During the period of bearing a child, all events are perceived with particular impressionability. Therefore, all relatives try to protect expectant mothers from additional worries. But there are situations when this is impossible to do. Any diagnosis that a doctor makes during pregnancy seems like an irreparable disaster.
Especially when the doctor says the phrase: “You have cervical erosion.” Although, before you panic, you need to understand the situation. Maybe these words are not so scary. And timely detection and treatment is better than ignorance about the disease.
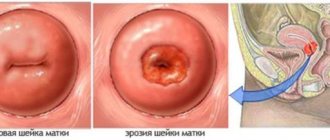
Panic has never brought success in any business. Therefore, the main thing is to calm down, especially since in such a situation it is very important. Erosion is a fairly common disease. It does not interfere with the pregnancy and birth of a healthy child if detected in a timely manner and treated correctly. This process means damage to the mucous membrane of the cervix. They can occur due to chemical, traumatic injuries, inflammatory processes or changes in hormonal levels.
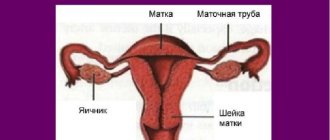
Erosion can begin as a result of genital infectious diseases, such as chlamydia, gonorrhea, trichomoniasis, human papillomavirus, genital herpes and others. The disease can also begin with the onset of pregnancy or as a result of difficult childbirth. It is very easily diagnosed during a routine gynecological examination, especially using a colposcope (microscope).
What is cervical erosion and causes
ESM is the most common gynecological disease. It represents local damage to the epithelial cover in the area of the vaginal part of the cervix (the organ connecting the uterus and vagina). Bright red wounds, ulcers and other external damage form on the mucous membrane. You can easily see them on the gynecological chair using a special mirror.
The most common causes of the disease include:
- inflammation of the female genital organs;
- sexually transmitted infections (chlamydia, gonorrhea, ureoplasmosis, candidiasis);
- the beginning of intimate life at an early age;
- frequent change of sexual partners;
- cyst, fibroma, endometriosis;
- any mechanical damage to organs: abortion, childbirth, surgery;
- hormonal and endocrine disorders.
The main sign of pathology is discharge with blood, which has a wide variety of character. The lower abdomen may also hurt during sexual intercourse, discomfort, burning, itching. Often these signs are perceived as thrush or the approach of the menstrual cycle. But if such sensations arose during pregnancy, then you should immediately tell your obstetrician-gynecologist about it.
Attention! Before planning a pregnancy, you must undergo a complete examination by a gynecologist. When cervical erosion is detected before conception, timely treatment and prevention of the disease, the likelihood of a calmer and safer pregnancy and childbirth increases.
What can cause brown discharge in the 2nd trimester?
In the first weeks of pregnancy, the presence of traces of blood is not uncommon. Why is this happening? There are five causes of bleeding in the short term.
Implantation
Victoria, 29 years old: “We tried to conceive for a long time. This month I finally tested positive. But even before the delay I noticed a smudge. It’s already fourteen weeks, everything seems to be fine, but I’m still worried. What was it?".
Mucous discharge in pregnant women, containing small inclusions of blood, can occur during the process of implantation of the fertilized egg into the uterine wall (that is, in the first 2 weeks after fertilization). Damage to the capillaries that accompanies this phenomenon provokes the appearance of characteristic streaks in the leucorrhoea.
Hormonal disbalance
Natalya, 27 years old: “I recently found out that I am pregnant. And my periods did not stop. True, they walked just a little bit at a time. I'm shocked! The last brown discharge was approximately 13 weeks pregnant. It's already twenty now. So unexpectedly I had to become a mother! Is it possible?"
Scanty brown discharge in the first trimester may be a consequence of hormonal changes. Typically, this phenomenon occurs on the days when a woman was supposed to have her period. The secretion most often has a spotting nature and does not pose any danger to the well-being of the fetus. It can easily be confused with menstruation. Most likely, these discharges will pass without a trace. In rare cases, the situation can be repeated for 2-3 cycles; in the second trimester it self-destructs.
