The uterus is the main female organ, the main purpose of which is to bear offspring. Throughout pregnancy, this organ, together with the growing fetus, greatly increases in size, and a few weeks after birth it returns to its original state. In addition, a woman's uterus may enlarge slightly with age.
Of course, these reasons are not pathological, but in other situations, an enlarged uterus may indicate serious diseases of the female genital area. In this article we will tell you about the cases in which the uterus can be enlarged if you are not pregnant and the test shows a negative result.
Cervical hypertrophy - causes
The causes of hypertrophy are due to the influence of many factors, including low location of organs and frequent diseases of the endocervix. Myoma is one of the causes of this phenomenon.
Cysts and genetic predisposition play a very important role in the development of hypertrophy. Hypertrophy occurs due to chronic inflammation. At the same time, tissues of the cervical canal grow in, which contributes to blockage of the passages.
Unfortunately, the disease can lead to infertility. In this case, an increase in the size of the cervix is observed, which occurs due to hyperplasia and hypertrophy.
Promotion
The process can be neurohumoral (natural), i.e., an increase in the size of the uterus occurs as a result of increased work of the endocrine glands during pregnancy, lactation or during menstruation.
Experts call this condition working; it does not require any medical care and does not cause the woman any particular inconvenience. Pathology is when uterine hypertrophy is provoked by any abnormal processes in the organ itself or by traumatic injuries. For example, the uterus can increase in size due to fibroids, endometriosis, a malignant tumor, and this can also be a consequence of surgical interventions, abortions, complicated childbirth, etc.
On a note:
Often the cause of uterine hypertrophy can be excessive secretion of hormones that stimulate the enlargement of the organ both as a whole and in its individual parts.
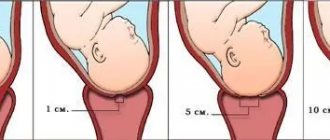
Cervical prolapse is divided into three stages:
- The external pharynx is located several centimeters above the labia.
- The pharynx is located at the level of the labia.
- The throat extends beyond the intimate lips.
To choose treatment tactics, it is very important to determine the degree of prolapse. If in the first stage the defect can be eliminated with the help of special exercises, then in the third stage surgical intervention is required.
With a prolonged course of the disease, which has become chronic, women complain of the following symptoms: discomfort in the groin, a feeling of the cervix falling out, pain during sexual intercourse, infertility, dull pain in the lower abdomen.
Location depending on cycle phase
Menstruation is a natural process that occurs in a woman every month. The main purpose is preparation for conception. It consists of:
- secretory stage;
- menstrual stage;
- proliferative stage.
The ovaries have the following phases:
- follicular;
- ovulatory;
- luteal
Attention! The uterus and ovaries are organs that perform different functions, but their phases must proceed synchronously. Otherwise, a woman may experience infertility, severe hormonal imbalances and other reproductive dysfunctions.
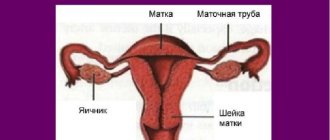
The cervix provides communication between the vaginal canal and the uterine cavity. It performs a drainage and protective function, ensuring the prevention of infectious flora from entering the cavity of the main reproductive organ. The way the cervix works depends on the phase of the cycle; at certain moments it rises or falls, changes its consistency, becomes elastic, soft or loose. Changes occur because during the cycle the cervix changes its position due to changes in tone that occur due to hormonal fluctuations.
Menstrual stage
During menstrual bleeding, organs are susceptible to bacterial infection. Due to the risk of infection, gynecologists do not recommend that women use tampons constantly and have sex with a partner without using a condom. On such a day, you cannot conduct an examination yourself and, if possible, it is better to postpone a visit to the gynecologist.
Normally, girls' periods last from 3 to 7 days. If the cycle lasts less than 4 days, it is considered short. During bleeding, the cervix lengthens and looks like a cone. This change can be seen by the gynecologist during the examination. Other symptoms may appear: abdominal pain, nausea, mood changes due to the action of hormones. There is slight redness of the genitals. On the first day or the day before, your breasts may swell.
