by subcutaneous injection, which should be prescribed by a specialist after a full examination.
Especially for beremennost.net - Elena Kichak
How to normalize FSH levels
In the process of normalizing FSH levels, more attention is paid to treating the underlying disease. However, there are a number of recommendations that will help balance hormone production.
Food and vitamins
- Diet with natural fatty acids (omega-3, omega-6, omega-9). Such foods are a rich source of hormones, including FSH. You need to eat more salmon, trout, sardines, anchovies and other types of fatty fish. Fish oil will be useful. Flax and borage oils, as well as sunflower oil, will be useful.
- Diet with greens and sea vegetables. To maintain FSH synthesis, products that have a beneficial effect on the endocrine system are needed. These are sea and dark green vegetables: cabbage, broccoli, spinach, as well as seaweed, nori, wakame. Women are advised to take five servings per day.
- Ginseng supplements. The product improves blood circulation, which, in turn, has a positive effect on the pituitary gland and hypothalamus. Women are advised to take one capsule twice daily or 500 mg. For men, ginseng helps increase libido and restore erectile function. The permissible limit must not be exceeded.
- Maca. This is a vegetable that grows in the mountains of South America. Its root improves the endocrine system and promotes the proper production of FSH. You can find a maca supplement at your pharmacy. The recommended dose is 2-3 thousand mg per day.
- Vitex. Chasteberry supplements help with the functioning of the endocrine system and the distribution of hormone regulators. The daily dose of Vitex is 900-1000 mg. The course lasts one month. The supplement is recommended for use before breakfast.
What hormonal medications did you take to stimulate ovulation?
- Gonal 34%, 4589 votes
4589 votes 34%4589 votes - 34% of all votes
- Clostilbegit 25%, 3327 votes
3327 votes 25%
3327 votes - 25% of all votes
- Menopur 17%, 2258 votes
2258 votes 17%
2258 votes - 17% of all votes
- Puregon 14%, 1920 votes
1920 votes 14%
1920 votes - 14% of all votes
- Decayed 8%, 1068 votes
1068 votes 8%
1068 votes - 8% of all votes
- Menogon 3%, 400 votes
400 votes 3%
400 votes - 3% of all votes
Total votes: 13562
Voted: 9988
January 17, 2018
×
You or from your IP have already voted.
Lifestyle
- Massage. To increase FSH levels, you need to massage the lower abdomen daily for 10-15 minutes. You can also massage your thumb (it is believed to be connected to the pituitary gland).
- Weight. You need to maintain a normal body mass index. It is calculated from the ratio of height and weight. An index of 18.5-25 units is considered the norm. A healthy weight promotes proper hormone production.
- Stress. In an anxious or depressed state, the body produces stress hormones that inhibit follicle-stimulating hormone. Yoga and exercises are recommended to relieve stress. Good rest and sleep are also important.
- Testosterone and estrogen. Excess of these hormones reduces FSH levels. To get rid of excess, you need to cleanse the liver. For this purpose, nutritional supplements and herbal teas are used.