Hydatidiform mole
Yulia, 22 years old: “It’s about the thirteenth week. We are visiting my husband's parents in the village. For several days I have been noticing some strange blood on my underwear, as if foaming. All the symptoms of toxicosis are obvious: nausea, severe weakness, dizziness in the morning. I haven't gone to the doctor yet. I can only get to the hospital every other day while I am on bed rest. Very worried! What could it be?".
The reason that causes the appearance of a bloody secretion, essentially reminiscent of menstrual flow with clots and characteristic bubbles, is a serious pathology - hydatidiform mole. This is a rare phenomenon, the essence of which is a disruption of the fertilization process. Namely: either an egg without chromosomes is fertilized, or a full-fledged egg is fertilized, but at the same time by 2 sperm.
In fact, it is a tumor, which in most cases is benign in nature and consists of many bubbles (cysts) filled with fluid. Blood loss occurs due to rejection of some of the vesicles and is accompanied by symptoms such as headache, nausea, vomiting, and fluctuations in blood pressure.
Svetlana, 24 years old: “I recently found out that I’m expecting a baby. The long-awaited two stripes! Now the dark periods have begun. I’m very afraid that it might turn out to be ectopic, since I have a lot of problems in gynecology (there was tubal obstruction). What kind of discharge can occur during an ectopic pregnancy?”
Pathological pregnancy is distinguished by a brown secretion with a dark tint. These are the first signs of an ectopic pregnancy before the delay. The meaning of the pathological process is contained in the name, that is, the fertilized egg is implanted not in the wall of the uterus, but outside it: in the fallopian tube, ovary, or even the abdominal cavity.
At the initial stage, the ectopic attachment does not reveal itself in any way. Differences appear at 5-6 weeks, when a woman’s condition suddenly worsens: weakness appears, severe cutting pain in the abdomen, and dark blood discharge may appear. You might think that it was your period after a delay. The intensity of blood loss can vary, since sometimes there is internal bleeding, and only a small part of it goes outside.
Yulia, 29 years old: “I lost my first child when I was 15 weeks pregnant. Then sudden bleeding began. After a long treatment I was able to conceive again. Now I'm 14 weeks pregnant and spotting has started. Is it really all over again? Could this kind of discharge occur during a miscarriage?”
Irina, 20 years old: “At first I noticed some kind of ichor, and today I started having discharge with clots during my 6-week pregnancy. Looks like normal menstruation. My stomach hurts and my lower back is strained. Maybe it was just a delay? But the test was positive, I haven’t gone to a consultation yet. Tell me, what could it be?"
Possibly a threat of miscarriage. This is a common cause of bleeding in the first weeks of pregnancy (up to 13 weeks). Pathological detachment of the ovum is accompanied by blood loss of varying intensity. At first, as a rule, this is spotting in early pregnancy (sometimes with mucous inclusions), and as the process progresses, their abundance increases significantly.
The second trimester is a time when any bleeding poses a danger to the well-being of the expectant mother and baby. There are two main reasons for such conditions: placental abruption and placental previa.
Placental abruption
Veronica, 24 years old: “I noticed brown discharge at 20 weeks of pregnancy. At the same time, my lower abdomen aches strangely. Recently I stumbled and fell, hitting my stomach quite hard. What could it be?"
Olga, 36 years old: “I’m 36. I’m expecting my first baby. Hypertensive. There was placental abruption at 10 weeks, then at 16 weeks of pregnancy. Today, at lunchtime again, there was a strange feeling in the lower abdomen, followed by brown discharge (like menstruation, maybe a little less). They took me away in an ambulance. Detachment again. Term 22 weeks. How does this threaten the child?
