Cervix during pregnancy
During pregnancy, the cervix undergoes many changes. Due to hormonal changes and increased blood circulation, her glands expand and grow. The muscle fibers located on the cervix during pregnancy turn into connective tissue.
She should maintain this appearance throughout her pregnancy. And towards the end it becomes softer and sharply shortens. Before labor begins, the internal cervical os usually expands.
Cervical length
This criterion is one of the main ones when examining a doctor. Its length should be shortened gradually. In the first trimester it is 45-35 mm long, in the second 34-24 mm, and by the third it reaches only 25-20 mm.
However, if its length does not reach acceptable values, then there is a serious risk of miscarriage.
The causes of shortening of the cervix may be:
- The presence of congenital anatomical changes. For example, lack of connective tissue;
- Hormonal changes at 15-28 weeks of pregnancy;
- Injuries, operations related to the muscle ring, as well as abortions and difficult childbirth.
During the normal course of pregnancy, the length changes as the fetus grows, and by the end of pregnancy it decreases sharply.
Monitoring of the cervix begins in the second trimester, since this is when pathologies can be detected using ultrasound. If, during an ultrasound scan at this time, a shortening of the length of the cervix and an enlargement of the pharynx are detected, this will indicate that the woman has isthmic-cervical insufficiency.
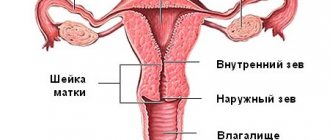
Vaginal examination
To determine the degree of readiness of the female genital organ, an obstetrician-gynecologist examines the vagina. In the maternity hospital, such an examination is carried out every 4-6 hours or in the presence of emergency indications, such as:
- amniotic fluid has broken;
- weak generic forces;
- polyhydramnios;
- narrow pelvis;
- before regional anesthesia;
- bleeding;
- painful contractions.
When examining the vagina, the doctor evaluates the thickness and degree of smoothing of the cervix. At the same time, the presence of scars on the soft tissue of the genital tract is determined. An obstetrician-gynecologist evaluates pelvic capacity and amniotic sac.
Based on subjective signs of dilatation, a partogram of labor activity is compiled. This group of signs includes the opening of the throat and contractions. The latter are assessed according to the following criteria:
- duration;
- power of manifestation;
- uterine activity.
Using a partograph, the dynamics of the opening of the pharynx is recorded. The obstetrician-gynecologist draws up a schedule. The horizontal curve displays the duration of labor in hours, and the vertical curve displays the dilation of the female genital organ in centimeters. Using the graph, the phase of labor is determined. If the curve rises steeply, then labor is effective.
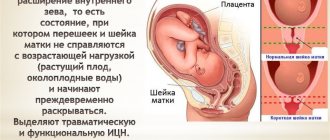
Isthmic-cervical insufficiency
ICI is the most common cause of miscarriage, that is, termination of pregnancy during the second trimester. This pathology manifests itself in the early opening of the cervix and its softening, which in turn serves as signs of termination of pregnancy. A miscarriage is caused by the dilation and opening of the cervix. This condition of the cervix leads to the fact that it is unable to hold the fetus in the uterus. Isthmic-cervical insufficiency can be of two types: organic (traumatic) and functional. The type of deficiency depends on the reasons why it formed.
Causes of isthmic-cervical insufficiency
Organic or traumatic ICI is caused by various injuries. The causes of organic (traumatic) ICI are:
- Presence of cervical injuries;
- Abortions or miscarriages;
- Scraping;
- Treatment of diseases such as cervical erosion or polyp.
Due to injury, the muscle tissue of the cervix becomes less elastic and scarred. Scar tissue, or scar, is made up of connective fibers that cannot stretch. The neck becomes stiffer. It also loses its ability to contract or stretch. Consequently, she is not able to hold the fetus inside the uterus. All this leads to the appearance of isthmic-cervical insufficiency.
