This article is posted for educational purposes only and does not constitute scientific material or professional medical advice. Always trust your doctor first!
Inflammation of the cervix is one of the most common diseases of the female reproductive system. According to statistics, about 70% of patients who seek help from a gynecologist face this problem. Most often these are girls and women of childbearing age. Both the inflammation itself and its complications can negatively affect the process of bearing and giving birth to a child and the very possibility of conception.
Development of isthmic-cervical insufficiency
In order to understand what ICN is, it is worth understanding physiology. The child in the womb continuously develops and, of course, increases in size. The uterus grows symmetrically to the fetus, as it has smooth muscles. The uterus is connected to the vagina, cervix, and at the very junction of this connection there is an isthmus, which contains muscle and connective tissue. All this is a ring that prevents the baby from being born prematurely. But this happens during the normal course of pregnancy.
Isthmic-cervical insufficiency during pregnancy is a pathology in which the cervix and isthmus fail to perform their main function.
As a rule, this pathology is especially dangerous when it comes to the second trimester of the first pregnancy. Almost ten percent of pregnant women suffer from this disease during this period. However, this does not mean that women undergoing a second or subsequent pregnancies are insured against it.
Cervicitis: general information
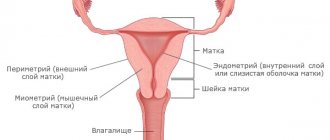
Photo of cervicitis
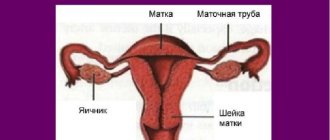
The cervix is a muscular tube about 4 cm long and about 2.5 cm wide, covered with epithelium. This is the junction of the vagina and the uterine cavity. The main function of this organ is to prevent the penetration of pathogenic infection into the uterine cavity, and then into the fallopian tubes and ovaries.
The cervical canal, located in the vaginal part of the cervix, is a fairly narrow formation. It prevents harmful microorganisms from penetrating into the uterine cavity due to the mucous plug that closes it, as well as due to the secretion secreted by the glands of the cervix. If such protection is violated, then the cervical canal can no longer perform its barrier functions and the process of inflammation of the cervix or cervicitis begins.
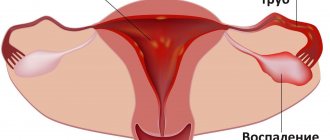
If inflammation occurs on the outer part of the cervix, which extends into the vagina, then exocervicitis is diagnosed; if the epithelium of the cervical canal becomes inflamed, then they speak of endocervicitis.
During the inflammatory process, the tissues of the walls of the cervical canal become swollen, the vessels of the cervix enlarge, and vasculitis occurs. With a prolonged course of the disease, vaginal varicose veins may also develop.
The lining of the cervical canal walls produces a large number of immune cells to fight infection. If they cope with this task, the disease goes away. If, for various reasons, this does not happen, then the process enters the chronic stage. In this case, it can last for years, periodically exacerbating.
Causes of cervicitis
Cervicitis is an infectious disease in which pathogenic microflora causes an inflammatory reaction. It can be
- infectious agents that enter the body exclusively through sexual contact. It is impossible to become infected with them if, for example, you sunbathe in a solarium without underwear or visit a sauna. This is a specific microflora: pathogens of gonorrhea and syphilis, as well as trichomonas, mycoplasma, ureaplasma, chlamydia and other pathogens of STDs.
- microbes that are commonly called opportunistic - nonspecific microflora; opportunistic microorganisms penetrate the cervix through the blood, lymph, or from the rectum. This could be staphylococcus, streptococcus, fungus of the candida family, E. coli, Klebsiella and others.
Cervicitis can have a different character
- Purulent, as a result of which the cervical canal is filled with pus. As a rule, the causative agent of this form of the disease is gonococci or opportunistic microorganisms.
- Productive when excess connective tissue, scars and septa occur during the healing process of inflammation.
- Proliferative, as a result of which the epithelium of the cervical canal grows and polyps form.
Factors that provoke inflammation of the cervix
Inflammation of the cervix can be caused by a variety of reasons. These are diseases that provoke the development of cervicitis, as well as the patient’s lifestyle itself.
