Curettage of the uterus in gynecology is carried out for various reasons, both therapeutic and diagnostic. In most cases, uterine curettage is performed to remove the remains of the fertilized egg after a frozen pregnancy or spontaneous abortion. Fetal death occurs due to hormonal, endocrine and infectious diseases in the woman’s body. But the listed pathologies lead not only to spontaneous miscarriages and missed abortions, but also to the formation of polyps and various tumors in the uterine cavity. After an operation, women, regardless of the reasons that caused it, are required to undergo an ultrasound scan in order to promptly detect developed complications caused by curettage.
Why fetal development freezes during pregnancy
A frozen or non-developing pregnancy can be caused by a number of factors, and the cause cannot always be determined accurately. These may be genetic abnormalities (if the process of chromosome division fails, defects are formed that are incompatible with life), hormonal imbalance (reduced production of progesterone or excessive levels of androgens - male sex hormones), infections - both of the genital area and other organs, taking prohibited drugs. during pregnancy of drugs, endocrine pathologies, negative external influences, etc.
In cases of frozen pregnancy, curettage of the uterus is necessary.
How to determine a frozen pregnancy
According to medical statistics, embryo freezing during intrauterine development occurs in the first 12 weeks of pregnancy. Less often, women can hear such a diagnosis in the second trimester (no more than 15% of cases). It is difficult to recognize a frozen pregnancy on your own. However, you should immediately seek help from a specialist if the following symptoms appear:
- an abrupt end to toxicosis, which is associated with a restructuring of the body and disappears gradually after the 12th–14th week;
- change in the condition of the breast - after conception, the mammary glands in women swell. If your breasts return to their previous state or nipple discharge appears, you should consult your doctor;
- Red or brown vaginal discharge is a dangerous sign; you should immediately call an ambulance.
In rare cases, uterine curettage is prescribed in the 2nd half of the term
If alarming symptoms appear, the doctor examines the woman and palpates the abdominal area. The problem can be recognized by the prolapse of the uterus, the discrepancy between its size and the period of pregnancy, and the absence of heartbeat after the 5th week.
To confirm a frozen pregnancy you need:
- blood test for thyroid, pituitary, adrenal and sex hormones;
- Ultrasound, which allows you to determine the condition of the embryo and the uterine cavity.
If the results of tests and ultrasound examinations do not correspond to the current period, the diagnosis is confirmed.
Based on the research results, the doctor decides to carry out the following manipulations:
- Medical abortion is a non-invasive method of ending a pregnancy that is recommended for women before the 6th week of the gestational period. The method involves taking hormonal drugs that provoke a miscarriage. It is rarely used, as it does not guarantee complete cleansing of the uterine cavity.
- Vacuum aspiration is a safe method of removing the fertilized egg for up to 5 weeks. It is carried out without dilating the cervix by inserting a catheter attached to a suction device, with the help of which the fertilized egg is sucked out.
- Scraping.
The surgery is performed in the operating room after general anesthesia is administered intravenously.
Curettage of the uterus
Many women receive a referral for curettage of the uterine cavity after a routine gynecological examination. But few doctors explain what this procedure is. Therefore, women begin to fear even the very name of this manipulation. Let us hasten to dispel unfounded fears and look in detail at what curettage is, how and why it is carried out.
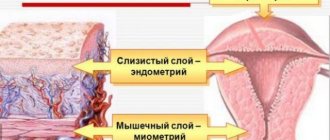
The uterine cavity is lined with endometrium - this is its mucous membrane. During the menstrual cycle, the thickness of the endometrium increases to accommodate the egg. When pregnancy does not occur, unclaimed cells leave the uterus along with menstrual flow.
When cleaning, the doctor removes the top layer of the epithelium of the uterus and cervix. The germ cells from which new mucous grows remain intact.
Scraping is the essence of the procedure, but the manipulation itself is called differently:
- Separate diagnostic curettage. Separate because tissue samples from the cervix and uterus are collected and examined separately.
- Diagnostic curettage under hysteroscopy control. This is a more precise procedure during which the doctor can observe what is happening using a hysteroscope.
Curettage is carried out using a curette or vacuum suction. The doctor selects the instrument depending on the indications for the procedure.
Perform curettage in Moscow
- Multidisciplinary medical: Voykovskaya metro station, st. Clara Zetkin 33/28. Cost – 15,000 rubles;
- Multidisciplinary medical: Kurskaya metro station, lane. Nastavnichesky 6 or 2nd Syromyatnichesky Lane 11. Price – 10,000 rubles;
- Multidisciplinary medical: Krasnoselskaya metro station, st. Nizhnyaya Krasnoselkaya 15/17. Price – 12100 rub;
- Multidisciplinary medical center NEARMEDIC: Polezhaevskaya metro station, Marshal Zhukov Ave. 38/1. The cost of the Russian Far East is 5900 rubles.
Source: https://ginomedic.ru/ginekologiya/procedury/vyskablivanie-matki.html
How is curettage done?
Anesthesia ensures a complete absence of unpleasant sensations. If there are contraindications, local anesthesia is used.
After the anesthesia begins to take effect, the doctor’s actions are as follows:
- genitals are disinfected;
- a gynecological speculum is inserted;
- the vagina and cervix are treated;
- a special substance is introduced that stimulates uterine contractions and endometrial rejection, which greatly simplifies the procedure;
- a curette is inserted into the uterus - a surgical spoon for curettage, with the help of which the organ is cleansed from the fertilized egg and the upper layer of the endometrium;
- instruments are removed from the vagina.
After the operation, the woman is taken to the ward.
The uterine curettage procedure is performed under general anesthesia.
Diagnostic curettage is the most informative procedure * Diana Clinic in St. Petersburg
Diagnostic curettage is the general name for a procedure performed with a special instrument to remove the top layer lining the uterus.
After curettage, the biomaterial is sent for laboratory histological analysis. CLICK TO MAKE AN APPOINTMENT, TEST OR ULTRASOUND
Types of diagnostic curettage of the uterus and cervix
The uterus is a female muscular organ, which is a cavity with an entrance through the cervix. The cervix is located in the vagina. During pregnancy, the fetus develops in a healthy uterus. The inner wall of the organ is covered with a mucous membrane, medically called the endometrium.
The endometrium is the most important part of the uterus, because it is thanks to it that the fertilized egg attaches and develops in the organ. During the menstrual cycle, the endometrium changes thickness, and if pregnancy does not occur, it peels off and comes out in the form of menstrual flow. In the next cycle everything repeats.