It is interesting to note that the duration of the cycle in girls can vary. Menstruation can last 5 days, after an interval of 28 days, and then the duration and abundance decreases or increases. Such changes do not always indicate the development of pathology, but should be a reason to consult a doctor.
During menstrual bleeding, the cervix meets the following characteristics:
- low tone;
- the cervix is drooping;
- peeling of the lining layer of the vagina is observed;
- the external pharynx is slightly open;
- cervical fluid is released in an average volume;
- acidity level is about 7.
This period occurs in conjunction with the follicular phase of the ovary, after which the reproductive organs and gonads are prepared for ovulation.
Proliferative stage
After menstrual bleeding, the endometrial layer is restored in the uterine cavity. Tissues grow due to the division of cells that form the integumentary and glandular epithelium. Stromas and blood networks are formed in the tissues of the lining membrane.
Interesting! Translated from Latin, proliferation means the creation of offspring. The course of this stage coincides with the second stage of the follicular phase and ends during the period of ovulation.
After menstruation, the following changes are characteristic of the cervix:
- thickening of the mucous membrane of the cervix occurs;
- the neck descends;
- the external pharynx narrows;
- the acidity level reaches 7.3 units.
The mucous membrane of the cervix consists of cylindrical cells that produce cervical fluid. Thick mucus clogs the opening of the pharynx and provides a barrier function, preventing the penetration of bacteria through the pharynx into the uterine cavity. After the release of the egg, the cervical fluid becomes watery and slippery, this condition makes it easier for sperm to penetrate the cervix.
Secretory stage
After ovulation, changes in the cervix occur synchronously with the luteal phase of the ovaries, the tone of the uterus gradually decreases and its consistency becomes soft. The external pharynx opens to the maximum and allows the tip of the finger to pass through. The diameter of the canal expands, the neck of the organ is located high, which makes it possible to shorten the path of sperm to the fallopian tube. The acidity of the channel also changes, it increases and is about 8 units. The glands located inside secrete secretions. Mucus flows out in significant volumes, it is transparent or white, non-sticky.
If fertilization has not occurred, a week after ovulation, preparation for the menstrual stage begins. A plug forms in the canal, the cervix hardens and descends, and the lumen of the cervical canal narrows. During pregnancy, the cervix is located high, and it is difficult to feel the pharynx.
Before menstrual bleeding, the parameters of the cervix are as follows:
- the surface is softened, loose, swollen;
- located at the bottom;
- the external pharynx opens, the cervical canal expands;
- the intensity of mucous secretion production decreases;
- the consistency of the secreted mucus is thick and viscous;
- acidity of the vaginal environment – no more than 6.5 units.
Before menstruation, the cervix is ready to allow the release of endometrial cells along with blood. A woman exhibits signs indicating that her period is approaching: nagging pain in the lower abdomen, general swelling, weight gain of 1-2 kg, vaginal dryness.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of hypertrophy is carried out after a visual examination of the patient using mirrors and palpation. Additionally, ultrasound and x-rays with contrast are used. Colposcopy, cytological analysis and biopsy are very informative.
These diagnostic techniques determine not only the exact size of the organ, but also reveal its location.
It is imperative to carry out differential diagnosis from cervical pregnancy. This is a manifestation of an ectopic pregnancy, when the embryo is displaced into the cervix, as a result of which it becomes swollen and enlarged.
Stages and symptoms of the disease
- Embryonic uterus (III degree) - its length does not exceed 3 cm. This defect is formed during intrauterine development.
- Infantile (II degree) - forming in early childhood, the uterus does not exceed 5 cm in length.
- Teenage (I degree) - slightly less than normal size, but this still leads to problems in pregnancy.