- The main cause of inflammation of the cervical mucosa is sexually transmitted diseases. First of all, these are gonorrhea and trichomoniasis - they account for about 25% of cases of cervicitis. But, as mentioned above, inflammation can also be caused by other bacteria and viruses that enter the body during sexual contact. The disease can be provoked by ureaplasmosis, chlamydia and other similar diseases.
- The cause of the spread of the inflammatory process is also viral diseases, as well as diseases caused by staphylococci and streptococci. This may be a disease of the gastrointestinal tract of a bacterial nature and even sore throat or pneumonia.
- There is a risk of the onset of an inflammatory process on the surface of the cervix with a general weakening of the immune system and the resulting vaginal dysbiosis.
- The condition of the cervical mucosa and characteristics of sexual life are also affected: constant change of sexual partners, improper use of contraceptives, in particular spermicides, douching with acid-containing products.
- There is a risk of cervicitis if the cervix is injured during an artificial abortion, a hysteroscopy procedure, or the installation and removal of an intrauterine device.
- Cervicitis can also develop in women during menopause. The so-called age-related inflammation of the cervix is due to the fact that the amount of estrogen in the blood of postmenopausal women decreases. As a result, the secretion of the cervical canal decreases, and it itself becomes thinner and therefore can begin to become inflamed.
- In rare cases, the cause of inflammation of the cervix may be an allergy to the latex from which condoms are made, as well as spermicides and lubricants used during sexual intercourse.
Why is cervicitis dangerous?
This disease does not directly threaten the patient’s life, but the following consequences may occur:
- The development of chronic inflammation of the cervix, which can subsequently spread to the uterus and appendages, affecting the peritoneum, bladder and kidneys.
- In advanced cases, adhesive disease of the pelvic organs develops, as a result of which the woman will not be able to become pregnant naturally.
- Sometimes inflammation in the uterus causes the development of cervical cancer.
Symptoms of cervicitis
Recognizing the disease can be quite difficult, especially if its course is chronic. A woman, especially a pregnant woman, can easily mistake minor changes in well-being for manifestations of psychosomatics.
You may suspect acute cervicitis if the following signs are observed:
- The nature of vaginal discharge changes, its quantity increases, and it acquires an unusual color and consistency. The nature of the discharge may vary depending on what caused the inflammation. So, with purulent cervicitis, they have an unpleasant odor, yellow-green color and thick consistency. With viral inflammation or chlamydia, cloudy yellowish or white mucus is observed.
- There may be nagging pain in the lower abdomen; sometimes a woman experiences pain during sexual intercourse. However, often inflammation of the cervix is not accompanied by pain.
- There may be a small amount of bloody discharge from the genitals before or after menstruation. Discharge becomes especially abundant after sexual intercourse.
- In the acute form of the disease, a sharp increase in body temperature to 38-39 degrees, enlargement of nearby lymph nodes, and signs of general malaise are possible.
Chronic cervicitis can occur with almost no symptoms. Often the only signs of the disease are white or yellow discharge from the genitals with virtually no odor, as well as uncomfortable sensations and pain during sexual intercourse.
In rare cases, if the cervical canal has completely lost its patency, a prolonged delay in menstruation may occur. In this case, women most often turn to gynecology regarding suspicion of pregnancy.
What causes isthmic-cervical insufficiency?
A weakening of the muscle ring, as a rule, results from decreased tone or a disturbed cervix. In addition, ICI may be affected by individual anatomical features or impairment of basic functions. Previous abortions, curettage, ruptures, and even breech presentation of the fetus - all this can contribute to the development of isthmic-cervical insufficiency and, as a result, the loss of the child.
Functional disorders are considered:
- Hyperandrogenism;
- Excess of androgens contained;
- Congenital dysplasia;
- Multiple pregnancy;
- Hormonal deficiency.
Typically these disorders occur in the first trimester. Starting from the twelfth week, the functioning of the child’s pancreas begins to affect the cervix if the mother’s androgens are excessive.
In addition, poorly functioning ovaries can affect isthmic-cervical insufficiency.
If a woman is carrying more than one child or has developed polyhydramnios, the cervix receives increased stress, which can also lead to ICI.
If a pregnant woman has underdeveloped genital organs, cervical rupture may occur and, as a consequence, cervical insufficiency. Most often this happens in the period from the sixteenth to the twenty-seventh week, but it can happen much earlier - at the twelve week period.