Functional ICN is caused by the following reasons:
- Hormonal disbalance. It can be caused by too much of the male hormone androgen or by a lack of progesterone. This problem usually appears around the 11th week of pregnancy. The cervix dilates and becomes weak;
- Polyhydramnios. A very serious cause, usually occurs in multiple pregnancies. Due to which the load on the uterus increases and ICN is formed;
- Pathologies in the uterus;
- Violation of the ratio of connective and muscle tissues.
All these reasons lead to softening of the cervix. It becomes more pliable and is unable to hold the fetus due to its growth, which results in increased pressure. Also, this type of isthmic-cervical insufficiency is observed in girls and women with impaired ovarian function. The presence of congenital ICI cannot be excluded.
The cause of ICI can be not only one specific cause, but also several in the aggregate, since this disease is individual for each woman.
In each type of ICI, the cervix begins to dilate due to the inability to hold the fetus inside the uterus. This causes the fetus to sink lower, which often leads to fetal infections. Dropping lower, the fetus puts strong pressure on the cervix, thereby opening it even more. Which ultimately leads to miscarriage or premature birth.
Performing gymnastics
In order for the birth to be easy and without gaps, it is recommended to perform special exercises when the first contractions appear. This exercise relieves pain, stimulates the uterus, relieves tension and stress. During pregnancy, it is recommended to constantly perform special gymnastics, which:
- promotes the development of mobility and flexibility of the pelvic bones, preventing the occurrence of back pain during labor;
- provides comfortable sitting in the maternity chair by stretching the thigh muscles;
- prevents the appearance of hemorrhoids after childbirth by maintaining the tone of the pelvic and vaginal muscles;
- promotes timely dilatation of the cervix.
To give birth to a baby with minimal consequences and without pain, it is recommended to perform exercises for each muscle group from the 5th month of pregnancy. The pelvic bones can be prepared for labor in the following way:
- 1. The woman in labor kneels, leaning on her hands.
- 2. Palms are placed at a distance of 30 cm from each other, and knees at a distance of 20 cm.
- 3. Hips are perpendicular to the floor.
- 4. The back slowly bends, and the buttocks rise as high as possible.
- 5. The exercise is performed with a deep breath.
- 1. Feet join and knees move apart.
- 2. Hands clasp ankles.
- 3. The body bends forward.
- breaststroke swimming relieves stress and weight from joints;
- walking and squatting - gradually promotes the lowering of the fetus along the canal;
- riding on a swing.
The above methods are the impetus for the natural birth of a full-term baby. With the help of such exercises, the shape of the woman in labor is maintained. But if contractions have already begun, special gymnastics are indicated to relieve pain. At the same time, it provides a comfortable state during labor, reduces tension in the nervous system and muscles, and provides the uterus with the maximum amount of oxygen.
The following exercises are allowed between contractions:
- 1. Place your feet shoulder-width apart, with your arms down. As you inhale, the upper limbs spread to the sides, and as you exit, they lower. The brushes are shaken.
- 2. In the same starting position, pull your elbows back, lifting your legs forward one by one.
- 3. In a similar starting position, move your arms and torso to the side.
- 4. Sit on a chair with your knees bent and your soles touching. The knees are spread apart.
- 5. Lying on the floor, bend your legs one by one, while tilting your knees in different directions.
- 6. Slow walking with cross steps.
Signs by which one can recognize isthmic-cervical insufficiency
It is almost impossible to recognize ICI in the early stages of pregnancy. During the second trimester, cervical dilatation can be detected by vaginal examination, speculum examination, or ultrasound. It is necessary to recognize the presence of insufficiency as quickly as possible in order to prevent miscarriage.
ICN can be recognized by the following features:
- The appearance of discharge with blood;
- Severe pain in the lower abdomen;
- Feeling of strong pressure in the vaginal area;
- Shortening and softening of the cervix;
- The ability to see the amniotic sac during examination;
- Inappropriate cervical length for the trimester in which the pregnancy occurs;
- Opening of the throat.
If any of these signs are detected, immediate treatment must be prescribed. In more serious cases, the pregnant woman must be sent for preservation.
When insufficiency is detected, it is important to note that prolapse or, in other words, protrusion of the amniotic sac is protruding. The degree of threat can be determined based on where the amniotic sac is located.