Against the background of its underdevelopment, there may be hypoplasia of the genital organs. Most often, the phenomenon is accompanied by underdevelopment of the ovaries:
- late onset of menstruation (menstruation occurs no earlier than 16 years of age, which indicates a lack of female sex hormones in the body)
- a woman with this disease may experience decreased libido and anorgasmia
- if pregnancy does occur, it is accompanied by miscarriages, premature birth, and weak labor
Hypertrophied cervix - Treatment
Treatment will depend on the nature of the pathological process that contributed to the development of hypertrophy. Treatment methods are, in most cases, conservative.
In severe cases, surgery or painless manipulations are performed, such as cryodestruction and diathermocoagulation.
Before any treatment tactics, diagnosis using colposcopy is prescribed. The doctor prescribes gentle and reliable methods of treatment if hypertrophy is caused by fibroids or an inflammatory process.
And in the first stage, therapeutic exercises that strengthen the muscles of the pelvic organs can help. You should not lift more than 5 kg.
To eliminate inflammation, antibacterial treatment and strengthening of the immune system are indicated. To treat fibroids, you need to take hormonal medications.
The surgical treatment method is a plastic correction. During the manipulation, the size of the organ is reduced while fertility is preserved and sexual activity is restored.
Sometimes diathermocoagulation, exposure to tissue with electric current and cauterization through cryodestruction are used.
In severe advanced cases, plastic surgery is performed to restore the physiological relationship of the intimate organs, or the cervix or uterus is removed if the woman does not want to maintain reproductive function.
A hypertrophied cervix can be treated at home. The effectiveness of treatment with folk remedies has not been proven, although in some cases (for example, with endocervicitis), tampons with aloe juice and sea buckthorn oil can help. The course of therapy lasts from two weeks to a month.
Cervical ectopia against the background of cervicitis
Ectopia is a disease similar in appearance to erosion. Previously, these pathologies were classified into one group, but with the advent of new generation diagnostic equipment it became clear that cervical ectopia has other causes.
Normally, the cervical epithelium should line the inside of the cervical canal, but for some reason it extends beyond its boundaries and is visible around the opening of the cervical canal. The tissues are not damaged - this is how ectopia differs from erosion.
Cervical ectopia can be congenital and constantly present in a woman, without causing her concern; it can appear during pregnancy, which also does not interfere with pregnancy and childbirth. If there are no manifestations such as pain, burning or itching, as well as pathological changes in cell structure, then ectopia does not require increased attention.
Epidermization of ectopia - what is it?
The healing or replacement of columnar epithelial cells by stratified squamous epithelium is called epidermization. The columnar epithelium is torn away from its place and is gradually replaced by reserve cells. Thus, the appearance of the cervix is restored and its internal cover is leveled. The red ulcers characteristic of pseudo-erosion disappear.
Chronic ectopia
Chronic ectopia is a congenital lesion of the epithelium, which is more pronounced during hormonal changes in adolescence or in nulliparous girls under 25 years of age. Chronic ectopia is not dangerous if there are no inflammatory processes, discharge or pain during sexual intercourse (dyspareunia).
The chronic process worsens during pregnancy, but does not require treatment. After childbirth, there is a chance that the cylindrical epithelium will take its place naturally - without drugs or surgical intervention.
Cervical hypertrophy - prevention
Preventive measures for hypertrophy include the prevention of tumor processes, timely treatment of erosion, dysplasia and inflammation of the cervix. The basis of good health is avoiding sexual intercourse at a very early age.
A serious approach to choosing sexual partners eliminates the risk of contracting STIs.
For example, the human papillomavirus can be in the body and not make itself felt for a long period of time. At this time, the infected person is a carrier of the HPV infection, which is easily transmitted through skin contact.
It is very important to monitor the woman’s condition after childbirth and promptly treat complications.
Every woman should be examined by her treating gynecologist at least once every six months. Have blood tests and cervical smears regularly.
Such techniques will be useful not only for preventing the disease, but also for the early detection of serious pathologies of the female reproductive system, and therefore preventing complications.
What are the causes of developmental defects?