Inna, 26 years old: “I started bleeding heavily at 25 weeks of pregnancy. He was urgently hospitalized. A 50% placental abruption was diagnosed. The doctors said that now I will be in the hospital under observation all the time. Is this condition really so dangerous?
Placental abruption is a dangerous condition that causes brown discharge in the second trimester, which ends at 28 weeks of pregnancy. In women, abruption is often accompanied by severe bleeding, and the fetus, when this pathology develops, experiences hypoxia and a lack of nutrients, because the placenta does not perform its functions.
There is also a feeling of tension and pain in the lower abdomen. Detachment can be triggered by injuries, arterial hypertension, short length of the umbilical cord, and the presence of scars on the body of the uterus. This condition is extremely insidious and requires emergency hospitalization, and sometimes surgical intervention, since after bleeding of this kind the death of the fetus is possible.
Alla, 26 years old: “I’m in my sixth month. What does brown discharge mean at 26 weeks of pregnancy? I feel the same as always, but today after cleaning I noticed traces of blood on the laundry. At the fifteenth week there was hypertonicity, there was a threat of miscarriage, it was kept in storage, but there was no bleeding. Has anyone experienced bleeding during the second trimester of pregnancy?
Yulia, 24 years old: “We are expecting a baby. Tests were normal, ultrasound showed lateral placenta previa. Is brown discharge normal at 16 weeks of pregnancy with a similar diagnosis? The doctor says that in the last few months I will have to go to the hospital. It's necessary?"
Inga, 22 years old: “The first time I noticed brown discharge was at 17 weeks of pregnancy. They sent me for an ultrasound. It turned out that I had complete placenta previa. I completed a course of treatment in a hospital and felt great. Discharge appeared again at 24 weeks of pregnancy. She was treated at home under her own responsibility. And again discharge at 27 weeks of pregnancy. The doctor insists on putting me in the hospital until the birth. It is necessary?"
Placenta previa is another abnormal condition in which the placenta is abnormally located. It partially or completely covers the uterine os. If the pathology is detected before the sixteenth week, then therapy is often carried out on an outpatient basis. The higher the gestational age, the greater the risk of bleeding.
Fetal growth increases pressure on the placenta. Bleeding often occurs suddenly, for example during sleep. The color of the discharge is scarlet, it is liquid, there is no pain. When sneezing, coughing, bowel movements or bladder emptying, blood loss increases. The 24th week of pregnancy is the period when a woman with placenta previa is often hospitalized in a hospital.
Both of these conditions pose a real threat. As a rule, they occur in the second trimester of pregnancy. But placental abruption can also occur in the third, and this is no less dangerous.
Whether erosion on the cervix will affect the conception of a child depends on what caused the pathology. If a woman was examined before pregnancy and did not have a violation of the epithelial tissue, then with a high degree of probability we can talk about hormonal causes. During pregnancy, a dramatic change in hormonal levels occurs: the secretion of estradiol sharply decreases, and progesterone levels increase. Many expectant mothers developed ectopia precisely because of these transformations.
Cervical erosion during pregnancy can be caused by:
- sexual infections;
- disturbance of vaginal microflora;
- rough sexual intercourse;
- decreased body resistance;
- introduction of douches, tampons, vaginal rings.