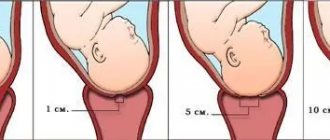
If the cervix shortens to a length of less than twenty-five centimeters in the twentieth to thirtieth weeks of pregnancy, premature birth may occur. If a specialist discovers at least some problems in a woman that could affect the development of ICI, she is put under special control. The cervix is constantly monitored, monitoring and ultrasound are performed.
The first signs of cervicitis
In acute cervicitis, signs of the disease are immediately noticeable. The woman develops copious mucopurulent discharge and pain in the lower abdomen. During a gynecological examination, swelling and hyperemia of the cervical canal, protrusion of the mucous membrane, and disruption of its structure (hemorrhage) are clearly visible. Discomfort and excessive discharge forces a woman to consult a doctor.
Chronic cervicitis occurs in an erased form and is often discovered by chance during a routine examination.
How to recognize isthmic-cervical insufficiency during pregnancy
Unfortunately, in most cases, a woman may not notice the danger and does not feel that her pregnancy is at risk. This is due to the fact that the dilation of the cervix occurs very slowly and does not have any characteristic signs. The only thing that can make a pregnant woman think that something is wrong is slight cramps in the abdomen.
A gynecologist sees this picture differently. Thanks to the gynecological speculum, he can detect a shortened and softened cervix in a state of dilatation, as well as the closure of the external pharynx and canal.
At the very beginning of pregnancy, a woman may notice bleeding and experience abdominal pain. This symptom is the first reason for concern. The main thing is to start active and rapid treatment.
Diagnosis of cervicitis
As a rule, the diagnosis of cervical inflammation is made during a routine examination or when visiting a doctor for other reasons.
The gynecologist makes a conclusion based on visual examination data, as well as test results.
During an examination in the mirrors, the doctor may detect the following signs of the disease:
- the cervix is enlarged due to inflammation;
- swelling is observed;
- a zone of erosion around the external pharynx is visible;
- there are various types of discharge from the cervical canal;
- There are pinpoint hemorrhages on it.
During the postmenopausal period, such a diagnosis can be made if there is thinning of the mucous membranes of the cervix and external genitalia.
Colposcopy helps clarify the diagnosis, as a result of which various complications of the disease can be identified.
As a rule, when inflammation is detected, a woman is given a number of concomitant diagnoses, including
- cervical erosion;
- colpitis - inflammation of the vaginal mucosa;
- vulvovaginitis - inflammation of the tissues of the vulva and vagina;
- bartholinitis - inflammation of the large gland of the vestibule of the vagina;
- endometritis – inflammation of the inner layer of the uterus;
- adnexitis - inflammation of the uterine appendages, etc.
This is explained by the fact that the causative agents of cervicitis are capable of inflaming not only the cervical area. They have an active effect on tissues and organs located in close proximity to it.
Laboratory diagnostic methods
The final diagnosis is made only after conducting and interpreting the results of a number of laboratory tests. The doctor may prescribe the following procedures:
- Swabs are taken from the vagina, urethra and cervix to determine the nature of the causative agent of the disease.
- The presence of sexually transmitted infections is checked using the PCR (polymer chain reaction) method. This test has a high degree of accuracy and does not produce false positive or false negative results.
- A cytology smear is taken from the cervix to identify possible pathological changes of a malignant nature, in particular dysplasia and other precancerous conditions.
- After examination in the mirrors, colcoscopy and cytological examination, the doctor may prescribe a histology test - a diagnostic procedure that allows you to most accurately identify the possibility of pathologies such as cervical cancer, dysplasia, endometriosis, fibroids, etc.
- Bacterial culture of vaginal discharge allows you to determine the causative agent of the infection.
- A blood test is performed for syphilis and HIV.
In order to correctly prescribe treatment, it is extremely important to identify the cause that caused the inflammation, since the same pathology can be caused by different pathogens. Thus, inflammation of the cervix is only part of the clinical picture of many diseases caused by completely different reasons.
Why is ICN dangerous?