- with congenital pathology, congenital or general infantilism manifests itself (due to damage to the embryo or the influence of hereditary factors)
- hormonal imbalances due to a malfunction in the body or hormonal treatment
- in youth, a slowdown in the development of an initially correctly formed uterus can be triggered by anorexia, underweight or excess weight, and disorders in the endocrine system
According to statistics, uterine hypotrophy is being diagnosed more and more often. This negatively affects pregnancy planning and bearing a fetus if it occurs. In most cases, long-term treatment is required, which does not necessarily bring results. There are cases when normalizing lifestyle and taking vitamins helps solve the problem. This different effect is explained by the severity of uterine hypoplasia.
Hypertrophy prognosis
If the hypertrophied cervix is not cured in time, the prognosis is quite sad. The severe stage of hypertrophy leads to infertility. It will be difficult for male reproductive cells to enter the changed size of the cervix, so the chances of fertilization are minimal.
In connection with the disease, a disruption of the epithelium appears, which leads to hormonal imbalance. If this happens, then pregnancy becomes impossible.
With cervical hypertrophy, the volume of the cervix increases, which leads to bleeding, the appearance of myomatous nodes, leukoplakia and other diseases, even cancer.
All this contributes to the recurrence of inflammation and tissue changes. Cyst ruptures and dystrophic disorders are also observed.
Remember that careful attention to yourself and regular examination by a gynecologist can prevent the development of many gynecological problems, including cervical hypertrophy.
Subscribe to our updates and don't forget to share information on social networks.
Best wishes! Be healthy!
Uterine hypoplasia: 10 causes, 3 symptoms, 4 treatment approaches, prognosis
Hypoplasia of the uterus is congenital, when at the stage of embryonic development of a girl there is a failure in the formation and formation of internal organs. The body of a pregnant woman is most sensitive to external influences (radiation, industrial hazards, infections, medications, severe stress), which also affect the child.
In addition, size discrepancy also occurs in adolescence, when all organs are actively growing and developing.
The causes of the disease can be divided into two groups.
Exogenous factors are called external causes, that is, acting from the outside:
- trauma, surgery on the genital organs in childhood and adolescence;
- damage to the central nervous system as a result of injury or disease, leading to a failure in the regulation of the reproductive system;
- heavy physical activity (including professional sports);
- bad habits impair blood supply and nutrition to organs, including the genitourinary area;
- insufficient nutrition, prolonged fasting leads to vitamin deficiency and deficiency of important elements necessary during the formation of the body;
- Frequent and severe stress reduces the body's adaptive forces, causing growth retardation and the impossibility of full formation.
Endogenous causes
Much more often, uterine hypoplasia is caused by endogenous (internal) causes:
- endocrine diseases: hypothalamic-pituitary dysfunction, thyroid dysfunction;
- tumors of the pituitary gland and hypothalamus;
- somatic diseases: decompensated heart defects, severe renal or liver failure, epilepsy;
- hereditary predisposition.
Degrees of uterine hypoplasia
The pregnant uterus, under the influence of hormones and the growing fetus, increases significantly. After delivery, the uterus contracts for several months, but it remains slightly larger than before pregnancy. Thus, the more births a woman has had, the larger the size of the uterus.
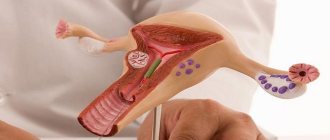
The length of the uterine body along with the cervical canal is measured with a special probe. For nulliparous women, this size should be at least 7 cm, for those who have given birth, at least 8 cm. The normal length of the cervix is about a third of the uterine length. The severity of the disease is determined by the size of the uterus.
I degree of hypoplasia is the most severe pathology. The uterus is very small in size, the cavity is usually not formed, which makes it impossible to bear a child.
The length of the probed uterus is no more than 3 cm, and basically the entire size falls on the cervix. This degree of underdevelopment is also called the fetal, rudimentary or embryonic uterus.
However, the fetal uterus is very rare and is usually a congenital pathology.