During curettage, the gynecologist removes the top layer of the endometrium (functional layer), leaving the germinal layer necessary for the formation of a new mucous membrane. The cervical canal is also scraped out.
The gynecologist may prescribe one of the procedure options.
- To diagnose pathologies of various etiologies of the cervical canal and the uterine cavity, separate diagnostic curettage (RDC) is performed. In this case, first the gynecologist scrapes out the cervical canal, then the uterine cavity itself.
- For more advanced diagnostics, hysteroscopy is performed together with separate diagnostic curettage - RDV + GS. In this case, a special device, a hysteroscope, is inserted into the uterine cavity to examine the walls of the uterus. Hysteroscopy helps in identifying pathological neoplasms in the uterine cavity and in monitoring the results of curettage.
Cleaning the uterus can be done with a curette or vacuum. Vacuum is a more modern method, but it cannot be classified as a diagnostic technique. Since vacuum cleaning does not allow removing tumors and taking mucosal tissue for analysis. This method is suitable for early abortion.
Why is diagnostic curettage performed?
Curettage may be prescribed in the following cases:
- To scrape the mucous membrane and send the material for histological examination - this makes it possible to identify oncology in the uterus and cervix;
- If it is necessary to remove a pathological formation in the uterus or cervical canal.
- To prepare for surgery related to uterine fibroids (a neoplasm in the thickness of the organ), if it is planned to preserve the uterus.
- For endometritis, to prepare the organ for treatment.
Symptoms for which curettage of the uterus and cervical canal is prescribed
Diagnostic curettage is necessary in case of disruption of the female reproductive organs, when ultrasound is not informative. If there are certain alarming symptoms, diagnostic curettage is prescribed to determine their causes. The most common reasons for diagnostic curettage are:
- bloody discharge from the vagina outside of menstrual periods;
- heavy, painful and prolonged periods;
- discharge after menopause;
- primary or secondary infertility;
- preparation for in vitro fertilization;
- changes in the organ mucosa detected on ultrasound of the uterus;
- changes in the cervical mucosa noticed on colposcopy;
- preoperative diagnosis before removal of fibroids, polyps and other neoplasms on the mucous membrane with preservation of the uterus;
- suspicion of the remains of a fertilized egg after a spontaneous abortion;
- endometrial pathology.
During diagnostic curettage, the doctor may:
- Remove particles of membranes remaining after an abortion or miscarriage (complication of abortion);
- Remove uterine polyps. Currently, this is the only way to get rid of these tumors. Polyps cannot be left behind, as they lead to infertility, grow quickly and can develop into cancer.
- Eliminate endometriotic growths - hyperplasia (thickening). Hyperplasia of the endometrium of the uterus is also treated only in this way.
- Stop uterine bleeding.
- Dissect synechiae - fusions of the uterine walls that prevent pregnancy. The procedure is performed with a hysteroscope.
- Take a tissue sample for cytological analysis (a laboratory assistant examines the biomaterial in the laboratory and identifies cancer and differentiates benign tumors).
The diagnostic curettage procedure is low-traumatic and does not require long-term recovery. It is performed under anesthesia and is therefore painless.
After the diagnostic curettage procedure, the resulting tissue sample from the uterine cavity is sent for histological analysis. The purpose of histology is to identify tissues affected by cancer cells or with the presence of precancerous changes.
Preparation for diagnostic curettage
Diagnostic curettage is prescribed a few days before the start of the next menstruation, since this period is most favorable for reducing blood loss and rapid restoration of uterine tissue.
If diagnostic curettage is combined with hysteroscopy, then the best period for its implementation will be the first days after the end of the next menstruation, when the endometrium is very thin and any of its changes and neoplasms can be easily detected by a hysteroscope.
Before curettage, the patient will have to undergo a series of general tests, which must be completed. Mandatory tests include:
2 days before the procedure, you should abstain from sexual activity, stop using intimate hygiene products and vaginal suppositories.
To ensure safe anesthesia, you should not eat or drink 8 hours before surgery.
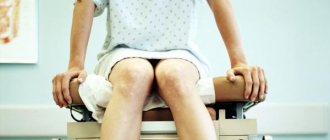
How the procedure is performed
The patient sits in a chair with supports, similar to the one in a gynecological examination room. Anesthesia is administered intravenously and will last for 15 to 25 minutes. All this time, the patient will be asleep and will not feel anything, and the doctors will begin the diagnostic curettage procedure.
A speculum will be inserted into the vagina to expose the cervix, which will then be secured with special forceps. This is necessary to secure the uterus and avoid its possible displacement.
A special metal rod, called a probe, is used to measure the uterine cavity by inserting it inside through the cervical canal. After this, the channel begins to expand.
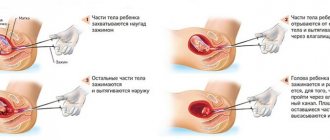
This is done using dilators of different sizes, which are inserted one by one into the cervical canal until it expands to such an extent that it can easily pass a curettage tool called a curette.
The shape of the curette resembles the shape of a small spoon with a sharpened side (the device has a long handle). The curette is inserted through the expanded canal into the uterine cavity, where curettage is performed with its sharpened side. The scraping is collected in a sterile jar for further sending for histology.
When combining diagnostic curettage with hysteroscopy, a hysteroscope is first inserted into the uterus, with the help of which the walls and cavity of the uterus are carefully examined, then curettage is performed. After the procedure, the hysteroscope is again inserted to once again examine the inside of the uterus to ensure that the curettage was carried out thoroughly.
After this, the forceps are removed from the cervix and the organ along with the vagina is treated with an antiseptic. Ice is placed on the patient’s stomach to speed up the contraction of the uterus and she is sent to the ward; after a few hours, or less often the next day, the patient is discharged with a course of antibiotic therapy.
Gynecology is a field of medicine that studies the sexual and reproductive health of the fair sex, and also helps women during pregnancy and childbirth. An appointment with a gynecologist is an obligatory part of every woman’s life.
Contraindications: when diagnostic curettage should not be done
The gynecologist will not prescribe the procedure if the patient has:
- Acute infectious diseases or inflammation in the genitals.
- HIV;
- Hepatitis;
- Syphilis.
Curettage can be performed after the infection and inflammation have subsided.
Pain and discharge after diagnostic curettage
After the anesthesia wears off, the patient may experience pain similar to that experienced by some women during menstruation. It is recommended to relieve pain with analgesics.
