The growth of the follicle and the subsequent ovulation of the egg that has matured in it are key processes that ensure the readiness of the female reproductive system for conception. Disruption of this natural mechanism is one of the most common causes of infertility. And all IVF programs include a stage of stimulating follicle growth to induce hyperovulation.
Depending on the protocol used, it is performed on the biological mother or an egg donor. In this case, folliculometry is required to track the number of maturing follicles, their size and readiness for ovulation.
Follicle size before ovulation
To conceive, they must develop normally so that a full-fledged egg is released from them. Let's consider what the dominant undergoes during the month.
Norm
What size should a follicle be before ovulation? When they reach seven days of age, their size is between 3-7 mm. On an ultrasound examination, the specialist will see several structural elements that have different stages of development. There shouldn't be more than a dozen of them. From the eighth to the tenth day, the dominant follicle is already visible, which grows to 14 mm. Everyone else becomes smaller and disappears. In 24 hours it increases by 3 mm.
1-2 days before the release of the egg, a vesicle is approximately 18-22 mm in size. It all depends on the menstrual cycle, on days 12-16 the ovulatory phase begins and it bursts.
Deviations
What follicle size before ovulation is abnormal? If before this, and on any day of the cycle, they are all approximately the same size and there is no dominant one, this is a bad signal. This can be seen on ultrasound diagnostics. If one follicle does not mature, then the egg will not be released, as it will not be able to conceive.
Sometimes there are two or three dominant follicles. Afterwards there may be two (three eggs) and the outcome is positive, that is, twins or triplets. Otherwise, the follicles freeze and do not develop further - this is called persistence. There is no ovulation.
Another deviation is the complete absence of follicles. In this case, the reproductive system is completely disrupted and infertility occurs.
Such deviations arise as a result of:
- improper functioning of the ovaries;
- failure, dysfunction of the endocrine system;
- the presence of pituitary or hypothalamic formations;
- frequent inflammatory processes in the reproductive organs;
- regular nervous breakdowns, stress or depression;
- climate change (moving to another country);
- early menopause.
To avoid serious complications, you should not neglect preventive examinations by a gynecologist. If you experience the slightest discomfort or abnormality in the pelvic organs, seek medical help immediately. The gynecologist will clearly tell you at your appointment what size the follicle should be during ovulation.
Sometimes the doctor makes a diagnosis of polycystic disease in question. Why? Everything is very simple. Not in all cases, the presence of multiple follicles indicates pathology. This may be temporary and will go away after ovulation. This sometimes occurs after birth control pills, malfunction of the thyroid or adrenal glands, or an excess of prolactin. To find out the cause and establish an accurate diagnosis, you should do an ultrasound examination on certain days of the cycle, which will help you see the dynamics. In addition, hormone tests are taken, the doctor examines the patient in a gynecological chair, and only after all this can we say something more confidently.
Menstrual cycle
Early phase
At the beginning of the menstrual cycle, the ovary contains 5-8 follicles less than 10 mm in size. During the process of maturation, one of them (in rare cases two) becomes dominant, reaching a size of 14 mm. On the 10th day of the cycle, it begins to distance itself and increase daily by about 2 mm until it ruptures. The remaining follicles begin to undergo a slow process of involution (atresia), their small fragments can be seen on ultrasound throughout the menstrual cycle.
Follicle maturation time
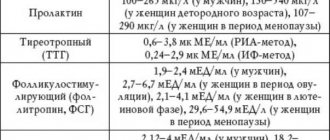
The blood supply to the ovaries increases significantly during the onset of ovulation under the influence of pituitary hormones - gonadotropins FSH and LH. The formation of new blood vessels leads to the appearance of a follicle shell called theca, which gradually begins to surround it from the outside and inside.
Ovulation period
Luteal phase
After ovulation, the walls of the empty follicle thicken, and its cavity is filled with blood clots - a red body is formed. If fertilization is unsuccessful, it quickly becomes overgrown with connective tissue and turns into a white body, which disappears after some time. In case of successful fertilization, the red body, under the influence of chorionic hormone, increases slightly in size and turns into the corpus luteum, which begins to produce a hormone called progesterone. It increases endometrial growth and prevents the release of new eggs and the onset of menstruation. The corpus luteum disappears at the 16th week of pregnancy.
Follicle size at ovulation
The woman herself will not be able to find out the size of the dominant follicle; even an obstetrician-gynecologist will not do this during an examination. To measure, you will need special equipment. Size plays a big role, because only a developed egg is capable of fertilization. When ovulation occurs, certain symptoms appear. Knowing them, it will be easier for a woman to protect herself from an unwanted pregnancy or, conversely, to choose the best day for conception.
Norm
What is the size of the follicle at ovulation? Immediately at the time the egg is released, the size of the dominant follicle is already 23-24 mm. After its rupture, the egg is alive for 2 days, no more. This is the most favorable period for fertilization.
Can ovulation occur if the size of the bubble formed is smaller than normal? This is unlikely, but if this happens, the underdeveloped egg will not be ready for fertilization.