The second degree of underdevelopment is called the infantile, or children's uterus. Unlike the fetal uterus, the children's uterus has a more regular anatomy and a pronounced cavity. However, the cervix occupies almost the entire length, and the proportional ratio of the length of the body to the cervix is 1:3. The length of the infantile uterus ranges from 3.5 to 5.5 cm.
III degree of uterine hypoplasia is synonymous with a teenage or hypoplastic uterus. The length of the uterine body predominates, and its proportion to the size of the cervix is 3:1. The length of the uterus measured with a probe is closer to the border of normal values and is equal to 5-7 cm.
From the point of view of childbearing, a hypoplastic uterus has the most favorable prognosis and treatment effect.
It is quite difficult to suspect such a disease on your own. Traditionally, the following symptoms force you to see a doctor:
- late onset of menarche (first menstruation) - later than 15-16 years;
- menstrual dysfunction. Menstruation is irregular and short-lived, usually very painful (algodysmenorrhea), the amount of menstrual blood is insignificant, but there may be heavy periods. With a fetal uterus, menstruation may be completely absent, or appear in the form of scanty spotting;
- Primary infertility, as a consequence of underdevelopment of the main reproductive organ, manifests itself in the form of habitual miscarriage - spontaneous miscarriages following each other. Pregnancies are more often terminated at short stages.
Often, uterine hypoplasia, especially grades I-II, is combined with delayed physical development. In appearance, girls are often short, thin, asthenic in build, with a uniform narrowing of the pelvis, and fragile shoulders. Secondary sexual characteristics are poorly developed - hypoplastic mammary glands, sparse hair on the genitals and armpits.
A gynecologist can assume the presence of uterine hypoplasia during examination when there are signs of general infantilism. During a vaginal examination, attention will be drawn to underdevelopment of the vulva, scant hair growth, a short and narrow vagina, and a disproportionate ratio of the uterus to the cervix. The leading criterion is a reduction in the size of the uterus.
Data from laboratory and instrumental studies help determine the diagnosis.
Ultrasound diagnostics provides the most information.
In addition to the reduced size, flattening of the uterine body and a pronounced anterior tilt - hyperanteflexia - will be characteristic. The fallopian tubes are usually long and twisted, which increases the likelihood of an ectopic pregnancy.
Often, with general infantilism, ultrasound can detect ovarian hypoplasia.
This is associated with a decrease in the formation of sex hormones, so determining the concentration of steroids plays a significant role in the diagnosis of uterine underdevelopment.
Another study that helps confirm uterine hypoplasia is hysterosalpingography (HSG). The uterine cavity and fallopian tubes are filled with a special contrast agent, after which a series of x-rays are taken. The resulting image allows you to see a small uterus with long fallopian tubes, which allows you to confirm the diagnosis.
To determine the hormonal status, the level of hormones in the blood is determined (androgens, estrogens, prolactin, follicle-stimulating and luteinizing hormones, T3, T4 - thyroid hormones).
In doubtful cases, the attending physician has the right to order an X-ray of the skull and an MRI of the brain.
Treatment approaches
Therapeutic tactics are determined by the severity of the disease and the reasons for the development of hypoplasia.
Hormonal drugs
The main treatment is to correct hormonal imbalances. Based on hormone levels, replacement therapy in a cyclic mode is indicated. The selection of drugs is carried out by an obstetrician-gynecologist.
If there is a lack of sex hormones, artificial analogues of estrogens and gestagens are selected (Estrofem, Duphaston, Femoston, Microfollin, Ovestin). The choice of drugs is purely individual, as it depends on the concentration of steroids and the response to the drugs.
If you have concomitant diabetes mellitus or thyroid pathologies, you will need to consult an endocrinologist.
Physiotherapy
Physiotherapy is used as an auxiliary method. Mud therapy and baths, UHF, laser therapy, magnet, ozokerite and paraffin applications are widely used.
The procedures help improve blood supply to the pelvic organs, endometrial growth, and stimulate the production of hormones by the ovaries.
A good effect is achieved by gynecological massage, which allows you to increase the elasticity of the ligamentous apparatus, eliminate hyperanteflexion, increase blood supply and contractility of the myometrium.