Symptoms of ESM during pregnancy
Discharge from the cervix is the main indicator of women's health. They indicate certain disturbances in the functioning of the female body. With ESM, there are the following types of discharge:
- white spotting. This is a transparent, non-thick mucus without aroma. They can appear after sexual intercourse, from a minor cold, from stress, or physical exertion. Such discharge does not require treatment during pregnancy. You can start therapy after childbirth;
- white thick. The discharge has a cheesy consistency and is odorless. This process indicates that a fungus of the genus candida has appeared against the background of ESM. The gynecologist prescribes conservative treatment to exclude the possibility of infection of the baby’s mucous membrane during childbirth and further complications during pregnancy;
- yellowish discharge. This is the first signal about infections such as trichomonas, staphylococcus, ureaplasma, chlamydia, etc. The nature of the discharge has a certain periodicity. After sexual intercourse or urination, vaginal mucus becomes abundant. Yellowishness has an unpleasant odor. With gonorrhea, purulent discharge gradually appears. There may be pain in the lower abdomen, a burning sensation in the perineum. Once the doctor determines the exact diagnosis, antibacterial intervention is necessary;
- pink, bloody. For pregnant women, this is the most dangerous discharge. It is difficult to immediately determine the cause. Bleeding can be the beginning of a miscarriage, ectopic fertilization, or placental abruption. If the main cause is erosion of the cervix, then the source of inflammation has become chronic and can harm the unborn child.
Light spotting with a small admixture of blood during ESM can occur after intimate intercourse, physical activity, or examination in a gynecological chair. They can be permanent. All this needs to be monitored, tested and prevented;
- brown, brown discharge. Mucus of this color is a serious symptom. You must immediately contact a specialist. During pregnancy, the uterus constantly grows, and the cervical canal stretches. This can lead to progression of erosion. The discharge is usually accompanied by severe pain in the lower abdomen. This indicates inflammation of the ovaries and uterus.
Pathological symptoms
When there is erosion on the cervix, the following manifestations are possible during pregnancy:
- brown discharge, indicating slight bleeding from the eroded surface;
- bright blood in small quantities appearing after a doctor’s examination or intimacy (contact bleeding);
- pulling sensations in the lower abdomen during physical activity (long walking, lifting heavy objects);
- inflammatory discharge (thick milky or watery leucorrhoea).
Most often, cervical erosion occurs against the background of inflammation caused by viruses or bacteria. The infection provides pathological symptoms in the form that the discharge becomes more abundant and the risk of bleeding increases.
The effect of the disease on the fetus
Cervical erosion is found in more than half of expectant mothers. It is believed that it does not affect pregnancy and childbirth in any way. But this question has a number of caveats. Against the background of decreased immunity, hormonal changes and external factors, an exacerbation of the disease is possible. In this case, extremely negative consequences on the fetus and childbirth are possible.
Complications depend on the stage of pregnancy.
1st trimester . Frequent brown discharge due to cervical erosion during pregnancy will be regarded by the doctor as a threat of miscarriage. The expectant mother may become overly emotional about these phenomena, become nervous and put the health of the fetus at risk. The inflammatory process in the first 12 weeks after conception can lead to spontaneous abortion and frozen pregnancy. The infection can get to the embryo, since during this period it does not have the necessary protection.
2nd trimester . Lack of treatment can lead to cervical incompetence. This manifests itself in shortening the length, cervical insufficiency, and spontaneous miscarriage. Any discharge with blood should be a reason to immediately call an ambulance.
3rd trimester . Erosion can disrupt the functioning of the placenta. In this case, the fetus will have congenital pathologies due to the ingress of microbes. There is a very high probability of violation of the integrity of the amniotic sac, leakage of amniotic fluid and premature birth.
Exacerbation of erosion, the presence of any infections (endocervicitis, mycoplasma, ureoplasma, chlamydia, etc.) can have a detrimental effect not only on the condition of the fetus during gestation, but also on childbirth. Multiple ruptures of the vaginal mucosa and episiotomy are common consequences of ESM.
Attention! Erosion of the cervix and other underlying diseases of this organ: leukoplakia, dysplasia, cyst, colpitis, polyps, ectropion and others, can occur unnoticed. Doctors call these diseases “cancer provocateurs.” With this diagnosis, amputation of the organ and the impossibility of pregnancy are possible. Periodic preventive examinations with a gynecologist will help you avoid such consequences.
Brown discharge regardless of gestational age
Brown discharge causes more concern for expectant mothers than any other.