Heavy bleeding with clots for several hours after curettage is considered normal. Within 7 to 10 days after this procedure, the presence of scanty yellowish, brown or bloody discharge will also be normal. But the absence of discharge after curettage may indicate spasm of the cervix and the accumulation of blood clots there.
Recovery after diagnostic curettage
The uterus, after diagnostic curettage, will fully recover after the end of the subsequent menstruation, when its mucous membrane and ovaries begin to work synchronously again.
For 2 weeks after this procedure, the woman needs to take care. Prohibited:
- be sexually active;
- use tampons;
- take a steam bath;
- douche;
- take aspirin and medications that contain it;
- engage in heavy physical labor and sports.
Menstruation after curettage may begin with a slight delay. The norm will be considered a delay of up to 4 weeks.
Complications after diagnostic curettage
When diagnostic curettage is performed by an experienced doctor, complications are extremely rare. But they can still be as follows:
- Damage to the uterine mucosa or excessive curettage - a situation where the curette damaged the growth layer of the uterus and the endometrium stopped growing;
- Inflammation of the uterus - occurs when antiseptic rules are violated or when a procedure is performed in the presence of a focus of inflammation.
- Hematometra - its cause is spasm of the cervix and accumulation of blood in its cavity;
- Tear of the cervix - occurs when it is stretched with forceps for fixation;
- Perforation of the uterus is its perforation (puncture) by an instrument inserted through the cervical canal.
Diagnostic curettage is an important method for diagnosing various gynecological ailments. It often happens that adequate treatment is impossible without this type of diagnosis.
And histological examination of tissue samples obtained during curettage allows the attending physician to use a minimum of drugs when prescribing treatment, since histology gives the most accurate result of the presence of a particular disease.
About consultation of a gynecologist in St. Petersburg/ Consultation of a gynecologist
Our clinic in St. Petersburg accepts gynecologists of the highest and first certification categories. All doctors have certificates confirming their qualifications, issued in St. Petersburg and Moscow. The cost of an initial appointment with a gynecologist is 1000 rubles, a consultation based on test results or ultrasound is 500 rubles.
You can make an appointment with a gynecologist without an insurance policy, registration in St. Petersburg and Russian citizenship.
You can apply to us without having an insurance policy, registration in St. Petersburg and Russian citizenship.
ATTENTION! IN THE CLINIC IS A DOCTOR SPEAKING IN ENGLISH LANGUAGE!
Source: https://medcentr-diana-spb.ru/ginekologiya/diagnosticheskoe-vyiskablivanie/
Complications after curettage
Curettage during a frozen pregnancy is a surgical intervention that can lead to the following complications:
- damage to the uterus, which entails another operation to restore its integrity;
- hemorrhage can lead to large volumes of blood loss or cause an inflammatory process in the uterus due to the accumulation of biological fluid and its clots in the organ cavity;
- inflammation is the result of the addition of an infection against the background of a decrease in local immunity;
- adhesions in the pelvic area are a dangerous complication that can go unnoticed for a long time and lead to infertility.
To prevent dangerous consequences, after curettage you should pay special attention to your health; for the entire postoperative period, the uterus becomes a large vulnerable wound. A woman may be bothered by spotting, similar to menstruation, accompanied by nagging pain in the lumbar region and lower abdomen, associated with intense contractions of the uterus (passes within 6-10 days). At this time, it is important to monitor personal hygiene and avoid physical activity and sexual intercourse. This will help prevent the opening of bleeding, the development of complications and the addition of infection.
After the operation, the doctor prescribes the woman antibacterial drugs to prevent infection, vaginal suppositories with chlorhexidine or iodine for local action. To speed up the healing process, suppositories with depanthenol are recommended. Recovery of the body can be determined by the onset of menstruation. The menstrual cycle usually returns to normal within 30–40 days after surgery.
Ultrasound after cleaning the uterus – Gynecology
According to statistics, from 10 to 25% of pregnancies end in miscarriages. To ensure that spontaneous termination of pregnancy does not negatively affect a woman’s health, it is necessary to conduct an ultrasound after a miscarriage.
Curettage of the uterus
Many women receive a referral for curettage of the uterine cavity after a routine gynecological examination. But few doctors explain what this procedure is. Therefore, women begin to fear even the very name of this manipulation. Let us hasten to dispel unfounded fears and look in detail at what curettage is, how and why it is carried out.
The uterine cavity is lined with endometrium - this is its mucous membrane. During the menstrual cycle, the thickness of the endometrium increases to accommodate the egg. When pregnancy does not occur, unclaimed cells leave the uterus along with menstrual flow.
When cleaning, the doctor removes the top layer of the epithelium of the uterus and cervix. The germ cells from which new mucous grows remain intact.
Scraping is the essence of the procedure, but the manipulation itself is called differently:
- Separate diagnostic curettage. Separate because tissue samples from the cervix and uterus are collected and examined separately.
- Diagnostic curettage under hysteroscopy control. This is a more precise procedure during which the doctor can observe what is happening using a hysteroscope.
Curettage is carried out using a curette or vacuum suction. The doctor selects the instrument depending on the indications for the procedure.
Indications
Gynecological cleansing can be carried out for diagnostic purposes, when it is necessary to obtain tissue for histological examination, or for therapeutic purposes, when a pathological formation is removed.
Curettage is a surgical method for treating a variety of pathologies, including:
Preparation
Most often, cleaning is carried out before menstruation - at this time the cervix is susceptible to dilation.
- coagulogram;
- general analysis of urine and blood;
- ECG;
- tests for HIV, hepatitis, syphilis;
- vaginal smear.
A few days before cleaning, stop douching, using vaginal medications, and refuse sexual intercourse.
How they do it
On the appointed day, you should come to the hospital on an empty stomach. Bring sanitary pads, a change of underwear, and a shirt.
The procedure is carried out in a small operating room on a table with legs, like in a gynecological chair. The anesthesiologist gives an intravenous injection, after which anesthesia occurs for 15-30 minutes. Modern anesthesia does not cause hallucinations: normal dreamless sleep occurs. Naturally, no pain will be felt during the operation.