There are 4 possible options for its location:
- The amniotic sac is located above the internal os;
- The amniotic sac is located at the level of the pharynx, but cannot be seen;
- The amniotic sac has dropped below the pharynx, that is, it has become located in the cervical canal and becomes noticeable upon examination. From which it follows that pathology has begun;
- The amniotic sac has descended into the vagina.
Therefore, a doctor can diagnose isthmic-cervical insufficiency using:
- Data that the woman had miscarriages in late pregnancy;
- Evidence that previous pregnancies ended in early premature birth. (Miscarriage);
- Information about the woman’s pregnancy through IVF;
- Data on prolapse of the membranes obtained during examination or established in past pregnancies;
- Data obtained during examination using a mirror, which show softening of the cervix and its shortening.
However, most often there are no symptoms, so it is difficult to determine even prolapse in advance. However, with the help of ultrasound, it is possible to establish the presence of isthmic-cervical insufficiency and determine the causes of its occurrence.
Symptoms of labor
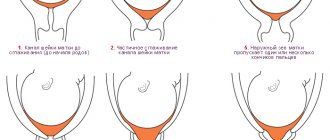
There are no symptoms when the female genital organ is dilated. This phenomenon can only be determined by an obstetrician-gynecologist by examining the vagina. To find out what happens to the cervix during labor, you need to study obstetric terms. Obstetricians-gynecologists determine the opening of the uterine pharynx using their fingers.
The measurement of the “obstetric finger” is carried out in centimeters. The opening of the cervix in one finger is equal to 2-3 cm. If the uterine os has opened by 3-4 cm, the uterus has opened equally. Regular contractions are indicated by the opening of the cervix to 4 fingers. If it is smoothed, then patency of 5 fingers is allowed.
The first signs of labor appear 2 weeks before the baby is born. The bottom of the organ drops within 2-3 weeks before the onset of contractions. In this case, the fetus is pressed against the pelvis. The woman in labor experiences the following sensations:
Treatment of isthmic-cervical insufficiency
Treatment is prescribed by a doctor after determining the exact cause of the appearance of ICI. For functional ICI, hormonal therapy is most often prescribed. It allows you to restore normal hormone levels and lasts 1-2 weeks. As the situation improves, medications are continued to maintain hormone levels and prevent cervical dilatation.
The next treatment option for ICI is the installation of a unloading pessary, which is called a Meyer ring. Its essence lies in the fact that a plastic ring is placed in the pregnant woman's vagina, which supports the cervix. This ring prevents early labor and cervical dilatation by evenly distributing the weight of the fetus. This method can be used at any stage of pregnancy, but it should only be used as an auxiliary method.
Another method is suturing. It is used in extreme cases when the pessary fails. The internal pharynx is sewn together so that it cannot open further. Suturing is a more serious method, which involves surgery at 17 weeks or slightly later.
Stimulation without drugs
It is also possible to stimulate the uterus without the use of various types of medications. It is possible to carry out such actions at home, but in any case you should first consult a doctor, because in some cases complications are possible. You can induce uterine contractions using a regular enema. Doctors have repeatedly noticed that after this pathology occurs, the mucous plug comes out, which allows the uterus to begin to open. However, in this case, you need to know that an enema is possible only if the day of the scheduled birth has already passed.
You can stimulate the dilatation of the cervix in a natural way as a result of sex. The uterus begins to contract, and increased blood flow is observed. Sperm also contains prostaglandins, popularly called the “birth hormone.” Speaking about stimulating the dilation of the cervix without the use of medications, it is necessary to note physical activity. in this case, it is recommended to walk up the stairs, walk for a long time, and do household chores. However, this technique is prohibited if a woman has placenta previa, hypertension and gestosis.
To summarize all of the above, it should be noted that none of the described actions can be carried out on your own initiative, without prior consultation with a gynecologist. Otherwise, you can harm not only your health, but also your child. Having all the necessary information, you can prevent such an unpleasant problem as the lack of dilatation of the cervix.