This is easily explained, because the brown color is, in fact, blood in a certain concentration. It is worth noting that brown discharge at 14 weeks of pregnancy is something different than discharge at 39 weeks of pregnancy. But there are situations when provoking factors are absolutely independent of gestational age. Olga, 27 years old: “24 weeks of pregnancy. Sometimes there is brown discharge. Could beige or light brown discharge during pregnancy be the result of cervical erosion?
Erosion may be accompanied by bleeding. This disease is treated by cauterization, but during the period of bearing the baby, this manipulation is not provided. Erosive lesions can make themselves felt by a characteristic secretion in the form of light brown discharge during pregnancy (ichor).
Irina, 30 years old: “I’m expecting a baby. Now 25 weeks. Purulent discharge appeared at 22 weeks of pregnancy. There is an admixture of blood in them, and terrible irritation has begun. I tried douching with chamomile - it became a little easier. I was tested for gardenelosis. Why were there traces of blood?
During pregnancy, brown discharge can be caused by an inflammatory process or an STD. Against the background of a decrease in local immunity, activation of opportunistic microorganisms or dormant infections is often observed. Such a secretion may contain brown streaks and inclusions of mucopurulent fluid.
Injuries
Irina, 30 years old: “Why might discharge appear at 37 weeks of pregnancy? The whole period went great. And this morning I noticed a smear on my daily planner (there was sex in the evening). I was very scared. It's still too early to give birth. Has anyone had brown discharge at the end of their term? What is this?"
Inna, 22 years old: “After examination, I noticed brown discharge on the chair at 34 weeks of pregnancy. What could have caused them?
Brown discharge at 37 weeks can appear both as a result of sex and after examination by a doctor. This is due to injury to the inner surface of the cervix. If they do not intensify, then there is no danger. If you notice discharge at 37 weeks of pregnancy, try to reduce your sexual activity.
Plug coming out
Yulia, 21 years old: “40 weeks of pregnancy, brown discharge. Nothing like this happened the entire time. What could it be?"
Natalya, 25 years old: “Is brown discharge at 39 weeks of pregnancy a sign of labor? More precisely, week 39 is already ending. I found a piece of thick mucus with brown specks on my underwear. Previously, there was a threat at 6 months of pregnancy, it was kept in storage, but everything was different. Maybe this is the same traffic jam? How long will it take for labor to begin?
Miroslava, 19 years old: “Thick reddish discharge appeared at 41 weeks of pregnancy. What is this?"
Brown discharge in late pregnancy usually means the beginning of the mucus plug that seals the entrance to the uterus and performs a protective function. Before birth, it tends to separate in several stages or at once. This condition is not dangerous. Brown discharge at 40 weeks of pregnancy indicates an imminent meeting between mother and baby.
Sometimes the passage of the mucus plug and the onset of labor are separated by a matter of hours. And sometimes it begins to gradually recede as early as 37 weeks of pregnancy. It all depends on the characteristics of the body. Discharge at 40 weeks of pregnancy or a little earlier looks like thick mucous fragments (sometimes with brown spots - streaks of blood). 41 weeks is the time when labor can begin every minute, and the discharge of mucus with blood is a characteristic sign.
Having considered the main reasons why discharge is possible during pregnancy in all trimesters, we note that in each case the most reasonable behavior would be to consult a doctor in a timely manner. This is especially true for sudden heavy bleeding. Even with minor discharge, unfortunately, without experience, understanding the signs of a particular deviation is extremely problematic.
Diagnosis of the disease
Brown discharge is not normal. To determine the true cause, a series of examinations and an examination by a gynecologist are carried out. Only after the problem is identified, therapy is prescribed. Diagnosis of discharge consists of the following procedures:
- urine and blood analysis;
- bacterial cultures and PCR;
- smear from the cervical canal;
- vaginal smear;
- examination of the cervix using a gynecological speculum;
- Ultrasound;
- colposcopy.