The operation is performed as follows:
- a speculum is inserted into the vagina;
- the neck is fixed with special forceps;
- a special rod is used to measure the internal size of the uterine cavity;
- using dilators - a set of metal sticks of different thicknesses - the cervical canal is expanded to the size of a small curette (an instrument similar to a sharpened spoon);
- the cervical mucosa is scraped out, the material for analysis is collected in a separate container;
- if necessary, a hysteroscope is inserted into the uterus - a thin tube with a camera, and the walls are examined;
- the top layer of the endometrium is removed with a curette, the material is collected for analysis;
- a hysteroscope is inserted to examine the result; if not everything has been removed, the curette is used again;
- remove the forceps from the neck, treat the external pharynx and vagina with an antiseptic, put ice on the stomach;
- The patient is transferred to a room where she needs to stay for several hours to be completely sure that no acute complications will develop.
- : Carrying out therapeutic curettage of the uterine cavity (curettage)
- Unlike curettage, with vacuum aspiration it is possible to remove:
- remnants of the fertilized egg or placenta;
- frozen pregnancy;
- hematometer;
- stop dysfunctional uterine bleeding.
During the operation, after dilation of the cervix, the tip of an aspirator syringe is inserted into the uterus, which creates a vacuum around the formation and draws it into itself without damaging the mucous membrane. This is the main difference between vacuum cleaning and curettage.
Examination and treatment after curettage
Tissues removed from the surface of the uterus and cervix are collected in separate jars and sent for histology. There the structure of cells is studied and their nature is determined to identify oncology. The analysis result will be ready in 10-15 days.
Medications after the procedure include a short course of antibiotics to prevent inflammation and a painkiller for abdominal pain.
Recovery
The first hours after the operation there will be copious discharge of blood with clots. After a few hours, the discharge will become less abundant, after a day it will become spotting, and will be observed for about 7-10 days.
If they stop earlier and at the same time a strong nagging pain appears in the lower abdomen, be sure to contact a gynecologist - this may be a sign of hematometra.
A slight nagging pain as during menstruation against the background of residual discharge is not a pathology.
For the first 10-15 days after surgery, you should refrain from:
- sexual intercourse;
- using tampons;
- douching;
- visiting a sauna, swimming in a pond, pool, bath;
- taking medications based on acetylsalicylic acid.
After 10-14 days, do not forget to visit the doctor: at this time the histology will be ready, based on the results of which additional treatment may be prescribed.
Menstruation after cleaning usually comes with a delay of several days. If your period has not started after 2 months, be sure to consult a doctor.
You can plan a pregnancy after curettage after a few weeks, but it is better to wait a couple of months before conceiving: during this time you will have time to undergo treatment, and the uterus and cervix will be completely restored.
Possible complications after curettage
Curettage can be tolerated quite easily if you see a good anesthesiologist and a careful gynecologist. Only in isolated cases do complications arise.
- Perforation of the uterus. The uterus can be pierced with any dilator or probe due to the fact that the cervix does not open or the uterine tissue is loose. Small perforations are closed on their own, and large ones are sutured;
- Cervical tear. The neck may be flabby, so the forceps sometimes slip when stretched, injuring the tissue. Small tears heal on their own, large ones require stitches;
- Inflammation of the uterus. Inflammation begins if the operation is performed against the background of inflammation, antiseptic requirements are violated, and antibiotics are not prescribed. For treatment, a course of antibiotics is prescribed.
- Hematometra. After curettage, the uterus bleeds. If the cervix suddenly closes (tight cervix), the blood cannot leave the uterus and clots form, causing inflammation and severe pain.
- Excessive curettage. If the doctor scrapes out a thick layer of tissue, the germ cells may be damaged. In this case, the mucous membrane does not grow. The condition is not corrected and threatens infertility.
Source: https://cmsch71.ru/molochnitsa/uzi-posle-chistki-matki.html
When to see a doctor
14 days after the operation, the woman must appear for an examination and ultrasound to assess the condition and degree of restoration of the uterus. If the following signs appear, you should immediately contact a gynecologist:
- bleeding lasts more than 10 days;
- foul odor from the genitals;
- brown or yellow discharge;
- sudden cessation of discharge;
- temperature increase;
- weakness, dizziness, fainting;
- absence of menstruation within 50 days.
The presence of such symptoms may indicate the development of inflammatory processes, which requires urgent drug treatment, or the accumulation of blood clots in the uterine cavity, the removal of which will be carried out with the help of drugs or surgery.
Symptoms for which curettage of the uterus and cervical canal is prescribed
Diagnostic curettage is necessary in case of disruption of the female reproductive organs, when ultrasound is not informative. If there are certain alarming symptoms, diagnostic curettage is prescribed to determine their causes. The most common reasons for diagnostic curettage are:
- bloody discharge from the vagina outside of menstrual periods;
- heavy, painful and prolonged periods;
- discharge after menopause;
- primary or secondary infertility;
- preparation for in vitro fertilization;
- changes in the organ mucosa detected on ultrasound of the uterus;
- changes in the cervical mucosa noticed on colposcopy;
- preoperative diagnosis before removal of fibroids, polyps and other neoplasms on the mucous membrane with preservation of the uterus;
- suspicion of the remains of a fertilized egg after a spontaneous abortion;
- endometrial pathology.
Pregnancy after curettage
Doctors do not recommend planning conception within six months after curettage, which is associated with physical and emotional recovery after the operation. Hormonal drugs are often prescribed. Carrying a fetus after curettage is a big burden on a woman’s body. Often, attempts to conceive earlier than 6 months can result in spontaneous termination of pregnancy in the early stages or the formation of defects in the development of the fetus. An immature woman may also not carry the baby to term and give birth prematurely.
Thus, curettage removes the fertilized egg. The operation allows you to maintain the health of your reproductive organs. It is painless due to the administration of intravenous anesthesia. The period of recovery of the body and the onset of the first menstruation occurs within 30–40 days. Doctors recommend planning pregnancy no earlier than six months after surgery.
Curettage of the uterus in gynecology is carried out for various reasons, both therapeutic and diagnostic. In most cases, uterine curettage is performed to remove the remains of the fertilized egg after a frozen pregnancy or spontaneous abortion. Fetal death occurs due to hormonal, endocrine and infectious diseases in the woman’s body. But the listed pathologies lead not only to spontaneous miscarriages and missed abortions, but also to the formation of polyps and various tumors in the uterine cavity. After an operation, women, regardless of the reasons that caused it, are required to undergo an ultrasound scan in order to promptly detect developed complications caused by curettage.
A gynecologist prescribes uterine curettage: should you agree or not? Diagnostic curettage
“I was cleaned” or “I was cleaned” - I often hear these phrases from my patients, and they sound to me as unbearable as the movement of foam plastic on glass. We colloquially call “cleaning” curettage of the uterus - the most common procedure performed in gynecology in the vast majority of cases without any indication for it.