Deviations
Sometimes deviations occur in the form of atresia and persistence. Atresia is a disorder in which the follicle does not break its integrity during ovulation. On the contrary, it began to shrink again, the unruptured follicle develops into a cyst-like formation.
For atresia:
- there is low progesterone;
- no corpus luteum;
- there is no free fluid behind the uterus.
This pathology is accompanied by the presence of amenorrhea and periodic bleeding, which occurs 3 to 4 times a year, similar to menstruation. Women who have this dysfunction cannot become pregnant.
The disease develops from the very beginning, that is, during puberty or as a result of hormonal failure, in which the level of lutropin and follicle-stimulating hormone decreases and the follicle does not reach the desired size. As a result, there are menstrual irregularities, amenorrhea and polycystic ovaries appear. The worst thing is infertility.
With persistence, rupture of a mature follicle does not occur. It is in the size of 22-24 mm for a week, then menstruation begins. Sometimes they are not there, and the unruptured blister degenerates into a cyst. This happens due to hormonal imbalances. The symptoms of this pathology are as follows:
- progesterone is reduced;
- estrogens are elevated;
- follicle on systematic ultrasound of the same size;
- there is no fluid in the space behind the uterus and corpus luteum;
- delay of menstruation;
- heavy menstruation.
To correct the situation, doctors prescribe hormonal therapy, which normalizes hormone levels. Sometimes laser therapy, ultrasound or electrical stimulation are indicated. Be sure to have good nutrition, healthy sleep, and vitamin supplementation. It is necessary to exclude stress and physical activity.
Causes of folliculogenesis disorders
The processes of folliculogenesis occur under the guidance of hormonal background and depend on the concentration and ratio of the hormones FSH, estradiol, luteinizing hormone, progesterone, testosterone, prolactin. Therefore, any deviation in the endocrine accompaniment can cause a disruption in the process of maturation of follicles, which will lead to the fact that maturation will proceed either too slowly or rapidly. In the first case, late ovulation is possible, in the second - early. Any of them is not very favorable for normal conception.
Disorders of folliculogenesis are varied. For example, with persistence there is no rupture of the follicular membrane. This phenomenon is usually associated with insufficient levels of the hormone LH. In this case, the egg becomes overripe, dies, and the follicle continues to be present on the surface of the reproductive gland for several more weeks. This causes disruption of the menstrual cycle, making conception during this period impossible.
When the follicle luteinizes, the corpus luteum begins to develop before rupture occurs, so ovulation also does not occur. And if the follicle does not mature to the required size, stopping its development suddenly, then they speak of follicular atresia. In all cases, the ovulation process is disrupted - the woman cannot conceive a baby.
The reasons why follicular development is disrupted are numerous. There are temporary factors, after eliminating which the cycle is restored, and a woman can become a mother without the help of doctors.
There are more serious reasons that require mandatory treatment, the help of reproductive specialists, embryologists and other specialists who are able to give a woman the happiness of motherhood even in completely seemingly hopeless cases.
Temporary disturbances can cause:
- excessive physical activity, professional sports;
- passion for mono-diets, sudden weight loss or weight gain in a short period of time;
- chronic stress, emotional instability, worries;
- work in an enterprise with a high level of occupational hazard (with paints, varnishes, nitrates, on the night shift, in conditions of strong vibration and increased electromagnetic radiation);
- trips and air travel, if they are associated with changes in climate and time zones;
- discontinuation of oral contraceptives;
- illnesses with an increase in body temperature suffered in the current month.
Often women do not notice impaired follicular maturation at all, because we do not always pay due attention to delayed menstruation or heavier discharge.
Among the pathological causes of impaired follicle maturation, one can note various diseases and conditions in which the endocrine system is disrupted:
- pathologies of the pituitary gland, hypothalamus;
- dysfunction of the ovaries;
- inflammatory and infectious diseases of the genital tract and pelvic organs;
- trauma to ovarian tissue, consequences of surgery;
- disruption of the thyroid gland and adrenal cortex.
Hormonal imbalances are often preceded by childbirth and abortion, bad habits, long-term use of antibiotics, antidepressants, and anticoagulants.
What size is needed to conceive?
In order for fertilization to occur in the future, the size of the follicle must be optimal.
The maximum follicle size is no higher than 25 mm and no less than 18 mm. If the indicators do not correspond to the norm, then fertilization is unlikely. If such a deviation is repeated from cycle to cycle, then an examination is necessary. The cause of the pathology must be treated immediately. Delay can lead to infertility.
Folliculometry: definition, possibilities
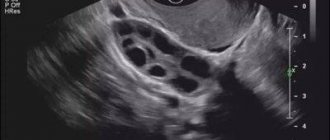
Folliculometry is an ultrasound diagnosis of the uterus, ovaries and follicles throughout the menstrual cycle.
The study is carried out using a special scanner and sensor , which are able to see the slightest changes in the reproductive system.