When entering a maternity hospital, every woman experiences serious stress, especially when this happens for the first time. And this is connected not only with the change from the usual environment of her home to a hospital one, but also with the fear of what awaits her, of the unknown, and various terms from doctors, incomprehensible to the expectant mother, only intensify the state of stress and anxiety.
Perhaps the first frightening term for a woman when examined by a doctor in a maternity hospital is “cervical dilatation,” because it is this indicator that determines the body’s readiness for childbirth.
It is important to understand the meaning of medical terms and indicators, since understanding what the doctor is talking about will allow the woman to feel calm and comfortable.
Papaverine (indications for use and beneficial properties)
As mentioned above, many women during pregnancy are associated with dilatation of the cervix in the second trimester, which leads to isthmic-cervical insufficiency or uterine hypertonicity. In order to prevent these types of pathologies, pregnant women are prescribed papaverine. Papaverine is a medicine that is produced in the form of suppositories or tablets.
This tool can cope with many problems. When muscle spasms occur, there is a need to eliminate them, which is possible with the help of progesterone. The lack of this hormone leads to uterine hypertonicity. Papaverine is also prescribed to increase this hormone. It helps relieve spasms and improve blood circulation in the reproductive organs.
This drug is not recommended for use in early pregnancy. The need for its use appears in the second and third trimester.
During this period of pregnancy, papaverine is used for abdominal pain and high blood pressure. However, it must be taken in combination with other medications. The drug helps relieve abdominal pain, prepare the cervix for childbirth, and also relieve pain during contractions.
Papaverine has a beneficial effect on the muscles of the uterus, relaxing them. The drug can also prevent the threat of miscarriage. The most important advantage of the medication is that it does not have a negative effect on the fetus.
Papaverine is prescribed in cases of threatened miscarriage and premature birth, as well as in the presence of uterine hypertonicity.
Girls and women who have kidney pathology and hypersensitivity to the substances contained in the drug are prohibited from taking the drug.
Papaverine is often prescribed before childbirth to significantly soften the cervix.
If there is a diagnosis of isthmic-cervical insufficiency, the use of papaverine is combined with magnesium sulfate. Usually these drugs are given on droppers. Medicines have a calming effect on the uterus. At the same time, it is necessary to give injections of papaverine to prevent the cervix from dilating even further.
It is recommended to use the drug in suppositories, as they are absorbed faster than tablets.
Video: 2nd trimester. Tonus, ultrasound, big gains
2nd trimester // TONUS/ Ultrasound/ BIG INCREASES
Video: ICN. My bedridden pregnancy
ICN. My bedridden pregnancy.
Video: my pregnancy 2nd trimester
My pregnancy is 2nd trimester. My doctor is a man
Phases of the uterine os
The first stage of labor is considered the longest. The uterine os opens during 2 phases: latent and active. The first of which lasts 5-6 hours from the first period. In this case, pain is absent or appears to a minor extent. The frequency of contractions is less than 2 in 10 minutes. The uterus contracts once every 30-40 seconds and relaxes once every 80-120 seconds. After each contraction, the visible part of the cervix is shortened, and the lower segment of the organ is lengthened.
The ongoing processes help fix the baby's head at the entrance to the pelvis. The amniotic fluid is divided into anterior and posterior. During the first birth, the latent phase is longer than during subsequent births. At the end of the phase, complete smoothing of the cervix occurs.
In the next phase, the uterus dilates from 4-8 cm. The frequency of contractions increases to 3-5 times in 10 minutes. The uterus contracts and relaxes for the same period (60-90 seconds). The active phase lasts 3-4 hours. During this period, intense labor activity is observed, the neck of the genital organ opens faster.
The baby's head moves through the birth canal. The cervix has descended down the uterine segment. At the end of the phase, the pharynx opens, the amniotic sac opens, and water pours out. If the cervix has opened to 8-10 cm, and the waters have receded, this is a timely outpouring of water. If the waters have broken and the cervix has opened up to 7 cm, it is an early rupture of water. When the pharynx dilates more than 10 cm, amniotomy is indicated.