This very established name - “cleaning” - already reflects a rough, clumsy and primitive approach to solving the problem.
By the way, the term smoothly passed from medical jargon into the vocabulary of many women who even believe that they need to “get clean” or “get clean” from time to time.
Perhaps they put the same meaning into this as the notorious “cleansing the body of toxins,” suggesting that “dirt” accumulates in this organ too.
Before continuing the story, it is necessary to explain what exactly we are talking about.
After curettage of the uterus: possible risks
Curettage is an outpatient medical procedure performed under intravenous anesthesia, during which the uterine mucosa is removed (scraped) using a special curette.
The procedure is called therapeutic and diagnostic, since it removes disease-modified tissue (if any), which can be examined under a microscope and an accurate diagnosis made.
From the previous sentence it is clear that curettage is carried out not only in the presence of a disease, but when it is suspected, that is, for the purpose of making a diagnosis.
So far everything is clear, logical and obvious. However, there is another side to this manipulation.
The procedure is performed with a sharp iron curette, with the help of which the mucous layer of the uterus is actually “torn off”, and inevitable injury to the uterus itself occurs.
As a result, there is a risk of several serious complications: damage to the growth layer of the endometrium (impairing its growth in the future), the appearance of adhesions in the uterine cavity, and the development of inflammation.
In addition, this procedure contributes to the development of a disease such as adenomyosis (uterine endometriosis) - due to the violation of the boundary between the layers of the uterus, which contributes to the growth of the endometrium into the uterine muscle. As a result, curettage may lead to problems with conception or trigger the development of adenomyosis.
It is quite obvious that such a procedure must be done strictly according to indications and the benefit-risk ratio must be seriously assessed. But this is possible anywhere, but not here, and this is very sad.
Scraping “just in case”
I think that in more than 80% of cases, curettage is carried out in vain, that is, either without any indication at all, or in cases where the problem can be solved with medication or through a simple outpatient procedure.
Here are situations in which you may be asked to perform curettage.
- You have been bleeding for a long time or have uterine bleeding.
- An ultrasound revealed that you have an endometrial polyp, endometrial hyperplasia, adenomyosis, uterine fibroids, or chronic endometritis.
- You are planning to undergo surgical treatment for uterine fibroids.
- You suspect an ectopic pregnancy.
- You complained that you have heavy menstruation, intermenstrual spotting or brown “spotting” before and/or after menstruation.
In general, people are sent for “cleaning” very often, even in the absence of the reasons that I listed above. Curettage often accompanies any surgical treatment in gynecology. It’s as if they are always trying to do it “at the same time” in order to “check, just in case,” whether everything is normal. It shouldn’t be this way; this is too frivolous an attitude towards a rather traumatic procedure.
When not to agree to scraping
So, instructions on how to avoid scraping .
- If you do not have heavy uterine bleeding (as they say, “it’s pouring down your legs”), but just prolonged bleeding and pregnancy (uterine and ectopic) is excluded, ask your doctor about the possibility of stopping the bleeding with medication. Yes it is possible. While taking the drug (I will immediately warn you that this is a hormonal drug, but it is safe), the bleeding may stop, and your condition will need to be re-evaluated after the next menstruation. In many cases, the treatment provided will be sufficient and nothing more will need to be done.
- If during an ultrasound you are found to have a polyp or endometrial hyperplasia, do not rush to agree to curettage. Ask your doctor about the possibility of prescribing the drug for you this cycle and then repeat the ultrasound after the end of the next menstruation. If a polyp or hyperplasia is confirmed, alas, curettage must be done under hysteroscopy control. But you have a very high chance that after menstruation there will be no indication for the procedure.
A polyp is a growth on the lining of the uterus (looks like a finger or mushroom), most often benign. There are polyps that are rejected during menstruation, and those that grow from the germ layer. The latter require removal.
Hyperplasia is a thickening of the mucous membrane of the uterine cavity. There are two types: simple and complex. Simple hyperplasia occurs most often, it is not dangerous, for its development there must be a mandatory reason (functional cyst in the ovary, polycystic ovary syndrome and several more). Usually, 10 days of taking the drug is enough for it to go away and not recur.
Complex hyperplasia - bad hyperplasia, an error in the structure of the endometrium, usually occurs after 35 years, more often against the background of excess body weight. It is treated first by removing the mucous membrane (scraping) and then by a multi-month course of hormonal drugs or by installing a Mirena intrauterine hormonal device. An accurate diagnosis is only possible with histological examination.
- If you are offered to do curettage only for diagnostic purposes before surgery or to clarify the condition of the mucous membrane, ask the doctor to start with an endometrial biopsy (another name is “pipe biopsy” or “aspiration biopsy”). This is a simple outpatient procedure that does not require any anesthesia. A thin tube is inserted into the uterine cavity and a small amount of tissue is sucked in, which is then sent to the laboratory for examination. This is a fairly informative analysis.
Important: the material obtained as a result of curettage or biopsy is only the mucous membrane of the uterus; it does not carry any information about other diseases. The fact is that curettage is often prescribed for the purpose of assessing uterine fibroids for its characteristics; So, scraping will not give any information.
- Remember, almost all modern ultrasound machines allow you to evaluate the uterine mucosa and identify signs of pathology in it. If the doctor writes during an ultrasound that the endometrium is not changed, and you do not have heavy menstruation or intermenstrual bleeding, then the likelihood that you have a pathology that requires curettage is close to zero.
- In general, the main manifestations of endometrial pathology (curettage is aimed only at this tissue) are bleeding, heavy menstruation and intermenstrual spotting. Thus, if you do not have this, discuss with your doctor whether his desire to perform curettage is justified.
- “Chronic endometritis” is a common diagnosis with ultrasound and in the results of histological findings after curettage. We are talking about chronic inflammation of the uterine mucosa. However, there are no generally accepted criteria for making this diagnosis using ultrasound in evidence-based medicine . Simple histology also cannot reliably confirm this diagnosis . Often this diagnosis is made where it does not exist, since they focus on “leukocytes”.
A reliable diagnosis is possible only by conducting a special type of study - immunohistochemistry. This study is not available in all laboratories, and the material for it can be obtained by biopsy rather than by curettage.
I think it is now clear that curettage is not necessary to confirm the diagnosis of “chronic endometritis”.