Vitamins and diet
A balanced diet helps maintain the body's defenses. The diet must contain animal proteins, as well as fresh vegetables, fruits and herbs.
It is worth abandoning “starvation” diets, vegetarianism, raw food diet, and overeating.
Taking vitamin complexes in courses has a general strengthening effect, improves tissue nutrition and increases the ability to regenerate.
ethnoscience
Traditional medicine is an auxiliary method and should be used only after consulting a specialist. The most commonly used are herbal infusions.
Decoctions of hogweed, knotweed, and sage contain natural phytoestrogens and help normalize hormonal levels. Chamomile, St. John's wort, and calendula are used for anti-inflammatory purposes.
Extracts of valerian, oregano, and lemon balm have a calming effect.
It is important to understand that any non-traditional treatment methods will not give a therapeutic effect, so using folk remedies is permissible only after consulting a specialist.
With uterine hypoplasia of the 1st degree, the prognosis is disappointing. Treatment usually does not produce significant results and focuses on maintaining menstrual function.
With severe hypoplasia, it is not possible to conceive and carry a pregnancy.
If folliculogenesis (the process of follicle growth and egg formation in the ovaries) is not impaired, you can resort to surrogacy through in vitro fertilization.
With grade II-III hypoplasia, after adequate therapy, the likelihood of pregnancy increases.
However, it is worth considering that despite the treatment, the risks of early miscarriage and premature birth remain high. Therefore, a pregnant woman needs to register her pregnancy as early as possible and attend an antenatal clinic in a timely manner.
Is it possible to warn?
Severe uterine hypoplasia is usually a congenital pathology, so it is difficult to prevent the development of the disease. However, thoughtful planning of pregnancy, maintaining a healthy lifestyle and eliminating the influence of harmful factors can reduce risks.
It is important to pay attention to the development of girls during puberty during the formation of the body. For the full formation of the reproductive system, you should avoid harmful factors, hypothermia, excessive stress, and bad habits. It is worth giving up diets in favor of a nutritious healthy diet.
Conclusion
Considering the congenital causes of underdevelopment of the uterus, it is impossible to completely prevent the occurrence of organ hypoplasia. However, we can reduce the risks of pathology.
It is important to remember that regular preventive examinations with a doctor will help to detect abnormalities in time and begin treatment as soon as possible.
Modern medicine has many treatment methods, so the diagnosis of uterine hypoplasia no longer sounds like a death sentence.
Article rating
We have put a lot of effort into making sure you can read this article and would welcome your feedback in the form of a rating. The author will be pleased to see that you were interested in this material. Thank you!
(7 4,86 of 5) Loading...
If you liked the article, share it with your friends!
You might be interested
Source: https://UstamiVrachey.ru/akusherstvo-i-ginekoloiya/gipoplaziya-matki
Diagnosis and treatment of uterine hypertrophy at the Best Clinic SMC
A standard examination by a gynecologist only gives an assumption about changes in the size of the uterus. The doctor receives more accurate information based on the results of ultrasound and hysteroscopy. Having determined the cause of hypertrophy, the doctor may leave the patient under observation if there are no serious indications for treatment, or prescribe additional research methods.
Conservative therapy or surgical intervention - the choice depends on the cause, the woman’s age, her individual characteristics, concomitant diseases, the presence of children or the desire to have them, and many other factors.
At the Best Clinic SMC, doctors very carefully approach each case individually, because not only the woman’s health, but also her entire future life depends on the correct diagnosis and the correct treatment. Applying all their knowledge and using modern methods and technologies, Best Clinic gynecologists and obstetricians try to preserve the only important female function - the ability to conceive, bear and give birth to a healthy baby.
Gynecological appointments at the Best Clinic SMC are carried out only by appointment due to the high workload of doctors. Therefore, take advantage of the opportunity provided on our website and make an appointment in advance with the clinic’s leading specialists by calling the numbers listed on the website or using the appointment form provided.