Causes of discharge
Various factors can provoke discharge during erosion:
- Inflammatory processes of the vulva. Adnexitis, endometritis, colpitis, vaginitis, and thrush can lead to disruption of the integrity of the endometrium and damage to blood vessels. As a result, a red tint appears in the discharge.
- Often there are erosions that bleed during examination on the gynecological chair, during sexual intercourse or improper use of tampons. Mechanical damage can also occur during childbirth, abortion, and diagnostic curettage.
- Endometriosis in women is the main reason why erosion can bleed during and without pregnancy. With the development of endometriosis, epithelial cells are destroyed, resulting in vascular damage.
- Infectious and other sexually transmitted diseases - ureaplasmosis, gonorrhea, trichomoniasis, mycoplasmosis, herpes, gardnerellosis, chlamydia and others. In this case, the discharge is greenish in color and also mixed with blood.
- Benign or malignant neoplasms. The cells of any neoplasm themselves are a suitable environment for the proliferation of pathogenic bacteria. In addition, due to its size, the neoplasm can damage blood vessels, causing uterine bleeding.
Erosion itself is not a reason for an increase or any other change in a woman’s vaginal discharge. Such symptoms occur only when blood vessels are damaged mechanically, due to infection, or as a polyp, fibroid, or other tumor grows.
Treatment before and during pregnancy
Treatment with radical methods for cervical erosion during pregnancy should be careful, but mandatory. Drastic methods with surgical intervention are contraindicated, as they can cause severe bleeding and miscarriage.
Moxibustion is considered an effective treatment method for ESM before or after pregnancy.
It comes in 5 types:
- Laser coagulation. A powerful beam of light emanating from a surgical laser cauterizes the affected tissue areas as precisely as possible. The main advantage of this method is the ability to act equally effectively on superficial and deep wounds in the cervix. Electrocoagulation takes approximately 10-20 minutes.
- Exposure to radio waves. This is the most painless method of cauterization. The mucous membrane heals quickly - within 2 - 3 weeks. The treatment is carried out within a few minutes and does not require special preparation. The impact apparatus is “Surgitron”.
- Chemical coagulation. This is the effect of organic acids on damaged areas. The procedure is especially relevant for pseudo-erosion - ectopia of the cervix (non-standard position of the cylindrical epithelium). One of the common drugs for chemical coagulation is Solkovagin. Active ingredients: nitric acid, zinc nitrate, oxalic and acetic acids.
- Cryodestruction is the freezing of erosion. The manipulator, aimed at the affected areas of the mucous membrane, hits them with liquid nitrogen (ultra-low temperature).
- Electrocoagulation. This is the most effective and at the same time consequential method of treating erosion. Electric current affects not only problem areas, but also damages healthy cells. The lower part of the cervical canal is severely damaged and microscopic scars are formed. The percentage chance of erosion reappearing is very low. But this poses serious risks during pregnancy and childbirth.
The operation to remove the affected part of the cervix is called conization. This procedure is prescribed for precancerous conditions. It also removes cysts, fibroids, cancerous tumors, polyps, dysplasia, and eliminates large postpartum scars.
The postoperative period lasts from several weeks to 2-3 months. Severe pain, heavy bleeding and mucous purulent discharge are possible. In this case, specialists prescribe antispasmodics and check whether large vessels are affected during the operation.
Some doctors believe that treatment of erosion with these methods should be started only after pregnancy and childbirth. The fact is that scars and sutures form at the site of the affected areas. They can, in rare cases, prevent conception. But modern innovative technologies make it possible to refute this fear. The sutures heal quickly after treatment of ectopia. Constant medical supervision is required.
Attention! The choice of treatment method and cauterization is carried out by a competent specialist. After all diagnostic procedures, the degree of cervical damage, progression, and possible contraindications are assessed. Only after this is surgical therapy prescribed.
With congenital erosion and in some cases, the disease can be completely asymptomatic during pregnancy and disappear on its own after childbirth.