In general, the diagnosis and treatment of this endometrial disease makes sense only within the framework of the problem of infertility and miscarriage.
In what situations should you agree to scraping?
- Heavy uterine bleeding: yes, curettage is a way to stop it.
- Suspicion of ectopic pregnancy (difficulty in making a diagnosis).
- Polyp or endometrial hyperplasia that has not disappeared after menstruation or drug treatment.
- Remains of membranes (after abortion, miscarriage, pregnancy).
- Any spotting after menopause.
Now, I hope you have reliable instructions on how to avoid possibly unnecessary surgery for you. Don't be afraid to ask your doctor questions.
Offer alternatives (endometrial biopsy, medication). Ask to justify the need for curettage. The answer “that’s how we do it” should not be accepted.
Of course, all this applies only to those situations in which there is no threat to your life and health (excessive bleeding).
Source: https://www.7ya.ru/article/Ginekolog-naznachaet-vyskablivanie-matki-soglashatsya-ili-net/
Reasons for performing an ultrasound
The procedure for curettage of the uterus during a frozen pregnancy or miscarriage is the removal of the remnants of the fertilized egg from the inner surface of the reproductive organ. A common consequence after surgery is endometritis. If an ultrasound examination and repeated surgical intervention are not carried out in time, if necessary, endometritis can provoke blood poisoning and removal of the uterus.
Ultrasound monitoring in the postoperative period is important, since inflammation of the mucous membranes of the reproductive organ, which occurs in a chronic form, leads to infertility. But you can suspect the presence of a problem before an ultrasound scan based on characteristic symptoms:
- nagging pain in the lower abdomen;
- weaknesses;
- increase in temperature;
- discharge the color of meat slop;
- general deterioration of health.
To confirm the pathology, the gynecologist prescribes an ultrasound examination of the pelvic organs to the patient. If there is an inflammatory process, the gynecologist prescribes antibiotics, enzyme preparations, and physiotherapeutic procedures to the woman.
Another consequence of uterine curettage, which is diagnosed using ultrasound, is an ovarian cyst. The tumor occurs as a result of hormonal changes in a woman’s body. A cyst is a formation filled with fluid. In 8 out of 10 cases, the cyst disappears on its own without surgery.
Only in the case of torsion do specific signs of an acute abdomen, severe pain, fever and fainting occur. If a cyst without torsion is detected, the patient is prescribed hormonal medications and physiotherapeutic treatment.
Complications after curettage of the uterus concern not only the physical, but also the psychological state of the woman. Often a frozen pregnancy affects the emotional state of the failed mother.
The need for an ultrasound after a miscarriage
According to statistics, from 10 to 25% of pregnancies end in miscarriages. To ensure that spontaneous termination of pregnancy does not negatively affect a woman’s health, it is necessary to conduct an ultrasound after a miscarriage.
Why do an ultrasound after a miscarriage?
Ultrasound after spontaneous abortion allows you to assess the condition of the uterus. If the fertilized egg is not fully released, the following complications may develop:
- large blood loss;
- development of infection with fever, pain, contractions and bleeding (in severe cases, mixed with pus);
- the formation of a polyp from part of the placenta, which can cause severe bleeding;
- oncological diseases of female organs;
- miscarriage of the next pregnancy.
If, during an ultrasound examination, remains of embryonic tissue are visible in the uterus, the woman undergoes gynecological cleansing after the ultrasound.
When to do an ultrasound after a miscarriage
An ultrasound after a spontaneous abortion is prescribed immediately in order to avoid complications that a miscarriage can cause.
If gynecological cleansing has been performed, a repeat examination is scheduled a week later in order to protect the woman from problems that may arise after curettage. If embryo remains are found in the uterus, a repeat cleaning procedure is performed.
Some women may have an early miscarriage when they do not yet know that they are pregnant. This may be indicated by prolonged bleeding that exceeds the duration of menstruation. If bleeding continues for more than 10 days, is accompanied by pain, contractions, and fever, you must urgently contact a gynecologist who will prescribe an ultrasound.
Preparation and research process
A precursor to spontaneous abortion may be a diagnosed threat of miscarriage on ultrasound. If a pregnant woman is hospitalized with complaints of bleeding and abdominal pain, she is immediately given an ultrasound examination of the pelvis.
For this, the transvaginal method is used, when the sensor is inserted into the vagina. This method allows you to obtain more complete information about the condition of the uterus from the 3rd week of pregnancy.
An ultrasound can track symptoms of a threatened miscarriage in the early stages - this is indicated by local thickening of one of the walls of the uterus, as well as an increased diameter of the internal pharynx.
The study helps assess the viability of the embryo by its cardiac activity. At later stages, fetal motor activity is assessed.
They also look at the body of the uterus and check its tone, measure the thickness of the endometrium, if there is placental abruption, record its size.
In some situations, in a hospital, an ultrasound examination is performed using the transabdominal method. In this case, the patient is advised to exclude gas-causing foods from her diet a few days before the procedure: fruits, vegetables, dairy products, baked goods, etc.
Ultrasound results: deviations and norms
After spontaneous termination of pregnancy, the condition of the pelvic organs is assessed by ultrasound. First of all, they look to see if there are any embryonic tissues left in the uterine cavity. The presence of fertilized egg residues is a recommendation for cleaning.
After this, the size of the uterus is assessed. Normally, its size after spontaneous abortion differs from the size of the uterus of nulliparous women. The cervix has a length of 2.6-3.6 cm, a width of 2.3-3.1 cm. The normal thickness of the cervix is 2.6-3.6 cm. The body of the uterus with normal examination results has the following dimensions: length 4.3 -5.5 cm, width 3.2-4.2 cm, thickness 4.1-5.1 cm. The contours should be smooth and clear.
If curettage was performed after a miscarriage, an ultrasound may show dilated uterine vessels. This is the norm - this is how the uterus is restored.
The condition of the cervix depends on the consequences of the miscarriage. If a woman has been prescribed mechanical cleaning, the cervix may be open.
Great importance in ultrasound examination after spontaneous abortion is given to the analysis of the endometrium.
Endometrium after miscarriage
After a miscarriage and cleaning, the endometrium should normally be thin. If the process went without complications, as the body recovers, the endometrium will return to its previous size.
It is impossible to name the normal thickness of the endometrium, because... depending on the phase of the cycle, it constantly changes.