It is a well-known fact that the human body contains not only beneficial and harmful bacteria, but also all kinds of infections. If usually many of them do not cause any serious problems to a person, then during pregnancy many of them become a kind of ticking time bomb. Some can affect the health of the child, others even affect the ability to give birth on time. While the cervix is dilating, amniotic fluid can flow out of the uterus at any time. As a result, the fetus becomes defenseless to the environment and can not only be infected, but also be completely rejected by the body.
We recommend reading: Miscarriage, Retrochorial hematoma during pregnancy, Leg cramps during pregnancy
As soon as the cervix dilates, the baby descends and if you do not react in time, premature birth or miscarriage may occur.
With this scheme, a woman learns that labor has begun precisely by the rupture of amniotic fluid, which in turn is a consequence of isthmic-cervical insufficiency. If the period is too short and the dilatation is large, the chances of saving the child are minimal.
What are the dangers of inflammatory diseases of the female genital organs?
During pregnancy
Inflammatory processes in the ovaries can lead to disruption of their functioning, while ovulation—the release of an egg from the ovary—does not occur at all (in this case, pregnancy is impossible) or occurs late. So, if normally ovulation occurs in the middle of the cycle, then with chronic salpingoophoritis, as a result of a disruption in the production of ovarian hormones, it occurs later than expected, almost before menstruation. In place of the egg after ovulation, a special gland is formed - the corpus luteum. This gland produces the hormones progesterones, which ensure the onset of pregnancy and are the main supporting factor in the first trimester. In chronic salpingoophoritis, ovulation occurs untimely, and the corpus luteum does not work fully, producing an insufficient amount of progesterone. This factor often causes the threat of termination of pregnancy in the first trimester.
As already mentioned, the main cause of ectopic pregnancy is also the inflammatory process. As a result, connective tissue grows and the lumen of the fallopian tubes narrows. In addition, the work of the cilia of the ciliated epithelium, the cells that cover the inside of the fallopian tubes and promote the advancement of the egg into the uterine cavity, is disrupted.
Features of childbirth
As a rule, labor with ICI is quite rapid. In order to minimize risks, the pregnant woman is placed under medical supervision. Next, she is continuously monitored and a course of therapy is prescribed until her condition returns to normal. Otherwise, the process of childbirth and the postpartum period is identical to women who do not have such problems.
If the cause of isthmic-cervical insufficiency is anatomical features, the woman may be prescribed a cesarean section so as not to injure the cervix.
If a woman strictly follows the doctors’ recommendations, there is every chance of saving the pregnancy and the baby.
How is ICI diagnosed?
As a rule, diagnosis is difficult due to the absence of symptoms. That is why you should not ignore scheduled visits to the gynecologist and avoid vaginal examinations. If this is not the first pregnancy and the woman has previously experienced such a pathology, the doctor monitors her even more closely than usual.
The responsibilities of a pregnancy specialist include monitoring the softening, length and dilatation of the cervix. In the early stages, this is done using ultrasound. In case of any deviations from the norm, he prescribes treatment appropriate to the situation.
In addition to ultrasound, X-rays are also used, which is performed by injecting a contrast agent into the uterus.
What is “cervicitis”?
An inflammatory process in the cervix, which can appear in women of any age and have an infectious and non-infectious etiology. More often, inflammation occurs after infection, and not vice versa.
Cervicitis is rarely an independent disease. As a rule, it is accompanied by colpitis, urethritis, endometritis or other pathologies of the woman’s genitourinary system.
The disease is characterized by certain symptoms, which, in the absence of an accurate diagnosis, can be confused with other similar pathologies. The range of infections that can provoke inflammation of the cervical canal is quite wide. Nonspecific pathogens usually enter through the bloodstream from other foci of inflammation, while specific pathogens enter through sexual contact. In addition, mucosal disorders can be caused by parasitic infections and various injuries.
The cervix is an important barrier that prevents infection from entering the reproductive organs. Under the influence of unfavorable factors, including infection, the protective properties of the cervix are reduced, which leads to the development of an inflammatory process and danger to other organs (uterus, fallopian tubes, ovaries).
Untimely or incorrect treatment can lead to chronicity of the process and subsequently to the development of erosion or hypertrophy.
The main category of patients are women of reproductive age. With regular visits to the gynecologist, the pathology is easy to notice and eliminate at the initial stage. Unfortunately, many discover it when the consequences have already occurred (miscarriage, erosion, polyps of the genital tract).