Discharge during cervical erosion has a certain characteristic. The gynecologist’s task during pregnancy is to create conditions so that the girl is not bothered by bloody, pinkish, brown and brown mucus.
Depending on the stage of erosion, localization of the lesion and individual characteristics of the body, pregnant women are prescribed the following treatment for ESM:
- antibacterial drugs;
- anti-inflammatory;
- agents that improve blood clotting;
- homeopathy – preparations based on medicinal herbs.
Folk remedies can remove the symptoms of the disease. Complex therapy will benefit a woman’s overall health and especially her sexual life. Healing drugs will not harm the fetus, but before starting it is recommended to consult with your doctor. The following will help get rid of chronic cervical discharge and pain:
- tampons with sea buckthorn oil;
- tampons with honey;
- tampons with herbal decoctions;
- douching with a small pressure herbal decoction.
Traditional methods
Erosion can be treated with douching, ointments, baths and phytotampons. However, all methods must be agreed upon with the attending physician. A huge amount of information in modern medical journals and the World Wide Web allows you to choose a thousand and one treatment methods. But not all methods can be used during pregnancy.
Any medicinal herb can cause allergies. Therefore, you should use only those herbs and oils from those plants in which you have confidence. For example, St. John's wort has too pronounced an effect in treatment, so it is not recommended for use during pregnancy. Also, aloe may not always be used due to its characteristics.
Many doctors flatly refuse to recommend douching. This is mainly due to the risk of introducing an infection into the vaginal mucosa or causing mechanical injury with the nozzle of the douche. This can only lead to aggravation of the situation. Therefore, choosing to douche should include the risks of this method.
This method is quite effective when inflammation of the cervix causes particular discomfort in the form of itching and burning. Douching is quite effective in eliminating abnormal discharge. The main thing is to adhere to the basic rules:
- You can douche for no more than 5 days;
- the tip should be soft rubber or silicone;
- sterilize the syringe before use;
- use a decoction only at a comfortable temperature (especially during pregnancy);
- pour in the broth very slowly.
Discharge during pregnancy after ESM treatment
Discharge is an absolutely normal physiological process in a woman’s body. Before pregnancy, the amount of mucus per day reaches 2 ml. Its consistency and color depend on the phases of the menstrual cycle. In the first half there is a transparent slight discharge. During the period of ovulation, they become astringent and change their pale color to white. May have a yellowish tint. In the second phase, mucus becomes more abundant.
What happens normally during gestation?
The microflora changes completely. The discharge becomes abundant and can reach up to 5 ml. per day. Normally, they should be odorless, transparent or light white.
Cervical erosion during pregnancy and discharge should be carefully monitored. Brown mucus can be the beginning of a miscarriage, placental abruption, frozen pregnancy, or ectopic pregnancy. Opening bleeding should immediately serve as a signal to call emergency help.
Erosion can cause pain during sexual intercourse and gynecological examination, and a pulling sensation in the lower abdomen. Serious diseases may also appear against the background of a weakened immune system: endometriosis, thrush, chlamydia, staphylococcal infection, ureoplasmosis and others.
Treatment of ESM in pregnant women is carried out using gentle methods. Only after childbirth can you resort to a more effective method - cauterization.
Video: What discharge should women be wary of?
What discharge should women be wary of? Gynecology
Features of treatment
During the gestation period, you need to follow a gentle treatment regimen. Therefore, each drug is prescribed with extreme caution. After all, the main goal of treatment is to maintain inflammation in the phase in which it appeared. And the main treatment (which is often carried out by cauterization) will be carried out after childbirth. Although there are not many drugs allowed during pregnancy, there are still enough drugs to choose the appropriate option for different types of diseases.
Often, inflammation of the cervix is accompanied by unpleasant sensations such as itching, burning or spotting. In this case, the doctor prescribes special suppositories that can stop bleeding or relieve acute inflammation, which causes discomfort.