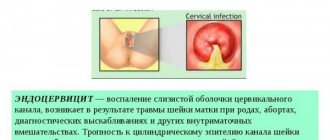
One of the most common complications after a miscarriage is the development of endometritis, an inflammatory process in the upper layer of the endometrium.
Endometritis can develop in the following cases:
- in case of incomplete miscarriage, when parts of the embryo tissue remain in the uterine cavity;
- during gynecological cleansing, when severe trauma occurs to all layers of the endometrium;
- in case of infection and microbes from the vagina;
- with the accumulation of blood clots.
After a miscarriage, blood and the remains of the fertilized egg are the environment in which microbes quickly begin to develop, causing an infectious and inflammatory process.
Endometritis can be asymptomatic and become a chronic disease. The occurrence of acute endometritis is characterized by the following symptoms:
- heat;
- bleeding from the vagina;
- cramping pain in the lower abdomen;
- nagging pain in the lower back;
- increased heart rate.
Symptoms of endometritis appear 1-3 days after spontaneous abortion or cleansing. In this case, you should immediately consult a doctor for a diagnosis.
A repeat ultrasound examination is prescribed, if the presence of embryonic tissue remains in the uterus is confirmed, curettage is performed. General therapy necessarily includes antibiotic treatment.
Endometritis can also be diagnosed during a gynecological examination by a doctor. The following signs indicate pathology:
- increase in the size of the uterus;
- pain when palpating the lower abdomen;
- shapelessness of the female organ;
- bloody or purulent discharge from the genital tract.
If no remains of the fertilized egg are found during inflammation of the endometrium, along with taking antibiotics, the following is prescribed:
- taking medications to contract the uterine muscle;
- anti-inflammatory drugs;
- antipyretic drugs;
- sedatives.
With this treatment, the symptoms of endometritis disappear after 5-7 days. In the future, a woman can carry and give birth to a healthy child.
Source: https://iDiagnost.ru/uzi/neobhodimost-provedeniya-uzi-posle-vykidysha
List of tests after curettage
After the operation, the woman is prescribed a series of tests to identify the cause of the missed abortion. Among the diagnostic measures it should be noted:
- Ultrasound of the pelvic organs;
- PCR testing for all sexually transmitted infections - viral and bacterial;
- hormone tests;
- immunogram;
- study of the karyotype of both spouses;
- tests for blood clotting pathologies (antiphospholipid syndrome, folate cycle mutations, thrombophilia);
- hysteroscopy.
Tests in the postoperative period help prepare the patient’s body for subsequent pregnancies.
If during the examination, remains of the fertilized egg are found in the uterine cavity after curettage, and the patient herself complains of sharp pain in the lower abdomen and heavy bleeding, then she is prescribed a repeat cleaning procedure. The consequences that develop after uterine curettage and remain unattended, in most cases become the reason for the impossibility of pregnancy or bearing a fetus in the future.
Diagnostic curettage
The diagnostic curettage procedure is carried out to diagnose diseases of the uterus and determine the causes of their occurrence. The procedure is carried out in a hospital hospital setting and involves removing part of the uterine mucosa for further research.
Curettage is performed under local anesthesia and lasts 15-20 minutes. During the procedure, the uterus is probed, its cervix is dilated and the mucous membrane is further cleaned, for which the doctor uses special instruments that look like ordinary tablespoons. The materials obtained during cleaning are sent for histological examination.
Medical curettage is a procedure with increased trauma; cleaning is best left to an experienced and highly qualified doctor. Contraindications to diagnostic curettage are:
• suspicion of uterine cancer,
• menstrual irregularities,
• acute inflammatory diseases of the pelvic organs,
• suspicion of a violation of the integrity of the uterine cavity.
In order to assess the patient’s health and restore the uterus, an ultrasound is performed after curettage.
Surgery
Curettage is used to eliminate adhesions of the uterine walls, stop uterine bleeding, remove polyps from the mucous membrane, treat endometritis and endometrial hyperplasia. In the case of an inflammatory process of the uterine mucosa, curettage is carried out in order to ensure complete treatment.
All curettage procedures are carried out under strict control, using modern means and instruments. The duration of the procedure depends on the complexity of the disease and the presence of various chronic diseases. Surgical curettage is in most cases performed under general anesthesia.
A prerequisite is to conduct an ultrasound after curettage and take medications to prevent possible infection. A repeat ultrasound examination is recommended 2-3 weeks after curettage.
Consequences of scraping
After the curettage procedure, it is recommended to abstain from sexual relations, taking warm and hot baths, douching and the use of hygienic tampons for 2-3 weeks. Almost every woman is interested in the possible consequences after cleansing. Of course, they do occur, but extremely rarely.
Most often, the consequence of surgery is tears and damage to the mucous membrane of the uterus and its cervix, which can provoke a sudden spasm of the uterus and slipping of instruments during surgery. The damage received during the operation is eliminated directly during the curettage process and does not cause discomfort or pain to the patient.
Endometriosis on ultrasound
The pathological condition is characterized by the growth of the inner layer of the uterus into the muscular layers of the organ. On ultrasound in case of disease, the gynecologist detects a heterogeneous structure of the myometrium with heterogeneous inclusions.
The condition means that in the muscle layer of the organ there are areas of the endometrium that look like small cysts on ultrasound. ECHO signs on ultrasound include an enlarged uterus, heterogeneous endometrium that does not correspond to the phase of the cycle. Endometriosis after curettage can develop if it is performed poorly, when the basal layer is removed with a curette and the myometrium is affected.
Preparation for diagnostic curettage
Diagnostic curettage is prescribed a few days before the start of the next menstruation, since this period is most favorable for reducing blood loss and rapid restoration of uterine tissue.
If diagnostic curettage is combined with hysteroscopy, then the best period for its implementation will be the first days after the end of the next menstruation, when the endometrium is very thin and any of its changes and neoplasms can be easily detected by a hysteroscope.
Before curettage, the patient will have to undergo a series of general tests, which must be completed. Mandatory tests include:
2 days before the procedure, you should abstain from sexual activity, stop using intimate hygiene products and vaginal suppositories.
To ensure safe anesthesia, you should not eat or drink 8 hours before surgery.
Ovarian cyst on ultrasound
During the examination, an ovarian cyst is visualized as a round-shaped formation filled with fluid, several centimeters in diameter. Using an ultrasound, the gynecologist determines not only the size of the tumor, but also its type, since cysts can be not only functional, but also represent a benign neoplasm that is not associated with the consequences of curettage and hormonal imbalance.