Basic treatment methods for ICI
If the diagnosis of isthmic-cervical insufficiency during pregnancy is confirmed, treatment is prescribed immediately. It can be either conservative or operative.
In cases where the cause is hormonal imbalance, hormone treatment is usually used. Thanks to correctly prescribed medications, hormonal levels can be restored within one to two weeks.
Next, the pregnant woman undergoes repeated tests and undergoes an examination, however, even if after this the opening stops, the drugs must be taken for some more time.
If hormonal therapy does not bring visible results, they resort to a pessary. A pessary is an oval or round plate, usually plastic or silicone. It is needed to forcefully narrow the internal pharynx.
Causes and prevention of cervicitis
The following factors can lead to inflammation of the cervix:
- Sexually transmitted diseases (chlamydia, gonorrhea, trichomoniasis). Transmitted sexually, affecting neighboring areas (urethra, vagina).
- Papillomavirus and genital herpes.
- Allergic reaction to latex or lubricant components.
- Activation of opportunistic flora after exposure to unfavorable factors (stress, hypothermia, rough sex, frequent douching).
- Poor hygiene, in particular, prolonged use of tampons during menstruation.
- Women's hormonal imbalances.
- Injuries to the cervix during diagnostic procedures, childbirth or abortion.
- Early onset of sexual activity or frequent changes of partner.
The vast majority of cervicitis is caused by sexually transmitted infections. To prevent infection, it is recommended to use barrier methods of contraception or have one sexual partner with whom the woman has previously undergone all the necessary examinations.
In case of accidental unprotected contact, infection can be prevented with the help of special medications. A prerequisite is the start of preventive measures within 1-2 days after contact. A doctor or a pharmacist at a pharmacy can recommend a medicine. One of these remedies is Miramistin.
A pessary is prescribed for:
- Incomplete closure of the pharynx;
- Multiple pregnancy.
A pessary is a kind of corrector. It reduces the load on the uterus, fixes the cervical canal, and completely closes the cervix.
The convenience of this method also lies in the fact that you can resort to it at any time. When installing a pessary, no painkillers are required, and in order not to disturb the microflora, the vagina is constantly sanitized and monitored using smears. In addition, the gynecologist must constantly monitor whether the structure has shifted. It is removed only at thirty-eight weeks or shortly before the expected date of birth.
By the way, a pessary can also be placed on a non-pregnant woman, while she is at the stage of planning conception. If she is faced with constant involuntary miscarriages, premature birth, as well as problems with the uterus (flabby, short), this procedure is sometimes life-saving.
However, this treatment option is not suitable for everyone. For example, if a woman suffers from diseases of the kidneys, liver, heart, or certain fetal defects were detected during previous pregnancies, a pessary will not be made.
Treatment of cervicitis
Treatment will only be effective if the underlying cause of the disease is eliminated. To do this, it is important to determine the pathogenic microflora that is present in the cervical canal and vagina, as well as to identify provoking factors that can cause relapse (a large number of sexual partners, stress, decreased immunity, and others).
Treatment of cervicitis consists of a comprehensive regimen, which may include:
- Antimicrobial drugs - antibiotics, antiviral or fungicidal agents, depending on the pathogenic flora isolated. For chronic cervicitis, the course of treatment will be longer. Depending on the area affected and the underlying cause of the disease, these medications may be prescribed in the form of vaginal patches or oral tablets. It is important not to interrupt the course of treatment, as it will then have to be repeated again.
- Hormonal drugs are prescribed when the cause of cervicitis is a hormonal imbalance. The gynecologist can prescribe such drugs both locally and for systemic use, for example, oral contraceptives.
- Immunostimulants. They are used for the viral etiology of cervicitis, as well as for women with reduced immunity as an additional line of therapy.
- Local antiseptics and anti-inflammatory agents. This includes douching or tampons soaked in a solution of chlorophyllipt, dimethyl sulfoxide, and silver nitrate.
- Vitamins. Prescribed as an additional line of therapy for any etiology of cervicitis.
Chronic cervicitis and inflammation caused by a viral pathogen are the worst to treat. For example, to get rid of the papilloma virus, treatment with interferons, cytostatics, as well as surgical removal of condylomas is necessary. In chronic cases, conservative drug therapy may be ineffective, so the patient is prescribed surgical treatment (laser therapy, cryotherapy, diathermocoagulation, etc.). However, before such methods, you should make sure that there is no infection in the genital tract.