Generally speaking, this is a regular ultrasound, which is performed several times during one menstrual cycle.
For the first time, the doctor prescribes a study on days 5-10 of the menstrual cycle, and then individually sets the timing of subsequent diagnostics.
The intervals between procedures are 2-3 days. The final decision on this issue is made by the doctor. It happens that ultrasound is performed only before the period of ovulation or exclusively after it.
Folliculometry is a highly informative diagnostic that can answer many questions.
Carried out in order to:
- Analyze the size of the follicles.
- Record the presence or absence of ovulation.
- Assess the function of the reproductive system.
- Choose the right day to conceive.
- Monitor the condition of functional cysts, as well as other benign neoplasms (fibroids).
- Monitor treatment.
- Analyze the regularity of menstruation.
- Examine endometrial growth.
- Calculate the size of the corpus luteum, starting from the period of ovulation.
- Diagnose infertility.
The possibilities of folliculometry are quite extensive. It all depends on what goal the gynecologist sets for carrying it out. Most often, such a procedure is needed to understand whether ovulation occurred in a certain menstrual cycle and whether it needs to be stimulated with medication.
As a result, it turns out that the dimensions of the “Graafian bubble” are constantly changing. Its diameter directly depends on the day of the menstrual cycle. In the first phase it constantly increases by 1-2 mm, and in the second it stops its development and regresses. If the dimensions of the capsule do not fit into the standard values, then folliculogenesis is impaired . In this case, a thorough diagnosis is required to identify the cause of the pathology and prescribe treatment.
What to do if the size does not correspond to the norm?
If the size of a mature follicle is smaller than normal, ovulation does not occur. This pathology needs to be treated. First of all, a woman must undergo diagnostics. The doctor will determine the cause of the dysfunction.
This usually occurs due to hormonal imbalance. In modern medicine, there are many drugs that help follicles develop normally and as a result, a full-fledged egg appears.
They can appoint:
- "Clomid";
- "Citrate""
- "Clomiphene";
- “Klostilbegit”, etc.
Treatment will begin between the 5th and 9th day of the menstrual cycle. The dose is prescribed by a specialist, who gradually increases it. The regimen is selected individually for each woman; starting to use such products on your own is strictly prohibited. The doctor will see whether there will be ovulation on an ultrasound examination, which monitors the entire therapeutic course.
No one can say how long to wait for normalization; some become pregnant after the 1st course, while others need 2 or more months.
In addition to medications, a woman should adjust her diet. A balanced and rational diet is an important point. It is necessary that the body receives vitamins, macro and microelements. Iodine, folic acid, magnesium, vitamin E, etc. are important. This is necessary for the normal functioning of the female reproductive system and to strengthen the immune system. You need to eat vegetables, fruits and grains every day.
The thyroid gland and the levels of all hormones are also checked. Hormonal medications bring everything back to normal, after which eggs will appear normally during ovulation.
You can try traditional methods, but before you start taking any herbs, you need to consult a doctor again.
Polycystic ovary syndrome
Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) is a set of symptoms caused by impaired ovarian function, increased levels of insulin in the blood, estrogens and androgens (male hormones) in women. PCOS causes menstrual irregularities, excess weight, acne and age spots, pelvic pain, depression and excess body hair.
Currently, the most common definition of polycystic ovary syndrome is the one adopted in 2003 by European experts. According to its content, a diagnosis is made if the examination is carried out during the first six days of the cycle and the woman simultaneously has two of the three symptoms:
- increased size of the ovaries: surface area more than 5.5 sq.cm, volume more than 8.5 KB.cm;
- the presence of at least twelve immature follicles less than 10 mm in size, most often located on the periphery of the ovary;
- the presence of stromal hypertrophy.
The examination is performed using an ultrasound machine and 3D ultrasound. The latter will help to determine the volume of the ovaries and count the number of immature follicles with greater accuracy.
The main methods of treating the syndrome are: lifestyle changes, medication and surgery. Treatment goals fall into four categories:
- reducing the level of insulin resistance;
- restoration of reproductive function;
- getting rid of excess hair growth and acne;
- restoration of a regular menstrual cycle.
For each of these goals, there is significant controversy regarding optimal treatment. One of the main reasons for this is the lack of large-scale clinical trials comparing different treatments. However, many experts recognize that reducing insulin resistance and body weight may have an impact on all treatment goals, as they are the main cause of the syndrome.
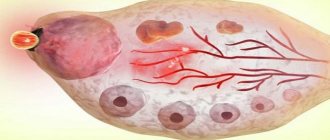
A follicle is a round-shaped capsule cell that is located along the ovary. There are approximately 10-12 of these at the beginning of the menstrual cycle. They begin to mature until one of them is ahead of its predecessors . Gynecologists call such a cell a “dominant follicle”, as well as a “Graafian vesicle”.
Inside its structure, an egg matures, which during ovulation is sent into the fallopian tubes. The size of the capsule changes with each day of the cycle. During ovulation, it reaches its maximum size, and subsequently bursts and forms the corpus luteum.