Sea buckthorn suppositories or baths have a very good effect on inflammation. Sea buckthorn has always been famous for its unique healing properties. In rare cases, the doctor may prescribe antibiotics or antiviral drugs. However, this is only possible in cases where taking the drugs is considered safer than the possibility of harming the fetus or harming the gestation process.
Doctors are often not against treatment with traditional methods, especially during pregnancy. However, these actions should also take place under the supervision of a doctor, because many people believe that they are able to cope with the disease themselves. And when inflammation of the cervix reaches an advanced stage, they begin to blame the doctors for not paying attention. Therefore, it is necessary to give an account that during the gestation period, both are responsible: both the doctor and the expectant mother herself.
What kind of discharge can there be?
If erosion bleeds, then the nature of vaginal secretion depends on the reason that caused such discharge. Most often there is scanty bleeding or mucus streaked or interspersed with blood. If there is a bacterial infection, the discharge may turn green or yellow, but may also contain blood.
If erosion occurs in a pregnant woman, you need to pay special attention to the nature of the vaginal mucus. Its shade, volume and frequency may indicate the development of a pathological disease.
Abundant
Usually erosion does not just bleed, the amount of discharge increases significantly. There may be moisture in the underwear, an unpleasant odor, and very often you have to use panty liners. In this case, heavy discharge may vary in structure and indicate different pathologies:
- watery and clear often accompany hormonal imbalance;
- thick ones accompany the inflammatory process; a green or yellow shade may indicate the content of pus;
- curdled inclusions indicate mycotic (fungal) infection of the epithelium and accompany candidiasis and some other diseases.
The volume of secretion increases during early pregnancy. In this case, erosion plays a big role in changing discharge. More often there are more of them due to the enlargement of the uterus as the fetus grows and the addition of the inflammatory process.
Brown
Any brown discharge indicates blood impurities. It appears as a result of damage to blood vessels as the tumor grows, trauma to the eroded area of the epithelium and with the development of infectious diseases.
A brown secretion can occur when squamous epithelium is replaced by columnar tissue. Cylindrical cells located on the vaginal part of the cervix are often traumatized in the following cases:
- damage to the mucous membrane during sexual intercourse and examination by a doctor;
- childbirth, abortion, surgery on the genitals;
- improper use of a tampon, douching.
During pregnancy, blood that turns the mucus brown is a warning sign, especially in the second and third trimester.
Yellow
The nature of vaginal secretion changes with the development of diseases such as ureaplasmosis or staphylococcal infection:
- Ureaplasmosis and erosion are often diagnosed simultaneously. Ureaplasma belongs to the opportunistic flora, is in the body in a “dormant” state and does not manifest itself. But when erosion appears, immunity decreases, and for a number of other reasons, it can actively begin to grow. It also affects discharge during erosion, turning it yellowish.
- Staphylococci also live in the body of any person without affecting health. But with stress, hypothermia, pregnancy, or decreased immunity, a staphylococcal infection causes purulent leucorrhoea, a feeling of heaviness in the lower back and lower abdomen, and cycle failure.
Possible complications
Erosion, although it occurs without pronounced symptoms, often causes various complications:
- Inflammatory diseases. The damaged area becomes an ideal place for pathogenic bacteria to live. The result can be infectious inflammatory diseases, for example, chlamydia, candidiasis, trichomoniasis. Erosion “opens the gate” to the uterine cavity, due to which pathogenic microorganisms penetrate directly into the main reproductive organ. As a result, a woman cannot become pregnant, since any inflammatory process is an obstacle to fertilization.
- Rebirth. In rare cases, erosion can lead to a malignant process. Cervical cancer is considered one of the most dangerous and most common cancers in women. The causes of oncology are untreated or undiagnosed erosion.
- Activation of the human papillomavirus. The appearance of condylomas can also be an impetus for the development of a precancerous condition.