If a specific infectious pathogen is identified, both sexual partners should undergo treatment, and sexual intercourse should be avoided during therapy.
Simultaneously with the elimination of the underlying cause (hormonal disorders, infection), a woman may be prescribed symptomatic medications to eliminate inflammation and itching. After a few weeks, a follow-up examination and bacteriological culture are carried out.
It is highly not recommended to self-medicate, especially with popular folk recipes. For example, douching disrupts the balance of vaginal microflora, reduces local protective properties and is not as beneficial as many people think. Folk remedies can only be used as an additional line of therapy. In this case, you should ask your doctor’s advice about which ingredients and in what form are best to use.
Surgical methods for cervical correction
For a pregnant woman, specialists may prescribe a surgical treatment method, such as cervical plastic surgery. In this case, sutures are placed on the pharynx using non-absorbable threads (as a rule, silk threads are used).
Before resorting to this method, all the nuances of a particular patient are studied. As a rule, the deadline for this procedure is seventeen weeks, however, in some cases it is done later. This operation is performed under general anesthesia. Anesthesia is selected very carefully so that it in no way affects the further course of the pregnancy or the baby.
Surgical correction is prescribed:
- For early miscarriages and premature births;
- With a progressive form of deficiency;
- For signs of isthmic-cervical insufficiency.
On the eve of the operation, a smear is taken to study the flora, and immediately before the operation, the vagina is sanitized. When there is uterine tone, medications are prescribed that can reduce it.
After the operation is completed, bed rest is usually not prescribed. You can immediately get up and walk, however, you need to adhere to prevention through No-shpa, Papaverine and Electrophoresis. The time during which you will need to stay in the hospital depends on what stage the ICN is at and on the course of the pregnancy as a whole. Typically this takes about five days. After this, every couple of weeks the woman needs to be seen by an observing doctor, who will examine the uterus using a mirror.
In this case, the exception is women with a sealed bladder; they are prescribed bed rest for more than a week.
If no complications are observed due to the stitches, then they are worn until the thirty-eighth week without touching, since after removal, labor may begin immediately.
If labor begins before the stitches are removed, the woman must urgently go to the hospital and report the stitches upon arrival so that they can be removed before they can injure the uterus.
In exceptional cases, threads can cut through tissue. This occurs due to the fact that the uterus contracts too actively, the cervix is severely stretched, or an inflammatory process has begun. It happens that the culprit is a specialist who performed the operation incorrectly.
When correction and surgery cannot be performed
Despite the fact that these treatment methods have been practiced for a long time and are not complex procedures, there are cases when these treatment methods are contraindicated.
The reasons for this may be:
- Bleeding;
- Inflammation in the pelvis;
- Internal fetal malformations;
- High uterine tone.
By the way, a pessary cannot always be inserted. Contraindications to it are also inflammation and repeated bleeding in the next trimesters. In addition, it is not done if we are talking about the so-called frozen pregnancy.
Symptoms of cervicitis
The cervix has a mucous and epithelial layer. Some pathogens show affinity for a certain type of tissue, for example, Trichomonas and chlamydia primarily affect the epithelium. With this etiology, the disease can go undetected for a long time. If the inflammation affects the mucous layer, the patient immediately notices intense discharge.
The color of the discharge depends on the nature of the pathogenic flora. They can be from white-yellow to gray-green, and may also contain blood. The consistency of the secretion also changes from liquid to thick. A woman cannot independently determine from which part of the cervix the discharge comes, as well as which microbe provoked it. Gynecological examination and tests are mandatory.
With a long course of cervicitis, colpitis and inflammation of the urinary tract join it. This causes additional symptoms and discomfort in the woman.
Symptoms that may appear with cervicitis:
- copious discharge;
- pain in the lower abdomen;
- frequent urge to urinate;
- discomfort during sexual intercourse;
- spotting after sex.
During a gynecological examination, the doctor notices the following changes:
- swelling and hyperemia of the cervix;
- minor hemorrhages;
- loose fabric structure;
- the presence of condylomas, ulcerations, erosion, discoloration of some areas;
- involvement in the inflammatory process of the vagina.