Using an ultrasound, the doctor can also see the presence of polycystic ovary syndrome. With the disease, the size of the ovary also increases - up to 10-13 cm3, with normal values 7-8 cm3. Another sign of polycystic disease, which is noticeable on ultrasound, includes thickening of the ovarian membrane and the presence of a large number of follicles in it.
To avoid complications after curettage of the uterus, it is important not only to undergo timely examinations prescribed by the doctor, but also to follow the recommendations of a specialist after the curettage procedure.
The first 8 weeks of pregnancy are considered the most critical in terms of pregnancy. If during this period something interferes with the intrauterine development of the fertilized egg, a frozen pregnancy occurs.
Why is diagnostic curettage performed?
Curettage may be prescribed in the following cases:
- To scrape the mucous membrane and send the material for histological examination - this makes it possible to identify oncology in the uterus and cervix;
- If it is necessary to remove a pathological formation in the uterus or cervical canal.
- To prepare for surgery related to uterine fibroids (a neoplasm in the thickness of the organ), if it is planned to preserve the uterus.
- For endometritis, to prepare the organ for treatment.
Why is ultrasound informative in case of intrauterine fetal death?
When diagnosing a frozen pregnancy, ultrasound is used to avoid errors. But first, the woman undergoes an examination by an obstetrician-gynecologist. The doctor then gives a referral for the procedure.
An ultrasound will show a frozen pregnancy even at an early stage, since transvaginal ultrasound examination determines the exact period and correlates the established norms with the indicators of the pregnant woman.
Measurement of basal temperature and a blood test for the presence of hCG are considered auxiliary methods in making a diagnosis.
See what this pregnancy looks like in the video:
Signs of pathology on ultrasound
In the first type of frozen pregnancy, the following signs are determined by ultrasound:
- the embryo is missing;
- pregnancy regresses in terms of timing;
- the size of the uterine cavity is 5–7 weeks;
- The fertilized egg is 2–2.5 centimeters in diameter.
In the second type, a frozen pregnancy can be determined by the following indicators:
- Ultrasound records the growth of the fetal egg, but inside the embryo is either absent or its residual tissue is visible;
- at the 8th week, the villous chorion, the future placenta, is not visible on an ultrasound scan;
- the size of the empty fertilized egg reaches 4.5–5 centimeters by the 10th week.
Ultrasound errors in identifying the described pathology are minimized. The sonologist conducts several studies to confirm this fact.
When the fertilized egg remains in the uterine cavity for a long time, the risk of a frozen pregnancy is reduced.
Additional signs of anembryonia include:
- the volume of amniotic fluid significantly exceeds the norm, polyhydramnios;
- the size of the uterus does not coincide with the established period, it lags behind;
- On ultrasound, the fetal egg is shown to be damaged - the contours are blurred, constrictions are noted.
To eliminate ultrasound errors when interpreting results, the doctor relies on the following factors:
- CTE, coccygeal-parietal size, 7 millimeters, and there is no fetal heartbeat;
- the size of the fertilized egg reached 2.5 centimeters, but the embryo did not appear;
- the embryo did not appear on repeated ultrasound diagnostics 12 days after the study revealed a fertilized egg and a yolk sac in the uterus.
How the procedure is performed
The patient sits in a chair with supports, similar to the one in a gynecological examination room. Anesthesia is administered intravenously and will last for 15 to 25 minutes. All this time, the patient will be asleep and will not feel anything, and the doctors will begin the diagnostic curettage procedure.
A speculum will be inserted into the vagina to expose the cervix, which will then be secured with special forceps. This is necessary to secure the uterus and avoid its possible displacement. A special metal rod, called a probe, is used to measure the uterine cavity by inserting it inside through the cervical canal. After this, the channel begins to expand. This is done using dilators of different sizes, which are inserted one by one into the cervical canal until it expands to such an extent that it can easily pass a curettage tool called a curette.
The shape of the curette resembles the shape of a small spoon with a sharpened side (the device has a long handle). The curette is inserted through the expanded canal into the uterine cavity, where curettage is performed with its sharpened side. The scraping is collected in a sterile jar for further sending for histology.
When combining diagnostic curettage with hysteroscopy, a hysteroscope is first inserted into the uterus, with the help of which the walls and cavity of the uterus are carefully examined, then curettage is performed. After the procedure, the hysteroscope is again inserted to once again examine the inside of the uterus to ensure that the curettage was carried out thoroughly.
After this, the forceps are removed from the cervix and the organ along with the vagina is treated with an antiseptic. Ice is placed on the patient’s stomach to speed up the contraction of the uterus and she is sent to the ward; after a few hours, or less often the next day, the patient is discharged with a course of antibiotic therapy.
Probability of error
In the early stages, the probability of error increases several times. Sometimes a woman herself does not suspect that she was pregnant. The risk of a frozen pregnancy decreases by the second trimester.
To independently check for a possible error if you suspect the cessation of intrauterine development of the embryo, pay attention to the following:
- History and course of previous pregnancies. There are always prerequisites for the appearance of anembryonia. These include an unhealthy lifestyle, gynecological diseases and more.
- Doctor's qualifications. However, you should not take medications if the situation with the embryo has not yet been clarified. It is better to undergo a paid examination in other clinics to eliminate errors.
- Unpleasant symptoms for the last 2 weeks. For example, the cessation of embryo development is indicated by such signs as bleeding after a positive test or the cessation of toxicosis.
During ultrasound, an error may be made in the early stages. That is why the study is repeated after 1–2 weeks.
To view a doctor about a similar pathology of pregnancy:
What should be normal and possible deviations
Thinning of the endometrium after cleaning, observed on ultrasound, is considered normal. The mucous layer will be restored by the next menstruation. With frequent abortions, the mucous membrane is injured, and its recovery becomes more and more insufficient each time. And finally, when a woman decides to give birth, the fertilized egg does not attach to the endometrium, and pregnancy does not occur.
There should be no particles of the fertilized egg remaining in the uterus, and its size will be restored within a week to a month.
There may be pink or bloody discharge after surgery. Their duration depends on the chosen method of abortion. If the discharge is slight, this is normal. Heavy bleeding indicates that fetal particles remain in the uterus or placental polyps are developing.
You will learn more about the consequences of medical abortion if you watch this video:
The appearance of pain and high temperature indicates an infection that has entered the uterus during a mini- or surgical abortion. To avoid infection, the doctor prescribes antibiotics. The presence of inflammation will also be visible on the ultrasound monitor.